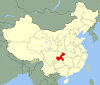
Chongqing
Chongqing
重庆市 | |
|---|---|
 Clockwise from top: Jiefangbei CBD Skyline, Temple of the White Emperor, Egongyan Bridge, Qutang Gorge, and the Great Hall of the People | |
 Location of Chongqing Municipality within China | |
| Coordinates: 29°33′30″N 106°34′00″E / 29.55833°N 106.56667°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Settled | c. 316 BC |
| Divisions - County-level - Township-level | 25 districts, 13 counties 1259 towns, townships, and subdistricts |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipality |
| • CPC Secretary | Chen Min'er |
| • Mayor | Tang Liangzhi |
| • Congress chairman | Zhang Xuan |
| • Conference chairman | Xu Jingye |
| Area | |
• Municipality | 82,403 km2 (31,816 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 472.8 km2 (182.5 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 244 m (801 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 1,709.4 m (5,608.3 ft) |
| Population (2015)[2] | |
• Municipality | 30,165,500 |
| • Density | 370/km2 (950/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 8,165,500 |
| • Urban density | 17,000/km2 (45,000/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 17 million |
| Demonym | Chongqinger |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 4000 00 – 4099 00 |
| Area code | 23 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-CQ |
| GDP | 2017 [4] |
| - Total | CNY1.95 trillion US$288.82 billion (18th) |
| - Per capita | CNY63,689 US$9,433 (10th) |
| HDI (2016) | 0.797[5] (17th) – high |
| Licence plate prefixes | 渝A, 渝D (Yuzhong, Jiangbei, Jiulongpo, Dadukou) 渝B (Nan'an, Shapingba, Beibei, Wansheng, Shuangqiao, Yubei, Banan, Changshou) 渝C (Yongchuan, Hechuan, Jiangjin, Qijiang, Tongnan, Tongliang, Dazu, Rongchang, Bishan) 渝F(Wanzhou, Liangping, Chengkou, Wushan, Wuxi, Zhongxian, Kaizhou, Fengjie, Yunyang) 渝G(Fuling, Nanchuan, Dianjiang, Fengdu, Wulong) 渝H (Qianjiang, Shizhu, Xiushan, Youyang, Pengshui) |
| Abbreviation | CQ / 渝; yú |
| City flower | Camellia[6] |
| City tree | Ficus lacor[7] |
| Website | CQ.gov.cn Template:Zh icon English.CQ.gov.cn |
| Chongqing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 "Chongqing" in Simplified (top) and Traditional (bottom) Chinese characters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 重庆 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 重慶 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | ⓘ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cong2-qin4 ([tsʰoŋ˨˩ tɕʰin˨˩˦]) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Chungking | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | "Doubled Celebration" | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chongqing ([ʈʂʰʊ̌ŋ.tɕʰîŋ] ⓘ), formerly romanized as Chungking,[a] is a major city in southwest China. Administratively, it is one of China's four direct-controlled municipalities (the other three are Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin), and the only such municipality in China located far away from the coast.[8] It is the largest city on Earth by city area.
Chongqing was a Sichuan province municipality during the Republic of China (ROC) administration, serving as its wartime capital during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945). The current municipality was created on 14 March 1997 to help the Three Gorges Dam migration, succeeding the sub-provincial city administration that was part of Sichuan Province.[9] Chongqing's population as of 2015[update] is just over 30 million with an urban population of 18.38 million. Of these, approximately 8.5 million people live in Chongqing central urban area; Fuling District, Wanzhou District and Qianjiang District are in fact cities in their own right, and along with the central urban area constitute a metropolitan area[10] housing 17 million people.[3] According to the 2010 census, Chongqing is the most populous Chinese municipality,[11] and also the largest direct-controlled municipality in China, and comprises 26 districts, eight counties, and four autonomous counties.
The official abbreviation of the city, "Yu" (渝), was approved by the State Council on 18 April 1997.[12] This abbreviation is derived from the old name of a part of the Jialing River that runs through Chongqing and feeds into the Yangtze River.
Chongqing has a significant history and culture and serves as the economic centre of the upstream Yangtze basin. It is a major manufacturing centre and transportation hub; a July 2012 report by the Economist Intelligence Unit described it as one of China's "13 emerging megalopolises".[13]
History
Ancient history
Tradition associates Chongqing with the State of Ba. This new capital was first named Jiangzhou (江州).[14]
Imperial era
Jiangzhou subsequently remained under Qin Shi Huang's rule during the Qin dynasty, the successor of the Qin State, and under the control of Han dynasty emperors. Jiangzhou was subsequently renamed during the Northern and Southern dynasties to Chu Prefecture (楚州), then in 581 AD (Sui dynasty) to Yu Prefecture (渝州), and later in 1102 during Northern Song to Gong Prefecture (恭州).[15] The name Yu however survives to this day as an abbreviation for Chongqing, and the city centre where the old town stood is also called Yuzhong (Central Yu).[14] It received its current name in 1189, after Prince Zhao Dun of the Southern Song dynasty described his crowning as king and then Emperor Guangzong as a "double celebration" (simplified Chinese: 双重喜庆; traditional Chinese: 雙重喜慶; pinyin: shuāngchóng xǐqìng, or chongqing in short). In his honour, Yu Prefecture was therefore renamed Chongqing subprefecture marking the occasion of his enthronement.
In 1362, (Yuan dynasty), Ming Yuzhen, a peasant rebelling leader, established the Daxia Kingdom (大夏) at Chongqing for a short time.[16] In 1621 (Ming dynasty), another short-lived kingdom of Daliang (大梁) was established by She Chongming (奢崇明) with Chongqing as its capital.[17] In 1644, after the fall of the Ming dynasty to rebel army, Chongqing, together with the rest of Sichuan, was captured by Zhang Xianzhong, who was said to have massacred a large number of people in Sichuan and depopulated the province with was also partially due to many people fleeing. The Manchus later conquered the province, and during the Qing dynasty, immigration to Chongqing and Sichuan took place with the support of Qing emperor.[18]
In 1890, the British Consulate General was opened in Chongqing.[19] The following year, the city became the first inland commerce port open to foreigners.[20] The French, German, US and Japanese consulates were opened in Chongqing in 1896–1904.[21][22][23][24]
Provisional capital of the Republic of China

During and after the Second Sino-Japanese War, from Nov 1937 to May 1946, it was Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek's provisional capital. After Britain, the United States, and other Allies entered the war in Asia in December 1941, one of the Allies' deputy commanders of operations in South East Asia (South East Asia Command SEAC), Joseph Stilwell, was based in the city. The city was also visited by Lord Louis Mountbatten, the Supreme Commander of SEAC which was itself headquartered in Ceylon, modern day Sri Lanka. Chiang Kai Shek as Supreme Commander in China worked closely with Stilwell.[25] The Japanese Air Force heavily bombed it. Due to its mountainous environment, many people were saved from the bombing. Due to the bravery, contributions and sacrifices made by the local people during World War II, Chongqing became known as the City of Heroes. Many factories and universities were relocated from eastern China to Chongqing during the war, transforming this city from inland port to a heavily industrialized city. In late November 1949 the Nationalist KMT government fled the city.[26]
Municipality status

