Delaware Valley
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2010) |
Delaware Valley
Greater Philadelphia Southeastern Pennsylvania Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington, PA-NJ-DE-MD MSA | |
|---|---|
 | |
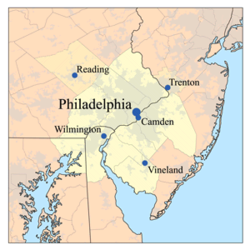 Map of the Lower Delaware Valley Metropolitan Area | |
| Country | |
| State | - - - - |
| Principal cities | Philadelphia Camden Wilmington Reading Trenton Atlantic City Vineland Hammonton Dover |
| Area | |
| • Urban | 1,981.4 sq mi (5,131.7 km2) |
| • Metro | 5,118 sq mi (13,256 km2) |
| Elevation | 0 - 1,080 ft (0 - 329 m) |
| Population (2013 est.) | |
| • Density | 2,746.32/sq mi (1,060.36/km2) |
| • Urban | 5,441,567 (5th) |
| • MSA | 6,034,678 (6th) |
| • CSA | 7,146,706 (8th) |
| MSA/CSA = 2013, Urban = 2010 | |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EST) |
The Delaware Valley is the valley through which the Delaware River flows. By extension, this toponym is commonly used to refer to Greater Philadelphia or Philadelphia metropolitan area ("the [Lower] Delaware Valley Metropolitan Area"), which straddles the Lower Delaware River just north of its estuary. The Delaware Valley Metropolitan Area is located at the southern part of the Northeast megalopolis and as such, the Delaware Valley can be described as either a metropolitan statistical area (MSA), or as a broader combined statistical area (CSA). The Delaware Valley Metropolitan Area is composed of several counties in southeastern Pennsylvania and southwestern New Jersey, one county in northern Delaware and one county in northeastern Maryland. The MSA has a population of over 6 million, while the CSA has a population of over 7.1 million (as of the 2010 Census Bureau count). Philadelphia, being the region's major commercial, cultural, and industrial center, wields a rather large sphere of influence that affects the counties that immediately surround it.
Some of the Delaware Valley's most well-known contributions to human civilization involve the region's higher education and medical institutions. The Delaware Valley has been influential upon American history and industry. The region are leaders in higher education, biotechnology, medicine, tourism and many others. With a gross domestic product of $388 billion, Philadelphia ranks ninth among world cities and fourth in the nation.[3]
The area has hosted many people and sites significant to American culture and history, particularly in the arts, where Philadelphia alone has more outdoor sculptures and murals than any other American city,[4] politics, including many influential people involved in politics such as Benjamin Franklin and Joe Biden, and the American Revolution. Philadelphia is famously known as "The Birthplace of America"[5] as the Declaration of Independence and Constitution were both drafted and signed there. On December 7, 1787, Delaware became the first state to ratify the Constitution, and has since promoted itself as "The First State".[6]
The Delaware Valley was home to many other instrumental moments in the American Revolution, including the First and Second Continental Congress, the preservation of the Liberty Bell, the Battles of Germantown, Brandywine, and Red Bank, the Siege of Fort Mifflin, the winter of 1777–78 at Valley Forge, the Philadelphia Convention, and many others. Philadelphia was one of the nation's capitals in the Revolutionary War, and served as temporary U.S. capital while Washington, D.C., was under construction.
Today, the area is home to some of the most prestigous universities in the world, such as the University of Pennsylvania, Drexel University, Villanova University, Saint Joseph's University, and Temple University.[7] The Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania is consistently ranked as the best business school in the world.[8]
Geography

In geology and geography, a strict sense of the term would incorporate the Delaware River's main drainage basin, and so encompass major tributaries such as the Schuylkill River and Lehigh River and their valleys or sub-basins. These extensions also apply culturally with decreasing degree gradually decreased by proximal distance because the ease of land travel enables a great deal of daily interaction; for example, the large number of commuters who travel daily 45–90 minutes creates cultural blends and parallel values.
In the course of their work, U.S. government agencies have reached various definitions of the Delaware Valley and the Greater Philadelphia Area. The Delaware Valley Regional Planning Commission (DVRPC) serves Philadelphia, four suburban Pennsylvania counties (Bucks County, Chester County, Delaware County, and Montgomery County), and four New Jersey counties (Burlington County, Camden County, Gloucester County, and Mercer County).[9] The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) defines metropolitan statistical area (MSAs), which are regions with relatively high population densities at their cores and close economic ties throughout their respective areas. Philadelphia is located in the Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington Metropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of the counties served by the DVRPC except for Mercer County, and also includes New Castle County, Delaware, Cecil County, Maryland, and Salem County, New Jersey. The OMB also groups one or more MSAs into larger combined statistical areas (CSAs), which reflect commuting patterns. MSAs and CSAs are not formal administrative divisions, but serve as useful tools for understanding the extent of metropolitan areas such as the Delaware Valley. The Philadelphia-Reading-Camden Combined Statistical Area includes all of the counties from the Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington Metropolitan Statistical Area, as well as Berks County, Pennsylvania, Kent County, Delaware, Atlantic County, New Jersey, Cape May County, New Jersey, and Cumberland County, New Jersey.
Population and economy
According to 2016 estimates from the United States Census Bureau, the Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington Metropolitan Statistical Area ranks as the seventh-largest MSA in the United States with 6,070,500 people.[10] According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington MSA had a gross domestic product of $431 billion, the ninth-largest among U.S. metropolitan areas.[11] 2016 Census Bureau estimates rank the Philadelphia-Reading-Camden Combined Statistical Area as the ninth-largest CSA in the United States, with 7,179,357 people.[12]
The Philadelphia-Camden-Wilmington Metropolitan Statistical Area's population of roughly 6 million people is comparable to that of countries such as Lebanon, Denmark, and Nicaragua. The MSA's nominal gross domestic product of $431 billion is comparable to countries such as Belgium, Iran, and Thailand. The MSA also ranks as the second most populous in the Northeastern United States after the New York metropolitan area, while the CSA is third-largest in the Northeast after the New York and Boston metropolitan areas. The Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area, which is part of Northeast Megalopolis but is considered part of the Southeastern United States under Census Bureau definitions, is also larger than the Philadelphia metropolitan area. Philadelphia itself is the sixth-most populous city in the United States and the third-most populous U.S. city east of the Mississippi River, after New York City and Chicago. Philadelphia's media market ranks fourth, behind New York City, Los Angeles, and Chicago, in Nielsen Media Market size rankings.[13]
Such educational institutions as Delaware Valley Regional High School in Alexandria Township and Delaware Valley College in Doylestown Township are named after the region. Likewise, Frenchtown's now defunct newspaper The Delaware Valley News was another example of the usage.
