Albanian language
| Albanian | |
|---|---|
| shqip, gjuha shqipe | |
| Pronunciation | [ʃcip] |
| Native to | Albania, Kosovo, Montenegro, Serbia, and Albanian diaspora |
Native speakers | 5.4 million in the Balkans (ca. 2011)[1] |
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects | |
| Latin (Albanian alphabet) Albanian Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Officially by the Social Sciences and Albanological Section of the Academy of Sciences of Albania |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sq |
| ISO 639-2 | alb (B) sqi (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | sqi – inclusive codeIndividual codes: aae – Arbëreshaat – Arvanitikaaln – Ghegals – Tosk |
| Glottolog | alba1267 |
| Linguasphere | to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) 55-AAA-aaa to 55-AAA-ahe (25 varieties) |
 Albanian dialects (The map does not indicate where the language is majority or minority). | |
Albanian (shqip [ʃcip], or gjuha shqipe [ˈɟuha ˈʃcipɛ]) is a language of the Indo-European family, in which it occupies an independent branch. It is an official language in Albania & [[Kosovo]. It also has a official minority status in Macedonia, Italy, Romania, Montenegro, Serbia, and others. The language has an official status in Ulcinj, southern Montenegro. Albanian is also spoken by large Albanian communities elsewhere in Europe, the Americas and Australia.
The two main dialects of Albanian are Gheg and Tosk. Gheg is primarily spoken in the north, while Tosk is spoken in the south. Standard Albanian is based on the Tosk dialect. The number of Albanian speakers in the Balkans is estimated to be approximately 5 million.[1]
Centuries-old communities speaking Albanian dialects can be found scattered in Croatia (the Arbanasi), Greece (the Arvanites and some communities in Epirus, Western Macedonia and Western Thrace),[2] Italy (the Arbëreshë immigrants in Italy)[3] as well as in Romania and Ukraine.[4] There is also a large Albanian diaspora.[5]
Geographic distribution
The language is spoken by approximately 7 million people primarily in Albania, Kosovo, Greece, Italy, Macedonia and Montenegro. However, due to the large Albanian diaspora, the total number of speakers is much higher than the native speakers in Southern Europe.[1]
Europe
The Albanian language is the official language of Albania and Kosovo. Albanian is a recognised minority language in Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, Romania,Macedonia and in Serbia. Albanian is also spoken by its Minority in Greece, specifically in the Thesprotia and Preveza regional units and in a few villages in Ioannina and Florina regional units in Greece.[2]
Albanian is the third most spoken language in Italy.[6] This is due to the mass Albanian immigration to Italy. Italy has a historical Albanian minority of about 500,000 which are scattered across southern Italy known as Arbëreshë. Approximately 1 million Albanians from Kosovo are dispersed throughout Germany, Switzerland and Austria. These are mainly refugees from Kosovo that migrated during the Kosovo War. In Switzerland, the Albanian language is the sixth most spoken language with 176,293 native speakers.
Americas
There are large numbers of Albanian speakers in the United States, Argentina, Chile, Uruguay and Canada. Some of the first ethnic Albanians to arrive in the United States were Arbëreshë. Arbëreshe have a strong sense of identity, and are unique in that they speak an archaic dialect of Tosk Albanian called Arbëreshë.
In North America (United States and Canada) there are approximately 250,000 Albanian speakers. It is spoken in the eastern area of the United States in cities like New York City, New Jersey, Boston, Philadelphia, Ohio, Connecticut and Detroit. Greater New Orleans has a large Arbëresh community. Oftentimes, wherever there are Italians, there are a few Arbëreshe mixed with them. Arbëreshe Americans, therefore are often indistinguishable from Italian Americans due to being assimilated into the Italian American community.[7]
In Argentina there are nearly 40,000 Albanian speakers, mostly in Buenos Aires.[8]
Asia and Oceania
Approximately 1.3 million people of Albanian ancestry live in Turkey, and more than 500,000 recognizing their ancestry, language and culture. There are other estimates, however, that place the number of people in Turkey with Albanian ancestry and or background upward to 5 million. However, the vast majority of this population is assimilated and no longer possesses fluency in the Albanian language, though a vibrant Albanian community maintains its distinct identity in Istanbul to this day.
In Egypt there are around 18,000 Albanians, mostly Tosk speakers.[9] Many are descendants of the Janissary of Muhammad Ali Pasha, an Albanian who became Wāli, and self-declared Khedive of Egypt and Sudan. In addition to the dynasty that he established, a large part of the former Egyptian and Sudanese aristocracy was of Albanian origin. In addition to the recent emigrants, there are older diasporic communities around the world.
Albanian is also spoken by Albanian diaspora communities residing in Australia and New Zealand.
Dialects

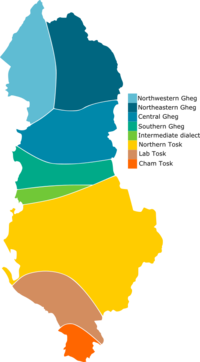
The Albanian language has two distinct dialects, Tosk which is spoken in the south, and Gheg spoken in the north.[10] Standard Albanian is based on the Tosk dialect. The Shkumbin river is the rough dividing line between the two dialects.[11]
Gheg is divided into four sub-dialects, in Northwest Gheg, Northeast Gheg, Central Gheg, and Southern Gheg. It is primarily spoken in northern Albania and throughout Montenegro, Kosovo and northwestern Macedonia. One fairly divergent dialect is the Upper Reka dialect, which is however classified as Central Gheg. There is also a diaspora dialect in Croatia, the Arbanasi dialect.
Tosk is divided into five sub-dialects, including Northern Tosk (the most numerous in speakers), Labërisht, Çam, Arvanitika, and Arbëresh. Tosk is spoken in southern Albania, southwestern Macedonia and northern and southern Greece. Cham Albanian is spoken in North-western Greece, while Arvanitika is spoken by the Arvanites in southern Greece. In addition Arbëresh is spoken by the Arbëreshë people, descendants of 15th and 16th century migrants who settled in southeastern Italy, in small communities in the regions of Sicily and Calabria.
Orthography

The Albanian language has been written using many different alphabets since the earliest records from the 14th century. The history of Albanian language orthography is closely related to the cultural orientation and knowledge of certain foreign languages among Albanian writers.[12] The earliest written Albanian records come from the Gheg area in makeshift spellings based on Italian or Greek. Originally, the Tosk dialect was written in the Greek alphabet and the Gheg dialect was written in the Latin script. Both dialects had also been written in the Ottoman Turkish version of the Arabic script, Cyrillic, and some local alphabets (Elbasan, Vithkuqi, Todhri, Veso Bey, Jan Vellara and others, see original Albanian alphabets). More specifically, the writers from northern Albania and under the influence of the Catholic Church used Latin letters, those in southern Albania and under the influence of the Greek Orthodox church used Greek letters, while others throughout Albania and under the influence of Islam used Arabic letters. There were initial attempts to create an original Albanian alphabet during the 1750–1850 period. These attempts intensified after the League of Prizren and culminated with the Congress of Manastir held by Albanian intellectuals from 14 to 22 November 1908, in Manastir (present day Bitola), which decided on which alphabet to use, and what the standardized spelling would be for standard Albanian. This is how the literary language remains. The alphabet is the Latin alphabet with the addition of the letters <ë>, <ç>, and ten digraphs: dh, th, xh, gj, nj, ng, ll, rr, zh and sh.
According to Robert Elsie:[13]
The hundred years between 1750 and 1850 were an age of astounding orthographic diversity in Albania. In this period, the Albanian language was put to writing in at least ten different alphabets – most certainly a record for European languages. ... the diverse forms in which this old Balkan language was recorded, from the earliest documents to the beginning of the twentieth century ... consist of adaptations of the Latin, Greek, Arabic, and Cyrillic alphabets and (what is even more interesting) a number of locally invented writing systems. Most of the latter alphabets have now been forgotten and are unknown, even to the Albanians themselves.[13]
Classification

The Albanian language occupies an independent branch of the Indo-European language tree.[14] In 1854, Albanian was demonstrated to be an Indo-European language by the philologist Franz Bopp. Albanian was formerly compared by a few Indo-European linguists with Germanic and Balto-Slavic, all of which share a number of isoglosses with Albanian.[15] Other linguists linked the Albanian language with Latin, Greek and Armenian, while placing Germanic and Balto-Slavic in another branch of Indo-European.[16][17][18]
Old Albanian
According to the central hypothesis of a project undertaken by the Austrian Science Fund, old Albanian had a significant influence on the development of many languages in the Balkans. This little-known language is being researched using all available texts before a comparison with other Balkan languages is carried out. The outcome of this work will include the compilation of a lexicon providing an overview of all old Albanian verbs.[19][needs update] As project leader Dr. Schumacher explains, the research is already bearing fruit:
So far, our work has shown that Old Albanian contained numerous modal levels that allowed the speaker to express a particular stance to what was being said. Compared to the existing knowledge and literature, these modal levels are actually more extensive and more nuanced than previously thought. We have also discovered a great many verbal forms that are now obsolete or have been lost through restructuring — until now, these forms have barely even been recognized or, at best, have been classified incorrectly.[19]
These verbal forms are crucial to explaining the linguistic history of Albanian and its internal usage. However, they can also shed light on the reciprocal relationship between Albanian and its neighbouring languages. The researchers are following various leads which suggest that Albanian played a key role in the Balkan Sprachbund. For example, it is likely that Albanian is the source of the suffixed definite article in Romanian, Bulgarian and Macedonian, as this has been a feature of Albanian since ancient times.[19]
History
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
 |
The first written mention of the Albanian language was on 14 July 1284 in Dubrovnik in modern Croatia when a crime witness named Matthew testified: "I heard a voice shouting on the mountainside in the Albanian language" (Template:Lang-lat).[20][21] The first audio recording of Albanian was made by Norbert Jokl on April 4, 1914 in Vienna.[22] During the five-century period of the Ottoman presence in Albania, the language was not officially recognized until 1909, when the Congress of Dibra decided that Albanian schools would finally be allowed.[23]
Linguistic affinities
Albanian is considered an isolate within the Indo-European language family; no other language has been conclusively linked to its branch. The only other language that is a sole surviving member of a branch of Indo-European is Armenian.
The Albanian language is part of the Indo-European language group and is considered to have evolved from one of the Paleo-Balkan languages of antiquity,[24][25][26] although it is still uncertain which particular Paleo-Balkan language represents the ancestor of Albanian, or where in Southern Europe that population lived.[27] In general there is insufficient evidence to connect Albanian with one of those languages, whether one of the Illyrian languages (which historians mostly confirm), or Thracian and Dacian.[28] Among these possibilities, Illyrian is typically held to be the most probable, though insufficient evidence still clouds the discussion.[29]
Although Albanian shares lexical isoglosses with Greek, Germanic, and to a lesser extent Balto-Slavic, the vocabulary of Albanian is quite distinct. In 1995, Taylor, Ringe and Warnow, using quantitative linguistic techniques, found that Albanian appears to comprise a "subgroup with Germanic". However, they argued that this fact is hardly significant, as Albanian has lost much of its original vocabulary and morphology, and so this "apparently close connection to Germanic rests on only a couple of lexical cognates – hardly any evidence at all".[30]
Early linguistic influences
The earliest loanwords attested in Albanian come from Doric Greek,[31] whereas the strongest influence came from Latin. According to Matthew C. Curtis, the loanwords do not necessarily indicate the geographical location of the ancestor of Albanian language.[32] However, according to other linguists, the borrowed words can help to get an idea about the place of origin and the evolution of the Albanian language.[33][34] According to another group of linguists, Albanian originates from an area located east of its present geographic spread due to the several common lexical items found between the Albanian and Romanian languages.[35]
The period during which Proto-Albanian and Latin interacted was protracted, lasting from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD.[36] Over this period, the lexical borrowings can be roughly divided into three layers, the second of which is the largest. The first and smallest occurred at the time of less significant interaction. The final period, probably preceding the Slavic or Germanic invasions, also has a notably smaller number of borrowings. Each layer is characterized by a different treatment of most vowels: the first layer follows the evolution of Early Proto-Albanian into Albanian; while later layers reflect vowel changes endemic to Late Latin (and presumably Proto-Romance). Other formative changes include the syncretism of several noun case endings, especially in the plural, as well as a large-scale palatalization.
