Allergy
You must add a |reason= parameter to this Cleanup template – replace it with {{Cleanup|reason=<Fill reason here>}}, or remove the Cleanup template.
This article deals specifically with IgE mediated hypersensitivity. For other types of allergic or hypersensitive reactions see the main article: Hypersensitivity
An allergy or Type I hypersensitivity is a immune malfunction whereby a person's body is hypersensitised to react immunologically to typically nonimmunogenic substances. When a person is hypersensitised these substances are known as allergens. The word allergy derives from the Greek words allos meaning "other" and ergon meaning "reaction" or "reactivity". Type I hypersensitivity is characterised by excessive activation of mast cells by immunoglobulin E resulting in a systemic inflammatory response that can result in symptoms as benign as a runny nose, to life-threatening anaphylactic shock and death.
History
The term and concept of "allergy" were coined by Viennese pediatrician Baron Clemens von Pirquet in 1906. He observed that the symptoms of some of his patients might have been a response to outside allergens such as dust, pollen, or certain foods. For a long time all hypersensitivities were thought to stem from the improper action of inflammatory immunoglobulin class IgE, however it soon became clear that several different mechanisms utilizing different effector molecules were responsible for the myriad of disorders previously classified as "allergies". A new four-class (now five) classification scheme was designed by P. G. H. Gell and R. R. A. Coombs. Allergy has since been kept as the name for Type I Hypersensitivity, characterised by classical IgE mediation of effects.
Signs and symptoms
Allergy is characterised by a local or systemic inflammatory response to allergens. Local symptoms are:
- Nose: swelling of the nasal mucosa (allergic rhinitis)
- Eyes: redness and itching of the conjunctiva (allergic conjunctivitis)
- Airways: bronchoconstriction, wheezing and dyspnoea, sometimes outright attacks of asthma
- Skin: various rashes, such as eczema, hives (urticaria) and contact dermatitis.
Systemic allergic response is also called anaphylaxis. Depending of the rate of severity, it can cause cutaneous reactions, bronchoconstriction, oedema, hypotension, coma and even death.
Hay fever is one example of an exceedingly common minor allergy - large percentages of the population suffer from hayfever symptoms in response to airborne pollen. Asthmatics are often allergic to dust mites. Apart from ambient allergens, allergic reactions can be due to medications.
Diagnosis
There are several methods for the diagnosis and assessment of allergies.
Skin test
The typical and most simple method of diagnosis and monitoring of Type I Hypersensitivity is by skin testing. Small amounts of suspected allergens and/or their extracts (pollen, grass, mite proteins, peanut extract etc.) are introduced to sites on the skin marked with pen or dye (it must be noted that ink/dye should be carefully selected, lest it cause an allergic response itself). The allergens are either injected intradermally or into small scratchings made into the patient's skin. If the patient is allergic to the substance then a visible inflammatory reaction will usually occur within 30 minutes. This response will range from slight reddening of the skin to full-blown hives in extremely sensitive patients.
Problems with skin test
While the skin test is probably the most preferred means of testing for its simplicity and economics, it is not without complications. Some people may display a delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reaction which can occur as far as 6 hours after application of the allergen and last up to 24 hours. This can also cause serious long-lasting tissue damage to the affected area.
In addition, the application of previously unencountered allergens can actually sensitize certain individuals to the allergen; that is, cause the inception of a new allergy in susceptible individuals.
Total IgE count
Another method used to qualify type I hypersensitivity is measuring the amount of serum IgE contained within the patient's serum. This can be determined through the use of radiometric and colormetric immunoassays. Even the levels the amount of IgE specific to certain allergens can be measured through use of the radioallergosorbent test (RAST).
Treatment
There are limited mainstream medical treatments for allergies, probably the most important factor in rehabilitation is the removal of sources of allergens from the home environment, and avoiding environments in which contact with allergens is likely. This can range from losing the family pets, or to primary schools having a strict no-peanut policy to protect a sensitive pupil.