Subregions
Sixteen counties in four states constitute the Philadelphia-Reading-Camden Combined Statistical Area. The five Pennsylvania counties in the MSA are collectively known as Southeastern Pennsylvania, and the four suburban counties from this region are sometimes called the "collar counties."[14] Aside from Philadelphia, major municipalities in Southeastern Pennsylvania include the inner suburbs of Upper Darby Township and Bensalem Township. Berks County, which forms its own MSA and contains the CSA's second largest city, Reading, is generally not considered to be part of Southeastern Pennsylvania and is sometimes assigned to South Central Pennsylvania.
The seven New Jersey counties in the CSA form South Jersey, although Ocean County, which is part of the New York CSA, is also sometimes considered to be part of South Jersey.[15] Atlantic County, Cape May County, and Cumberland County each form their own respective metropolitan statistical areas. Atlantic City and the Jersey Shore are major tourist destinations for people from inside and outside of the Delaware Valley. Other major municipalities in South Jersey include Cherry Hill and Camden, which is across the Delaware River from Philadelphia.
The two counties of Delaware in the CSA constitute a majority of Delaware's land mass and population. Wilmington is the most populous city in Delaware and the fifth-most populous municipality in the Delaware Valley. The lone Maryland county in the Philadelphia-Reading-Camden Combined Statistical Area is part of the region known as the Eastern Shore of Maryland.
Although Mercer County in Central Jersey is often considered part of the Delaware Valley from a cultural perspective, it is classified as part of New York's CSA by the OMB. Mercer County and two counties in Pennsylvania's Lehigh Valley, Lehigh County and Northampton County, are part of the Philadelphia media market. Caroline County, Maryland is also part of the Philadelphia media market.[16]
List of counties
| County | State | Seat | 2010 Pop.[17] | 2016 Pop.[17] | Pop. Change | Area[18] | MSA[19] | Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kent | DE | Dover | 162,310 | 174,827 | 7.7% | 279.4 mi2 | Dover MSA | |
| New Castle | DE | Wilmington | 538,479 | 556,987 | 3.4% | 426.3 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Cecil | MD | Elkton | 101,108 | 102,603 | 1.5% | 348.2 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Atlantic | NJ | Mays Landing | 274,549 | 270,991 | -1.3% | 561.2 mi2 | Atlantic City-Hammonton MSA | |
| Burlington | NJ | Mount Holly | 448,734 | 449,284 | 0.1% | 804.8 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Camden | NJ | Camden | 513,657 | 510,150 | -0.7% | 222.3 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Cape May | NJ | Cape May Court House | 97,265 | 94,430 | -2.9% | 255.2 mi2 | Ocean City MSA | |
| Cumberland | NJ | Bridgeton | 156,898 | 153,797 | -2% | 489.3 mi2 | Vineland-Millville-Bridgeton MSA | |
| Gloucester | NJ | Woodbury | 288,288 | 292,330 | 1.4% | 324.9 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Salem | NJ | Salem | 66,083 | 63,436 | -4% | 337.8 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Berks | PA | Reading | 411,442 | 414,812 | 0.8% | 859.2 mi2 | Reading MSA | |
| Bucks | PA | Doylestown | 625,249 | 626,399 | 0.2% | 607.6 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Chester | PA | West Chester | 498,886 | 516,312 | 3.5% | 756 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Delaware | PA | Media | 558,979 | 563,402 | 0.8% | 184.2 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Montgomery | PA | Norristown | 799,874 | 821,725 | 2.7% | 781 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Philadelphia | PA | Philadelphia | 1,526,006 | 1,576,872 | 3.3% | 135.1 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | |
| Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | 5,965,343 | 6,070,500 | 1.8% | 4928.2 mi2 | Philadelphia–Camden–Wilmington MSA | - | ||
| Philadelphia–Reading–Camden CSA | 7,067,807 | 7,179,357 | 1.6% | 7372.5 mi2 | N/A | - | ||
List of largest municipalities


These municipalities are all within the Philadelphia-Reading-Camden Combined Statistical Area.
| City | Pop.[20] | County | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Philadelphia | 1,567,872 | Philadelphia | PA |
| Reading | 87,575 | Berks | PA |
| Upper Darby Township | 82,765 | Delaware | PA |
| Camden | 74,420 | Camden | NJ |
| Wilmington | 71,502 | New Castle | DE |
| Cherry Hill | 70,976 | Camden | NJ |
| Gloucester Township | 64,049 | Camden | NJ |
| Vineland | 60,876 | Cumberland | NJ |
| Bensalem Township | 60,354 | Bucks | PA |
| Lower Merion Township | 58,220 | Montgomery | PA |
| Abington Township | 55,640 | Montgomery | PA |
| Bristol Township | 54,170 | Bucks | PA |
| Haverford Township | 48,893 | Delaware | PA |
| Washington Township | 48,301 | Gloucester | NJ |
| Evesham Township | 45,578 | Burlington | NJ |
| Middletown Township | 45,318 | Bucks | PA |
| Egg Harbor Township | 43,747 | Atlantic | NJ |
| Mount Laurel | 41,849 | Burlington | NJ |
| Northampton Township | 39,562 | Bucks | PA |
| Winslow Township | 39,417 | Camden | NJ |
| Historical population (estimates) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1850 | 405,000 | - |
| 1860 | 608,000 | 50.12% |
| 1870 | 747,000 | 22.86% |
| 1880 | 949,000 | 27.04% |
| 1890 | 1,180,000 | 24.34% |
| 1900 | 1,454,000 | 10.44% |
| 1910 | 1,746,000 | 8.26% |
| 1920 | 2,072,000 | 18.67% |
| 1930 | 2,264,000 | 9.27% |
| 1940 | 2,538,000 | 12.10% |
| 1950 | 3,297,000 | 29.90% |
| 1960 | 4,419,000 | 34.09% |
| 1970 | 5,323,000 | 20.46% |
| 1980 | 5,239,000 | -1.57% |
| 1990 | 5,435,000 | 3.74% |
| 2000 | 5,687,000 | 4.66% |
| 2010 | 5,965,000 | 4.89% |
| 2017 | 6,029,312 | 1.07% |
| Populations for the Philadelphia Metropolitan Area
Source: city-data.com | ||
Statistical history
When metropolitan areas were originally defined in 1950, most of the area now in the Delaware Valley was split between four metropolitan areas, or "standard metropolitan areas," as they were called. The Philadelphia SMA comprised Philadelphia, Bucks, Chester, Delaware and Montgomery counties in Pennsylvania and Burlington, Camden and Gloucester counties in New Jersey. The Wilmington SMA comprised New Castle County in Delaware and Salem County in New Jersey, while Berks County was the Reading SMA and Atlantic County was the Atlantic City SMA.