A brief period followed, between the 7th and the 9th centuries, that was marked by heavy borrowings from Southern Slavic, some of which predate the "o-a" shift common to the modern forms of this language group. Starting in the latter 9th century, there was a period characterized by protracted contact with the Proto-Romanians, or Vlachs, though lexical borrowing seems to have been mostly one sided: from Albanian into Romanian. Such borrowing indicates that the Romanians migrated from an area where the majority was Slavic (i.e. Middle Bulgarian) to an area with a majority of Albanian speakers (i.e. Dardania, where Vlachs are recorded in the 10th century).[citation needed] Their movement is presumably related to the expansion of the Bulgarian Empire into Albania around that time.
Latin influence
Jernej Kopitar (1780–1844) was the first to note Latin's influence on Albanian and claimed "the Latin loanwords in the Albanian language had the pronunciation of the time of Emperor Augustus".[37] Kopitar gave examples such as Albanian qiqer ‘chickpea’ from Latin cicer, qytet ‘city, town’ from civitas, peshk ‘fish’ from piscis, and shigjetë ‘arrow’ from sagitta. The hard pronunciations of Latin ⟨c⟩ and ⟨g⟩ are retained as palatal and velar stops in the Albanian loanwords. Gustav Meyer (1888)[38] and Wilhelm Meyer-Lübke (1914)[39] later corroborated this. Meyer noted the similarity between the Albanian verbs shqipoj ‘to speak clearly, enunciate’ and shqiptoj ‘to pronounce, articulate’ and the Latin word excipio (meaning to welcome). Therefore, he believed that the word Shqiptar ‘Albanian person’ was derived from shqipoj, which in turn was derived from the Latin word excipere. Johann Georg von Hahn, an Austrian linguist, had proposed the same hypothesis in 1854.[40]
Eqrem Çabej also noticed, among other things, the archaic Latin elements in Albanian:[41]
- Latin /au/ becomes Albanian /a/ in the earliest loanwords: aurum → ar ‘gold’; gaudium → gaz ‘joy’; laurus → lar ‘laurel’. Latin /au/ is retained in later loans, but is altered in a way similar to Greek: causa ‘thing’ → kafshë ‘thing; beast, brute’; laud → lavd.
- Latin /ō/ becomes Albanian /e/ in the oldest Latin loans: pōmus → pemë ‘fruit tree’; hōra → ora ‘hour’. An analogous mutation occurred from Proto-Indo-European to Albanian; PIE *nōs became Albanian ne ‘we’, PIE *oḱtō + suffix -ti- became Albanian tetë ‘eight’, etc.
- Latin unstressed internal and initial syllables become lost in Albanian: cubitus → kub ‘elbow’; medicus → mjek ‘physician’; palūdem ‘swamp’ → VL padūle → pyll ‘forest’. An analogous mutation occurred from Proto-Indo-European to Albanian. In contrast, in later Latin loanwords, the internal syllable is retained: paganus → pagan; plaga → plagë ‘wound’, etc.
- Latin /tj/, /dj/, /kj/ palatalized to Albanian /s/, /z/, /c/: vitium → ves ‘vice; worries’; rationem → arsye ‘reason’; radius → rreze ‘ray; spoke’; facies → faqe ‘face, cheek’; socius → shok ‘mate, comrade’, shoq ‘husband’, etc. In turn, Latin /s/ was altered to /ʃ/ in Albanian.
Haralambie Mihăescu demonstrated that:
- Some 85 Latin words have survived in Albanian but not (as inherited) in any Romance language. A few examples include Late Latin celsydri → dial. kulshedër → kuçedër ‘hydra’, hībernus → vërri ‘winter pasture’, sarcinārius ‘used for packing, loading’ → shelqëror ‘forked peg, grapnel, forked hanger’, solanum ‘nightshade’, lit. ‘sun plant’ → shullë(r) ‘sunny place out of the wind, sunbathed area’, splēnēticus → shpretkë ‘spleen’, trifurcus → tërfurk ‘pitchfork’.[42]
- 151 Albanian words of Latin origin were not inherited in Romanian. A few examples include Latin amicus → Albanian mik ‘friend’, inimicus → armik ‘foe, enemy’, rationem → arsye, benedicere → bekoj, bubulcus ‘ploughman, herdsman’ → bulk, bujk ‘peasant’, calicis → qelq ‘drinking glass’, castellum → kështjellë ‘castle’, centum → qind ‘hundred’, gallus → gjel ‘rooster’, iunctūra → gjymtyrë ‘limb; joint’, medicus → mjek ‘doctor’, retem → rrjetë ‘net’, spērāre → dial. shp(ë)rej shpresoj ‘to hope’ pres ‘await’, voluntās (voluntatis) → vullnet ‘will; volunteer’.[43]
- Some Albanian church terminology have phonetic features which demonstrate their very early borrowing from Latin. A few examples include Albanian bekoj ‘to bless’ from benedicere, engjëll ‘angel’ from angelus, kishë ‘church’ from ecclesia, i krishterë ‘Christian’ from christianus, kryq ‘cross’ from crux (crucis), (obsolete) lter ‘altar’ from Latin altārium, mallkoj ‘to curse’ from maledicere, meshë ‘mass’ from missa, murg ‘monk’ from monacus, peshkëp ‘bishop’ from episcopus, and ungjill ‘gospel’ from evangelium.[44]
Other authors[45] have detected Latin loanwords in Albanian with an ancient sound pattern from the 1st century BC,[clarification needed] for example, Albanian qingël(ë) ‘saddle girth; dwarf elder’ from Latin cingula and Albanian e vjetër ‘old, aged; former’ from "vjet" but influenced by Latin veteris. The Romance languages inherited these words from Vulgar Latin: cingula became Romanian chinga ‘girdle; saddle girth’, and Vulgar Latin veterānus became Romanian bătrân ‘old’.
Albanian, Basque, and the surviving Celtic languages such as Breton and Welsh are the non-Romance languages today that have this sort of extensive Latin element dating from ancient Roman times, which has undergone the sound changes associated with the languages. Other languages in or near the former Roman area either came on the scene later (Turkish, the Slavic languages, Arabic) or borrowed little from Latin despite coexisting with it (Greek, German), although German does have a few such ancient Latin loanwords (Fenster ‘window’, Käse ‘cheese’, Köln).
Romanian scholars such as Vatasescu and Mihaescu, using lexical analysis of the Albanian language, have concluded that Albanian was heavily influenced by an extinct Romance language that was distinct from both Romanian and Dalmatian. Because the Latin words common to only Romanian and Albanian are significantly less than those that are common to only Albanian and Western Romance, Mihaescu argues that the Albanian language evolved in a region with much greater contact to Western Romance regions than to Romanian-speaking regions, and located this region in present-day Albania, Kosovo and Western Macedonia, spanning east to Bitola and Pristina.[46]
Historical presence and location


The place and the time where the Albanian language was formed is uncertain.[47] American linguist Eric Hamp stated that during an unknown chronological period a pre-Albanian population (termed as "Albanoid" by Hamp) inhabited areas stretching from Poland to the southwestern Balkans.[48] Further analysis has suggested that it was in a mountainous region rather than on a plain or seacoast:[49] while the words for plants and animals characteristic of mountainous regions are entirely original, the names for fish and for agricultural activities (such as ploughing) are borrowed from other languages.[50]
A deeper analysis of the vocabulary, however, shows that this could be a consequence of a prolonged Latin domination of the coastal and plain areas of the country, rather than evidence of the original environment where the Albanian language was formed. For example, the word for 'fish' is borrowed from Latin, but not the word for 'gills', which is native. Indigenous are also the words for 'ship', 'raft', 'navigation', 'sea shelves' and a few names of fish kinds, but not the words for 'sail', 'row' and 'harbor' – objects pertaining to navigation itself and a large part of sea fauna. This rather shows that Proto-Albanians were pushed away from coastal areas in early times (probably after the Latin conquest of the region) thus losing large parts (or the majority) of sea environment lexicon. A similar phenomenon could be observed with agricultural terms. While the words for 'arable land', 'corn', 'wheat', 'cereals', 'vineyard', 'yoke', 'harvesting', 'cattle breeding', etc. are native, the words for 'ploughing', 'farm' and 'farmer', agricultural practices, and some harvesting tools are foreign. This, again, points to intense contact with other languages and people, rather than providing evidence of a possible Urheimat.[citation needed]

The centre of Albanian settlement remained the Mat river. In 1079, they were recorded farther south in the valley of the Shkumbin river.[51] The Shkumbin, a seasonal stream that lies near the old Via Egnatia, is approximately the boundary of the primary dialect division for Albanian, Tosk and Gheg. The characteristics of Tosk and Gheg in the treatment of the native and loanwords from other languages are evidence that the dialectal split preceded the Slavic migration to the Balkans,[52][53][36] which means that in that period (the 5th to 6th centuries AD), Albanians were occupying nearly the same area around the Shkumbin river, which straddled the Jireček Line.[54][49]
References to the existence of Albanian as a distinct language survive from the 14th century, but they failed to cite specific words. The oldest surviving documents written in Albanian are the "formula e pagëzimit" (Baptismal formula), Un'te paghesont' pr'emenit t'Atit e t'Birit e t'Spertit Senit. ("I baptize thee in the name of the Father, and the Son, and the Holy Spirit") recorded by Pal Engjelli, Bishop of Durrës in 1462 in the Gheg dialect, and some New Testament verses from that period.
Linguists Stefan Schumacher and Joachim Matzinger (University of Vienna) acert that the first literary records of Albanian date from the 16th century.[55][56] The oldest known Albanian printed book, Meshari, or "missal", was written in 1555 by Gjon Buzuku, a Roman Catholic cleric. In 1635 Frang Bardhi wrote the first Latin–Albanian dictionary. The first Albanian school is believed to have been opened by Franciscans in 1638 in Pdhanë.
One of the earliest dictionaries of Albanian language was written in 1693 which was an Italian language manuscript authored by Montenegrin sea captain Julije Balović Pratichae Schrivaneschae and includes a multilingual dictionary of hundreds of the most often used words in everyday life in the Italian, Slavo-Illirico, Greek, Albanian and Turkish languages.[57]
Proto-IE features
Although Albanian has been referred to as the "weird sister" for several words that do not correspond to IE cognates, it has retained many proto-IE features: for example, the demonstrative pronoun **ḱo- is ancestral to Albanian ky/kjo and English he but not to English this or to Russian etot.