On 14 March 1997, the Eighth National People's Congress decided to merge the Sub-provincial city with the neighbouring Fuling, Wanxian, and Qianjiang prefectures that it had governed on behalf of the province since September 1996. The resulting single division became Chongqing Municipality, containing 30,020,000 people in forty-three former counties (without intermediate political levels). The municipality became the spearhead of China's effort to develop its western regions and to coordinate the resettlement of residents from the reservoir areas of the Three Gorges Dam project. Its first official ceremony took place on 18 June 1997. On 8 February 2010, Chongqing became one of the four National Central/Core cities, the other three are Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin.[27] On 18 June 2010, Liangjiang New Area was established in Chongqing, which is the third State-level new areas at the time of its establishment.[28]
Organised crime and the gang trials
In the first decade of the 21st century, the city became notorious for organised crime and corruption. Gangsters oversaw businesses involving billions of yuan and the corruption reached into the law-enforcement and justice systems. In 2009, city authorities under the auspices of municipal Communist Party secretary Bo Xilai undertook a large-scale crackdown, arresting 4,893 suspected gangsters, "outlaws" and corrupt cadres, leading to optimism that the period of gangsterism was over.[29] However, local media later highlighted the apparent reliance by the authorities on torture to extract confessions upon which convictions were based. In December 2009, one defence lawyer was controversially arrested and sentenced to 18 months in prison for "coaching his client to make false claims of torture" and in July 2010, another lawyer released videotapes of his client describing the torture in detail.[30] In 2014, four policemen involved in the interrogation were charged with the practice of "opposed illegal interrogation techniques", considered by observers to be torture.[31] The number of security cameras increased significantly in the early 2010s to the highest of any city in the world at around 500,000.[citation needed]
Geography
Physical geography and topography
Chongqing is situated at the transitional area between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the plain on the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in the sub-tropical climate zone often swept by moist monsoons. It often rains at night in late spring and early summer, and thus the city is famous for its "night rain in the Ba Mountains", as described by poems throughout Chinese history including the famous Written on a Rainy Night-A Letter to the North by Li Shangyin.[32] The municipality reaches a maximum width of 470 kilometres (290 mi) from east to west, and a maximum length of 450 km (280 mi) from north to south.[33] It borders the following provinces: Hubei in the east, Hunan in the southeast, Guizhou in the south, Sichuan in the west and northwest, and Shaanxi to the north in its northeast corner.[34]
Chongqing covers a large area crisscrossed by rivers and mountains. The Daba Mountains stand in the north, the Wu Mountains in the east, the Wuling Mountains in the southeast, and the Dalou Mountains in the south. The whole area slopes down from north and south towards the Yangtze River valley, with sharp rises and falls. The area is featured by a large geological massif, of mountains and hills, with large sloping areas at different heights.[35] Typical karst landscape is common in this area, and stone forests, numerous collections of peaks, limestone caves and valleys can be found in many places. The Longshuixia Gap (龙水峡地缝), with its natural arch-bridges, has made the region a popular tourist attraction. The Yangtze River runs through the whole area from west to east, covering a course of 665 km (413 mi), cutting through the Wu Mountains at three places and forming the well-known Three Gorges: the Qutang, the Wuxia and the Xiling gorges.[36] Coming from northwest and running through "the Jialing Lesser Three Gorges" of Libi, Wentang and Guanyin, the Jialing River joins the Yangtze in Chongqing.[37]
The central urban area of Chongqing, or Chongqing proper, is a city of unique features. Built on mountains and partially surrounded by the Yangtze and Jialing rivers, it is known as a "mountain city" and a "city on rivers".[38] The night scene of the city is very illuminated, with millions of lights and their reflection on the rivers. With its special topographical features, Chongqing has the unique scenery of mountains, rivers, forests, springs, waterfalls, gorges, and caves. Li Bai, a famous poet of the Tang dynasty, was inspired by the natural scenery and wrote this epigram.[39]
Specifically, the central urban area is located on a huge folding area (similar to the landscape of the Appalachian Mountains in the United States), and the Yuzhong District, Nan'an District, Shapingba District and Jiangbei District are located right on a big syncline. And the "Southern Mountain of Chongqing" (Tongluo Mountain), along with the Zhongliang Mountain are two anticlines next to the syncline of downtown.[40]
Leaving at dawn the White Emperor crowned with cloud,
I've sailed a thousand li through canyons in a day.
With the monkeys' adieus the riverbanks are loud,
My skiff has left ten thousand mountains far away.
Climate
All climatic data listed below comes from the central parts of the city.
- Annual average
- 18.39 °C (65.1 °F)[41]
- January average
- 7.9 °C (46.2 °F)[41]
- August average
- 28.3 °C (82.9 °F)[41]
- Historical Temperature range
- From −1.8 °C (29 °F) on 15 December 1975 to 43.0 °C (109 °F) on 15 August 2006[42][43]
- Total annual hours of sunshine
- 955
- Annual precipitation
- 1,108 millimetres (43.6 in)
Chongqing has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa/Cfa), and for most of the year experiences very humid conditions. Known as one of the "Three Furnaces" of the Yangtze River, along with Wuhan and Nanjing, its summers are long and among the hottest and most humid in China, with highs of 33 to 34 °C (91 to 93 °F) in July and August in the urban area.[44] Winters are short and somewhat mild, but damp and overcast. The city's location in the Sichuan Basin causes it to have one of the lowest annual sunshine totals nationally, at only 1,055 hours, lower than much of Northern Europe; the monthly percent possible sunshine in the city proper ranges from a mere 8% in December and January to 48% in August. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from −1.8 °C (29 °F) on 15 December 1975 (unofficial record of −2.5 °C (27 °F) was set on 8 February 1943) to 43.0 °C (109 °F) on 15 August 2006 (unofficial record of 44.0 °C (111 °F) was set on 8 and 9 August 1933).[42][45]
As exemplified by Youyang County below, conditions are often cooler in the southeast part of the municipality due to the higher elevations there.
| Climate data for Chongqing (Shapingba District, 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
34.0 (93.2) |
36.5 (97.7) |
38.9 (102.0) |
39.8 (103.6) |
42.0 (107.6) |
43.0 (109.4) |
41.9 (107.4) |
35.1 (95.2) |
29.2 (84.6) |
21.5 (70.7) |
43.0 (109.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.3 (50.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
27.2 (81.0) |
29.4 (84.9) |
33.0 (91.4) |
33.2 (91.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
21.7 (71.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
11.5 (52.7) |
22.1 (71.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 7.9 (46.2) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
22.6 (72.7) |
25.1 (77.2) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.3 (82.9) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.6 (65.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
9.3 (48.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 6.2 (43.2) |
8.0 (46.4) |
11.2 (52.2) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
22.1 (71.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
16.5 (61.7) |
12.2 (54.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −1.8 (28.8) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
1.2 (34.2) |
2.8 (37.0) |
10.8 (51.4) |
15.5 (59.9) |
19.2 (66.6) |
17.8 (64.0) |
14.3 (57.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−1.8 (28.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 19.7 (0.78) |
23.4 (0.92) |
43.0 (1.69) |
96.5 (3.80) |
146.7 (5.78) |
193.8 (7.63) |
186.0 (7.32) |
135.1 (5.32) |
105.6 (4.16) |
85.7 (3.37) |
48.2 (1.90) |
24.3 (0.96) |
1,108 (43.63) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 10.0 | 9.8 | 11.9 | 14.3 | 15.5 | 15.7 | 12.5 | 11.3 | 12.7 | 16.1 | 11.5 | 9.8 | 151.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84 | 80 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 81 | 76 | 74 | 79 | 85 | 84 | 85 | 80 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 20.6 | 29.7 | 64.9 | 93.6 | 109.4 | 97.7 | 158.6 | 167.0 | 106.6 | 50.4 | 35.9 | 20.4 | 954.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 8 | 11 | 18 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 42 | 48 | 28 | 18 | 13 | 8 | 24 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[41] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Youyang Tujia and Miao Autonomous County, elevation 827 m (2,713 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 21.4 (70.5) |
27.9 (82.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
33.4 (92.1) |
35.3 (95.5) |
35.6 (96.1) |
36.7 (98.1) |
37.5 (99.5) |
35.6 (96.1) |
31.9 (89.4) |
26.7 (80.1) |
20.9 (69.6) |
37.5 (99.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) |
10.1 (50.2) |
14.2 (57.6) |
20.2 (68.4) |
24.4 (75.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
20.3 (68.5) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.1 (50.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.1 (39.4) |
6.3 (43.3) |
9.8 (49.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
19.5 (67.1) |
22.7 (72.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
24.9 (76.8) |
21.3 (70.3) |
15.9 (60.6) |
11.3 (52.3) |
6.3 (43.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.6 (34.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
11.8 (53.2) |
15.9 (60.6) |
19.4 (66.9) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.3 (70.3) |
17.9 (64.2) |
13.1 (55.6) |
8.3 (46.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.6 (21.9) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
1.4 (34.5) |
5.9 (42.6) |
11.5 (52.7) |
14.6 (58.3) |
14.3 (57.7) |
10.7 (51.3) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 30.9 (1.22) |
38.3 (1.51) |
57.1 (2.25) |
114.8 (4.52) |
201.8 (7.94) |
232.4 (9.15) |
199.7 (7.86) |
153.8 (6.06) |
87.1 (3.43) |
116.9 (4.60) |
61.5 (2.42) |
22.3 (0.88) |
1,316.6 (51.84) |
| Average precipitation days | 11.8 | 11.7 | 15.0 | 15.7 | 17.3 | 16.9 | 15.7 | 14.2 | 10.6 | 15.3 | 10.5 | 10.4 | 165.1 |
| Average snowy days | 8.5 | 4.4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 3.9 | 19.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 | 82 | 81 | 79 | 79 | 81 | 78 | 76 | 79 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 41.6 | 39.1 | 63.6 | 82.4 | 102.7 | 91.6 | 147.2 | 158.3 | 115.9 | 73.9 | 75.4 | 53.5 | 1,045.2 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 13 | 12 | 17 | 21 | 24 | 22 | 35 | 39 | 32 | 21 | 24 | 17 | 23 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[46][47][48] | |||||||||||||
Air quality
As one of the most polluted cities in China, Chongqing, with over 100 days of fog per year,[49] is also known as the "Fog City" (雾都), like San Francisco, and a thick layer of fog shrouds it for 68 days per year during the spring and autumn.[50][51] During the Second Sino-Japanese War, this special weather possibly played a role in protecting the city from being overrun by the Imperial Japanese Army.
According to the National Environmental Analysis released by Tsinghua University and the Asian Development Bank in January 2013, Chongqing is among one of the ten most air-polluted cities in China. Also according to this report, seven of the ten most air-polluted cities in China including Taiyuan, Beijing, Urumqi, Zhengzhou, Xi'an, Jinan and Shijiazhuang.[52]
Administrative divisions
Chongqing is the largest of the four direct-controlled municipalities of the People's Republic of China. The municipality is divided into 38 subdivisions (3 were abolished in 1997, and Wansheng and Shuangqiao districts were abolished in October 2011[53]), consisting of 26 districts, 8 counties, and 4 autonomous counties. The boundaries of Chongqing municipality reach much farther into the city's hinterland than the boundaries of the other three provincial level municipalities (Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin), and much of its administrative area, which spans over 80,000 square kilometres (30,900 sq mi), is rural.
| Administrative divisions of Chongqing | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| |||||||||||||
| Division code[54] | Division | Area in km2[55] | Population 2010[56] | Seat | Postal code | Subdivisions[57] | |||||||
| Subdistricts | Towns | Townships [n 1] |
Ethnic townships | Residential communities | Villages | ||||||||
| 500000 | Chongqing | 82403 | 28,846,170 | Yuzhong | 400000 | 181 | 567 | 233 | 14 | 2324 | 5235 | ||
| 500101 | Wanzhou | 3457 | 1,563,050 | Chenjiaba Subdistrict | 404000 | 11 | 29 | 10 | 2 | 187 | 448 | ||
| 500102 | Fuling | 2946 | 1,066,714 | Lizhi Subdistrict | 408000 | 8 | 12 | 6 | 108 | 310 | |||
| 500103 | Yuzhong | 23 | 630,090 | Qixinggang Subdistrict | 400000 | 12 | 78 | ||||||
| 500104 | Dadukou | 102 | 301,042 | Xinshancun Subdistrict | 400000 | 5 | 2 | 48 | 32 | ||||
| 500105 | Jiangbei | 221 | 738,003 | Cuntan Subdistrict | 400000 | 9 | 3 | 88 | 48 | ||||
| 500106 | Shapingba | 396 | 1,000,013 | Qinjiagang Subdistrict | 400000 | 18 | 8 | 140 | 86 | ||||
| 500107 | Jiulongpo | 431 | 1,084,419 | Yangjiaping Subdistrict | 400000 | 7 | 11 | 107 | 105 | ||||
| 500108 | Nan'an | 263 | 759,570 | Tianwen Subdistrict | 400000 | 7 | 7 | 85 | 61 | ||||
| 500109 | Beibei | 754 | 680,360 | Beiwenquan Subdistrict | 400700 | 5 | 12 | 63 | 117 | ||||
| 500110 | Qijiang | 2747 | 1,056,817 | Gunan Subdistrict | 400800 | 5 | 25 | 99 | 365 | ||||
| 500111 | Dazu | 1433 | 721,359 | Tangxiang Subdistrict | 400900 | 3 | 24 | 103 | 197 | ||||
| 500112 | Yubei | 1452 | 1,345,410 | Shuangfengqiao Subdistrict | 401100 | 14 | 12 | 155 | 215 | ||||
| 500113 | Banan | 1834 | 918,692 | Longzhouwan Subdistrict | 401300 | 8 | 14 | 87 | 198 | ||||
| 500114 | Qianjiang | 2397 | 445,012 | Chengxi Subdistrict | 409700 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 80 | 138 | |||
| 500115 | Changshou | 1423 | 770,009 | Fengcheng Subdistrict | 401200 | 4 | 14 | 31 | 223 | ||||
| 500116 | Jiangjin | 3200 | 1,233,149 | Jijiang Subdistrict | 402200 | 4 | 24 | 85 | 180 | ||||
| 500117 | Hechuan | 2356 | 1,293,028 | Nanjin Street Subdistrict | 401500 | 7 | 23 | 61 | 327 | ||||
| 500118 | Yongchuan | 1576 | 1,024,708 | Zhongshan Road Subdistrict | 402100 | 7 | 16 | 52 | 208 | ||||
| 500119 | Nanchuan | 2602 | 534,329 | Dongcheng Subdistrict | 408400 | 3 | 15 | 15 | 58 | 185 | |||
| 500120 | Bishan | 912 | 586,034 | Bicheng Subdistrict | 402700 | 6 | 9 | 43 | 142 | ||||
| 500151 | Tongliang | 1342 | 600,086 | Bachuan Subdistrict | 402500 | 3 | 25 | 57 | 269 | ||||
| 500152 | Tongnan | 1585 | 639,985 | Guilin Subdistrict | 402600 | 2 | 20 | 21 | 281 | ||||
| 500153 | Rongchang | 1079 | 661,253 | Changyuan Subdistrict | 402400 | 6 | 15 | 75 | 92 | ||||
| 500154 | Kaizhou | 3959 | 1,160,336 | Hanfeng Subdistrict | 405400 | 7 | 26 | 7 | 78 | 435 | |||
| 500155 | Liangping | 1890 | 687,525 | Liangshan Subdistrict | 405200 | 2 | 26 | 7 | 33 | 310 | |||
| 500156 | Wulong | 2872 | 351,038 | Gangkou Town | 408500 | 12 | 10 | 4 | 24 | 184 | |||
| 500229 | Chengkou Co. | 3286 | 192,967 | Gecheng Subdistrict | 405900 | 2 | 6 | 17 | 22 | 184 | |||
| 500230 | Fengdu Co. | 2896 | 649,182 | Sanhe Subdistrict | 408200 | 2 | 23 | 5 | 53 | 277 | |||
| 500231 | Dianjiang Co. | 1518 | 704,458 | Guixi Subdistrict | 408300 | 2 | 23 | 2 | 62 | 236 | |||
| 500233 | Zhong Co. | 2184 | 751,424 | Zhongzhou Town | 404300 | 22 | 5 | 1 | 49 | 317 | |||
| 500235 | Yunyang Co. | 3634 | 912,912 | Shuangjiang Subdistrict | 404500 | 4 | 22 | 15 | 1 | 87 | 391 | ||
| 500236 | Fengjie Co. | 4087 | 834,259 | Yong'an Town | 404600 | 19 | 8 | 4 | 54 | 332 | |||
| 500237 | Wushan Co. | 2958 | 495,072 | Gaotang Subdistrict | 404700 | 11 | 12 | 2 | 30 | 308 | |||
| 500238 | Wuxi Co. | 4030 | 414,073 | Baichang Subdistrict | 405800 | 2 | 15 | 16 | 38 | 292 | |||
| 500240 | Shizhu Co. | 3013 | 415,050 | Nanbin Town | 409100 | 17 | 15 | 29 | 213 | ||||
| 500241 | Xiushan Co. | 2450 | 501,590 | Zhonghe Subdistrict | 409900 | 14 | 18 | 59 | 208 | ||||
| 500242 | Youyang Co. | 5173 | 578,058 | Taohuayuan Town | 409800 | 15 | 23 | 8 | 270 | ||||
| 500243 | Pengshui Co. | 3903 | 545,094 | Hanjia Subdistrict | 409600 | 11 | 28 | 55 | 241 | ||||
| Divisions in Chinese and varieties of romanizations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Sichuanese Pinyin | |
| Chongqing Municipality | 重庆市 | Chóngqìng Shì | cong2 qin4 si4 | |
| Wanzhou District | 万州区 | Wànzhōu Qū | wan4 zou2 ngou4 | |
| Fuling District | 涪陵区 | Fúlíng Qū | ||
| Yuzhong District | 渝中区 | Yúzhōng Qū | yu2 zong1 ngou4 | |
| Dadukou District | 大渡口区 | Dàdùkǒu Qū | da4 du4 kou3 ngou4 | |
| Jiangbei District | 江北区 | Jiāngběi Qū | ||
| Shapingba District | 沙坪坝区 | Shāpíngbà Qū | ||
| Jiulongpo District | 九龙坡区 | Jiǔlóngpō Qū | ||
| Nan'an District | 南岸区 | Nán'àn Qū | ||
| Beibei District | 北碚区 | Běibèi Qū | ||
| Qijiang District | 綦江区 | Qíjiāng Qū | ||
| Dazu District | 大足区 | Dàzú Qū | ||
| Yubei District | 渝北区 | Yúběi Qū | ||
| Banan District | 巴南区 | Bānán Qū | ||
| Qianjiang District | 黔江区 | Qiánjiāng Qū | ||
| Changshou District | 长寿区 | Chángshòu Qū | ||
| Jiangjin District | 江津区 | Jiāngjīn Qū | ||
| Hechuan District | 合川区 | Héchuān Qū | ho2 cuan1 ngou4 | |
| Yongchuan District | 永川区 | Yǒngchuān Qū | yun3 cuan1 ngou4 | |
| Nanchuan District | 南川区 | Nánchuān Qū | ||
| Bishan District | 璧山区 | Bìshān Qū | ||
| Tongliang District | 铜梁区 | Tóngliáng Qū | ||
| Tongnan District | 潼南区 | Tóngnán Qū | ||
| Rongchang District | 荣昌区 | Róngchāng Qū | ||
| Kaizhou District | 开州区 | Kāizhōu Qū | ||
| Liangping District | 梁平区 | Liángpíng Qū | ||
| Wulong District | 武隆区 | Wǔlóng Qū | ||
| Chengkou County | 城口县 | Chéngkǒu Xiàn | ||
| Fengdu County | 丰都县 | Fēngdū Xiàn | ||
| Dianjiang County | 垫江县 | Diànjiāng Xiàn | ||
| Zhong County | 忠县 | Zhōngxiàn | ||
| Yunyang County | 云阳县 | Yúnyáng Xiàn | ||
| Fengjie County | 奉节县 | Fèngjié Xiàn | ||
| Wushan County | 巫山县 | Wūshān Xiàn | ||
| Wuxi County | 巫溪县 | Wūxī Xiàn | ||
| Shizhu Tujia Autonomous County | 石柱土家族自治县 | Shízhù Tǔjiāzú Zìzhìxiàn | ||
| Xiushan Tujia and Miao Autonomous County | 秀山土家族苗族自治县 | Xiùshān Tǔjiāzú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn | ||
| Youyang Tujia and Miao Autonomous County | 酉阳土家族苗族自治县 | Yǒuyáng Tǔjiāzú Miáozú Zìzhìxiàn | ||
| Pengshui Miao and Tujia Autonomous County | 彭水苗族土家族自治县 | Péngshuǐ Miáozú Tǔjiāzú Zìzhìxiàn | ||
- ^ Including other township related subdivisions.