Immunotherapy
Hyposensitization is a form of immunotherapy where the patient is gradually vaccinated against progressively larger doses of the allergen in question. This can either reduce the severity or eliminate hypersensitivity altogether. It relies on the progressive skewing of IgG ("the blocking antibody") production, as opposed to the excessive IgE production seen in hypersensitivity type I cases.
In the 1960s, Dr. Len McEwen in the United Kingdom developed a treatment for allergies known as enzyme potentiated desensitization, or EPD. EPD uses much lower doses of antigens than conventional treatment, with the addition of an enzyme. EPD is available in the United Kingdom and Canada, and was available in the United States until 2001, when the Food and Drug Administration revoked its approval for an investigative study being performed. Since that time an American counterpart to EPD, known as Low Dose Antigens, or LDA, has been formulated from components approved by the FDA, and is available for treatment from a small number of doctors in the United States. EPD (and LDA) is still considered experimental by many mainstream doctors and medical insurance companies, and many doubt that it is more effective than a placebo.
A third form of immunotherapy involves the intravenous injection of monoclonal anti-IgE antibodies. These bind to free and B-cell IgE signalling such sources for destruction. They do not bind to IgE already bound to the Fc receptor on basophils and mast cells as this would stimulate the allergic inflammatory response.
Chemotherapy
Several antagonistic drugs are used to block the action of allergic mediators, preventing activation of cells and degranulation processes. They include antihistamines, cortisone, adrenalin (epinephrine), theophylline and Cromolyn sodium. These drugs help alleviate the symptoms of allergy but play little role in chronic alleviation of the disorder. They can play an imperative role in the acute recovery of someone suffering from anaphylaxis (which is why those allergic to bee stings often carry an adrenalin needle with them at all times).
Alternative therapies
In alternative medicine, a number of treatment modalities are considered effective by its practitioners in the treatment of allergies, particularly traditional Chinese medicine. However, none of these have been backed up by good quality evidence. On the contrary, they are generally criticised by mainstream medical researchers to be supported only by anecdotes, which makes them effective only as placebos.
Pathophysiology
All hypersensitivities result from an aberration somewhere in the normal immune process. However the exact cause of such malfunctions are not always been apparent, and several arguments from genetic-basis, environmental-basis and intermediate proponents exist with varying validity and acceptance.
Acute response
The difference between a type I hypersensitivity reaction against an allergen to the normal humoral response against a foreign body is that plasma cells secrete IgE as opposed to either IgM (against novel antigens) or IgG (against immunized antigens). IgE binds to Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells and basophils, both involved in the acute inflammatory response.
When IgE is first secreted it binds to the Fc receptors on a mast cell or basophil, and such a IgE-coated cell is said to sensitized to the allergen in question. A later exposure by the same allergen causes reactivation of these IgE, which then signal for the degranulation of the sensitized mast cell or basophil. These granules release histamine and other inflammatory chemical mediators (cytokines, interleukins, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins) into the surrounding tissue causing several systemic effects, such as vasodilation, mucous secretion, nerve stimulation and smooth muscle contraction. This results in the previously described symptoms of rhinorrhea, itchiness, dyspnea, and anaphylaxis. Depending on the individual, allergen, and mode of introduction, the symptoms can be system-wide (calliscal anaphylaxis), or localised to particular body systems (for example, asthma to the respiratory system; eczema to the dermis)
Late-phase response
After the chemical mediators of the acute response subside, late phase responses can often occur. This is due to the migration of other leukocytes such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils and macrophages to the initial site. The reaction is usually seen 4-6 hours after the original reaction and can last from 1-2 days. Cytokines from mast cells may also play a role in the persitence of long-term effects. Late phase responses seen in asthma are slightly different to those seen in other allergic responses.