Albanian is compared to other Indo-European languages below, but note that Albanian has exhibited some notable instances of semantic drift (such as motër meaning "sister" rather than "mother".
| Albanian | muaj | ri | nënë | motër | natë | hundë | tre-tri | zi | kuqe | verdhë | kaltër | ujk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proto-Indo-European | mḗh₁n̥s | newijos | méh₂tēr | swésōr | nókʷts | nas | treies | kr̥snós | h₁rudhrós | ǵʰelh₃wos | bʰlēwos | wĺ̥kʷos |
| English | month | new | mother | sister | night | nose | three | black | red | yellow | blue | wolf |
| Latin | mēnsis | novus | māter | soror | noct- | nāsus | trēs | āter, niger | ruber | helvus | flāvus | lupus |
| Lithuanian | mėnesis | naujas | motina | sesuo | naktis | nosis | trys | juodas | raudonas | geltonas | mėlynas | vilkas |
| Old Church Slavonic | мѣсѧць měsęcь |
новъ novъ |
мати mati |
сестра sestra |
ношть noštь |
носъ nosъ |
три, триѥ tri, trije |
чрънъ črъnъ |
чръвенъ črъvenъ |
жлътъ žlъtъ |
син҄ь siņь |
влькъ vlьkъ |
| Ancient Greek | μην- men- |
νέος néos |
μήτηρ mḗtēr |
ἀδελφή adelphḗ |
νυκτ- nukt- |
ῥιν- rhin- |
τρεῖς treîs |
μέλας mélas |
ἐρυθρός eruthrós |
χλωρός khlōrós |
ξανθός ksanthós |
λύκος lúkos |
| Armenian | ամիս amis |
նոր nor |
մայր mayr |
քույր k'uyr |
գիշեր gišer |
քիթ k'it |
երեք yerek' |
սեւ sev |
կարմիր karmir |
դեղին deġin |
Կապույտ kapuyt |
գայլ gayl |
| Irish | mí | nua | máthair | deirfiúr | oíche | srón | trí | dubh | dearg | buí | gorm | faolchú |
| Sanskrit | मास māsa |
नव nava |
मातृ mātr̥ |
स्वसृ svasr̥ |
नक्त/निश् nakta/niś |
नस nasa |
त्रि tri |
काल/कृष्ण kāla/kr̥ṣṇa |
रुधिर rudhira |
हरि hari |
पीत pīta |
वृक vr̥ka |
Albanian–PIE phonological correspondences
Phonologically, Albanian is not so conservative. Like many IE stocks, it has merged the two series of voiced stops (e.g. both *d and *dʰ became d). In addition, voiced stops tend to disappear in between vowels. There is almost complete loss of final syllables and very widespread loss of other unstressed syllables (e.g. mik, 'friend' from Lat. amicus). PIE *o appears as a (also as e if a high front vowel i follows), while *ē and *ā become o, and PIE *ō appears as e. The palatals, velars, and labiovelars all remain distinct before front vowels, a conservation found otherwise in Luvian and related Anatolian languages. Thus PIE *ḱ, *k, and *kʷ become th, q, and s, respectively (before back vowels *ḱ becomes th, while *k and *kʷ merge as k).[citation needed] A minority of scholars reconstruct a fourth laryngeal phoneme *h4 which survives as Alb. h word-initially (Albanian herdhe, 'testicle' but Hittite arki- 'testicle', from PIE *h₄órǵʰiyeh₂).[58][dubious – discuss]
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *p | p | *pékʷ- 'to cook' | pjek 'to cook, roast, bake' |
| *b | b | *sorbéye- 'to drink, slurp' | gjerb 'to drink' |
| *bʰ | b | *bʰaḱeh₂ 'bean' | bathë 'broad bean' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *t | t | *túh₂ 'thou' | ti 'you (singular)' |
| *d | d | *diHtis 'light' | ditë 'day' |
| dh[* 1] | *pérd- 'to fart' | pjerdh 'to fart' | |
| g | *dl̥h₁gʰós 'long' | gjatë 'long' (Tosk dial. glatë) | |
| *dʰ | d | *dʰégʷʰ- 'burn' | djeg 'to burn' |
| dh[* 1] | *gʰórdʰos 'enclosure' | gardh 'fence' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *ḱ | th | *ḱéh₁mi 'I say' | them 'I say' |
| s[* 1] | *ḱuk 'horn' | sutë 'doe' | |
| k[* 2] | *ḱreh₂u 'limb' | krah 'arm' | |
| ç/c[* 3] | *ḱentro- 'to stick' | çandër 'prop' | |
| *ǵ | dh | *ǵómbʰos 'tooth, peg' | dhëmb 'tooth' |
| d[* 4] | *ǵēusnō 'to enjoy' | dua 'to love, want' | |
| *ǵʰ | dh | *ǵʰed-ye- 'to defecate' | dhjes 'to defecate' |
| d[* 4] | *ǵʰr̥sdʰi 'grain, barley' | drithë 'grain' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *k | k | *kágʰmi 'I catch, grasp' | kam 'I have' |
| q | *klaw-eye- 'to weep' | qaj 'to weep, cry' (Gheg qanj, Salamis kla) | |
| *g | g | *h₃lígos 'sick' | ligë 'bad' |
| gj | *h₁rewg- 'to retch' | regj 'to tan hides' | |
| *gʰ | g | *gʰórdʰos 'enclosure' | gardh 'fence' |
| gj | *gʰédnye- 'to get' | gjej 'to find' (Gheg gjêj) |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *kʷ | k | *kʷeh₂sleh₂ 'cough' | kollë 'cough' |
| s | *kʷélH- 'to turn' | sjell 'to fetch, bring' | |
| q | *kʷṓd 'this' | këtë 'this' | |
| *gʷ | g | *gʷr̥ 'stone' | gur 'stone' |
| z | *gʷērHu 'heaviness' | zor 'heaviness; trouble' | |
| *gʷʰ | g | *dʰégʷʰ- 'to burn' | djeg 'to burn' |
| z | *h₁en-dʰogʷʰéye- 'to ignite' | ndez 'to kindle, turn on' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *s | gj[* 1] | *séḱstis 'six' | gjashtë 'six' |
| h[* 2] | *nosōm 'us' (gen.) | nahe 'us' (dat.) | |
| sh[* 3] | *bʰrewsinos 'break' | breshër 'hail' | |
| th[* 4] | *gʷésdos 'leaf' | gjeth 'leaf' | |
| h[* 5] | *sḱi-eh₂ 'shadow' | hije 'shadow' | |
| f[* 6] | *spélnom 'speech' | fjalë 'word' | |
| sht[* 7] | *h₂osti 'bone' | asht 'bone' | |
| th[* 8] | *suh₁s 'swine' | thi 'boar' | |
| ∅ | h₁ésmi I am | jam 'to be' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *y | gj[* 1] | *yés- 'to ferment' | gjesh 'to knead' |
| j[* 2] | *yuHs 'you' (nom.) | ju 'you (plural)' | |
| ∅[* 3] | *bʰéryō 'bear, carry' | bie(r) 'to bring' | |
| h[* 4] | *streh₂yeh₂ 'straw' | strohë 'kennel' | |
| *w | v | *woséye- 'to dress' | vesh 'to wear, dress' |
| *m | m | *meh₂tr-eh₂ 'maternal' | motër 'sister' |
| *n | n | *nōs 'we' (acc.) | ne 'we' |
| nj | *eni-h₁ói-no 'that one' | një 'one' (Gheg njâ, njo, nji ) | |
| ∅/^ | *pénkʷe 'five' | pesë 'five' (Gheg pês) | |
| r | *ǵʰeimen 'winter' | dimër 'winter' (Gheg dimën) | |
| *l | l | *h₃lígos 'sick' | ligë 'bad' |
| ll | *kʷélH- 'turn' | sjell 'to fetch, bring' | |
| *r | r | *repe/o 'take' | rjep 'peel' |
| rr | *wrh₁ḗn 'sheep' | rrunjë 'yearling lamb' | |
| *n̥ | e | *h₁n̥men 'name' | emër 'name' |
| *m̥ | e | *wiḱm̥ti 'twenty' | (një)zet 'twenty' |
| *l̥ | uj | *wĺ̥kʷos 'wolf' | ujk 'wolf' (Chamian ulk) |
| *r̥ | ri, ir | *ǵʰr̥sdom 'grain, barley' | drithë 'grain' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *h₁ | ∅ | *h₁ésmi 'I am' | jam 'to be' |
| *h₂ | ∅ | *h₂r̥tḱos 'bear' | ari 'bear' |
| *h₃ | ∅ | *h₃ónr̥ 'dream' | ëndërr 'dream' |
| *h₄ | h | *h₄órǵʰiyeh₂ 'testicle' | herdhe 'testicle' |
| PIE | Albanian | PIE | Albanian |
|---|---|---|---|
| *i | i | *sínos 'bosom' | gji 'bosom, breast' |
| e | *dwigʰeh₂ 'twig' | degë 'branch' | |
| *ī < *iH | i | *dīHtis 'light' | ditë 'day' |
| *e | e | *pénkʷe 'five' | pesë 'five' (Gheg pês) |
| je | *wétos 'year' (loc.) | vjet 'last year' | |
| *ē | o | *ǵʰēsreh₂ 'hand' | dorë 'hand' |
| *a | a | *bʰaḱeh₂ 'bean' | bathë 'bean' |
| e | *h₂élbʰit 'barley' | elb 'barley' | |
| *o | a | *gʰórdʰos 'enclosure' | gardh 'fence' |
| *ō | e | *h₂oḱtōtis 'eight' | tetë 'eight' |
| *u | u | *supnos 'sleep' | gjumë 'sleep' |
| *ū < *uH | y | *suHsos 'grandfather' | gjysh 'grandfather' |
| i | *mūs 'mouse' | mi 'mouse' |
Standard Albanian
Since World War II, standard Albanian used in Albania has been based on the Tosk dialect. Kosovo and other areas where Albanian is official adopted the Tosk standard in 1969.[59]
Elbasan-based standard
Until the early 20th century, Albanian writing developed in three main literary traditions: Gheg, Tosk, and Arbëreshë. Throughout this time, an intermediate subdialect spoken around Elbasan served as lingua franca among the Albanians, but was less prevalent in writing. The Congress of Manastir of Albanian writers held in 1908 recommended the use of the Elbasan subdialect for literary purposes and as a basis of a unified national language. While technically classified as a southern Gheg variety, the Elbasan speech is closer to Tosk in phonology and practically a hybrid between other Gheg subdialects and literary Tosk.[59]
Between 1916 and 1918, the Albanian Literary Commission met in Shkodër under the leadership of Luigj Gurakuqi with the purpose of establishing a unified orthography for the language. The Commission, made up of representatives from the north and south of Albania, reaffirmed the Elbasan subdialect as the basis of a national tongue. The rules published in 1917 defined spelling for the Elbasan variety for official purposes. The Commission did not, however, discourage publications in one of the dialects, but rather laid a foundation for Gheg and Tosk to gradually converge into one.[59]
When the Congress of Lushnje met in the aftermath of World War I to form a new Albanian government, the 1917 decisions of the Literary Commission were upheld. The Elbasan subdialect remained in use for administrative purposes and many new writers embraced for creative writing. Gheg and Tosk continued to develop freely and interaction between the two dialects increased.
Tosk standard
At the end of World War II, however, the new communist regime radically imposed the use of the Tosk dialect in all facets of life in Albania: administration, education, and literature. Most Communist leaders were Tosks from the south.[59] Standardization was directed by the Albanian Institute of Linguistics and Literature of the Academy of Sciences of Albania.[60] Two dictionaries were published in 1954: an Albanian language dictionary and a Russian–Albanian dictionary. New orthography rules were eventually published in 1967[60] and 1973 Drejtshkrimi i gjuhës shqipe (Orthography of the Albanian Language).[61]
Until 1968, Kosovo and other Albanian-speaking areas in the former Yugoslavia followed the 1917 standard based on the Elbasan dialect, though it was gradually infused with Gheg elements in an effort to develop a Kosovan language separate from communist Albania's Tosk-based standard.[62] Albanian intellectuals in the former Yugoslavia consolidated the 1917 twice in the 1950s, culminating with a thorough codification of orthographic rules in 1964.[63] The rules already provided for a balanced variety that accounted for both Gheg and Tosk dialects, but only lasted through 1968. Viewing divergences with Albania as a threat to their identity, Kosovars arbitrarily adopted the Tosk project that Tirana had published the year before. Although it was never intended to serve outside of Albania, the project became the "unified literary language" in 1972, when approved by a rubberstamp Orthography Congress.[59] Only about 1 in 9 participants were from Kosovo. The Congress, held at Tirana, authorized the orthography rules that came out the following year, in 1973.
