Radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution
Radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution or SRN1 in organic chemistry is a type of substitution reaction in which a certain substituent on an aromatic compound is replaced by a nucleophile through an intermediary free radical species:[1]
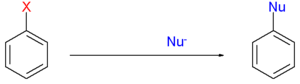
The substituent X is a halide and nucleophiles can be sodium amide, an alkoxide or a carbon nucleophile such as an enolate.[2] In contrast to regular nucleophilic aromatic substitution, deactivating groups on the arene are not required.[3]
This reaction type was discovered in 1970 by Bunnett and Kim[4] and the abbreviation SRN1 stands for substitution radical-nucleophilic unimolecular as it shares properties with an aliphatic SN1 reaction. An example of this reaction type is the Sandmeyer reaction.
Reaction mechanism
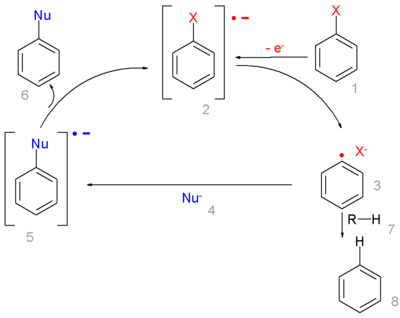
In this radical substitution the aryl halide 1 accepts an electron from an radical initiator forming a radical anion 2. This intermediate collapses into an aryl radical 3 and a halide anion. The aryl radical reacts with the nucleophile 4 to a new radical anion 5 which goes on to form the substituted product by transferring its electron to new aryl halide in the chain propagation. Alternatively the phenyl radical can abstract any loose proton from 7 forming the arene 8 in a chain termination reaction.
The involvement of a radical intermediate in a new type of nucleophilic aromatic substitution was invoked when the product distribution was compared between a certain aromatic chloride and an aromatic iodide in reaction with potassium amide. The chloride reaction proceeds through a classical aryne intermediate:
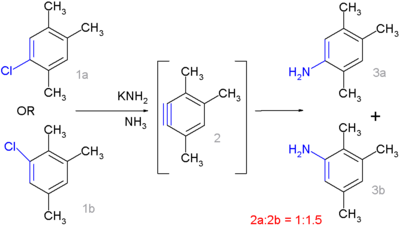
The isomers 1a and 1b form the same aryne 2 which continues to react to the anilines 3a and 3b in a 1 to 1.5 ratio. Clear-cut cine-substitution would give a 1:1 ratio but additional steric and electronic factors come into play as well.
Replacing chlorine by iodine in the 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene moiety drastically changes the product distribution:

It now resembles ipso-substitution with 1a forming preferentially 3a and 1b forming 3b. Radical scavengers suppress ipso-substitution in favor of cine-substitution and the addition of potassium metal as an electron donor and radical initiator does exactly the opposite.[5]
See also
References
- ^ Radical-Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution, Chapter 10; Rossi, R. A.; Guastavino, J. F; Buden, M. E. (2016). Arene Chemistry: Reaction Mechanisms and Methods for Aromatic Compounds (Jacques Mortier Ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 243–268. doi:10.1002/9781118754887. ISBN 978-1-118-75498-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Phenomenon of radical anion fragmentation in the course of aromatic SRN reactions Roberto A. Rossi Acc. Chem. Res.; 1982; 15(6) pp 164 – 170; doi:10.1021/ar00078a001.
- ^ Rossi, R. A.; Pierini, A. B.; Santiago, A. N. Org. React. 1999, 54, 1. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or054.01
- ^ Evidence for a radical mechanism of aromatic "nucleophilic" substitution Joseph F. Bunnett and Jhong Kook Kim J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1970; 92(25) pp 7463 – 7464. (doi:10.1021/ja00728a037)
- ^ Alkali metal promoted aromatic "nucleophilic" substitution Joseph F. Bunnett and Jhong Kook Kim J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 7464 – 7466. (doi:10.1021/ja00728a038)