Genetic basis
There is much evidence to support the genetic basis of allergy, as allergic parents are more likely to have allergic children, and their allergies are likely to be stronger than those from non-allergic parents. However some allergies are not consistent along genealogies with parents being allergic to peanuts, but having children allergic to ragweed, or siblings not sharing the same allergens.
Ethnicity has also been shown to play a role in some allergies. Interestingly, in regards to asthma, it has been suggested that different genetic loci are responsible for asthma in Caucasians, Hispanics, and African-Americans.
The hygiene hypothesis
One theory that has been gaining strength is the "hygiene hypothesis". This theory maintains that since children in more affluent countries are leading a cleaner and cleaner life (less exposure to dirt, extra use of disinfectants, etc), their immune systems have less exposure to parasites and other pathogens than children in other countries or in decades past. Their immune systems may, therefore, have many "loaded guns", cells which might have targeted, say, the intestinal worms that no longer cause trouble in affluent neighbourhoods. Having no reasonable target, these cells inadvertently become activated by environmental antigens that might only cause minor reactions in others. It is the symptoms of this exaggerated response that is seen as the allergic reaction.
Many common allergies such as asthma have seen huge increases in the years since the second world war, and many studies appear to show a correlation between this and the increasingly affluent and clean lifestyles in the west. This is supported by studies in less developed countries that do not enjoy western levels of cleanliness, and similarly do not show western levels of incidences of asthma and other allergies. During this same period, air quality, at one time considered the "obvious" cause of asthma, has shown a considerable improvement. This has led some researchers to conclude that it is our "too clean" upbringing that is to blame for the lack of immune system stimulation in early childhood.
Alternative views
Another theory is the exponential use and abuse of chemicals in affluent nations since the second world war. Vast numbers of chemicals are introduced into our indoor and outdoor environments with little or no testing regarding their toxicity to living beings. Many believe that air quality is getting worse rather than better, particularly if one considers indoor air quality as well as outdoor. (Indoor air quality has become significantly worse since building codes changed in the 1970s to make buildings more air-tight to conserve energy. This affects buildings built since that time.) Adverse reactions to toxins vary considerably from one person to another, and can involve extremes in symptoms including the neurological and endocrine systems as well as the more commonly recognized allergy symptoms listed above.
In 2004, a joint Swedish-Danish research team found a very strong link between allergies in children and the phthalates DEHP and BBzP, commonly used in PVC.
Allergies are also viewed by some medical practitioners as a negative consequence of the use and abuse of antibiotics and vaccinations. This mainstream Western approach to treatment and prevention of infectious disease has been used in the more affluent "First world" for a longer period of time than in the rest of the world, hence the much greater commonality of allergies in the First world. It is hypothesized that use of antibiotics and vaccination affect the immune system, and that allergies are a dysfunctional immune response. There is, however, very little evidence to support this view.
Common allergens
In addition to foreign proteins found in foreign serum (from blood transfusions) and vaccines, common allergens include:
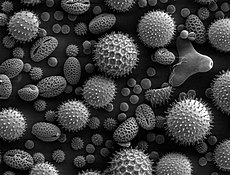
- Plant pollens
- rye grass
- ragweed
- timothy grass
- birch trees
- Mold spores
- Drugs
- penicillins
- sulfanomides
- salicylates (also found naturally in numerous fruits)
- local anaesthetics
- Foods

The house dust mite, its faeces and chitin are common allergens around the home - Insect products
- beesting venom
- wasp sting venom
- cockroach calyx
- dust mites
- Animal hair and dander
See also
- [ http://www.home-remedies-for-you.com/remedy/Allergies.html Home Remedies for Allergies]
References
- Goldsby RA, Kindt TK, Osborne BA and Kuby J (2003) Immunology, 5th Edition, W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, New York, ISBN 0-7167-4947-5
- The Association between Asthma and Allergic Symptoms in Children and Phthalates in House Dust: A Nested Case-Control Study