More recent dictionaries from the Albanian government are Fjalori Drejtshkrimor i Gjuhës Shqipe (1976) (Orthographic Dictionary of the Albanian Language)[64] and Dictionary of Today's Albanian language (Fjalori Gjuhës së Sotme Shqipe) (1980).[60][65] Prior to World War II, dictionaries consulted by developers of the standard have included Lexikon tis Alvanikis glossis (Albanian: Fjalori i Gjuhës Shqipe (Kostandin Kristoforidhi, 1904),[66] Fjalori i Bashkimit (1908),[66] and Fjalori i Gazullit (1941).[12]
Calls for reform
Since the fall of the communist regime, Albanian orthography has stirred heated debate among scholars, writers, and public opinion in Albania and Kosovo, with hardliners opposed to any changes in the orthography, moderates supporting varying degrees of reform, and radicals calling for a return to the Elbasan dialect. Criticism of Standard Albanian has centred on the exclusion of the 'me+' infinitive and the Gheg lexicon. Critics say that Standard Albanian disenfranchises and stigmatizes Gheg speakers, affecting the quality of writing and impairing effective public communication. Supporters of the Tosk standard view the 1972 Congress as a milestone achievement in Albanian history and dismiss calls for reform as efforts to "divide the nation" or "create two languages." Moderates, who are especially prevalent in Kosovo, generally stress the need for a unified Albanian language, but believe that the 'me+' infinitive and Gheg words should be included. Proponents of the Elbasan dialect have been vocal, but have gathered little support in the public opinion. In general, those involved in the language debate come from diverse backgrounds and there is no significant correlation between one's political views, geographic origin, and position on Standard Albanian.
Many writers continue to write in the Elbasan dialect but other Gheg variants have found much more limited use in literature. Most publications adhere to a strict policy of not accepting submissions that are not written in Tosk. Some print media even translate direct speech, replacing the 'me+' infinitive with other verb forms and making other changes in grammar and word choice. Even authors who have published in the Elbasan dialect will frequently write in the Tosk standard.
In 2013, a group of academics for Albania and Kosovo proposed minor changes to the orthography.[67] Hardline academics boycotted the initiative,[68] while other reformers have viewed it as well-intentioned but flawed and superficial.[67] Media such as Rrokum and Java have offered content that is almost exclusively in the Elbasan dialect. Meanwhile, author and linguist Agim Morina has promoted Shqipe e Përbashkët or Common Albanian, a reformed version of the Tosk standard that aims at reflecting the natural development of the language among all Albanians.[69][59] Common Albanian incorporates the 'me+' infinitive, accommodates for Gheg features, provides for dialect-neutral rules that favor simplicity, predictability, and usage trends.[70][71] Many modern writers have embraced Common Albanian to various extents, especially in less formal writing.[72]
Education
Albanian is the medium of instruction in most Albanian schools. The literacy rate in Albania for the total population, age 9 or older, is about 99%. Elementary education is compulsory (grades 1–9), but most students continue at least until a secondary education. Students must pass graduation exams at the end of the 9th grade and at the end of the 12th grade in order to continue their education.
Phonology
Standard Albanian has 7 vowels and 29 consonants. Like English, Albanian has dental fricatives /θ/ (like the th in thin) and /ð/ (like the th in this), written as th and dh, which are rare cross-linguistically.
Gheg uses long and nasal vowels, which are absent in Tosk, and the mid-central vowel ë is lost at the end of the word. The stress is fixed mainly on the last syllable. Gheg n (femën: compare English feminine) changes to r by rhotacism in Tosk (femër).
Consonants
| Labial | Dental | Alveolar | Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | velar. | ||||||||
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | (ŋ) | |||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | |||||
| voiced | b | d | ɡ | ||||||
| Affricate | voiceless | t͡s | t͡ʃ | c͡ç | |||||
| voiced | d͡z | d͡ʒ | ɟ͡ʝ | ||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | θ | s | ʃ | h | |||
| voiced | v | ð | z | ʒ | |||||
| Approximant | l | ɫ | j | ||||||
| Flap | ɾ | ||||||||
| Trill | r | ||||||||
Notes:
- The contrast between flapped r and trilled rr is the same as in Spanish or Armenian. In most of the dialects, as also in standard Albanian, the single "r" changes from an alveolar flap /ɾ/ into a retroflex flap [ɽ], or even an alveolar approximant [ɹ] when it is at the end of a word.
- The palatal nasal /ɲ/ corresponds to the Spanish ñ and the French and Italian gn. It is pronounced as one sound, not a nasal plus a glide.
- The ll sound is a velarised lateral, close to English dark L.
- The letter ç is sometimes written ch due to technical limitations because of its use in English sound and its analogy to the other digraphs xh, sh, and zh. Usually it is written simply c or more rarely q with context resolving any ambiguities.
- The position of q and gj sound is not clear. Many speakers merge them into the palatoalveolar sounds ç and xh. This is especially common in Northern Gheg, but is increasingly the case in Tosk as well.[73] Other speakers reduced them into /j/ in consonant clusters, such as in the word fjollë, which before standardization was written as fqollë ( < Medieval Greek φακιολης).
- The ng can pronounced as /ŋ/ in final position, otherwise is an allophone of n before k and g.
- Before q and gj, the n is always pronounced /ɲ/ but this is not reflected in the orthography.
- /θ, ð, ɫ/ are interdental.
Vowels
| IPA | Description | Written as | English approximation |
|---|---|---|---|
| i | Close front unrounded vowel | i | seed |
| ɛ | Open-mid front unrounded vowel | e | bed |
| a | Open central unrounded vowel | a | father, Spanish casa |
| ə | Schwa | ë | about, the |
| ɔ | Open-mid back rounded vowel | o | law |
| y | Close front rounded vowel | y | French tu, German Lüge |
| u | Close back rounded vowel | u | boot |
Schwa
Although the Indo-European schwa (ə or -h2-) was preserved in Albanian, in some cases it was lost, possibly when a stressed syllable preceded it.[74] Until the standardization of the modern Albanian alphabet, in which the schwa is spelled as ë, as in the work of Gjon Buzuku in the 16th century, various vowels and gliding vowels were employed, including ae by Lekë Matrënga and é by Pjetër Bogdani in the late 16th and early 17th century.[75][76] The schwa in Albanian has a great degree of variability from extreme back to extreme front articulation.[77] Within the borders of Albania, the phoneme is pronounced about the same in both the Tosk and the Gheg dialect due to the influence of standard Albanian. However, in the Gheg dialects spoken in the neighbouring Albanian-speaking areas of Kosovo and Macedonia, the phoneme is still pronounced as back and rounded.[77]
Grammar
Albanian has a canonical word order of SVO (subject–verb–object) like English and many other Indo-European languages.[78] Albanian nouns are inflected by gender (masculine, feminine and neuter) and number (singular and plural). There are five declensions with six cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), although the vocative only occurs with a limited number of words, and the forms of the genitive and dative are identical (a genitive is produced when the prepositions i/e/të/së are used with the dative). Some dialects also retain a locative case, which is not present in standard Albanian. The cases apply to both definite and indefinite nouns, and there are numerous cases of syncretism.
The following shows the declension of mal (mountain), a masculine noun which takes "i" in the definite singular:
| Indefinite singular | Indefinite plural | Definite singular | Definite plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | një mal (a mountain) | male (mountains) | mali (the mountain) | malet (the mountains) |
| Accusative | një mal | male | malin | malet |
| Genitive | i/e/të/së një mali | i/e/të/së maleve | i/e/të/së malit | i/e/të/së maleve |
| Dative | një mali | maleve | malit | maleve |
| Ablative | (prej) një mali | (prej) malesh | (prej) malit | (prej) maleve |
The following shows the declension of the masculine noun zog (bird), a masculine noun which takes "u" in the definite singular:
| Indefinite singular | Indefinite plural | Definite singular | Definite plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | një zog (a bird) | zogj (birds) | zogu (the bird) | zogjtë (the birds) |
| Accusative | një zog | zogj | zogun | zogjtë |
| Genitive | i/e/të/së një zogu | i/e/të/së zogjve | i/e/të/së zogut | i/e/të/së zogjve |
| Dative | një zogu | zogjve | zogut | zogjve |
| Ablative | (prej) një zogu | (prej) zogjsh | (prej) zogut | (prej) zogjve |
The following table shows the declension of the feminine noun vajzë (girl):
| Indefinite singular | Indefinite plural | Definite singular | Definite plural | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | një vajzë (a girl) | vajza (girls) | vajza (the girl) | vajzat (the girls) |
| Accusative | një vajzë | vajza | vajzën | vajzat |
| Genitive | i/e/të/së një vajze | i/e/të/së vajzave | i/e/të/së vajzës | i/e/të/së vajzave |
| Dative | një vajze | vajzave | vajzës | vajzave |
| Ablative | (prej) një vajze | (prej) vajzash | (prej) vajzës | (prej) vajzave |
The definite article is placed after the noun as in many other Balkan languages, like in Romanian, Macedonian and Bulgarian.
- The definite article can be in the form of noun suffixes, which vary with gender and case.
- For example, in singular nominative, masculine nouns add -i, or those ending in -g/-k/-h take -u (to avoid palatalization):
- mal (mountain) / mali (the mountain);
- libër (book) / libri (the book);
- zog (bird) / zogu (the bird).
- Feminine nouns take the suffix -(i/j)a:
- veturë (car) / vetura (the car);
- shtëpi (house) / shtëpia (the house);
- lule (flower) / lulja (the flower).
- For example, in singular nominative, masculine nouns add -i, or those ending in -g/-k/-h take -u (to avoid palatalization):
- Neuter nouns take -t.
Albanian has developed an analytical verbal structure in place of the earlier synthetic system, inherited from Proto-Indo-European. Its complex system of moods (six types) and tenses (three simple and five complex constructions) is distinctive among Balkan languages. There are two general types of conjugations.
Albanian verbs, like those of other Balkan languages, have an "admirative" mood (mënyra habitore) that is used to indicate surprise on the part of the speaker or to imply that an event is known to the speaker by report and not by direct observation. In some contexts, this mood can be translated using English "apparently".
- Ti flet shqip. "You speak Albanian." (indicative)
- Ti fliske shqip! "You (surprisingly) speak Albanian!" (admirative)
- Rruga është e mbyllur. "The street is closed." (indicative)
- Rruga qenka e mbyllur. "(Apparently,) The street is closed." (admirative)
For more information on verb conjugation and on inflection of other parts of speech, see Albanian morphology.
Word order
Albanian word order is relatively free.[79] To say 'Agim ate all the oranges' in Albanian, one may use any of the following orders, with slight pragmatic differences:
- SVO: Agimi i hëngri të gjithë portokallët.
- SOV: Agimi të gjithë portokallët i hëngri.
- OVS: Të gjithë portokallët i hëngri Agimi.
- OSV: Të gjithë portokallët Agimi i hëngri.
- VSO: I hëngri Agimi të gjithë portokallët.
However, the most common order is subject–verb–object, and negation is expressed by the particles nuk or s' in front of the verb, for example:
- Toni nuk flet anglisht "Tony does not speak English";
- Toni s'flet anglisht "Tony doesn't speak English";
- Nuk e di "I do not know";
- S'e di "I don't know".