In 1960, Cecil County was added to what was now the Wilmington Standard Metropolitan Statistical Area. In 1980, Cumberland County was defined as the Vineland-Millville-Bridgeton SMSA.
In 1990, the Philadelphia, Wilmington and Vineland-Millville-Bridgedon SMSAs were merged with the Trenton SMSA as the Philadelphia-Wilmington-Trenton Consolidated Metropolitan Statistical Area. At the same time, Cape May County was added to the Atlantic City SMSA. Kent County became the Dover MSA in 2000, and it and Atlantic City were added to the Philadelphia CSA in 2010.
Characteristics



The Delaware Valley is home to extensive populations of Irish Americans, German Americans, English Americans, Ukrainian Americans, Italian Americans, Swedish-Americans (which have a museum located at FDR Park in South Philadelphia), Polish Americans, Scottish Americans, Scotch-Irish Americans, Greek Americans, African Americans, Asians such as Chinese, Indian, Korean and Vietnamese, Armenians, Arabs and Turks, and Pakistanis, Israelis (while American Jews form a significant ethno-religious community), Hispanics. Within the Hispanic population, the vast majority are Puerto Ricans, though other groups include Dominicans and Mexicans.[22] There is a significant West Indian community. There is even a small Native American community known as Lenapehoking for Lenni-Lenape Indians of West Philadelphia.
Philadelphia's suburbs contain a high concentration of malls, the two largest of which have at least 5,000,000 square feet (460,000 m2) of office space, and at least 600,000 square feet (56,000 m2) of retail. These are the King of Prussia Mall in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, which is the largest in the United States (leasable sq. feet of retail space), and the Cherry Hill Mall in Cherry Hill, New Jersey, which was the first enclosed mall on the East Coast. Malls, office complexes, strip shopping plazas, expressways, and tract housing are common sights, and more and more continue to replace rolling countryside, farms, woods, and wetlands. However, due to strong opposition by residents and political officials, many acres of land have been preserved throughout the Delaware Valley. Older townships and large boroughs such as Cheltenham, Norristown, Jenkintown, Upper Darby and West Chester retain distinct community identities while engulfed in suburbia. The fastest-growing counties[as of?] are Chester, Montgomery, Bucks, and Gloucester. Upper Darby, in Delaware County is the largest township in the United States.[citation needed] Sometimes Reading is included in the Delaware Valley Metro Area. [citation needed]
Mid-Atlantic American English and its subset, Philadelphia English, are two common dialects of American English in Philadelphia and the Delaware Valley.
Climate
The Delaware Valley has four distinct seasons with ample precipitation and is divided by the 0 °C (32 °F) January isotherm. Most of Philadelphia and the NJ portion, almost all of the DE and MD portions, part of Delaware County, and extreme southern portions of Bucks and Chester Counties have a humid subtropical climate (Cfa.) The remainder of the Delaware Valley has a hot-summer humid continental climate (Dfa.) Snow amounts may vary widely year-to-year and normally do vary widely within the Delaware Valley. The region has only two ski areas: Bear Creek Ski and Recreation Area in eastern Berks County and Spring Mountain in central Montgomery County.
Using the -3 °C January isotherm as a boundary, all of the Delaware Valley is humid subtropical except for portions of Berks County and higher areas of northern Chester County. The warm-summer humid continental climate (Dfb) only exists in higher areas of Berks where all monthly temperatures average below 22 °C.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °F (°C) | 74 (23) |
79 (26) |
87 (31) |
95 (35) |
97 (36) |
102 (39) |
104 (40) |
106 (41) |
102 (39) |
96 (36) |
84 (29) |
73 (23) |
106 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 63.3 (17.4) |
63.5 (17.5) |
73.8 (23.2) |
84.3 (29.1) |
90.2 (32.3) |
94.8 (34.9) |
97.1 (36.2) |
94.8 (34.9) |
90.6 (32.6) |
82.6 (28.1) |
72.4 (22.4) |
64.2 (17.9) |
98.1 (36.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 41.3 (5.2) |
44.3 (6.8) |
52.8 (11.6) |
64.7 (18.2) |
74.4 (23.6) |
83.2 (28.4) |
87.8 (31.0) |
85.8 (29.9) |
78.9 (26.1) |
67.2 (19.6) |
55.9 (13.3) |
46.0 (7.8) |
65.2 (18.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 33.7 (0.9) |
35.9 (2.2) |
43.6 (6.4) |
54.5 (12.5) |
64.3 (17.9) |
73.5 (23.1) |
78.7 (25.9) |
76.8 (24.9) |
69.9 (21.1) |
58.2 (14.6) |
47.4 (8.6) |
38.6 (3.7) |
56.3 (13.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 26.0 (−3.3) |
27.5 (−2.5) |
34.3 (1.3) |
44.3 (6.8) |
54.2 (12.3) |
63.9 (17.7) |
69.6 (20.9) |
67.9 (19.9) |
60.9 (16.1) |
49.2 (9.6) |
38.8 (3.8) |
31.2 (−0.4) |
47.3 (8.5) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 10.7 (−11.8) |
13.7 (−10.2) |
20.8 (−6.2) |
33.0 (0.6) |
43.1 (6.2) |
53.2 (11.8) |
62.2 (16.8) |
60.3 (15.7) |
49.5 (9.7) |
37.1 (2.8) |
26.4 (−3.1) |
19.0 (−7.2) |
8.6 (−13.0) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −7 (−22) |
−11 (−24) |
5 (−15) |
14 (−10) |
28 (−2) |
44 (7) |
51 (11) |
44 (7) |
35 (2) |
25 (−4) |
8 (−13) |
−5 (−21) |
−11 (−24) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.13 (80) |
2.75 (70) |
3.96 (101) |
3.47 (88) |
3.34 (85) |
4.04 (103) |
4.38 (111) |
4.29 (109) |
4.40 (112) |
3.47 (88) |
2.91 (74) |
3.97 (101) |