|
|
|
a Indicates with which district the division was associated below prior to the merging of Chongqing, Fuling, Wanxian (now Wanzhou) and Qianjiang in 1997.
Central Chongqing
Districts
The urban area of Chongqing is known as Central Chongqing (重庆主城区). Spanning approximately 5,473 square kilometres (2,113 square miles), it includes the following nine districts:[58][59]
- Yuzhong District (渝中区, or "Central Chongqing District"), the central and most densely populated district, where government and international business offices and the city's best shopping are located in the district's Jeifangbei CBD area. Yuzhong is located on the peninsula surrounded by E-ling Hill, Yangtze River and Jialing River.
- Jiangbei District (江北区, or "River North District"), located to the north of Jialing River.
- Shapingba District (沙坪坝区), roughly located between Jialing River and Zhongliang Mountain.
- Jiulongpo District (九龙坡区), roughly located between Yangtze River and Zhongliang Mountain.
- Nan'an District (南岸区, or "Southern Bank District"), located on the south side of Yangtze River.
- Dadukou District (大渡口区)
- Banan District (巴南区, or "Southern Chongqing District"). Previously called Ba County, and changed to the current name in 1994. Its northern area merged into central Chongqing, and its capital town Yudong is a satellite city of Central Chongqing.
- Yubei District (渝北区, or "Northern Chongqing District"). Previously called Jiangbei County, and changed into the current name in 1994. Its southern area merged into Central Chongqing, and the capital town Lianglu Town is a satellite city of Central Chongqing.
- Beibei District (北碚区), a satellite city northwest of Central Chongqing.
Landforms
Central Chongqing is in the eastern edge of Sichuan Basin. Yangtze River meets its major tributary stream, Jialing River, in Central Chongqing. The city is located on a big syncline valley. Two tributary ranges of Huaying Mountain (Zhongling Mountain and Tongluo Mountain) roughly forms the eastern and western boundaries of Central Chongqing. The highest point in downtown is the top of E-ling Hill, which is a smaller syncline hill that keeps Yangtze River and Jialing River apart for some more kilometres. The elevation of E-ling Hill is 379 metres (1,243 feet). The lowest point in Central Chongqing is Chaotian Gate, where the two rivers merge with each other. The altitude there is 160 metres (520 feet). The average height of Central Chongqing is 259 metres (850 feet). In the near-suburban Chongqing, however, there are several high mountains. The highest one is called Wugong Ling Mountain, with the altitude of 1,709.4 metres (5,608 feet).
Bridges