However, the verb can optionally occur in sentence-initial position, especially with verbs in the non-active form (forma joveprore):
- Parashikohet një ndërprerje "An interruption is anticipated".
In imperative sentences, the particle mos is used for negation:
- Mos harro "do not forget!".
Numerals
|
Literary tradition
Earliest undisputed texts

The earliest known texts in Albanian:
- the "formula e pagëzimit" (Baptismal Formula), which dates back to 1462 and was authored by Pal Engjëlli (or Paulus Angelus) (c. 1417 – 1470), Archbishop of Durrës. Engjëlli was a close friend and counsellor of Skanderbeg.[80] It was written in a pastoral letter for a synod at the Holy Trinity in Mat and read in Latin characters as follows: Unte paghesont premenit Atit et Birit et Spertit Senit (standard Albanian: "Unë të pagëzoj në emër të Atit, të Birit e të Shpirtit të Shenjtë"; English: "I baptize you in the name of the Father and the Son and the Holy Spirit"). It was discovered and published in 1915 by Nicolae Iorga.[81]
- the Fjalori i Arnold von Harfit (Arnold Ritter von Harff's lexicon), a short list of Albanian phrases with German glosses, dated 1496.[82]
- a song, recorded in the Greek alphabet, retrieved from an old codex that was written in Greek. The document is also called "Perikopeja e Ungjillit të Pashkëve" or "Perikopeja e Ungjillit të Shën Mateut" ("The Song of the Easter Gospel, or "The Song of Saint Matthew's Gospel"). Although the codex is dated to during the 14th century, the song, written in Albanian by an anonymous writer, seems to be a 16th-century writing. The document was found by Arbëreshë people who had emigrated to Italy in the 15th century.[83]
- The first book in Albanian is the Meshari ("The Missal"), written by Gjon Buzuku between 20 March 1554 and 5 January 1555. The book was written in the Gheg dialect in the Latin script with some Slavic letters adapted for Albanian vowels. The book was discovered in 1740 by Gjon Nikollë Kazazi, the Albanian archbishop of Skopje. It contains the liturgies of the main holidays. There are also texts of prayers and rituals and catechetical texts. The grammar and the vocabulary are more archaic than those in the Gheg texts from the 17th century. The 188 pages of the book comprise about 154,000 words with a total vocabulary of c. 1,500 different words. The text is archaic yet easily interpreted because it is mainly a translation of known texts, in particular portions of the Bible. The book also contains passages from the Psalms, the Book of Isaiah, the Book of Jeremiah, the Letters to the Corinthians, and many illustrations. The uniformity of spelling seems to indicate an earlier tradition of writing. The only known copy of the Meshari is held by the Apostolic Library.[84] In 1968 the book was published with transliterations and comments by linguists.
Disputed earlier texts

In 1967 two scholars claimed to have found a brief text in Albanian inserted into the Bellifortis text, a book written in Latin dating to 1402–1405.[85]
"A star has fallen in a place in the woods, distinguish the star, distinguish it.
Distinguish the star from the others, they are ours, they are.
Do you see where the great voice has resounded? Stand beside it
That thunder. It did not fall. It did not fall for you, the one which would do it.
...
Like the ears, you should not believe ... that the moon fell when ...
Try to encompass that which spurts far ...
Call the light when the moon falls and no longer exists ..."
Dr. Robert Elsie, a specialist in Albanian studies, considers that "The Todericiu/Polena Romanian translation of the non-Latin lines, although it may offer some clues if the text is indeed Albanian, is fanciful and based, among other things, on a false reading of the manuscript, including the exclusion of a whole line."[86]
Ottoman period
In 1635, Frang Bardhi (1606–1643) published in Rome his Dictionarum latinum-epiroticum, the first known Latin-Albanian dictionary. Other scholars who studied the language during the 17th century include Andrea Bogdani (1600–1685), author of the first Latin-Albanian grammar book, Nilo Katalanos (1637–1694) and others.[87]
Vocabulary
Albanian is known within historical linguistics as a case of a language which, although surviving through many periods of foreign rule and multilingualism, saw a "disproportionately high" influx of loans augmenting and replacing much of its vocabulary.[88] Other languages influenced Albanian and high-end estimates classify the majority of Albanian vocabulary as loanwords, suggesting that more than 90% of the present Albanian vocabulary is Latin, Greek, Slavic, Italian and Turkish loanwords, with the biggest[failed verification] influence being Latin.[89] The chief sources of (Proto-) Albanian are (Ancient) Greek, Latin and Slavic, while Ancient Greek loanwords are scarce the Latin loanwords are of extreme importance in phonology.[90] The presence of loanwords from more well-studied languages from time periods before Albanian was attested, reaching deep back into the Classical Era, has been of great use in phonological reconstructions for earlier ancient and medieval forms of Albanian.[88] Some words in the core vocabulary of Albanian have no known etymology linking them to Proto-Indo-European or any known source language, and as of 2018 are thus tentatively attributed to an unknown, unattested, pre-Indo-European substrate language; some words among these include zemër (heart) and hekur (iron).[91] Some among these putative pre-IE words are thought to be related to putative pre-IE substrate words in neighboring Indo-European languages, such as lule (flower), which has been tentatively linked to Latin lilia and Greek leirion[92]
Lexical distance of Albanian in a lexicostatistical analysis of the Ukrainian linguist Tyshchenko(the lower figure - the higher similarity): 49% Slovenian, 53% Romanian, 56% Greek, 82% French, 86% Macedonian, 86% Bulgarian.[93][94]
Cognates with Illyrian
- Andena/Andes/Andio/Antis — personal Illyrian names based on a root-word and- or ant-, found in both the southern and the Dalmatian-Pannonian (including modern Bosnia and Herzegovina) onomastic provinces; cf. Alb. andë (northern Albanian dialect, or Gheg) and ëndë (southern Albanian dialect or Tosk) "appetite, pleasure, desire, wish"; Andi proper name, Andizetes, an Illyrian people inhabiting the Roman province of Panonia.[95]
- aran "field"; cf. Alb. arë; plural ara[96]
- Ardiaioi/Ardiaei, name of an Illyrian people, cf. Alb. ardhja "arrival" or "descent", connected to hardhi "vine-branch, grape-vine", with a sense development similar to Germanic *stamniz, meaning both stem, tree stalk and tribe, lineage. However, the insufficiency of this hypothesis is that so far there is no certainty as to the historical or etymological development of either ardhja/hardhi or Ardiaioi, as with many other words.[95]
- Bilia "daughter"; cf. Alb. bijë, dial. bilë[97]
- Bindo/Bindus, an Illyrian deity from Bihać, Bosnia and Herzegovina; cf. Alb. bind "to convince" or "to make believe", përbindësh "monster".[98]
- bounon, "hut, cottage"; cf. Alb bun[99]
- brisa, "husk of grapes"; cf. Alb bërsí "lees, dregs; mash" ( < PA *brutiā)[100]
- Barba- "swamp", a toponym from Metubarbis; possibly related to Alb. bërrakë "swampy soil"[100]
- can- "dog"; related to Alb. qen[100]
- Daesitiates, a name of an Illyrian people, cf. Alb. dash "ram", corresponding contextually with south Slavonic dasa "ace", which might represent a borrowing and adaptation from Illyrian (or some other ancient language).[95]
- mal, "mountain"; cf. Alb mal[101]
- bardi, "white"; cf. Alb bardhë[102]
- drakoina "supper"; cf. Alb. darke, dreke[103]
- drenis, "deer"; cf. Alb dre, dreni[99]
- delme "sheep"; cf. Alb dele, Gheg dialect delme[104]
- dard, "pear"; cf. Alb dardhë[105]
- Hyllus (the name of an Illyrian king); cf. Alb. yll (hyll in some northern dialects) "star", also Alb. hyj "god", Ylli proper name.[103]
- sīca, "dagger"; cf. Alb thikë or thika "knife"[106]
- Ulc-, "wolf" (pln. Ulcinium); cf. Alb ujk "wolf", ulk (Northern Dialect)[107]
- loúgeon, "pool"; cf. Alb lag, legen "to wet, soak, bathe, wash" ( < PA *lauga), lëgatë "pool" ( < PA *leugatâ), lakshte "dew" ( < PA laugista)[108]
- mag- "great"; cf. Alb. i madh "big, great"[100]
- mantía "bramblebush"; Old and dial. Alb mandë "berry, mulberry" (mod. Alb mën, man)[citation needed]
- rhinos, "fog, mist"; cf. Old Alb ren "cloud" (mod. Alb re, rê) ( < PA *rina)[109]
- Vendum "place"; cf. Proto-Alb. wen-ta (Mod. Alb. vend)[103]
Loanwords
Early Greek loans
There are some 30 Ancient Greek loanwords in Albanian.[110] Many of these reflect a dialect which voiced its aspirants, as did the Macedonian dialect. Other loanwords are Doric; these words mainly refer to commodity items and trade goods and probably came through trade with a now-extinct intermediary.[31]
- bletë; "hive, bee" < Attic mélitta "bee" (vs. Ionic mélissa).[111]
- drapër; "sickle" < (NW) drápanon[112]
- kumbull; "plum" < kokkúmelon[112]
- lakër; "cabbage, green vegetables" < láchanon "green; vegetable"[113]
- lëpjetë; "orach, dock" < lápathon[114]
- leva (lyej); "to smear, oil" < *liwenj < *elaiwā < Gk elai(w)ṓn "oil"[clarification needed]
- mokër; "millstone" < (NW) māchaná "device, instrument"[110]
- mollë; "apple" < mēlon "fruit"[115]
- pjepër; "melon" < pépōn
- presh; "leek" < práson[113]
- shpellë; "cave" < spḗlaion
- trumzë; "thyme" < (NW) thýmbrā, thrýmbrē[112]
Gothic loans
Some Gothic loanwords were borrowed through Late Latin, while others came from the Ostrogothic expansion into parts of Praevalitana around Nakšić and the Gulf of Kotor in Montenegro.
- fat; "groom, husband" < Goth brūþfaþs "bridegroom"[116]
- horr; "scoundrel", horrë; "hussy, whore" < Goth hors "adulterer", *hora "whore"[citation needed]
- shkulkë; "boundary marker for pastures made of branches" < Late Latin sculca < Goth skulka "guardian"[citation needed]
- shkumë; "foam" < Late Latin < Goth skūma[citation needed]
- tirq; "trousers" < Late Latin tubrucus < Goth *þiobrok "knee-britches"; cf. OHG dioh-bruoh, Eng thigh, breeches[citation needed]
Other loans
It is assumed[by whom?] that Greek and Balkan Latin (the ancestor of Romanian and other Balkan Romance languages) exerted a great influence on Albanian. Examples of words borrowed from Latin: qytet < civitas (city), qiell < caelum (sky), mik < amicus (friend).
After the Slavs arrived in the Balkans, the Slavic languages became an additional source of loanwords. The rise of the Ottoman Empire meant an influx of Turkish words; this also entailed the borrowing of Persian and Arabic words through Turkish. Some Turkish personal names, such as Altin, are common. There are some loanwords from Modern Greek, especially in the south of Albania. Many borrowed words have been replaced by words with Albanian roots or modern Latinized (international) words.
See also
- Tosk Albanian
- Gheg Albanian
- Arbëresh language
- Arvanitika
- Illyrian languages
- Messapian language
- IPA/Albanian
- Thraco-Illyrian
Notes
Bibliography
- Ajeti, Idriz. “La présence de l’albanais dans les parlers des populations slaves de la Péninsule balkanique à la lumière de la langue et de la toponymie”, Studia Albanica 2 (1968): 131–6.
