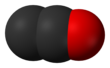
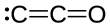Dicarbon monoxide
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by 114.142.214.184 (talk) at 07:38, 8 February 2018. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 07:38, 8 February 2018 by 114.142.214.184 (talk)
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Oxoethenylidene
| |||
| Other names
Ketenylidene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2O | |||
| Molar mass | 40.021 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Chemical compound
Dicarbon monoxide (C2O) is molecule that contains two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is a linear molecule that, because of its simplicity, is of interest in a variety of areas. It is, however, so extremely reactive that it is not encountered in everyday life. It is classified as a cumulene and an oxocarbon.[1]
Hi
References
- ^ Frenking, Gernot; Tonner, Ralf "Divalent carbon(0) compounds" Pure and Applied Chemistry 2009, vol. 81, pp. 597-614. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-08-11-03
| Common oxides | |
|---|---|
| Exotic oxides | |
| Polymers | |
| Compounds derived from oxides | |
Hidden categories:
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Articles with short description
- Short description matches Wikidata
- All stub articles