With many bridges on Yangtze River and Jialing River in urban area, Central Chongqing is sometimes called the Bridge Capital of China. The first major bridge built in urban Chongqing is the Niujiaotuo Jialing River Bridge built in 1958. The first bridge on Yangtze River is the Shibanpo Yangtze River Bridge (or Chongqing Yangtze River Bridge) built in 1977.
Until 2014, within the range of Central Chongqing, there are 20 bridges on Yangtze River and 28 bridges on Jialing River. Bridges in Chongqing have various structures and shapes, making Chongqing a museum of bridges.
Aerial tramway
Chongqing is the only Chinese city that keeps public aerial tramways. Historically there were three aerial tramways in Chongqing: the Yangtze River Tramway, the Jialing River Tramway and the South Mountain Tramway. Currently, only Yangtze River Tramway is still operating. This tramway is 1,160 metres (3,810 feet) long, connecting the southern and northern banks of Yangtze River. The daily passenger volume is about 10,000.
Demographics

| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1949 | 1,003,000 | — |
| 1979 | 6,301,000 | +528.2% |
| 1983 | 13,890,000 | +120.4% |
| 1996 | 15,297,000 | +10.1% |
| 1997[60]* | 28,753,000 | +88.0% |
| 2000[60] | 28,488,200 | −0.9% |
| 2005[60] | 27,980,000 | −1.8% |
| 2008[60] | 28,390,000 | +1.5% |
| 2012[60] | 28,846,170 | +1.6% |
| 2013[60] | 29,700,000 | +3.0% |
| 2014[61] | 29,914,000 | +0.7% |
| 2015[62] | 30,170,000 | +0.9% |
| *Population size in 1997 was affected by expansion of administrative divisions. | ||
According to a July 2010 article from the official Xinhua news agency, the municipality has a population of 32.8 million, including 23.3 million farmers. Among them, 8.4 million farmers have become migrant workers, including 3.9 million working and living in urban areas of Chongqing.[63] The metropolitan area encompassing the central urban area was estimated by the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) to have, as of 2010[update], a population of 17 million.[64][3]
This would mean that the locally registered farmers who work in other jurisdictions number 4.5 million, reducing the local, year-round population of Chongqing in 2010 to 28.3 million, plus those who are registered in other jurisdictions but live and work in Chongqing. According to China's 2005 statistical yearbook, of a total population of 30.55 million, those with residence registered in other jurisdictions but residing in the Chongqing enumeration area numbered 1.4 million, including 46,000 who resided in Chongqing "for less than half-year". An additional 83,000 had registered in Chongqing, but not yet settled there.[65]
The 2005 statistical yearbook also lists 15.22 million (49.82%) males and 15.33 million (50.18%) females.[65]
In terms of age distribution in 2004, of the 30.55 million total population, 6.4 million (20.88%) were age 0–14, 20.7 million (67.69%) were 15–64, and 3.5 million (11.46%) were 65 and over.[66]
Of a total 10,470,000 households (2004), 1,360,000 consisted of one person, 2,940,000 two-person, 3,190,000 three-person, 1,790,000 four-person, 783,000 five-person, 270,000 six-person, 89,000 seven-person, 28,000 eight-person, 6,000 nine-person, and 10,000 households of 10 or more persons per household.[67]
Politics

Chongqing has been, since 1997, a direct-controlled municipality in the Chinese administrative structure, making it a provincial-level division with commensurate political importance. The municipality's top leader is the secretary of the municipal committee of the Communist Party of China ("party chief"), which, since 2007, has also held a seat on the Politburo of the Communist Party of China, the country's second highest governing council. Under the Soviet-inspired nomenklatura system of appointments, individuals are appointed to the position by the central leadership of the Communist Party, and bestowed to an official based on seniority and adherence to party orthodoxy, usually given to an individual with prior regional experience elsewhere in China and nearly never a native of Chongqing. Notable individuals who have held the municipal Party Secretary position include He Guoqiang, Wang Yang, Bo Xilai, Zhang Dejiang, and Sun Zhengcai, the latter three were Politburo members during their term as party chief. The party chief heads the municipal party standing committee, the de facto top governing council of the municipality. The standing committee is typically composed of 13 individuals which includes the party chiefs of important subdivisions and other leading figures in the local party and government organization, as well as one military representative.
The municipal People's Government serves as the day-to-day administrative authority, and is headed by the mayor, who is assisted by numerous vice mayors and mayoral assistants. Each vice mayor is given jurisdiction over specific municipal departments. The mayor is the second-highest-ranking official in the municipality. The mayor usually represents the city when foreign guests visit.[68]
The municipality also has a People's Congress, theoretically elected by lower level People's Congresses. The People's Congress nominally appoints the mayor and approves the nominations of other government officials. The People's Congress, like those of other provincial jurisdictions, is generally seen as a symbolic body. It convenes in full once a year to approve party-sponsored resolutions and local regulations and duly confirm party-approved appointments. On occasion the People's Congress can be venues of discussion on municipal issues, although this is dependent on the actions of individual delegates. The municipal People's Congress is headed by a former municipal official, usually in their late fifties or sixties, with a lengthy prior political career in Chongqing. The municipal Political Consultative Conference (zhengxie) meets at around the same time as the People's Congress. Its role is to advise on political issues. The zhengxie is headed by a leader who is typically a former municipal or regional official with a lengthy career in the party and government bureaucracy.
Military
Chongqing was the wartime capital of China during the Second Sino-Japanese war (i.e., World War II), and from 1938 to 1946,[69] the seat of administration for the Republic of China's government before its departure to Nanjing and then Taiwan.[70] It also contains a military museum named after the Chinese Korean War hero Qiu Shaoyun.[71]
Chongqing used to be the headquarters of the 13th Group Army of the People's Liberation Army, one of the two group armies that formerly comprise the Chengdu Military Region, which in 2016 was re-organized into the Western Theater Command.[72]
Economy





Chongqing was separated from Sichuan province and made into a municipality in its own right in 14 March 1997[73] in order to accelerate its development and subsequently China's relatively poorer western areas (see China Western Development strategy).[74] An important industrial area in western China,[75] Chongqing is also rapidly urbanising. For instance, statistics[76] suggest that new construction added approximately 137,000 square metres (1,470,000 square feet) daily of usable floor space to satisfy demands for residential, commercial and factory space. In addition, more than 1,300 people moved into the city daily, adding almost 100 million yuan (US$15 million) to the local economy.
Traditionally, due to its geographical remoteness, Chongqing and neighbouring Sichuan have been important military bases in weapons research and development.[77] Chongqing's industries have now diversified but unlike eastern China, its export sector is small due to its inland location. Instead, factories producing local-oriented consumer goods such as processed food, cars, chemicals, textiles, machinery and electronics are common.
Chongqing is China's third largest centre for motor vehicle production and the largest for motorcycles. In 2007, it had an annual output capacity of 1 million cars and 8.6 million motorcycles.[78] Leading makers of cars and motor bikes includes China's fourth biggest automaker; Changan Automotive Corp and Lifan Hongda Enterprise, as well as Ford Motor Company, with the US car giant having 3 plants in Chongqing. The municipality is also one of the nine largest iron and steel centres in China and one of the three major aluminium producers. Important manufacturers include Chongqing Iron and Steel Company and South West Aluminium which is Asia's largest aluminium plant.[79] Agriculture remains significant. Rice and fruits, especially oranges, are the area's main produce. Natural resources are also abundant with large deposits of coal, natural gas, and more than 40 kinds of minerals such as strontium and manganese. Coal reserves ≈ 4.8 billion tonnes. Chuandong Natural Gas Field is China's largest inland gas field with deposits of around 270 billion m3 – more than 1/5 of China's total. Has China's largest reserve of strontium (China has the world's 2nd biggest strontium deposit). Manganese is mined in the Xiushan area. although the mining sector has been criticised for being wasteful, heavily polluting and unsafe.[80] Chongqing is also planned to be the site of a 10 million ton capacity refinery operated by CNPC (parent company of PetroChina) to process imported crude oil from the Sino-Burma pipelines. The pipeline itself, though not yet finished, will eventually run from Sittwe (in Myanmar's western coast) through Kunming in Yunnan before reaching Chongqing[81] and it will provide China with fuels sourced from Myanmar, the Middle East and Africa. Recently, there has been a drive to move up the value chain by shifting towards high technology and knowledge intensive industries resulting in new development zones such as the Chongqing New North Zone (CNNZ).[82] Chongqing's local government is hoping through the promotion of favorable economic policies for the electronics and information technology sectors, that it can create a 400 billion RMB high technology manufacturing hub which will surpass its car industry and account for 25% of its exports.[83]
The city has also invested heavily in infrastructure to attract investment.[78][84] The network of roads and railways connecting Chongqing to the rest of China has been expanded and upgraded reducing logistical costs. Furthermore, the nearby Three Gorges Dam which is the world's largest, will not only supply Chongqing with power once completed but also allows oceangoing ships to reach Chongqing's Yangtze River port.[85] These infrastructure improvements have led to the arrivals of numerous foreign direct investors (FDI) in industries ranging from car to finance and retailing; such as Ford,[86] Mazda,[87] HSBC,[88] Standard Chartered Bank,[89] Citibank,[90] Deutsche Bank,[91] ANZ Bank,[92] Scotiabank,[93] Wal-Mart,[94] Metro AG[95] and Carrefour,[96] among other multinational corporations.
Chongqing's nominal GDP in 2011 reached 1001.1 billion yuan (US$158.9 billion) while registering an annual growth of 16.4%. However, its overall economic performance is still lagging behind eastern coastal cities such as Shanghai. For instance, its per capita GDP was 22,909 yuan (US$3,301) which is below the national average. Nevertheless, there is a massive government support to transform Chongqing into the region's economic, trade, and financial centre and use the municipality as a platform to open up the country's western interior to further development.[97]
Chongqing has been identified by the Economist Intelligence Unit in the November 2010 Access China White Paper as a member of the CHAMPS (Chongqing, Hefei, Anshan, Maanshan, Pingdingshan and Shenyang), an economic profile of the top 20 emerging cities in China.[98]
Economic and technological development zones
The city includes a number of economic and technological development zones:
- Chongqing Chemical Industrial Park[99]
- Chongqing Economic & Technological Development Zone[100]
- Chongqing Hi-Tech Industry Development Zone[101]
- Chongqing New North Zone (CNNZ)[102]
- Chongqing Export Processing Zone[103]
- Jianqiao Industrial Park (located in Dadukou District)[104]
- Liangjiang New Area[105]
- Liangjiang Cloud Computing Center (the largest of its kind in China)[106]
Chongqing itself is part of the West Triangle Economic Zone, along with Chengdu and Xi'an.
Transport
Since its elevation to national-level municipality in 1997, the city has dramatically expanded its transportation infrastructure. With the construction of railways and expressways to the east and southeast, Chongqing is a major transportation hub in southwestern China.
As of October 2014, the municipality had 31 bridges across the Yangtze River including over a dozen in the city's urban core.[107] Aside from the city's first two Yangtze River bridges, which were built, respectively, in 1960 and 1977, all of the other bridges were completed since 1995.
River port