- Ajeti, Idriz. “Për historinë e marrëdhënieve të hershme gjuhësore shqiptare-sllave”, Studime Filologjike 4 (1972): 83–94 (reprint in Gjurmime albanologjike – Seria e shkencave filologjike II – 1972. Pristina: 1974, pp. 33–44).
- Arapi, Inna. Der Gebrauch von Infinitiv und Konjunktiv im Altalbanischen mit Ausblick auf das Rumänische. Hamburg: Kovač, 2010.
- Banfi, Emanuele. Linguistica balcanica. Bologna: Zanichelli, 1985.
- Banfi, Emanuele. Storia linguistica del sud-est europeo: Crisi della Romània balcanica tra alto e basso medioevo. Milan: Franco Angeli, 1991.
- Bonnet, Guillaume. Les mots latins de l’albanais. Paris–Montréal: L'Harmattan, 1998.
- Bopp, Franz. “Über das Albanesische in seinen verwandtschaftlichen Beziehungen”, in Königliche Preußische Akademie der Wissenschaften. Abhandlungen der philosophisch-historischen Klasse. Berlin: J. Stargardt, 1855, pp. 459–549.
- Boretzky, Norbert. Der türkische Einfluss auf das Albanische. 2 vols. vol. 1: Phonologie und Morphologie der albanischen Turzismen; vol. 2: Wörterbuch der albanischen Turzismen. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 1975.
- Buchholz, Oda & Wilfried Fiedler. Albanische Grammatik. Leipzig: VEB Verlag Enzyklopädie, 1987.
- Çabej, Eqrem. “Disa probleme themelore të historisë së vjetër të gjuhës shqipe”, Buletin i Universitetit Shtetëror të Tiranës. Seria e Shkencave Shoqërore 4 (1962): 117-148 (In German Studia Albanica 1 (1964))
- Çabej, Eqrem. “Zur Charakteristik der lateinischen Lehnwörter im Albanischen”, Revue roumaine de linguistique 7, vol. 1 (1962): 161–99 (In Albanian “Karakteristikat e huazimeve latine të gjuhës shqipe”, Studime Filologjike 2 (1974): 14-51)
- Çabej, Eqrem. “Rreth disa çështjeve të historisë së gjuhës shqipe”, Buletin i Universitetit Shtetëror të Tiranës. Seria e Shkencave Shoqërore 3 (1963): 69-101. (In Romanian Studii și cercetări lingvistiche 4 (1954))
- Çabej, Eqrem. “Mbi disa rregulla të fonetikës historike të shqipes”, Studime Filologjike 2 (1970): 77-95 (In German “Über einige Lautregeln des Albanischen”, Die Sprache 18 (1972): 132–54)
- Çabej, Eqrem. “L'ancien nom national des albanais”, Studia Albanica 1 (1972): 1-40.
- Çabej, Eqrem. “Problemi i vendit të formimit të gjuhës shqipe”, Studime Filologjike 4 (1972): 3-27.
- Çabej, Eqrem. Studime etimologjike në fushë të shqipes. 7 vols. Tirana: Akademia et Shkencave e Republikës Popullore të Shqipërisë, Instituti i Gjuhësisë dhe i Letërsisë, 1976–2014.
- Camaj, Martin. Albanische Wortbildung. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 1966.
- Camaj, Martin. Albanian Grammar. Trans. Leonard Fox. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 1984.
- Camarda, Demetrio. Saggio di grammatologia comparata sulla lingua albanese. Livorno: Successore di Egisto Vignozzi, 1864.
- Camarda, Demetrio. Appendice al saggio di grammatologia comparata sulla lingua albanese. Prato, 1866.
- Campbell, George L., ed. Compendium of the World's Languages, 2nd edn. Vol. 1: Abaza to Kurdish, s.v. “Albanian”. London–NY: Routledge, 2000, pp. 50–7.
- Cimochowski, Wacław. “Recherches sur l'histoire du sandhi dans la langue albanaise”, Lingua Posnaniensis 2 (1950): 220–55.
- Cimochowski, Wacław. “Des recherches sur la toponomastique de l'Albanie”, Lingua Posnaniensis 8 (1960): 133–45.
- Cimochowski, Wacław. “Pozicioni gjuhësor i ilirishtes ballkanike në rrethin e gjuhëve indoevropiane”, Studime Filologjike 2 (1973).
- Demiraj, Bardhyl. Albanische Etymologien: Untersuchungen zum albanischen Erbwortschatz. Amsterdam–Atlanta: Rodopi, 1997.
- Demiraj, Shaban. “Albanian”, in The Indo-European Languages. Edited by Anna Giacalone Ramat & Paolo Ramat. London-NY: Routledge, 1998, pp. 480–501.
- Demiraj, Shaban. Gramatikë historike e gjuhës shqipe. Tirana: 8 Nëntori, 1986.
- Demiraj, Shaban. Gjuha shqipe dhe historia e saj. Tirana: Shtëpia botuese e librit universitar, 1988.
- Demiraj, Shaban. Fonologjia historike e gjuhës shqipe. (Akademia e Shkencave e Shqiperise. Instituti i Gjuhesise dhe i Letersise). Tirana: TOENA, 1996.
- Demiraj, Shaban. Prejardhja e shqiptarëve në dritën e dëshmive të gjuhës shqipe. Tirana: Shkenca, 1999.
- De Simone, Carlo. “Gli illiri del Sud. Tentativo di una definizione”, Iliria 1 (1986).
- Desnickaja, Agnija. Albanskij jazyk i ego dialekty. Leningrad: Nauka, 1968.
- Desnickaja, Agnija. “Language Interferences and Historical Dialectology”, Linguistics 113 (1973): 41–57.
- Desnickaja, Agnija. Osnovy balkanskogo jazykoznanija. Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
- Domi, Mahir. “Prapashtesa ilire dhe shqipe, përkime dhe paralelizma”, Studime Filologjike 4 (1974).
- Domi, Mahir. “Considérations sur les traits communs ou parallèles de l'albanais avec les autres langues balkaniques et sur leur étude”, Studia Albanica 1 (1975).
- Fortson IV, Benjamin W. “Albanian”, in Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction, 2nd edn. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010, pp. 446–58 (1st edn. 2004, pp. 390–9).
- Genesin, Monica. “Albanian”, in Encyclopedia of the Languages of Europe. Edited by Glanville Price. Oxford: Blackwell, 1998, pp. 4–8.
- Gjinari, Jorgji. “Për historinë e dialekteve të gjuhës shqipe”, Studime Filologjike 4 (1968).
- Gjinari, Jorgji. “Mbi vazhdimësinë e ilirishtes në gjuhën shqipe”, Studime Filologjike 3 (1969).
- Gjinari, Jorgji. “Struktura dialektore e shqipes e parë në lidhje me historinë e popullit”, Studime Filologjike 3 (1976).
- Gjinari, Jorgji. “Dëshmi të historisë së gjuhës shqipe për kohën dhe vendin e formimit të popullit shqiptar”, Studime Filologjike 3 (1982).
- Gjinari, Jorgji. Dialektologjia shqiptare. Pristina: Universiteti, 1970.
- Gjinari, Jorgji, Bahri Beci, Gjovalin Shkurtaj, & Xheladin Gosturani. Atlasi dialektologjik i gjuhës shqipe, vol. 1. Naples: Università degli Studi di Napoli L’Orientali, 2007.
- Hamp, Eric P. “Albanian”, in Encyclopedia of Language and Linguistics. 2 vols. Edited by R. E. Asher. Oxford: Pergamon, 1994, pp. 1:65–7.
- Huld, Martin E. Basic Albanian Etymologies. Columbus, OH: Slavica Publishers, 1984.
- Katičić, Radoslav. Ancient Languages of the Balkans. 2 vols. The Hague–Paris: Mouton, 1976.
- Kocaqi, Altin. “Dokumente historiko-gjuhësore: vëndi i shqipes ndër gjuhët evropiane”. Albania: Marin Barleti, 2013. ISBN 9995604701.
- Kopitar, Jernej K. “Albanische, walachische und bulgarische Sprache”, Jahrbücher der Literatur (Wien) 46 (1829): 59–106.
- Kretschmer, Paul. Einleitung in die Geschichte der griechischen Sprache. Göttingen, 1896.
- Kretschmer, Paul. “Sprachliche Vorgeschichte des Balkans”, Revue internationale des études balkaniques 2, no. 1 (1935): 41–8.
- Lloshi, Xhevat. “Substandard Albanian and Its Relation to Standard Albanian”, in Sprachlicher Standard und Substandard in Südosteuropa und Osteuropa: Beiträge zum Symposium vom 12.-16. Oktober 1992 in Berlin. Edited by Norbert Reiter, Uwe Hinrichs & Jirina van Leeuwen-Turnovcova. Berlin: Otto Harrassowitz, 1994, pp. 184–94.
- Lloshi, Xhevat. “Albanian”, in Handbuch der Südosteuropa-Linguistik. Edited by Uwe Hinrichs. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 1999, pp. 277–99.
- Lloshi, Xhevat. Rreth alfabetit të shqipes: me rastin e 100-vjetorit të Kongresit të Manastirit. Skopje–Pristina–Tirana: Logos-A, 2008.
- Lambertz, Maximilian. Lehrgang des Albanischen. 3 vols., vol. 1: Albanisch-deutsches Wörterbuch; vol. 2: Albanische Chrestomathie; vol. 3: Grammatik der albanischen Sprache. Berlin: Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschaften 1954; Berlin 1955; Halle an der Saale 1959.
- Mallory, J.P. & D. Q. Adams. “Albanian language”, in Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. London: Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997, pp. 8–11.
- Matzinger, Joachim. “Die Albaner als Nachkommen der Illyrier aus der Sicht der historischen Sprachwissenschaft”, in Albanische Geschichte: Stand und Perspektiven der Forschung. Edited by Oliver Jens Schmitt & Eva Frantz. Munich: R. Oldenburg Verlag, 2009, pp. 13–35.
- Matzinger, Joachim. “Der lateinisch-albanische Sprachkontakt und seine Implikationen für Vorgeschichte des Albanischen und der Albaner”, in Südosteuropäische Romania: Siedlungs-/Migrationsgeschichte und Sprachtypologie. Edited by Wolfgang Dahmen et al. Tübingen: Narr Verlag, 2012, pp. 75–103.
- Mayer, Anton. Die Sprache der alten Illyrier. 2 vols. Vienna: Österreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften, 1957/1959.
- Mann, Stuart E. An Albanian Historical Grammar. Hamburg: Helmut Buske, 1977.
- Meyer, Gustav. “Albanesische Studien I. Die Pluralbildungen der albanesischen Nomina”, in Sitzungsberichte der philosophisch-historischen Classe der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften 104 (1883): 257–362.
- Miklošič, Franz. Albanische Forschungen. 2 vols., vol. 1: Die slavischen Elemente im Albanischen; vol. 2: Die romanischen Elemente im Albanischen. Vienna: Karl Gerold's Sohn, 1870.
- Mihăescu, Haralambie. “Les éléments latins de la langue albanaise”, Révue des études sud-est européennes 4 (1966): 5–33, 323–53.
- Mihăescu, Haralambie. La langue latine dans le sud-est de l’Europe. Bucharest: Editura Academiei; Paris: Les Belles Lettres, 1978.
- Newmark, Leonard, Philip Hubbard, & Peter Prifti. Standard Albanian: A Reference Grammar for Students. Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1982.
- Ölberg, Hermann. “Einige Uberlegungen zur Autochtonie der Albaner auf der Balkanhalbinsel”, in Akten der internationalen albanologischen Kolloquiums, Innsbruck, 1972, zum Gedächtnis an Norbert Jokl. Edited by Hermann M. Ölberg. Innsbruck: Institut für Sprachwissenschaft der Universität Innsbruck, 1977.