44.11 (1,120) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 7.1 (18) |
8.4 (21) |
3.6 (9.1) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.2 (0.51) |
3.5 (8.9) |
23.1 (59) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 11.0 | 9.7 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.1 | 8.9 | 9.3 | 9.1 | 8.6 | 11.0 | 120.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 4.1 | 3.8 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 12.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 66.2 | 63.6 | 61.7 | 60.4 | 65.4 | 67.8 | 69.6 | 70.4 | 71.6 | 70.8 | 68.4 | 67.7 | 67.0 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 19.8 (−6.8) |
21.0 (−6.1) |
28.6 (−1.9) |
37.0 (2.8) |
49.5 (9.7) |
59.2 (15.1) |
64.6 (18.1) |
63.7 (17.6) |
57.2 (14.0) |
45.7 (7.6) |
35.6 (2.0) |
25.5 (−3.6) |
42.3 (5.7) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 155.7 | 154.7 | 202.8 | 217.0 | 245.1 | 271.2 | 275.6 | 260.1 | 219.3 | 204.5 | 154.7 | 137.7 | 2,498.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 52 | 52 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 61 | 61 | 61 | 59 | 59 | 52 | 47 | 56 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Source 1: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point and sun 1961–1990)[26][27][24] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas (UV index)[28] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Philadelphia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average sea temperature °F (°C) | 41.8 (5.5) |
39.9 (4.4) |
41.2 (5.1) |
46.7 (8.2) |
53.9 (12.2) |
66.3 (19.0) |
74.0 (23.3) |
75.9 (24.4) |
71.4 (21.9) |
64.2 (17.9) |
55.1 (12.8) |
47.7 (8.8) |
56.5 (13.6) |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 9.0 | 12.2 |
| Source: Weather Atlas [28] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Atlantic City International Airport, 1991–2020 normals,[c] extremes 1874–present[d] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 78 (26) |
76 (24) |
87 (31) |
94 (34) |
99 (37) |
106 (41) |
105 (41) |
103 (39) |
99 (37) |
96 (36) |
84 (29) |
77 (25) |
106 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 63.5 (17.5) |
64.8 (18.2) |
73.2 (22.9) |
83.2 (28.4) |
89.3 (31.8) |
94.5 (34.7) |
96.9 (36.1) |
94.6 (34.8) |
90.1 (32.3) |
82.8 (28.2) |
72.7 (22.6) |
65.3 (18.5) |
98.1 (36.7) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 43.2 (6.2) |
45.8 (7.7) |
52.6 (11.4) |
63.3 (17.4) |
72.5 (22.5) |
81.5 (27.5) |
86.6 (30.3) |
84.8 (29.3) |
78.5 (25.8) |
67.7 (19.8) |
57.1 (13.9) |
48.1 (8.9) |
65.1 (18.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 34.1 (1.2) |
36.0 (2.2) |
42.6 (5.9) |
52.5 (11.4) |
61.9 (16.6) |
71.4 (21.9) |
76.9 (24.9) |
75.0 (23.9) |
68.4 (20.2) |
57.1 (13.9) |
46.8 (8.2) |
38.7 (3.7) |
55.1 (12.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 25.1 (−3.8) |
26.2 (−3.2) |
32.6 (0.3) |
41.7 (5.4) |
51.4 (10.8) |
61.3 (16.3) |
67.2 (19.6) |
65.2 (18.4) |
58.2 (14.6) |
46.4 (8.0) |
36.6 (2.6) |
29.4 (−1.4) |
45.1 (7.3) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 6.5 (−14.2) |
9.7 (−12.4) |
16.1 (−8.8) |
26.7 (−2.9) |
36.0 (2.2) |
46.2 (7.9) |
55.9 (13.3) |
53.8 (12.1) |
43.5 (6.4) |
31.0 (−0.6) |
20.4 (−6.4) |
14.0 (−10.0) |
4.4 (−15.3) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −10 (−23) |
−11 (−24) |
2 (−17) |
12 (−11) |
25 (−4) |
37 (3) |
42 (6) |
40 (4) |
32 (0) |
20 (−7) |
10 (−12) |
−7 (−22) |
−11 (−24) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.38 (86) |
3.23 (82) |
4.52 (115) |
3.32 (84) |
3.34 (85) |
3.58 (91) |
4.47 (114) |
4.59 (117) |
3.55 (90) |
4.14 (105) |
3.37 (86) |
4.47 (114) |
45.96 (1,167) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 5.7 (14) |
5.9 (15) |
2.2 (5.6) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.1 (0.25) |
3.2 (8.1) |
17.4 (44) |
| Average extreme snow depth inches (cm) | 3.6 (9.1) |
3.1 (7.9) |
1.3 (3.3) |
0.1 (0.25) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.9 (4.8) |
6.0 (15) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.8 | 10.4 | 10.9 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 9.9 | 9.9 | 9.2 | 8.5 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 10.8 | 120.1 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 3.0 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 8.9 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 69.5 | 69.0 | 66.9 | 66.4 | 70.7 | 72.9 | 73.9 | 75.7 | 76.4 | 74.8 | 72.8 | 70.6 | 71.6 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | 21.6 (−5.8) |
23.2 (−4.9) |
30.0 (−1.1) |
37.9 (3.3) |
49.5 (9.7) |
59.4 (15.2) |
64.8 (18.2) |
64.2 (17.9) |
57.7 (14.3) |
46.4 (8.0) |
37.0 (2.8) |
27.0 (−2.8) |
43.2 (6.2) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 150.8 | 157.9 | 204.5 | 218.9 | 243.9 | 266.2 | 276.3 | 271.3 | 227.6 | 200.5 | 147.4 | 133.8 | 2,499.1 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 50 | 53 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 60 | 61 | 64 | 61 | 58 | 49 | 46 | 56 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1.6 | 2.6 | 4.2 | 6.0 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 8.6 | 7.7 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 5.0 |
| Source 1: NOAA (relative humidity, dew point and sun 1961–1990)[30][31][32] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: UV Index Today (1995 to 2022)[33] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Doylestown, Pennsylvania | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 39 (4) |
43 (6) |
52 (11) |