Chongqing is one of the most important inland ports in China. There are numerous luxury cruise ships that terminate at Chongqing, cruising downstream along the Yangtze River to Yichang, Wuhan, Nanjing or even Shanghai.[108] In the recent past, this provided virtually the only transportation option along the river. However, improved rail, expressways and air travel have seen this ferry traffic reduce or been cancelled altogether, thus most of the river ferry traffic consists of mostly leisure cruises for tourists rather than local needs. Improved access by larger cargo vessels has been made due to the construction of the Three Gorges Dam. This allows bulk transport of goods along the Yangtze River. Coal, raw minerals and containerized goods provide the majority of traffic plying this section of the river. Several port handling facilities exists throughout the city, including many impromptu river bank sites.[109]
Railways

Major train stations in Chongqing:
- Chongqing Railway Station in Yuzhong, accessible via Metro Lines 1 & 3 (Lianglukou Metro Station), is the city's oldest railway station and located near the city centre. The station handles mostly long-distance trains. There are plans for a major renovation and overhaul of this station, thus many services have been transferred to Chongqing North Railway Station.
- Chongqing North Railway Station is a station handling many long-distance services and high-speed rail services to Chengdu, Beijing and other cities. It was completed in 2006 and is connected to Metro Line
- Chongqing West Railway Station is in Shapingba, a station handling many long-distance services and high-speed rail services to many cities. It is completed in 2018
- Shapingba Railway Station is in Shapingba, near Shapingba CBD, accessible via Metro Line 1. It handles many local and regional train services. It is completed in 2018.
Chongqing is a major freight destination for rail with continued development with improved handling facilities. Due to subsidies and incentives, the relocation and construction of many factories in Chongqing has seen a huge increase in rail traffic.
Chongqing is a major rail hub regionally.
- Chengdu–Chongqing Railway to Chengdu
- Sichuan-Guizhou Railway to Guiyang
- Xiangyang–Chongqing Railway to Hubei
- Chongqing–Huaihua Railway to Hunan
- Chongqing-Suining Railway (Sichuan province) express railway
- Chongqing-Lichuan Railway to Hubei
- Chongqing–Lanzhou Railway (Gansu) railway (under construction)
Highways

Traditionally, the road network in Chongqing has been narrow, winding and limited to smaller vehicles because of the natural terrain, large rivers and the huge population demands on the area, especially in the Yuzhong District. In other places, such as Jiangbei, large areas of homes and buildings have recently been cleared to improve the road network and create better urban planning. This has seen many tunnels and large bridges needing to be built across the city. Construction of many expressways have connected Chongqing to neighbouring provinces. Several ring roads have also been constructed. The natural mountainous terrain that Chongqing is built on makes many road projects difficult to construct, including for example some of the world's highest road bridges.[110]
Unlike many other Chinese cities, it is rare for motorbikes, electric scooters or bicycles to be seen on Chongqing Roads. This is due to the extremely hilly and mountainous nature of Chongqing's roads and streets. However, despite this, Chongqing is a large manufacturing centre for these types of vehicles.[111]
- Chongqing-Chengdu Expressway
- Chongqing-Chengdu 2nd Expressway (under construction)
- Chongqing-Wanzhou-Yichang Highway (Wanzhou-Yichang section under construction)
- Chongqing-Guiyang Highway
- Chongqing-Changsha Expressway (Xiushan-Changsha section under construction)
- Chongqing-Dazhou-Xi'a Highway (Dazhou-Xi'an section under construction)
- Chongqing-Suining Expressway
- Chongqing-Nanchong Expressway
- China National Highway 210
- China National Highway 212
Airports

The major airport of Chongqing is Chongqing Jiangbei International Airport (IATA: CKG, ICAO: ZUCK). It is located in Yubei District. The airport offers a growing network of direct flights to China, South East Asia, the Middle East, North America, and Europe. It is located 21 km (13 mi) north of the city-centre of Chongqing and serves as an important aviation hub for south-western China.[112] Jiangbei airport is a hub for China Southern Airlines, Chongqing Airlines, Sichuan Airlines, China Express Airlines, Shandong Airlines and Hainan Airlines's new China West Air. Chongqing also is a focus city of Air China, therefore it is very well connected with Star Alliance and Skyteam's international network. The airport currently has three parallel runways in operation. It serves domestic routes to most other Chinese cities, as well as international routes to Auckland, New York City, London, Los Angeles, Moscow, Doha, Dubai, Seoul, Bangkok, Phuket, Osaka, Singapore, Chiang Mai, Phnom Penh, Siem Reap, Malé, Bali, Zadar, Tokyo, Kuala Lumpur, Batam, Rome and Helsinki.
Chongqing airport is also a 72-hour transit visa-free airport for foreigners in many countries(Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Russia, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Cyprus, Bulgaria, Romania, Ukraine, Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Republic of Montenegro, Macedonia, Albania, United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile, Australia, New Zealand, South Korea, Japan, Singapore, Brunei, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar).
Currently, Jiangbei airport has three terminals. Terminal 1 is the oldest original terminal and is no longer in use. Terminal 2 is a larger building split into Halls A and B serving domestic flights. The first, second and third phase of the airport came into operation in January 1990, December 2004, and December 2010 respectively. This domestic terminal is capable of handling 30 million passengers while its international terminal is able to handle more than 1 million passengers annually. Terminal 3A together with the third runway began operations on August 29,[113] 2017. A fourth terminal and runway are planned to start construction in 2019.
Chongqing airport was the 10th busiest airport nationwide in 2010 measured by passenger traffic, handling 15,802,334 people. By 2015 this number doubled to more than 30,000,000 passengers annually. The airport was also the 11th busiest airport by cargo traffic and by traffic movements in China. During the first half of year 2011, Chongqing airport handled 8.87 million passengers, and surpassed Hangzhou Xiaoshan International Airport (8.48 million) to become the 9th busiest airport in terms of passenger traffic in mainland China.[114]
Freight development has increased, especially in the export of high value electronics, such as laptop computers. It is envisaged that Chongqing can become the global leading exporter of these products by air, signs of this potential rise being the addition of cargo routes to Frankfurt,[115] Sydney, Chicago, and New York City.[116][117]
Currently, Chongqing Airport is the only facility in central and western China that has metro access (CRT Line 3 and Line 10) to its central city, and two runways in normal use.[118]
There are two other airports in Chongqing Municipality: Qianjiang Wulingshan Airport (IATA: JIQ, ICAO: ZUQJ) and Wanzhou Wuqiao Airport (IATA: WXN, ICAO: ZUWX). They are both class 4C airports and serve passenger flights to some domestic destinations including Beijing, Shanghai and Kunming. Two more airports are being constructed soon: Wulong Xiannüshan Airport and Wushan Shennüfeng Airport.
Public transport

Public transport in Chongqing consist of metro, intercity railway, a ubiquitous bus system and the world's largest monorail network.
According to the Chongqing Municipal Government's ambitious plan in May 2007, Chongqing is investing 150 billion RMB over 13 years to finish a system that combines underground metro lines with heavy monorail (erroneously called 'light rail' in China).
As of 2017[update], four metro lines, the 14 km (8.7 mi) long CRT Line 1, a conventional subway, and the 19 km (12 mi) long heavy monorail CRT Line 2 (through Phase II), Line 3, a heavy monorail connects the airport and the southern part of downtown.,[119] Line 6, runs between Beibei, a commuter city in the far north to the centre.[120] Line 5 is due to open late 2017.
By 2020 CRT will consist of 6 straight lines and 1 circular line resulting in 363.5 km (225.9 mi) of road and railway to the existing transportation infrastructure and 93 new train stations will be added to the 111 stations that are already in place.[121]
By 2050, Chongqing will have as many as 18 lines planned to be in operation.[122]
Culture
Language

The language native to Chongqing is Southwestern Mandarin. More precisely, the great majority of the municipality, save for Xiushan, speak Sichuanese, including the primary Chengdu-Chongqing dialect and Minjiang dialect spoken in Jiangjin and Qijiang.[123] There are also a few speakers of Xiang and Hakka in the municipality, due to the great immigration wave to the Sichuan region (湖广填四川) during the Ming and Qing dynasties. In addition, in parts of southeastern Chongqing, the Miao and Tujia languages are also used by some Miao and Tujia people.[124]
Tourism

As the provisional Capital of China for almost ten years (1937 to 1945), the city was also known as one of the three headquarters of the Allies during World War II, as well as being a strategic center of many other wars throughout China's history. Chongqing has many historic war-time buildings or sites, some of which have since been destroyed. These sites include the People's Liberation Monument, located in the center of Chongqing city. It used to be the highest building in the area, but is now surrounded and dwarfed by numerous shopping centres. Originally named the Monument for the Victory over Axis Armies, it is the only building in China for that purpose.[125] Today, the monument serves as a symbol for the city. The General Joseph W. Stilwell Museum, dedicated to General "Vinegar Joe" Stilwell, a World War II general.[126] the air force cemetery in the Nanshan area, in memory of those air force personnel killed during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945), and the Red Rock Village Museum, a diplomatic site for the Communist Party in Chongqing led by Zhou Enlai during World War II, and Guiyuan, Cassia Garden, where Mao Zedong signed the "Double 10 (10 October) Peace Agreement" with the Kuomintang in 1945.[127]
- The Baiheliang Underwater Museum, China's first underwater museum,[128]
- The Memorial of Great Tunnel Massacre, a former air-raid shelter where a major massacre occurred during World War II.
- The Great Hall of the People in Chongqing is based on the Great Hall of the People in Beijing. This is one of the largest public assembly buildings in China which, though built in modern times, emulates traditional architectural styles. It is adjacent to the densely populated and hilly central district, with narrow streets and pedestrian only walkways,[129]
- The large domed Three Gorges Museum presents the history, culture, and environment of the Three Gorges area and Chongqing.
- Chongqing Science and Technology Museum has an IMAX theatre.
- Luohan Si, a Ming dynasty temple,[130]
- Huangguan Escalator, the second longest escalator in Asia.
- Former sites for embassies of major countries during the 1940s. As the capital at that time, Chongqing had many residential and other buildings for these officials.[131]