- Ölberg, Hermann. “Kontributi i gjuhësisë për çështjen e atdheut ballkanik të shqiptarëve”, Studime Filologjike 3 (1982).
- Pedersen, Holger. “Bidrag til den albanesiske Sproghistorie”, in Festskrift til Vilhelm Tomsen. Kopenhagen: Gyldendal, 1894, pp. 246–57.
- Pedersen, Holger. “Albanesisch”, Kritischer Jahrbericht 9, vol. 1 (1905): 206–17. Erlangen (1909).
- Pellegrini, Giovan Battista. “I rapporti linguistici interadriatici e l’elemento latino dell’albanese”, Abruzzo 19 (1980): 31-71.
- Pellegrini, Giovan Battista. “Disa vëzhgime mbi elementin Latin të shqipes” [Some observations on the Latin element of the Albanian language], Studime Filologjike 3 (1982); (in Italian) “Alcune osservazioni sull’elemento latino dell’albanese”, Studia Albanica 1983: 63–83.
- Pellegrini, Giovan Battista. Avviamento alla linguistica albanese. Edizione rinnovata. Rende: Università degli studi della Calabria, Centro editoriale e librario, 1997.
- Pisani, Vittore. “L’albanais et les autres langues indo-européennes”, in Mélanges Henri Grégoire II. Brussels, 1950, pp. 519–38; reprint in Saggi di linguistica storica: Scritti scelti. Torino: Rosenberg & Sellier, 1959, pp. 96–114.
- Pisani, Vittore. “Les origines de la langue albanaise, questions de principe et de méthode”, Studia Albanica 1 (1964): 61–8.
- Pisani, Vittore. “Sulla genesi dell'albanese”, in Akten der internationalen albanologischen Kolloquiums, Innsbruck, 1972, zum Gedächtnis an Norbert Jokl. Edited by Hermann M. Ölberg. Innsbruck: Institut für Sprachwissenschaft der Universität Innsbruck, 1977, pp. 345–66.
- Orel, Vladimir. Albanian Etymological Dictionary. Leiden: Brill, 1998.
- Orel, Vladimir. A Concise Historical Grammar of the Albanian Language: Reconstruction of Proto-Albanian. Leiden: Brill, 2000.
- Riza, Selman. Studime albanistike. Pristina 1979.
- Rusakov, Alexander. “Albanian”, in The Indo-European Languages, 2nd edn. Edited by Mate Kopović. London–NY: Routledge, 2014, pp. 552–608.
- Schumacher, Stefan & Joachim Matzinger. Die Verben des Altalbanischen: Belegwörterbuch, Vorgeschichte und Etymologie. Wiesbaden: Otto Harrassowitz, 2013.
- Svane, Gunnar. Slavische Lehnwörter im Albanischen. Århus: Aarhus University Press, 1992.
- Tagliavini, Carlo. La stratificazione del lessico albanese: Elementi indoeuropei. Bologna: Casa editrice Prof. Riccardo Pàtron, 1965.
- Thumb, Albert. “Altgriechische Elemente des Albanesischen”, Indogermanische Forschungen 26 (1909): 1–20.
- von Hahn, Johann Georg. Albanesische Studien. 3 vols. Jena: F. Mauko, 1854.
- Watkins, Calvert. “Proto-Indo-European: Comparison and Reconstruction”, in The Indo-European Languages. Edited by Anna Giacalone Ramat & Paolo Ramat. London-NY: Routledge, 1998, pp. 25–73.
- Ylli, Xhelal. Das slawische Lehngut im Albanischen. 2 vols., vol. 1: Lehnwörter; vol. 2: Ortsnamen. Munich: Verlag Otto Sagner, 1997/2000.
- Ylli, Xhelal & Andrej N. Sobolev. Albanskii gegskii govor sela Muhurr. Munich: Biblion Verlag, 2003. ISBN 3-932331-36-2
- Zheji, Petro. "Roli mesianik i shqipes" (The messianic role of the Albanian language). Albania: UET Press, 2015. ISBN 978-9928-190-24-6.
- Zheji, Petro. "Libri i aforizmave" (Book of aphorisms). Albania: Media Print, 2012. ISBN 9789928080813.
References
- ^ a b c Albanian at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Arbëresh at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Arvanitika at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Gheg at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Tosk at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - ^ a b Euromosaic project (2006). "L'arvanite/albanais en Grèce" (in French). Brussels: European Commission. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 21 January 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Robert Elsie". The Albanian Language. 25 November 1972. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ Fatjona Mejdini (3 May 2013). "Albania Aims to Register its Huge Diaspora". Balkan Insight. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ "Linguistic diversity among foreign citizens in Italy". Statistics of Italy. 25 July 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ Edwin E. Jacques, The Albanians: An Ethnic History from Prehistoric Times to the Present, 1995
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2016. Retrieved 9 July 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Saunders 2011, p. 98. "In addition to the recent emigrants, there are older diasporic communities around the world. There are upwards of 5 million ethnic Albanians in the Turkish Republic; however, the vast majority of this population is assimilated and no longer possesses fluency in the language, though a vibrant Albanian community maintains its distinct identity in Istanbul to this day. Egypt also lays claim to some 18,000 Albanians, supposedly lingering remnants of Mohammad Ali's army."
- ^ Gjinari, Jorgji. Dialektologjia shqiptare
- ^ Concise Encyclopedia of Languages of the World By Keith Brown, Sarah Ogilvie Contributor Keith Brown, Sarah Ogilvie Edition: illustrated Published by Elsevier, 2008 ISBN 0-08-087774-5, ISBN 978-0-08-087774-7
- ^ a b Lloshi 2008, p. 12.
- ^ a b Elsie, Robert. (2017). Albanian Alphabets: Borrowed and Invented. London, UK: CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 9781544294094.
- ^ Fortson, Benjamin W (2004). Indo-European language and culture: an introduction. Blackwell Publishing. p. 390. ISBN 1-4051-0315-9. Retrieved 28 May 2010. Albanian forms its own separate branch of Indo-European; it is the last branch to appear in written records
- ^ Watkins, Calvert. "Proto-Indo-European: Comparison and Reconstruction", in The Indo-European Languages, Anna Giacalone Ramat and Paolo Ramat, eds. London: Routledge, 1998.
- ^ Google Books, Mallory, J. P. and Adams, D. Q.: The Oxford Introduction to Proto-Indo-European and the Proto-Indo-European World
- ^ JHholm.de, Holm, Hans J.: The Distribution of Data in Word Lists and its Impact on the Subgrouping of Languages. In: Christine Preisach, Hans Burkhardt, Lars Schmidt-Thieme, Reinhold Decker (eds.): Data Analysis, Machine Learning, and Applications. Proc. of the 31st Annual Conference of the German Classification Society (GfKl), University of Freiburg, 7–9 March 2007. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg-Berlin
- ^ HJholm.de A possible Homeland of the Indo-European Languages And their Migrations in the Light of the Separation Level Recovery (SLRD) Method – Hans J. Holm
- ^ a b c "FWF Austrian Science Fund – Press – (Old) Albanian – Living legacy of a dead language?". Fwf.ac.at. Retrieved 22 September 2010.
- ^ Nicholas Geoffrey Lemprière Hammond (1976). Migrations and invasions in Greece and adjacent areas. Noyes Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-8155-5047-1. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ Zeitschrift für Balkanologie. R. Trofenik. 1990. p. 102. Retrieved 23 January 2013.
- ^ Robert Elsie (2010). Historical Dictionary of Albania. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 216. ISBN 978-0-8108-6188-6. Retrieved 30 September 2013.
- ^ Torte, Rexhep (4 August 2009). "Përfundoi shënimi i 100-vjetorit të Kongresit të Dibrës". Albaniapress.
- ^ Fine, JA. The Early medieval Balkans. University of Michigan Press, 1991. p. 11. Google Books
- ^ In his latest book, Eric Hamp supports the thesis that the Illyrian language belongs to the Northwestern group, that the Albanian language is descended from Illyrian, and that Albanian is related to Messapic which is an earlier Illyrian dialect (Comparative Studies on Albanian, 2007).
- ^ Roger D. Woodard. The ancient languages of Europe.
The modern Albanian language, it has been conjectured, is descendent directly from ancient Illyrian ...
- ^ Curtis, Matthew Cowan. "Slavic-Albanian Language Contact, Convergence, and Coexistence". ProQuest LLC. p. 16. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
It is generally accepted that Albanians continue one of the ancient languages of the Balkans, although scholars disagree on which language they spoke and what area of the Balkans they occupied before the Slavs' migration to the Balkans.
- ^ Curtis, Matthew Cowan. "Slavic-Albanian Language Contact, Convergence, and Coexistence". ProQuest LLC. p. 18. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
So while linguists may debate about the ties between Albanian and older languages of the Balkans, and while most Albanians may take the genealogical connection to Illyrian as incontrovertible, the fact remains that there is simply insufficient evidence to connect Illyrian, Thracian, or Dacian with any language, including Albanian
- ^ Template:Cite article
- ^ Ann Taylor; Donald Ringe; Tandy Warnow (2000). "Character based reconstruction of a linguistic cladogram". In John Charles Smith; Delia Bentley (eds.). General issues and non-Germanic Languages. Historical Linguistics 1995. Selected papers from the 12th International Conference on Historical Linguistics, Manchester, August 1995. Vol. 1. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing. p. 400.
- ^ a b Huld, Martin E. (1986). "Accentual Stratification of Ancient Greek Loanwords in Albanian". Zeitschrift für vergleichende Sprachforschung. 99 (2): 245–253.
- ^ Curtis, Matthew Cowan. "Slavic-Albanian language contact, convergence, and coexistence". ProQuest LLC. p. 16.
The number of loanwords is not necessarily a compelling argument for geographical placement, as loanwords may be replaced in subsequent developments of the language (especially considering the copious borrowing that Albanian later did from Latin and Slavic before any lexicon of Albanian was ever compiled) ... regarding the homeland of the Albanians.
- ^ Douglas Q. Adams (January 1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5.
The loan words from Greek and Latin date back to before the Christian era and suggest that the ancestors of the Albanians must have occupied Albania by then to have absorbed such loans from their historical neighbors. As the Illyrians occupied the Albanian territory at this time, they are the most likely recipients of such loans.
- ^ Vladimir Orel (2000). A concise historical grammar of the Albanian language: reconstruction of Proto-Albanian. BRILL. p. 23. ISBN 978-90-04-11647-4.
Latin loanwords are of extreme importance for the history of Albanian phonology, especially its vocalism. The duration of the borrowing was so long that loanwords reflect several distinct chronological stages.
- ^ Curtis, Matthew Cowan. "Slavic-Albanian language contact, convergence, and coexistence". ProQuest LLC. p. 17.
One other point that some scholars make is the fact that Albanian and Romanian share many lexical items; this has led some to believe that Albanian originated east of its present geographical spread (Georgiev 1957; Hamp 1994).
- ^ a b Mallory & Adams 1997, p. 9.
- ^ Kopitar 1829, p. 254.
- ^ Meyer 1888, p. 805.
- ^ Meyer-Lübke 1914, p. 32.
- ^ Bardhyl Demiraj (2010). Wir sind die Deinen. Studien zur albanischen Sprache, Literatur und Kulturgeschichte, dem Gedenken an Martin Camaj (1925–1992) gewidmet. Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3-447-06221-3.
- ^ Çabej 1962, pp. 13–51.
- ^ Mihaescu 1966, pp. 1, 30.
- ^ Mihaescu 1966, pp. 1, 21.
- ^ Mihaescu 1966, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Rosetti 1986, pp. 195–197.