63 (17) |
74 (23) |
82 (28) |
87 (31) |
85 (29) |
77 (25) |
66 (19) |
55 (13) |
44 (7) |
64 (18) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 24 (−4) |
25 (−4) |
33 (1) |
42 (6) |
52 (11) |
61 (16) |
66 (19) |
65 (18) |
57 (14) |
45 (7) |
37 (3) |
29 (−2) |
45 (7) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.94 (100) |
2.87 (73) |
4.24 (108) |
3.85 (98) |
4.81 (122) |
3.61 (92) |
4.72 (120) |
4.34 (110) |
4.66 (118) |
3.35 (85) |
3.74 (95) |
3.80 (97) |
47.93 (1,217) |
| Source: Weather Channel [34] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Reading, Pennsylvania | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 71 (22) |
77 (25) |
88 (31) |
97 (36) |
96 (36) |
97 (36) |
102 (39) |
102 (39) |
100 (38) |
92 (33) |
82 (28) |
77 (25) |
102 (39) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 38 (3) |
42 (6) |
51 (11) |
63 (17) |
73 (23) |
82 (28) |
86 (30) |
84 (29) |
77 (25) |
66 (19) |
54 (12) |
43 (6) |
63 (17) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 22 (−6) |
24 (−4) |
32 (0) |
41 (5) |
51 (11) |
61 (16) |
65 (18) |
64 (18) |
56 (13) |
44 (7) |
36 (2) |
27 (−3) |
44 (6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −20 (−29) |
−8 (−22) |
−2 (−19) |
16 (−9) |
26 (−3) |
39 (4) |
46 (8) |
42 (6) |
30 (−1) |
20 (−7) |
8 (−13) |
−4 (−20) |
−20 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.92 (74) |
2.93 (74) |
3.56 (90) |
3.69 (94) |
4.03 (102) |
4.50 (114) |
4.67 (119) |
3.80 (97) |
4.42 (112) |
3.78 (96) |
3.44 (87) |
3.58 (91) |
45.32 (1,151) |
| Source: The Weather Channel[35] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Dover, Delaware (1981−2010 normals) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 43.4 (6.3) |
47.0 (8.3) |
54.9 (12.7) |
65.7 (18.7) |
74.7 (23.7) |
83.2 (28.4) |
87.0 (30.6) |
85.2 (29.6) |
79.3 (26.3) |
68.8 (20.4) |
58.5 (14.7) |
47.4 (8.6) |
66.3 (19.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 27.1 (−2.7) |
29.0 (−1.7) |
35.6 (2.0) |
44.3 (6.8) |
53.8 (12.1) |
63.4 (17.4) |
68.4 (20.2) |
67.0 (19.4) |
60.1 (15.6) |
48.7 (9.3) |
39.8 (4.3) |
31.0 (−0.6) |
47.4 (8.6) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.41 (87) |
3.07 (78) |
4.31 (109) |
3.88 (99) |
4.25 (108) |
4.00 (102) |
4.09 (104) |
4.36 (111) |
4.13 (105) |
3.42 (87) |
3.48 (88) |
3.65 (93) |
46.05 (1,171) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 4.6 (12) |
7.7 (20) |
.3 (0.76) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
.2 (0.51) |
2.9 (7.4) |
15.7 (40.67) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.1 | 9.6 | 10.0 | 11.3 | 10.9 | 9.1 | 9.3 | 8.6 | 8.3 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 10.3 | 113.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 2.2 | 1.9 | .3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | .9 | 5.3 |
| Source: NOAA[36] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Wilmington, Delaware (New Castle Airport), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1894–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 75 (24) |
78 (26) |
86 (30) |
97 (36) |
98 (37) |
102 (39) |
103 (39) |
107 (42) |
100 (38) |
94 (34) |
85 (29) |
75 (24) |
107 (42) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 40.2 (4.6) |
43.5 (6.4) |
52.4 (11.3) |
63.5 (17.5) |
73.0 (22.8) |
81.8 (27.7) |
86.1 (30.1) |
84.2 (29.0) |
77.4 (25.2) |
66.2 (19.0) |
55.7 (13.2) |
44.6 (7.0) |
64.1 (17.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 24.6 (−4.1) |
26.8 (−2.9) |
33.6 (0.9) |
43.0 (6.1) |
52.6 (11.4) |
62.6 (17.0) |
67.6 (19.8) |
66.1 (18.9) |
58.2 (14.6) |
46.1 (7.8) |
37.4 (3.0) |
28.7 (−1.8) |
45.6 (7.6) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −14 (−26) |
−15 (−26) |
2 (−17) |
11 (−12) |
30 (−1) |
40 (4) |
48 (9) |
43 (6) |
32 (0) |
23 (−5) |
11 (−12) |
−7 (−22) |
−15 (−26) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.01 (76) |
2.68 (68) |
3.92 (100) |
3.50 (89) |
3.95 (100) |
3.88 (99) |
4.57 (116) |
3.25 (83) |
4.32 (110) |
3.42 (87) |
3.10 (79) |
3.48 (88) |
43.08 (1,094) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 5.9 (15) |
8.3 (21) |
1.9 (4.8) |
0.3 (0.76) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.4 (1.0) |
3.4 (8.6) |
20.2 (51) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 10.5 | 9.4 | 10.7 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 10.3 | 9.9 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 10.3 | 117.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 4.3 | 3.6 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 11.8 |
| Source: NOAA[37][38] | |||||||||||||
Colonial history
The valley was the territory of the Susquehannock and Lenape, who are recalled in place names throughout the region. The region became part of the Dutch colony of New Netherland after the exploration of Delaware Bay in 1609. The Dutch called the Delaware River the Zuyd Rivier, or South River, and considered the lands along it banks and those of its bay to be the southern flank of its province of New Netherland. In 1638, it began to be settled by Swedes, Forest Finns, Dutch, and Walloons and became the colony of New Sweden, though this was not officially recognized by the Dutch Empire which re-asserted control in 1655. The area was taken by the English in 1664.[39] The name Delaware comes from Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr, who had arrived at Jamestown, Virginia in 1610, just as original settlers were about to abandon it, and thus maintaining the English foothold on the North American continent.