- Wuxi County, noted as a major tourism area of Chongqing,[132]
- The Dazu Rock Carvings, in Dazu county, are a series of Chinese religious sculptures and carvings, dating back as far as the 7th century A.D., depicting and influenced by Buddhist, Confucian and Taoist beliefs. Listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Dazu Rock Carvings are made up of 75 protected sites containing some 50,000 statues, with over 100,000 Chinese characters forming inscriptions and epigraphs.,[133]
- The Three Natural Bridges and Furong Cave in Wulong Karst National Geology Park, Wulong County are listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site as part of the South China Karst),[134][135]
- Ciqikou is a 1000-year-old town in the Shapingba District of Chongqing. It is also known as "Little Chongqing". The town, located next to the lower reaches of the Jialing River, was at one time an important source of china-ware and used to be a busy commercial dock during the Ming and Qing dynasties,[136]


- Fishing Town or Fishing City, also called the "Oriental Mecca" and "the Place That Broke God's Whip", is one of the three great ancient battlefields of China. It is noted for its resistance to the Mongol armies during the Southern Song dynasty (1127–1279) and the location where the Mongol leader Möngke Khan died in 1259,[137]
- Xueyu Cave in Fengdu County is the only example of a pure-white, jade-like karst cave in China,[138]
- Fengdu Ghost City in Fengdu County is the Gate of the Hell in traditional Chinese literature and culture.
- Snowy Jade Cave, see Xueyu Cave (above).
- Baidi Cheng, a peninsula in Yangtze River, known due to a famous poem by Li Bai.
- The Chongqing Zoo, a zoo that exhibits many rare species including the giant panda, the extremely rare South China tiger, and the African elephant.[139]
- Chongqing Amusement Park.
- Chongqing Grand Theatre, a performing arts centre.
- Foreigners' Street is an amusement park, including the Porcelain Palace, the world's largest toilet. Also the location of the abortive Love Land development in 2009.
- The Black Mountain Valley (Heishangu).[140]
- The Jindao Valley (Golden Blade Valley).[citation needed]
- Mount Jinfo (Golden Buddha Mountain).[141]
- Major hot-springs around the city.[citation needed]
- Gele Mountain and the Red Rocks, a memorial park for the 1949 Chinese revolution.[citation needed]
- Nanshan (Southern Mountain of Chongqing), or Tongluo Mountain academically. There are tons of places of interests in this mountain, including the Laojun Temple, the Wenfeng Pagoda, the Great Golden Eagle, the Tu Shan Temple, the Huangge Path, the former residential halls of Chiang Kai-shek, etc.[citation needed]
- Tu Shan (Mount. Tu), a part of Southern Mountain of Chongqing (Tongluo Mountain).[citation needed] It is believed to be the place where Da Yu, the founder of Xia dynasty, met his wife Tushan Shi.
- Daxuecheng, or university town ,where many famous universities are situated, is the one and only place where shared bicycles like ofo are widely available.
Media
The Chongqing People's Broadcast Station is Chongqing's largest radio station.[142] The only municipal-level TV network is Chongqing TV, claimed to be the 4th largest television station in China.[143] Chongqing TV broadcasts many local-oriented channels, and can be viewed on many TV sets throughout China. The Chongqing Daily is the largest newspaper group, controlling more than 10 newspapers and one news website.[144]
Cuisine
Chongqing food is part of Sichuan cuisine. Chongqing is known for its spicy food. Its food is normally considered numbing because of the use of Sichuan pepper, also known as Sichuan peppercorn, containing hydroxy alpha sanshool. Chongqing's city centre has many restaurants and food stalls where meals often cost less than RMB10. Local specialties here include dumplings and pickled vegetables and, different from many other Chinese cuisines, Chongqing dishes are suitable for the solo diner as they are often served in small individual sized portions.[145] Among the delicacies and local specialties are these dishes:
- Chongqing hot pot – Chongqing's local culinary specialty which was originally from the Northern China. Tables in hot pot restaurants usually have a central vat, or pot, where food ordered by the customers is boiled in a spicy broth. As well as beef, pork, lotus and other vegetables, items such as pig's kidney, brain, duck's bowels and cow's stomach are often consumed.[146]
- Chongqing noodles – common noodles dishes in Chongqing
- Jiangtuan fish – since Chongqing is located along Jialing River, visitors have a good opportunity to sample varieties of aquatic products. Among them, is a fish local to the region, Jiangtuan fish: Hypophthalmichthys nobilis although more commonly known as bighead carp.[147] The fish is often served steamed or baked.[148]
- Pork leg cooked with rock candy – A common household dish of the Chongqing people, the finished dish, known as red in colour and tender in taste, has been described as having strong and sweet aftertaste.[149]
- Qianzhang (skimmed soy bean cream) – Qianzhang is the cream skimmed from soybean milk. In order to create, this several steps must be followed very carefully. First, soybeans are soaked in water, ground, strained, boiled, restrained several times and spread over gauze until delicate, snow-white cream is formed. The paste can also be hardened, cut into slivers and seasoned with sesame oil, garlic and chili oil. Another variation is to bake the cream and fry it with bacon, which is described as soft and sweet.[150]
- Quanshui Chicken (Spring Water Chicken) – Quanshui Chicken is cooked with the natural spring water in the Southern Mountain of Chongqing.
- Xiao mian (little noodle) – lamian noodles with chili oil and rich mixtures of spices and ingredients.
Sports and recreation
Association football
Professional association football teams in Chongqing include:
Chongqing Lifan is a professional Chinese football club who currently plays in the Chinese Super League. They are owned by the Chongqing-based Lifan Group, which manufactures motorcycles, cars and spare parts.[151] Originally called Qianwei (Vanguard) Wuhan, the club formed in 1995 to take part in the recently developed, fully professional Chinese football league system. They would quickly rise to top tier of the system and experience their greatest achievement in winning the 2000 Chinese FA Cup,[152] and coming in fourth within the league. However, since then they have struggled to replicate the same success, and have twice been relegated from the top tier.[153]
Chongqing FC was an association football club located in the city, and competed in China League One, the country's second-tier football division, before being relegated to the China League Two, and dissolving due to a resultant lack of funds.[154]
Chongqing is also the birthplace of soccer games in southwestern China. Soccer was introduced to this region in as early as 1905 by some British soldiers and missionaries. They founded a varsity soccer team at the predecessor of modern-day Guangyi High School (also known as Chongqing No.5 High School), and trained them to be a highly skilled team. A professional soccer stadium was constructed on the Guangyi campus in the Southern Mountain. It was the first professional soccer stadium in southwestern China. The Guangyi varsity team beat English and French naval teams and even the Sheffield Wednesday team in friendlies.
Basketball
Chongqing Soaring Dragons became the 20th team playing in Chinese Basketball Association in 2013. They play at Datianwan Arena, in the same sporting complex as Datianwan Stadium.[155]
Sport venues
Sport venues in Chongqing include:
- The Chongqing Olympic Sports Center is a multi-purpose stadium. It is currently used mostly for football matches, as it has a grass surface, and can hold 58,680. It was built in 2002 and was one of main venues for the 2004 AFC Asian Cup.[156]
- Yanghe Stadium is a multi-use stadium that is currently used mostly for football matches. The stadium holds 32,000 people, and is the home of Chongqing Lifan in the Chinese Super League. The stadium was purchased by the Lifan Group in 2001 for RMB80 million and immediately replaced Datianwan Stadium as the home of Chongqing Lifan.[157]
- Datianwan Stadium is a multi-purpose stadium that is currently used mostly for football matches. The stadium has a capacity 32,000 people, and up until 2001 was the home of Chongqing Lifan.[158]
Religion
Religion in Chongqing[159][note 1]
The predominant religions in Chongqing are Chinese folk religions, Taoist traditions and Chinese Buddhism. According to surveys conducted in 2007 and 2009, 26.63% of the population believes and is involved in cults of ancestors, while 1.05% of the population identifies as Christian.[159]
The reports didn't give figures for other types of religion; 72.32% of the population may be either irreligious or involved in worship of nature deities, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, folk religious sects.
Notable historic figures
- Ba Manzi: a legendary hero of Ba kingdom in Zhou dynasty
- Yan Yan: a loyal general during Three Kingdoms period
- Qin Liangyu: a popular heroine in Ming dynasty who fought against Manchus
- Nie Rongzhen: marshal of the People's Liberation Army of China
- Liu Bocheng: an early leader of Chinese communist party during Anti-Japanese War
Education
Colleges and universities