- ^ Madgearu, Alexandru; Gordon, Martin. The Wars of the Balkan Peninsula: Their Medieval Origins. pp. 146–147.
- ^ "Mythifying the Albanians: A Historiographical Discussion on Vasa Efendi's "Albania and the Albanians"". balkanologie.revues.org.
- ^ Curtis, Matthew Cowan. "Slavic-Albanian Language Contact, Convergence, and Coexistence". ProQuest LLC. p. 17.
... for example, argues that from some indeterminate time a pre-Albanian (in Hamp's terms, Albanoid) population inhabited areas stretching from Poland to the current area
- ^ a b Hamp 1963.
- ^ Fine 1991, p. 10.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991, pp. 52–53.
- ^ Brown & Ogilvie 2008, p. 23.
- ^ Fortson 2004, p. 392.
- ^ Demiraj 1999.
- ^ Stefan Schumacher, "The development of the PIE middle in Albanian", in Bjarne Simmelkjaer et al. (eds.), "Etymology and the European Lexicon", Wiesbaden 2016.
- ^ Joachim Matzinger, "Albanian".171. contribution in: Peter O. Müller et al. (eds.), "An International Handbook of the Languages of Europe", Volume 5, Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston, 2016, p. 3124
- ^ Pantić, Miroslav (1990). Književnost na tlu Crne Gore i Boke Kotorske od XVI do XVIII veka. Srpska književna zadruga. p. 98.
- ^ J. P. Mallory; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European culture. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5. ISBN 1-884964-98-2, ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5
- ^ a b c d e f Agim Morina, "Udhërrëfyes i shkurtë i historisë së standardizimit të shqipes," DodonaPress (2015-02-21), also in Plisi.org (2015-02-24).
- ^ a b c Lloshi 2008, p. 10.
- ^ Kostallari, Androkli (1973). Drejtshkrimi i gjuhës shqipe. "Instituti i Gjuhësisë dhe i Letërsisë" ( in "Akademia e Shkencave e RPS të Shqipërisë", today "Akademia e Shkencave e Republikës së Shqipërisë").
- ^ Tomasz Kamusella. 2016. The idea of a Kosovan languagein Yugoslavia’s language politics (pp 217-237). International Journal of the Sociology of Language. Vol 242.
- ^ "Drejtshkrimi Prishtinë 1964 - Wikisource". wikisource.org. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Kostallari, Androkli (1976). Fjalori drejtshkrimor i gjuhës shqipe. "Instituti i Gjuhësisë dhe i Letërsisë" (in "Akademia e Shkencave e RPS të Shqipërisë", today "Akademia e Shkencave e Republikës së Shqipërisë").
- ^ Fjalori i Gjuhës së Sotme Shqipe. Tirana: Academy of Sciences of Albania. 1980. Retrieved 7 July 2010.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ a b Lloshi 2008, p. 9.
- ^ a b Morina, Agim (16 March 2016). "Sugjerime e vërejtje rreth ndryshimeve në drejtshkrim". Plisi.org. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Vrapi, Julia (27 April 2013). "Emil Lafe: Këshilli Ndërakademik për Gjuhën Shqipe ecën pa busull, ende pa një platformë shkencore të miratuar njëzëri". Sot.com.al. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Morina, Agim (10 October 2017). "Libri i Mary Motesit për Kosovën: Shqip me paskajore". Plisi.org.
- ^ Bërlajolli, Gazmend (13 August 2014). "Ekonomizimi i pjesores – mundësi për shqipen e përbashkët". Plisi.org. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Bërlajolli, Gazmend (17 July 2016). "Standardi dhe gegnishtja". Plisi.org. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Mjeku, Getoar (24 April 2016). "Po ndryshon shqipja standarde". Plisi.org. Retrieved 26 May 2018.
- ^ Kolgjini, Julie M. (2004). Palatalization in albanian : an acoustic investigation of stops and affricates. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Texas at Arlington. ISBN 0496859366.
- ^ Orel, Vladimir (2000). A concise historical grammar of the Albanian language: reconstruction of Proto-Albanian. BRILL. p. 3. ISBN 978-90-04-11647-4. Retrieved 15 December 2010
- ^ de Vaan, Michiel. "PIE *e in Albanian" (PDF). p. 72. Retrieved 16 December 2010.
- ^ Elsie, Robert; (London, Centre for Albanian Studies; England) (2005). Albanian literature: a short history. I.B.Tauris. p. 16. ISBN 978-1-84511-031-4. Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ a b Granser, Thedor; Moosmüller, Sylvia. "The schwa in Albanian" (PDF). Institute of Acoustics of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. Retrieved 15 December 2010.
- ^ Maxwell, Daniel Newhall. (1979). A Crosslinguistic Correlation between Word Order and Casemarking institution. Bloomington: Indiana University Pub.
- ^ Aida Kurani; Anisa Trifoni. "Syntactic Similarities and Differences between Albanian and English". Eujournal.org. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ Prifti 1982, p. 3.
- ^ Iorga & 1s971, p. 102.
- ^ Anamali 2002, p. 311.
- ^ Lloshi 2008, p. 97.
- ^ "Meshari". National Library of Albania. Retrieved 14 May 2010.
- ^ Todericiu 1967.
- ^ Elsie 1986, p. 158–162.
- ^ Marmullaku 1975, p. 17.
- ^ a b Matasovic, Ranko (2018). A Grammatical Sketch of Albanian for students of Indo-European. Page 6.
- ^ Millar, Robert McColl; Trask, Larry (2015). Trask's Historical Linguistics. Routledge. p. 292. ISBN 9781317541776.
Albanian seems to have lost more than 90 per cent of its original vocabulary in favour of loans from Latin, Greek, Hungarian, Slavonic, Italian and Turkish.
- ^ Orel, Vladimir Ė (2000). A Concise Historical Grammar of the Albanian Language: Reconstruction of Proto-Albanian. BRILL. ISBN 9004116478.
- ^ Matasovic, Ranko (2018). Page 35.
- ^ Orel, Vladimir (2000). A Concise Historical Grammar of the Albanian Language. Brill, Leiden. Page 191.
- ^ "Excel File_Lexical-Distance-Matrix". Alternative Transport. 19 November 2016.
- ^ "How much does language change when it travels?". Alternative Transport. 4 May 2015.
- ^ a b c "Cultural Treasure of Bosnia and Herzegovina edition-Prehistoric and Ancient Period- Book 2- Illyrian Bosnia and Herzegovina-an Overview of a Cultural Legacy/ Ancient Illyrians of Bosnia and Herzegovina | Ardian Adžanela Adzanela Axhanela". Academia.edu. 1 January 1970. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
- ^ Suart E. Mann (1977). An Albanian Historical Grammar. Buske. ISBN 978-3-87118-262-4.
- ^ Sborník prací Filozofické fakulty brněnské univerzity : Řada klasická. 3 June 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2017.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Ushaku, Ruzhdi, Hulumtime etnoliguistike, chapter: The continuation of Illyrian Bind in Albanian Mythology and Language, Fakulteti filologjise, Prishtine, 2000, p. 46-48
- ^ a b Mayani, Zĕchariă (1962). The Etruscans begin to speak. Souvenir Press. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Illyrian Glossary". bizland.com. Archived from the original on 17 June 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Stipčević, Aleksandar (1977). The Illyrians: history and culture. Noyes Press. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ^ Linguistic Society of America (1964). Language, Volumes 1–3. Linguistic Society of America. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ^ a b c Orel, Vladimir; Albanian Etymological Dictionary, Brill, 1998 ISBN 90 04 11024 0
- ^ Diokletian und die Tetrarchie: Aspekte einer Zeitenwende. Millennium Studies. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ^ Homeric whispers: intimations of orthodoxy in the Iliad and Odyssey. p. 72. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Albanien: Schätze aus dem Land der Skipetaren. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Ancient Indo-European dialects: proceedings, Volume 1963. Millennium Studies. Retrieved 25 June 2011.
- ^ An Albanian historical grammar. 1977. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ Indo-european language and culture: an introduction Blackwell textbooks in linguistics Author Benjamin W. Fortson Edition 2, illustrated, reprint Publisher John Wiley and Sons, 2009 ISBN 1-4051-8896-0, ISBN 978-1-4051-8896-8 p.465
- ^ a b The Field of Linguistics, Volume 2 Volume 1 of World of linguistics Authors Bernd Kortmann, Johan Van Der Auwera Editors Bernd Kortmann, Johan Van Der Auwera Publisher Walter de Gruyter, 2010 ISBN 3-11-022025-3, ISBN 978-3-11-022025-4 p.412
- ^ Vladimir Orel (2000) postulates a Vulgar Latin intermediary for no good reason. Mallory & Adams (1997) erroneously give the word as native, from *melítiā, the protoform underlying Greek mélissa; however, this protoform gave Albanian mjalcë "bee", which is a natural derivative of Proto-Albanian *melita "honey" (mod. mjaltë).
- ^ a b c Ancient Indo-European dialects: proceedings, Volume 1963 Ancient Indo-European Dialects: Proceedings, University of California, Los Angeles. Center for Research in Languages and Linguistics Authors Henrik Birnbaum, Jaan Puhvel, University of California, Los Angeles. Center for Research in Languages and Linguistics Editors Henrik Birnbaum, Jaan Puhvel Publisher University of California Press, 1966 p.102
- ^ a b A concise historical grammar of the Albanian language: reconstruction of Proto-Albanian Author Vladimir Ė. Orel Publisher BRILL, 2000 ISBN 90-04-11647-8, ISBN 978-90-04-11647-4 p.23
- ^ A concise historical grammar of the Albanian language: reconstruction of Proto-Albanian Author Vladimir Ė. Orel Publisher BRILL, 2000 ISBN 90-04-11647-8, ISBN 978-90-04-11647-4 p.102
- ^ Guillaum Bonnet, Les mots latins de l'albanais (Paris: L'Harmattan, 1998), 324.
- ^ The word fat has both the meaning of "fate, luck" and "groom, husband". This may indicate two separate words that are homophones, one derived from Gothic and the other from Latin fātum; although, Orel (2000) sees them as the same word. Similarly, compare Albanian shortë "fate; spouse, wife" which mirrors the dichotomy in meaning of fat but is considered to stem from one single source—Latin sortem "fate".
External links
- Albanian Lessons (free online through the Linguistics Research Center at UT Austin)
- Albanian Translation
- Albanian Google Translate
- Albanian Dictionary
- Albanian Swadesh list of basic vocabulary words (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
- Albanian basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- Albanian Grammar, Victor A. Friedman
- Albanian Symbol Codes, Penn State website
- Doctor John Bassett Trumper discussing the classification of Albanian within Indo-European on YouTube
- The emblematic figure of the Albanian linguist, Pr. Eqrem ÇABEJ (1908–1980, by Prof. Remzi Përnaska on the cultural website Albania (fr), (sh), (en)
- Dictionaries
- Albanian Online Dictionary (40 000 lemmas)
- English – Albanian / Albanian – English
- Dictionary on Western Barbarisms and Albanian Responsible Words entry on the National Library of Albania (Hysenbegasi, Arion. Fjalor i barbarizmave perëndimore në gjuhën shqipe dhe fjalëve përgjegjëse shqipe. Ombra GVG, Tirana, 2011)
- Fjalor Shqip Online
- HathiTrust Digital Library
- Use dmy dates from April 2012
- Albanian language
- Indo-European languages
- Illyrian languages
- Languages of Albania
- Languages of Bulgaria
- Languages of Greece
- Languages of Italy
- Languages of Kosovo
- Languages of the Republic of Macedonia
- Languages of Romania
- Languages of Montenegro
- Languages of Serbia
- Languages of Sicily
- Languages of Turkey
- Subject–verb–object languages