Transportation
Many residents commute to jobs in Philadelphia, Camden, and Wilmington with the help of expressways and trains. Commutes from one suburb to another are also common, as office parks have sprung up in new commercial centers such as King of Prussia, Fort Washington, Cherry Hill, and Plymouth Meeting.
Commuter rail
Formerly, the region was served by the Delaware Valley Railway.

- SEPTA Regional Rail
- Airport Line connecting Central Philadelphia with Philadelphia International Airport in Philadelphia and Delaware Counties.
- Wilmington/Newark Line connecting Philadelphia to the Wilmington, DE area (with limited weekday service to Newark, DE), via Chester City and Delaware County.
- Warminster Line connecting Philadelphia with southeastern Montgomery County and Warminster in Bucks County.
- West Trenton Line connecting Philadelphia north to the Trenton, NJ area, serving Montgomery and Bucks County, PA between Jenkintown, PA and Yardley, PA, with the final stop in Ewing, NJ.
- Media/Elwyn Line connecting Philadelphia to central Delaware County.
- Paoli/Thorndale Line connecting Philadelphia with the affluent Main Line area and western Chester County near Coatesville.
- Lansdale/Doylestown Line connecting Philadelphia with Lansdale in central Montgomery County and Doylestown in Bucks County.
- Manayunk/Norristown Line connecting Philadelphia with Conshohocken and Norristown in Montgomery County.
- Cynwyd Line connecting Philadelphia with Bala Cynwyd on the Philadelphia/Montgomery County line (limited weekday service)
- Trenton Line connecting Philadelphia to Trenton, NJ, serving Bucks County.
- Fox Chase Line connecting Central Philadelphia with the Fox Chase area in Philadelphia.
- Chestnut Hill East Line and Chestnut Hill West Line connecting Central Philadelphia with the Chestnut Hill area of the city.
- New Jersey Transit
- Atlantic City Line connecting Philadelphia to Atlantic City, NJ with connections to PATCO Speedline in Lindenwold, NJ.
- River Line connecting Camden (NJ) to Trenton (NJ) running along the east bank of the Delaware River.
- MARC
- Penn Line connecting Perryville, MD to Baltimore, MD and Washington D.C., and in the future will connect to SEPTA at Newark, DE.
- PATCO Speedline connecting Philadelphia to Lindenwold, NJ in Camden County with connections to NJT's Atlantic City Line.
Major highways

Pennsylvania
 I-76 (Schuylkill Expressway)
I-76 (Schuylkill Expressway)
 I-78 / US 22
I-78 / US 22 I-95 (Delaware Expressway)
I-95 (Delaware Expressway) I-176
I-176

 I-76 / I-276 / Penna Turnpike
I-76 / I-276 / Penna Turnpike I-476 (Blue Route)
I-476 (Blue Route)
 I-476 / Penna Turnpike NE Extension
I-476 / Penna Turnpike NE Extension
 I-676 / US 30 (Vine Street Expressway)
I-676 / US 30 (Vine Street Expressway) US 1 (Lincoln Expressway/Roosevelt Boulevard/City Line Avenue/Kennett-Oxford Bypass)
US 1 (Lincoln Expressway/Roosevelt Boulevard/City Line Avenue/Kennett-Oxford Bypass) US 13
US 13 US 30 (Lancaster Avenue/Lincoln Highway)
US 30 (Lancaster Avenue/Lincoln Highway) US 202 (Wilmington Pike/Highway/Dekalb Pike/Highway/Doylestown Pike/Lower York Road)
US 202 (Wilmington Pike/Highway/Dekalb Pike/Highway/Doylestown Pike/Lower York Road) US 222 (Outer Bypass/Shillington Bypass)
US 222 (Outer Bypass/Shillington Bypass) US 322 (Conchester Highway/Horseshoe Pike)
US 322 (Conchester Highway/Horseshoe Pike) US 422 (Pottstown Expressway/West Shore Bypass)
US 422 (Pottstown Expressway/West Shore Bypass) PA 12 (Warren Street Bypass)
PA 12 (Warren Street Bypass) PA 61 (Centre Avenue/Pottsville Pike)
PA 61 (Centre Avenue/Pottsville Pike) PA 63 (Woodhaven Road/Welsh Road/Sumneytown Pike)
PA 63 (Woodhaven Road/Welsh Road/Sumneytown Pike) PA 100 (Pottstown Pike)
PA 100 (Pottstown Pike) PA 309 (Fort Washington Expressway/Bethlehem Pike/Sellersville-Souderton Bypass)
PA 309 (Fort Washington Expressway/Bethlehem Pike/Sellersville-Souderton Bypass) PA 611 (Doylestown Bypass/Easton Road/Old York Road)
PA 611 (Doylestown Bypass/Easton Road/Old York Road)
New Jersey
 N.J. Turnpike
N.J. Turnpike G.S. Parkway
G.S. Parkway A.C. Expressway
A.C. Expressway I-76
I-76 I-295
I-295 I-676 (North-South Freeway)
I-676 (North-South Freeway) US 9
US 9 US 30
US 30 US 40
US 40 US 130
US 130 US 206
US 206 US 322
US 322 Route 38
Route 38 Route 42 (North-South Freeway)
Route 42 (North-South Freeway) Route 55
Route 55 Route 70
Route 70 Route 73
Route 73 Route 90
Route 90
Delaware
Maryland
Delaware River Bridges


- New Hope–Lambertville Bridge[40]
- Scudder Falls Bridge (no toll)
- Delaware River – Turnpike Toll Bridge
- Burlington–Bristol Bridge
- Tacony–Palmyra Bridge
- Betsy Ross Bridge
- Ben Franklin Bridge
- Walt Whitman Bridge
- Commodore Barry Bridge
- Delaware Memorial Bridge
Airports
Major:
- Philadelphia International Airport (PHL), located 15 miles southwest of Center City Philadelphia, is the main international airport serving the immediate Delaware Valley Area
- Newark Liberty International Airport (EWR), while not in the Delaware Valley, is a major airport serving certain regions of the Delaware Valley, including Bucks County and New Jersey. It is located 60 miles northeast of Center City Philadelphia, and 25 miles northeast of Trenton.