- Chongqing University (重庆大学)
- Southwest University (西南大学)
- Southwest University of Political Science and Law (西南政法大学)
- Third Military Medical University (第三军医大学)
- Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (重庆邮电大学)
- Chongqing University of Technology (重庆理工大学)
- Chongqing Jiaotong University (重庆交通大学)
- Chongqing Medical University (重庆医科大学)
- Chongqing Normal University (重庆师范大学)
- Chongqing Technology and Business University (重庆工商大学)
- Chongqing Three Gorges University (重庆三峡学院)
- Chongqing Telecommunication Institute (重庆通讯学院)
- Chongqing University of Science and Technology (重庆科技学院)
- Sichuan Fine Arts Institute (四川美术学院)
- Sichuan International Studies University (四川外国语大学)
- University of Logistics (后勤工程学院)
- Chongqing University of Arts and Science (重庆文理学院)
- Yangtze Normal University (长江师范学院)
- Chongqing University of Education (重庆第二师范学院)
High schools
- Chongqing Railway High School(重庆铁路中学)
- Chongqing Nankai Secondary School (重庆南开中学)
- Bashu Secondary School (巴蜀中学)
International schools
- Yew Chung International School of Chongqing (重庆耀中国际学校)[160]
- KL International School of Chongqing Bashu (重庆市诺林巴蜀外籍人员子女学校)[161]
International relations
Consulates
| Consulate | Date | Consular District |
| Canada Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 05.1998 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| United Kingdom Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 03.2000 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| Cambodia Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 12.2004 | Chongqing, Hubei, Hunan, Shaanxi |
| Japan Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 01.2005 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi |
| Denmark Consulate, Chongqing[162] | 07.2005 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| Philippines Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 12.2008 | Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| Hungary Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 02.2010 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Gansu |
| Ethiopia Consulate-General, Chongqing[162] | 11.2011 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| Italy Consulate-General, Chongqing[163] | 12.2013 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan |
| Netherlands Consulate-General, Chongqing[163] | 01.2014 | Chongqing, Sichuan, Shaanxi |
Twin towns – sister cities
Chongqing has sister city relationships many cities of the world including:
 Toulouse, France (1982)
Toulouse, France (1982) Seattle, United States (1983)
Seattle, United States (1983) Toronto, Canada (1986)
Toronto, Canada (1986) Hiroshima, Japan (1986)
Hiroshima, Japan (1986) Leicester, United Kingdom (1993)
Leicester, United Kingdom (1993) Voronezh, Russia (1993)
Voronezh, Russia (1993) Zaporizhia Oblast, Ukraine (2002)
Zaporizhia Oblast, Ukraine (2002) Mpumalanga, South Africa (2002)
Mpumalanga, South Africa (2002) Düsseldorf, Germany (2004)
Düsseldorf, Germany (2004) Brisbane, Australia (2005)
Brisbane, Australia (2005) Shiraz, Iran (2005)
Shiraz, Iran (2005) Aswan, Egypt (2005)
Aswan, Egypt (2005) Busan, South Korea (2007)
Busan, South Korea (2007) Sør-Trøndelag, Norway (2007)
Sør-Trøndelag, Norway (2007) Chiang Mai Province, Thailand (2008)
Chiang Mai Province, Thailand (2008) Córdoba, Argentina (2010)
Córdoba, Argentina (2010) Pest, Hungary (2010)
Pest, Hungary (2010) Bangkok, Thailand (2005)
Bangkok, Thailand (2005) Antwerp, Belgium (2011)
Antwerp, Belgium (2011) Bahia, Brazil (2011)
Bahia, Brazil (2011) Detroit, United States (2011)
Detroit, United States (2011) New York, United States (2011)
New York, United States (2011) Chennai, India (2015)
Chennai, India (2015)
See also
- Major national historical and cultural sites in Chongqing
- List of cities in China by population and built-up area
- List of twin towns and sister cities in China
Notes
- ^ Ch'ungk'ing, Ch'ung K'ing, Chongking, and other renderings are also found in older literature. The Beijing-based Standard Chinese pronunciation is rendered in Wade-Giles as Ch'ung-ch'ing, and in the latter 20th century this form was used officially in Taiwan and in Western academic literature.
- ^ The data was collected by the Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS) of 2009 and by the Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) of 2007, reported and assembled by Xiuhua Wang (2015)[159] in order to confront the proportion of people identifying with two similar social structures: ① Christian churches, and ② the traditional Chinese religion of the lineage (i. e. people believing and worshipping ancestral deities often organised into lineage "churches" and ancestral shrines). Data for other religions with a significant presence in China (deity cults, Buddhism, Taoism, folk religious sects, Islam, et. al.) was not reported by Wang.
- ^ This may include:
- Buddhists;
- Confucians;
- Deity worshippers;
- Taoists;
- Members of folk religious sects;
- Small minorities of Muslims;
- And people not bounded to, nor practicing any, institutional or diffuse religion.
References
Citations
- ^ "Doing Business in China – Survey". Ministry of Commerce – People's Republic of China. Archived from the original on 5 August 2013. Retrieved 2013-08-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ 2015年重庆常住人口3016.55万人 继续保持增长态势 [2016年重庆常住人口3670万人 继续保持增长态势] (in Chinese). Chongqing News. 28 January 2016. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ^ a b c OECD Urban Policy Reviews: China 2015, OECD READ edition. OECD. 18 April 2015. p. 37. doi:10.1787/9789264230040-en. ISBN 9789264230033. ISSN 2306-9341.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help)Linked from the OECD here - ^ "Statistical Communiqué of Chongqing on the 2017 National Economic and Social Development / 重庆市2017年国民经济和社会发展统计公报" (in Chinese). Statistical Bureau of Chongqing. 11 March 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ 《2013中国人类发展报告》 (PDF) (in Chinese). United Nations Development Programme China. 2013. Retrieved 14 May 2014.
- ^ "City Flower". En.cq.gov.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "City Tree". En.cq.gov.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "China's Direct-Controlled Municipalities". Geography.about.com. 14 March 1997. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ 中央机构编制委员会印发《关于副省级市若干问题的意见》的通知. 中编发[1995]5号. 豆丁网. 19 February 1995. Archived from the original on 29 May 2014. Retrieved 2014-05-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); templatestyles stripmarker in|publisher=at position 1 (help) - ^ 程正龙. 2015年重庆常住人口3016.55万人 继续保持增长态势-今日重庆-华龙网. cq.cqnews.net. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- ^ 最新中国城市人口数量排名(根据2010年第六次人口普查). www.elivecity.cn. 2012. Retrieved 28 May 2014.
- ^ "Chongqing's Official Abbreviation". English.cri.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "EIU Report". Eiu.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Kim Hunter Gordon, Jesse Watson (2011). Chongqing & The Three Gorges. pp. 38–40. ISBN 978-7-5022-5215-1.
- ^ "Chongqing's History with the State of Ba". Chongqing Municipal Government. 6 December 2007.
- ^ "Ming Yuzhen Information". Neohumanism.com. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ^ Nicola di Cosmo, Don J. Wyatt. Political Frontiers, Ethnic Boundaries, and Human Geographies in Chinese History. Retrieved 2 July 2012.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) The last Manchu dynasty - ^ "UK Consulate Page". Cq.xinhuanet.com. 30 December 2004. Archived from the original on 23 August 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Chongqing Opens Itself To Foreigners". Mitchellteachers.org. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "French Consulate Page". Cq.xinhuanet.com. 30 December 2004. Archived from the original on 23 August 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Japanese Consulate Page". Chongqing.cn.emb-japan.go.jp. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "US Consulate Page". Us-passport-service-guide.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "German Consulate Page". 2011.cqlib.cn. Archived from the original on 23 August 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Chiang Kai-shek & Stilwell, Joseph - ^ "WWII Era History of Chongqing". .needham.k12.ma.us. 23 October 1944. Archived from the original on 6 June 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Chongqing becomes 5th National Central city". English.peopledaily.com.cn. 10 February 2010. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Establishment of the Liangjiang New Area". Gochina.scmp.com. 25 November 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Chongqing on the mend after crackdown on criminal gangs Archived 4 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine, SCMP, 5 October 2009
- ^ lawyer reveals Bo Xilai's use of torture Archived 20 June 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 August 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Morning Post Gang trials - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Bashan Poems - ^ "Location of Chongqing". En.cq.gov.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 24 October 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Chongqing's bordering provinces - ^ Chongqing Topography. "Mountains in Sichuan and Chongqing". Fodors.com. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The Three Gorges Corp". Ctg.com.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Yangtze River". Chinese National Tourism Office, US Chinese Embassy. Retrieved 31 March 2014.
- ^ Murphy, Ryan (28 December 2010). "Trip to Chongqing". Elevendegreesnorth.blogspot.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Poems of Li Bai". Poemhunter.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Chongqing Mountains Data - ^ a b c d 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值数据集 (1971–2000年) (in Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. May 2011. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 2011-05-23.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "无标题文档". Archived from the original on 13 October 2012. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 28 August 2010.
- ^ 中国气象局 国家气象信息中心 (in Chinese). Guangzhou Popular Science News Net (广州科普资讯网). 12 September 2007. Archived from the original on 18 March 2013. Retrieved 2014-11-12.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Extreme Temperatures Around the World". Retrieved 22 May 2013.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 25 May 2010.
- ^ "Chongqing Municipality". IES Global. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ "Chongqing – City of Hills, Fog and Spicy Food". China.com. Retrieved 17 July 2011.
- ^ Lin, Yutang.1944. The Vigil of a Nation. The John Day Company. New York. 262 pages
- ^ "WEATHER & EXTREME EVENTS 7 of 10 Most Air-Polluted Cities Are in China". JAN 16, 2013. Imaginechina/Corbis. http://news.discovery.com. Retrieved 1 September 2014.
{{cite news}}: External link in|agency= - ^ 重庆调整部分行政区划:4区(县)并为2区. News.163.com. 17 March 2010. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ 国家统计局统计用区划代码 Archived 5 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ 《保定经济统计年鉴2011》
- ^ shi, Guo wu yuan ren kou pu cha ban gong; council, Guo jia tong ji ju ren kou he jiu ye tong ji si bian = Tabulation on the 2010 population census of the people's republic of China by township / compiled by Population census office under the state; population, Department of; statistics, employment statistics national bureau of (2012). Zhongguo 2010 nian ren kou pu cha fen xiang, zhen, jie dao zi liao (Di 1 ban. ed.). Beijing Shi: Zhongguo tong ji chu ban she. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ 《中国民政统计年鉴2012》
- ^ "Position of Five Function Districts in Chongqing". Chongqing Municipal Government. 22 September 2013. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ 五大功能区域: 都市功能核心区 [Five Functional Districts: Urban-function Core District]. CQNEWS Corporation. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f 统计年鉴2014 [Statistical Yearbook 2014] (in Chinese). Statistics Bureau of Chongqing. 9 February 2015. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ 2014年重庆市国民经济和社会发展统计公报 [Chongqing Economic and Social Development Statistical Bulletin 2014] (in Chinese). Chongqing Bureau of Statistics. 16 March 2015. Archived from the original on 23 May 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Annual Total Population by Provinces. National Bureau of Statistics China. Retrieved 15 May 2018.
{{cite web}}: Invalid|script-title=: missing prefix (help) - ^ "China's Chongqing starts household registration reform". Xinhua News. 2 July 2010. Archived from the original on 21 August 2010. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ CNBC.com, Justina Crabtree; special to (20 September 2016). "A tale of megacities: China's largest metropolises". CNBC.
slide 8
