Dithiothreitol
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3S)-1,4-Bis(sulfanyl)butane-2,3-diol | |
| Other names
(2S,3S)-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol (no longer recommended)
D-threo-1,4-Dimercaptobutane-2,3-diol D-threo-1,4-Dimercapto-2,3-butanediol 1,4-Dithio-D-threitol Cleland's reagent Reductacryl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.427 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 154.253 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 42 to 43 °C (108 to 109 °F; 315 to 316 K) |
| Boiling point | 125 to 130 °C (257 to 266 °F; 398 to 403 K) at 2 mmHg |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
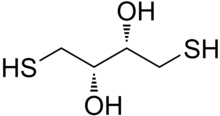
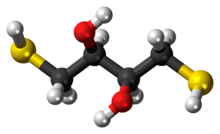
Dithiothreitol (DTT) is the common name for a small-molecule redox reagent also known as Cleland's reagent.[2] DTT's formula is C4H10O2S2 and the chemical structure of one of its enantiomers in its reduced form is shown on the right; its oxidized form is a disulfide bonded 6-membered ring (shown below). The reagent is commonly used in its racemic form, as both enantiomers are reactive. Its name derives from the four-carbon sugar, threose. DTT has an epimeric ('sister') compound, dithioerythritol (DTE).
Reducing agent
DTT is a reducing agent; once oxidized, it forms a stable six-membered ring with an internal disulfide bond. It has a redox potential of -0.33 V at pH 7.[1] The reduction of a typical disulfide bond proceeds by two sequential thiol-disulfide exchange reactions and is illustrated below. The reduction usually does not stop at the mixed-disulfide species because the second thiol of DTT has a high propensity to close the ring, forming oxidized DTT and leaving behind a reduced disulfide bond. The reducing power of DTT is limited to pH values above 7, since only the negatively charged thiolate form -S− is reactive (the protonated thiol form -SH is not); the pKa of the thiol groups is 9.2 and 10.1.

Applications
DTT is used as a reducing or "deprotecting" agent for thiolated DNA. The terminal sulfur atoms of thiolated DNA have a tendency to form dimers in solution, especially in the presence of oxygen. Dimerization greatly lowers the efficiency of subsequent coupling reactions such as DNA immobilization on gold in biosensors. Typically DTT is mixed with a DNA solution and allowed to react, and then is removed by filtration (for the solid catalyst) or by chromatography (for the liquid form). The DTT removal procedure is often called "desalting." Generally, DTT is used as a protecting agent that prevents oxidation of thiol groups.
DTT is frequently used to reduce the disulfide bonds of proteins and, more generally, to prevent intramolecular and intermolecular disulfide bonds from forming between cysteine residues of proteins. However, even DTT cannot reduce buried (solvent-inaccessible) disulfide bonds, so reduction of disulfide bonds is sometimes carried out under denaturing conditions (e.g., at high temperatures, or in the presence of a strong denaturant such as 6 M guanidinium chloride, 8 M urea, or 1% sodium dodecylsulfate). DTT is oftentimes used along with sodium dodecylsulfate in SDS-PAGE to further denature proteins by reducing their disulfide bonds to allow for better separation of proteins during electrophoresis. Conversely, the solvent exposure of different disulfide bonds can be assayed by their rate of reduction in the presence of DTT.
DTT can also be used as an oxidizing agent. Its principal advantage is that effectively no mixed-disulfide species are populated, in contrast to other agents such as glutathione. In very rare cases, a DTT adduct may be formed, i.e., the two sulfur atoms of DTT may form disulfide bonds to different sulfur atoms; in such cases, DTT cannot cyclize since it has no such remaining free thiols.
Properties
Due to air oxidation, DTT is a relatively unstable compound whose useful life can be extended by refrigeration and handling in an inert atmosphere. Oxidation presents further complications as oxidized DTT exhibits a strong absorbance peak at 260 nm. Since thiols are less nucleophilic than their conjugate bases, thiolates, DTT becomes less potent as the pH lowers. (2S)-2-Amino-1,4-dimercaptobutane (dithiobutylamine or DTBA) is a new dithiol reducing agent that somewhat overcomes this limitation of DTT.[3] Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) is an alternative reducing agent that is more stable and effective at low pH.
DTT's half-life is 40 hours at pH 6.5 and 1.4 hours at pH 8.5 and 20 °C and it decreases further with increasing temperature. The presence of EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) to chelate divalent metal ions (Fe2+, Cu2+ and others) considerably increases the half-life of DTT in solution.[4]
References
- ^ a b M.J.O'Neil, ed. by (2001). Merck Index : an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, & biologicals : 13th ed (13. ed.). United States: MERCK & CO INC. ISBN 0-911910-13-1.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ Cleland, W. W. (1964). "Dithiothreitol, a new protective reagent for SH groups". Biochemistry. 3: 480–482. doi:10.1021/bi00892a002. PMID 14192894.
- ^ Lukesh, III, J. C.; Palte, M. J.; Raines, R. T. (2012). "A potent, versatile reducing agent from aspartic acid". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134 (9): 4057–4059. doi:10.1021/ja211931f. PMC 3353773. PMID 22353145.
- ^ Stevens, R; Stevens, L; Price, N. C (1983) The Stabilities of Various Thiol Compounds used in Protein Purifications. Biochemical Education, 11 (2), 70. DOI: 10.1016/0307-4412(83)90048-1