Secondary:
- Lehigh Valley International Airport (ABE)
- Northeast Philadelphia Airport (PNE)
- New Castle Airport (ILG)
- Reading Regional Airport (RDG)
- Atlantic City International Airport (ACY)
Colleges and universities
Delaware
- Delaware College of Art and Design
- Delaware State University
- Goldey-Beacom College
- University of Delaware
- Wesley College
- Widener University School of Law
- Wilmington University
New Jersey
- Rider University
- Rowan University
- Rutgers School of Law–Camden
- Rutgers University (Camden)
- Stockton University
- The College of New Jersey
Pennsylvania
- Albright College
- Alvernia University
- Arcadia University
- Bryn Mawr College
- Cabrini College
- Cairn University
- Chestnut Hill College
- Cheyney University of Pennsylvania
- Curtis Institute of Music
- Delaware Valley College
- DeVry University
- Drexel University
- Eastern University
- Gwynedd-Mercy College
- Harcum College
- Haverford College
- Holy Family University
- Immaculata University
- Kutztown University of Pennsylvania
- La Salle University
- Lincoln University
- Manor College
- Moore College of Art and Design
- Neumann University
- Peirce College
- Penn State Abington
- Penn State Berks
- Penn State Brandywine
- Penn State Great Valley
- Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
- Rosemont College
- Saint Joseph's University
- Swarthmore College
- Temple University
- Jefferson - Philadelphia University + Thomas Jefferson University
- University of Pennsylvania
- University of the Arts (Philadelphia)
- University of the Sciences in Philadelphia
- Ursinus College
- Valley Forge Christian College
- Valley Forge Military Academy and College
- Villanova University
- West Chester University
- Westminster Theological Seminary
- Widener University
Culture
Sports teams

Listing of the professional sports teams in the Delaware Valley
- National Basketball Association (NBA)
- Major League Baseball (MLB)
- Minor League Baseball (MiLB)
- National Football League (NFL)
- National Hockey League (NHL)
- Major League Soccer (MLS)
- Arena Football (AFL)
- NBA G League
- National Lacrosse League (NLL)
Media
The two main newspapers are The Philadelphia Inquirer and the Philadelphia Daily News, owned by the Philadelphia Media Network. Local television channels include KYW-TV 3 (CBS), WPVI 6 (ABC), WCAU 10 (NBC), WHYY-TV 12 (PBS), WPHL-TV 17 (MyNetworkTV), WTXF 29 (FOX), WPSG 57 (CW), and WPPX 61 (Ion). Radio stations serving the area include: WRTI, WIOQ, WDAS (AM), and WTEL.
Area codes
- 215/267: The City of Philadelphia and some of its northern suburbs
- 610/484: Southeastern Pennsylvania outside Philadelphia, including the western suburbs, the Lehigh Valley, and most of Berks County
- 856: Southwestern New Jersey, including Camden, Cherry Hill, and Vineland
- 609: Central and Southeastern New Jersey, including Trenton, Atlantic City and the Jersey Shore
- 302: Delaware
- 410/443/667: Eastern half of Maryland, including Cecil County
- 717: South Central Pennsylvania, including Western Berks County
Politics
Philadelphia itself is heavily Democratic, having voted for the Democratic candidate in every presidential election since 1936. The surrounding suburban counties are key political areas in Pennsylvania, which itself is an important swing state in federal politics.[42] South Jersey has consistently voted Democratic at the presidential level in recent years, although the region is slightly more Republican-leaning than North Jersey and has voted for Republicans at the state and local level.[43] New Castle County's Democratic lean and large share of Delaware's population has tended to make Delaware as a whole vote for Democrats, while the less populous Kent County is more competitive.[44] Recent well-known political figures from the Greater Philadelphia area include former Vice President Joe Biden and former Pennsylvania Governor Ed Rendell.
Congressional districts
The following congressional districts of the United States House of Representatives are located partly or entirely in the Delaware Valley CSA. Italicized counties are not part of the CSA.
| District | Incumbent | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | PVI | Incumbent | Party | Counties |
| DE-AL | D+6 | Lisa Blunt Rochester | D | Kent, New Castle, and Sussex |
| MD-1 | R+14 | Andy Harris | R | Cecil and several other counties |
| NJ-1 | D+13 | Donald Norcross | D | Burlington, Camden, and Gloucester |
| NJ-2 | R+1 | Frank LoBiondo | R | Atlantic, Burlington, Camden, Cape May, Cumberland, Gloucester, Ocean, and Salem |
| NJ-3 | R+2 | Tom MacArthur | R | Burlington and Ocean |
| PA-1 | D+31 | Bob Brady | D | Delaware and Philadelphia |
| PA-2 | D+40 | Dwight Evans | D | Montgomery and Philadelphia |
| PA-6 | R+2 | Ryan Costello | R | Berks, Chester, Lebanon, and Montgomery |
| PA-7 | R+1 | Pat Meehan | R | Berks, Chester, Delaware, Lancaster, and Montgomery |
| PA-8 | R+2 | Brian Fitzpatrick | R | Bucks and Montgomery |
| PA-13 | D+15 | Brendan Boyle | D | Montgomery and Philadelphia |
| PA-15 | R+4 | Charlie Dent | R | Berks, Dauphin, Lebanon, Lehigh, and Northampton |
| PA-16 | R+5 | Lloyd Smucker | R | Berks, Chester, and Lancaster |
Additionally, the Delaware Valley is represented in the United States Senate by the eight Senators from Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania.
Lexicon note
Some believe that the term "Delaware Valley" is not entirely a synonym for "Greater Philadelphia". "Greater Philadelphia" implies that the region is centered on the city in an economic and cultural context, while "Delaware Valley" is a more generic geographic term that does not imply that any part is of more consequence than any other. Several organizations, such as KYW Radio and the Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation, consciously use the term "Greater Philadelphia" to assert that Philadelphia is the center of the region, referring to the less urbanized areas as "Philadelphia's countryside".[45] Others note that the customary media usage of the term omits the majority of the length of the Delaware River's valley that is not in metropolitan Philadelphia.
WPVI-TV uses the slogan, "The Delaware Valley's leading news program" for their Action News broadcast, since that program has led the ratings for news programs in the Philadelphia market for over 30 years.
See also
Notes
- ^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the highest and lowest temperature readings during an entire month or year) calculated based on data at said location from 1991 to 2020.
