Ischioanal fossa
| Ischioanal fossa | |
|---|---|
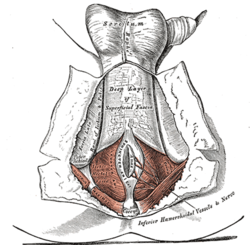 The perineum. The integument and superficial layer of superficial fascia reflected. (Ischiorectal fossa labeled at bottom left.) | |
 The posterior aspect of the rectum exposed by removing the lower part of the sacrum and the coccyx. (Ischiorectal fossa labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa ischioanalis |
| TA98 | A09.5.04.001 |
| TA2 | 2446 |
| FMA | 22059 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The Ischiorectal Fossa (or ischioanal fossa) is somewhat prismatic in shape, with its base directed to the surface of the perineum, and its apex at the line of meeting of the obturator and anal fasciæ.
Boundaries
It is bounded:
- medially by the Sphincter ani externus and the anal fascia;
- laterally, by the tuberosity of the ischium and the obturator fascia;
- anteriorly, by the fascia of Colles covering the Transversus perinæi superficialis, and by the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm;
- posteriorly, by the Glutæus maximus and the sacrotuberous ligament.
Crossings
Crossing the space transversely are the inferior hemorrhoidal vessels and nerves; at the back part are the perineal and perforating cutaneous branches of the pudendal plexus; while from the forepart the posterior scrotal (or labial) vessels and nerves emerge.
The internal pudendal vessels and pudendal nerve lie in Alcock's canal on the lateral wall. The fossa is filled with fatty tissue across which numerous fibrous bands extend from side to side.
External links
- Anatomy image: apmalefrontal4-8 at the College of Medicine at SUNY Upstate Medical University
- Anatomy photo:41:04-0103 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: The Ischioanal Fossa"
- Anatomy image:9246 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Diagram at emory.edu
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 425 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 425 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