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Residence Status of Population by Region and Sex (2004)". National Bureau of Statistics of China, in allcountries.org. 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Age Composition and Dependency Ratio of Population by Region (2004)". National Bureau of Statistics of China, in allcountries.org. 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Number and Size of Family Households by Region (2004)". National Bureau of Statistics of China, in allcountries.org. 2005. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Page, Jeremy (15 March 2012). "Chongqing Party Chief Position". Online.wsj.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Kuo, Ping-chia. "Chongqing History: The Modern Period". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ^ "Chongqing, once a wartime capitol". En.cq.gov.cn. 14 March 1997. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Qiu Shaoyun Memorial Hall". Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Pike, John (21 November 2003). "A history of the 13th Army Group". Globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Chinese vice premier urges Chongqing to become economic engine for western regions Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine – Embassy of the People's Republic of China in Australia – retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ China urges reform, development of Chongqing municipality Archived 23 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine – Xinhua News Agency – retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ "Market Profiles on Chinese Cities and Provinces (hktdc.com)". Tdctrade.com. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Wikinomics: How Mass Collaboration Changes Everything," Don Tapscott and Anthony D. Williams, Penguin, p. 218, 2006.
- ^ Chongqing Municipality(重慶市) Archived 7 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine – The Australia-China Chamber of Commerce and Industry of New South Wales – retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ a b Critical Eye on Chongqing – Pillar of the West Archived 6 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine – China Business Review – retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ MacKie, Nick (4 May 2005). "China's west seeks to impress investors". BBC News. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ A survey in 2005 by China's State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) found 13 firms in the manganese triangle had breached targets on the release of hexavalent chromium and ammonia-nitrogen – in the worst case, by a factor of 180. The cleanup ordered by SEPA resulted in firms closing and the expenditure of 280 million yuan.
- ^ "Asia Times Online: China Business News : China-Myanmar pipeline projects on track". Atimes.com. 24 April 2007. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ welcome to www.cnnz.gov.cn Archived 7 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "China Business News : HP Foxcom Setup Laptop Plants in Chongqing". The China Perspective. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Chongqing Investment Zone Profiles". Allroadsleadtochina.com. 30 May 2007. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ China's Three Gorges Dam Archived 3 May 2016 at the Wayback Machine – CNN – retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ Dee-Ann Durbin (28 August 2012). "Ford building sixth plant in China". Associated Press. Retrieved 20 March 2017.
- ^ Seetharaman, Deepa. "Mazda in Chongqing". Reuters.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "HSBC opens bank in Chongqing". Hsbc.com.cn. 28 December 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Standard Chartered open a bank in Chongqing" (PDF). Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Citibank opens branch in Chongqing". Citigroup.com. 31 March 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Deutsche Bank opens Chongqing branch - ^ "ANZ Bank opens a branch in Chongqing". Anz.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Page Not Found | Scotiabank". scotiabank.com. Retrieved 16 October 2016.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - ^ Yue, Terril. "Wal-Mart reopens Chongqing locations". Reuters.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Multinational Grocery Stores in Chongqing[dead link]
- ^ Tan, Kenneth (12 November 2007). "Chongqing Carrefour Stampede". Shanghaiist.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Innovative City in West China Chongqing (PDF) Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine – Jon Sigurdson and Krystyna Palonka of Stockholm School of Economics, EIJS – retrieved on 1 February 2009.
- ^ "The Rise of The 'Champs' – New Report Maps Business Opportunity in China's Fastest Growing Cities". Sourcewire.com. 9 November 2010. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Industrial Park". Chinaknowledge.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "CETD". Hktdc.com. 19 September 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "CHTIDT". En.cq.gov.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "CNNZ". English.cq.gov.cn. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Contact:. "CEPZ". Rightsite.asia. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ "Jianqiao Industrial Park Profile". Hktdc.com. 19 September 2011. Retrieved 29 December 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 October 2016. Retrieved 2012-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Liangjiang New Area - ^ "New cloud computing center". En.cq.gov.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Chongqing Urban Bridges Archived 12 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chongqing's Cruise Industry
- ^ "Chongqing Ports Details". Service-industries-research.hktdc.com. 19 July 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Black, Simon (12 July 2011). "Chongqing: World's Largest Construction Project". Articles.businessinsider.com. Archived from the original on 18 January 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Bicycles rare in Chongqing Archived 12 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "CJIA Stats". Theairdb.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "China's Chongqing Airport begins third terminal, runway operations". atwonline.com. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
- ^ 2010年全国机场吞吐量排名 (in Chinese). Civil Aviation Administration of China. 21 March 2012. Archived from the original on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 23 March 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Frankfurt-Chongqing Route". Thechinatimes.com. 27 March 2012. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ 颜培 (23 April 2012). "Chongqing's new cargo routes". China.org.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Chongqing's Rising Technology Exports". Ft.cq.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Chongqing Airport Profile Archived 30 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Line 2 & 1". English.cqnews.net. 15 December 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Planning of Chongqing Line 6". Cn.siemens.com. 30 December 2010. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Chongqing City Transport". English.cqnews.net. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Chongqing Daily (23 March 2008)
- ^ 翟时雨 (Ruo Shiyu) (2003). "中篇第四节:四川话的分区 (The divisions of the Sichuan dialect)". 《汉语方言学》 [The Study of Chinese Languages] (in Chinese). Southwest China Normal University Press (西南师范大学出版社). ISBN 7-5621-2942-8.
- ^ 苗族:特色苗语 [The Miao People: Characteristics of the Miao language]. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 31 July 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "People's Liberation Monument". Chongqingwomen.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "General Joseph Stillwell Museum". Travelchinaguide.com. 17 May 1944. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Red Rock Village Museum". Beijingfeeling.com. 15 September 2013. Archived from the original on 23 June 2011. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Chongqing: The First Underwater Museum in China has Been Built and Opened". Chinahush. 21 May 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Great Hall of the People". Placesonline.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Luohan Si". Fodors.com. 28 May 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ www.chinaeducenter.com. "Embassies List". Chinaeducenter.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Wuxi County". English.51766.com. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Dazu Rock Carvings". China.org.cn. 12 September 2003. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "China: Three Natural Bridges National Geopark". Naturalarches.org. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Furong Cave". Gxnu.edu.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Ciqkou". Blog.seattlechinesegarden.org. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Fishing Town". Chongqingwomen.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ Xueyu Cave Archived 18 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Chongqing Zoo Profile and Pictures". Travelchinaguide.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Black Mountain Valley". Travelchinaguide.com. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- ^ "Jinfo Mountain". Travelchinaguide.com. Retrieved 26 November 2017.
- ^ "Chinese radio stations". Chinaculture.org. 24 September 2003. Archived from the original on 22 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Bandurski, David (1 June 2011). "Chongqing's TV revolution". Cmp.hku.hk. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Chongqing Daily's Bo Xilai Coverage". Theepochtimes.com. Archived from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ SinoHotelGuide.com. "Chongqing Dining Overlook" (in Dutch). Sinohotelguide.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Chongqing Hot Pot & Dining Guide". Travelchinaguide.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Bighead Carp, or Jiangtuan Fish". Nas.er.usgs.gov. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Jiangtuan Fish". Chinatravelcompass.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Chongqing Dining, Dining in Chongqing, Chongqing cuisine, Chongqing Food, Chongqing restaurants". Chinatourguide.com. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Qianzhang". Chinatourguide.com. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Lifan Group buys Chongqing soccer team". China.org.cn. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "2000 Chinese FA Cup". Rsssf.com. 8 March 2007. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Chongqing Lifan F.C". Soccerway.com. 9 January 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 2015-07-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Chongqing FC folds - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 2015-08-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Beijing Ducks vs. Chongqing - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 June 2012. Retrieved 2012-06-06.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Official Site - ^ "Yanghe Stadium profile". Footballgroundmap.com. 13 September 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
- ^ "Datianwan Stadium profile". Worldstadiums.com. Archived from the original on 3 February 2013. Retrieved 10 December 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c China General Social Survey 2009, Chinese Spiritual Life Survey (CSLS) 2007. Report by: Xiuhua Wang (2015, p. 15) Archived 25 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 October 2014. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Website in English - ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 November 2016. Retrieved 2015-05-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Website in English - ^ a b c d e f g h "各国驻华领馆领区一览表 (in Simplified Chinese)". 中华人民共和国外交部. 8 May 2007.
- ^ a b "荷兰意大利有望年内在渝设领事馆 (in Simplified Chinese)". 和讯财经. 8 May 2013. Archived from the original on 30 April 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Sources
- Danielson, Eric N. (2005). "Chongqing," pp.325–362 in The Three Gorges and the Upper Yangzi. Singapore: Marshall Cavendish/Times Editions. ISBN 981-232-599-9.
- Danielson, Eric N. (2005). "Revisiting Chongqing: China's Second World War Temporary National Capital," in Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, Hong Kong Branch, Vol.45. Hong Kong: Royal Asiatic Society, Hong Kong Branch.
- Huang, Jiren (1999). Lao Chongqing (Old Chongqing): Ba Shan Ye Yu (part of the "Lao Cheng Shi" series). Nanjing: Jiangsu Meishu Chubanshe (Jiangsu Fine Arts Publishing House).
- Kapp, Robert A. (1974). "Chungking as a Center of Warlord Power, 1926–1937", pp. 143–170 in The Chinese City Between Two Worlds, ed. by Mark Elvin and G. William Skinner. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
- Kapp, Robert A. (1973). Szechwan and the Chinese Republic: Provincial Militarism and Central Power, 1911–1938. New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Liao, Qingyu (2005). Chongqing Ge Le Shan Pei Du Yizhi (The Construction of War-time Capital on the Gele Mountain, Chongqing). Chengdu: Sichuan University Press.
- Long, Juncai (2005). Sui Yue Ya Feng de Jiyi: Chongqing Kang Zhan Yizhi (Covered Memory of Flowing Years: Site[s] of [the] Anti-Japanese War in Chongqing). Chongqing: Southwest University Press.
- McIsaac, Lee (2000). "The City as Nation: Creating a Wartime Capital in Chongqing," in Remaking the Chinese City, 1900–1950, ed. by Joseph W. Esherick. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
- Xu; Dongsheng Liu; Yuchuan (1998). Chongqing Jiu Ying (Old Photos of Chongqing). Beijing: People's Fine Arts Publishing House.
External links
- Chongqing
- Cities in China
- Municipalities of China
- Metropolitan areas of China
- Western China
- Populated places on the Yangtze River
- Port cities and towns in China
- Province-level divisions of China
- Populated places established in the 5th century BC
- 5th-century BC establishments in China
- Requests for audio pronunciation (English)