- ^ Official temperature and precipitation measurements for Philadelphia were taken at the Weather Bureau Office in downtown from January 1872 to 19 June 1940, and at Philadelphia Int'l from 20 June 1940 to the present.[23] Snowfall and snow depth records date to 1 January 1884 and 1 October 1948, respectively.[24] In 2006, snowfall measurements were moved to National Park, New Jersey directly across the Delaware River from the airport.[25]
- ^ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the highest and lowest temperature readings during an entire month or year) calculated based on data at said location from 1991 to 2020.
- ^ The official climatology station for Atlantic City was at the Weather Bureau Office downtown from January 1874 to 15 June 1958 and Atlantic City Int'l (ACY) in Egg Harbor Township since 16 June 1958.[29] ACY's location in the Pine Barrens and distance away from the coast and urban heat island of downtown Atlantic City largely account for its markedly colder temperatures at night as compared to downtown; for example, from 1959 to 2013, there were 50 days with a low of 0 °F (−18 °C) or lower, while in the same period, the corresponding number of days at downtown was 2. The National Weather Service ceased regular snowfall observations at downtown after the winter of 1958–59.
References
- ^ "Welsh Mountain". Retrieved May 5, 2016.
- ^ "MyTopo – Welsh Mountain area". Retrieved May 5, 2016.
- ^ "Global city GDP rankings 2008–2025". Pricewaterhouse Coopers. Archived from the original on May 4, 2011. Retrieved November 20, 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Gateway to Public Art in Philadelphia Archived August 10, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Fairmount Park Art Association.
- ^ "Words and Their Stories: Nicknames for Philadelphia and Boston". Voice of America. Retrieved July 11, 2017.
- ^ "The First to Ratify" would be more accurate, as the beginnings of the states themselves date back to the Declaration of Independence, celebrated July 4, 1776, when what was to become the State of Delaware was still the three lower counties of Pennsylvania with the governor in Philadelphia, and not establishing independence from that body until September 20, 1776. According to Delaware's own website, "Delaware became a state in 1776, just two months after the signing of the Declaration of Independence." (ref-pdf) Therefore Delaware was actually the last of the thirteen colonies to establish itself as a state. Additionally, the Delaware State Quarter is minted with this nickname, yet shows Caesar Rodney on horseback in commemoration of how he was the last delegate to show up to the Continental Congress for the historic vote for independence. And with regard to the original Articles of Confederation, Delaware was the 12th of the 13 states to ratify.
- ^ Tucker, Laura (November 25, 2014). "Philadelphia". QS Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. Retrieved October 11, 2015.
- ^ "The 50 best business schools in the world".
- ^ "Greater Philadelphia Economic Development Framework" (PDF). September 2009. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2016". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 30, 2017.
- ^ Analysis, US Department of Commerce, BEA, Bureau of Economic. "Bureau of Economic Analysis". www.bea.gov. Retrieved October 4, 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2016 - United States -- Combined Statistical Area; and for Puerto Rico". United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 2017. Retrieved April 20, 2016.
- ^ "Local Television Market Universe Estimates" (PDF). Nielsen. The Nielsen Company. September 24, 2016. Retrieved April 11, 2017.
- ^ Bond, Michaelle (November 7, 2017). "In historic win, Delco Dems take council seats". Philly.com. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ Stirling, Steven (April 24, 2015). "Here are the North, Central and South Jersey borders as determined by you (INTERACTIVE)". NJ.com. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ "PHILADELPHIA DESIGNATED MARKET DATA". TruckAds. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ a b "County Population Totals and Components of Change: 2010-2016". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ "Land Area, Population, and Density for States and Counties: 1990". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ "OMB BULLETIN NO. 13-01" (PDF). Office of Management and Budget. February 28, 2013. p. 107. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 19, 2013. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Community Facts". American FactFidner. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 4, 2018.
- ^ "Global Philadelphia". Global Philadelphia Association. Retrieved February 2, 2015.
- ^ "Dominicans in the Delaware Valley". Medgar Evers College. Archived from the original on February 16, 2011. Retrieved May 13, 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ ThreadEx; search for location= "PA - Philadelphia", variable= "Station thread"
- ^ a b "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved April 13, 2016.
- ^ Wood, Anthony R. "Snow total at airport gets a boost A new measuring station and technique likely contributed to two 8-inch-plus readings". Philly.com. The Inquirer. Archived from the original on July 28, 2014. Retrieved June 10, 2014.
- ^ "Summary of Monthly Normals 1991–2020". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved June 13, 2021.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for PHILADELPHIA/INT'L ARPT PA 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- ^ a b "Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA - Monthly weather forecast and Climate data". Weather Atlas. Retrieved May 17, 2019.
- ^ Threadex
- ^ "NowData – NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ "Station: ATLANTIC CITY INTL AP, NJ". U.S. Climate Normals 2020: U.S. Monthly Climate Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on June 8, 2024. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ "WMO Climate Normals for ATLANTIC CITY, NJ 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on June 8, 2024. Retrieved August 11, 2021.
- ^ "Historical UV Index Data - Atlantic City, NJ". UV Index Today. Retrieved April 22, 2023.
- ^ Average weather for Doylestown Weather Channel Retrieved May 12, 2008
- ^ "Climate Statistics for Reading, Pennsylvania". Retrieved March 10, 2012.
- ^ "Station Name: DE DOVER". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ^ "NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved December 14, 2011.
- ^ "Station Name: DE WILMINGTON NEW CASTLE CO AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved May 5, 2014.
- ^ *Family Search.com: Map of Delaware Valley in 17th century showing forts & settlements with date of founding
- ^ "New Hope-Lambertville Route 202 Toll Bridge". Delaware River Joint Toll Brice Commission. Archived from the original on February 25, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The 50 best business schools in the world".
- ^ Cohen, Micah (October 29, 2012). "In Pennsylvania, the Democratic Lean Is Slight, but Durable". New York Times. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ Cohen, Micah (July 14, 2012). "In Blue New Jersey, Red Spots May Be Sign of the Past". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ Cohen, Micah (August 31, 2012). "Delaware: A Small Example of a Larger Trend". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- ^ Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation.
Further reading
- Jean R. Soderlund, Lenape Country: Delaware Valley Society before William Penn. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2014.
- Mark L. Thompson, The Contest for the Delaware Valley: Allegiance, Identity, and Empire in the Seventeenth Century. Baton Rouge, LA: Louisiana State University Press, 2013.



