2019 Pacific typhoon season
| 2019 Pacific typhoon season | |
|---|---|
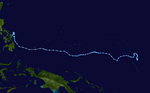
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | December 31, 2018 |
| Last system dissipated | Season ongoing |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Wutip |
| • Maximum winds | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 920 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 6 |
| Total storms | 2 |
| Typhoons | 1 |
| Super typhoons | 1 (unofficial) |
| Total fatalities | 19 total |
| Total damage | $158.433 million (2019 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2019 Pacific typhoon season is an ongoing event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season runs throughout 2019, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Pabuk, developed on January 1, becoming the earliest-forming tropical storm of the western Pacific Ocean on record, breaking the previous record held by Typhoon Alice in 1979. The season's first typhoon, Wutip, reached typhoon status on February 20. Wutip further intensified into a super typhoon on February 23, becoming the strongest February typhoon on record,[1] and the strongest tropical cyclone recorded in February in the Northern Hemisphere.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean to the north of the equator between 100°E and 180th meridian. Within the northwestern Pacific Ocean, there are two separate agencies that assign names to tropical cyclones which can often result in a cyclone having two names. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) will name a tropical cyclone should it be judged to have 10-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph) anywhere in the basin, while the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in their area of responsibility located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N–25°N regardless of whether or not a tropical cyclone has already been given a name by the JMA. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) are given a number with a "W" suffix.
Seasonal forecasts
| TSR forecasts Date |
Tropical storms |
Total Typhoons |
Intense TCs |
ACE | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (1965–2017) | 26 | 16 | 9 | 294 | [2] |
| Other forecasts Date |
Forecast Center |
Period | Systems | Ref | |
| February 7, 2019 | PAGASA | January–March | 1–2 tropical cyclones | [3] | |
| February 7, 2019 | PAGASA | April–June | 2–4 tropical cyclones | [3] | |
| 2018 season | Forecast Center |
Tropical cyclones |
Tropical storms |
Typhoons | Ref |
| Actual activity: | JMA | 6 | 2 | 1 | |
| Actual activity: | JTWC | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Actual activity: | PAGASA | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
During the year several national meteorological services and scientific agencies forecast how many tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons will form during a season and/or how many tropical cyclones will affect a particular country. These agencies included the Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) Consortium of University College London, PAGASA and Taiwan's Central Weather Bureau. The first forecast of the year was released by PAGASA on February 7, within its seasonal climate outlook for the period January–June.[3] The outlook noted that one to two tropical cyclones were expected between January and March, while two to four were expected to develop or enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility between April and June. Moreover, PAGASA predicts an 80% chance of a weak El Niño presence during February-March-April period.[3]
Season summary

The season started with Tropical Storm Pabuk active to the east of Thailand, which had formed on the last day of 2018, becoming the earliest-forming tropical storm of the Western Pacific Ocean on record, breaking the previous record held by Typhoon Alice in 1979. The storm tracked westward for three days before crossing over to the North Indian Ocean. A weak tropical depression formed near the Philippines and was named Amang by PAGASA, but quickly degenerated into a remnant low. Typhoon Wutip (Betty) developed on February 18 and became the season's first super typhoon. A month later, a Tropical Depression 03W formed, and was named "Chedeng" by PAGASA.
Systems
Tropical Storm Pabuk
| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 31, 2018 – January 4, 2019 (Exited basin) |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical disturbance formed over the southern portion of the South China Sea on December 28, 2018,[4] and it absorbed the remnants of Tropical Depression 35W (Usman) on December 30.[5] Under high vertical wind shear, the low-pressure area remained disorganized until December 31 when it was upgraded to a tropical depression by both the JMA and the JTWC.[6] As it was designated 36W by the JTWC, it was unofficially the last system of the 2018 typhoon season.[7] At around 06:00 UTC on January 1, 2019, the system was upgraded to the first tropical storm of the 2019 typhoon season and named Pabuk by the JMA, surpassing Typhoon Alice in 1979 to become the earliest-forming tropical storm of the northwest Pacific Ocean on record.[8] At that time, Pabuk was about 650 km (405 miles) southeast of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam and drifted westward slowly with a partially exposed low-level circulation center.[9]
Under marginal conditions including warm sea surface temperatures, excellent poleward outflow but strong vertical wind shear, Pabuk struggled to intensify further for over two days until it accelerated west-northwestward and entered the Gulf of Thailand on January 3, where vertical wind shear was slightly weaker. It became the first tropical storm over the gulf since Muifa in 2004. Moreover, it tried to form an eye revealed by microwave imagery.[10] On January 4, the Thai Meteorological Department reported that Pabuk had made landfall over Pak Phanang, Nakhon Si Thammarat at 12:45 ICT (05:45 UTC), although other agencies indicated a landfall at peak intensity between 06:00 and 12:00 UTC.[11] Pabuk became the first tropical storm to make landfall over southern Thailand since Linda in 1997. Shortly after 12:00 UTC, the JMA issued the last full advisory for Pabuk as it exited the basin into the North Indian Ocean.[12][13]
One of the islands in the south of Thailand, Koh Samui, appeared to have been spared much of the brunt of the storm with no confirmed deaths. Beaches were closed, but even with the bad weather approaching, tourists on the popular island in the Gulf of Thailand continued to visit bars and restaurants catering to them.[14]
In Vietnam, Pabuk caused one death,[15] and the losses were estimated at ₫27.87 billion (US$1.2 million).[16] Eight people in Thailand were killed,[17] and the estimated losses in the country were estimated about US$150 million.[18] Pabuk also killed one person in Malaysia.[19]
Tropical Depression 01W (Amang)
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | January 4 – January 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
The JTWC upgraded a disturbance north of Bairiki to a tropical depression with the designation 01W late on January 4 and expected some intensification,[20] but it failed to develop and the JTWC downgraded it back to a disturbance on January 6.[21] The system continued drifting westwards for two weeks without development. On January 19, the JMA upgraded the low-pressure area to a tropical depression when it was already located about 200 km (120 mi) west of Palau.[22]Tropical Depression 01W (Amang) moved northwest and made landfall in the Samar-Bicol Area, dissipating on January 22.
The depression indirectly triggered landslides and flash floods in Davao Oriental and Agusan del Norte, killing 9 and leaving 1 missing.[23][24] Agricultural losses were at PH₱216.49 million (US$4.11 million).[25]
Typhoon Wutip (Betty)
| Violent typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | February 18 – March 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-min); 920 hPa (mbar) |
A low pressure area formed just south of the Marshall Islands on February 16. It then began to gradually organize while moving westward, just south of Federated States of Micronesia. The system was upgraded to a tropical depression by the JMA on February 18, with the JTWC following suit on the following day. On February 20, the tropical depression intensified into a tropical storm and received the name Wutip from the JMA. On February 21, Wutip strengthened into a severe tropical storm, before intensifying further into a typhoon later that day.[citation needed] On February 23, Wutip intensified further, reaching its initial peak intensity as a Category 4-equivalent super typhoon with maximum 10-minute sustained winds of 185 km/h (115 mph), 1-minute sustained winds of 250 km/h (155 mph), and a minimum pressure of 925 hPa (mbar), while passing to the southwest of Guam, surpassing Typhoon Higos from 2015 as the strongest February typhoon on record.[1] Wutip underwent an eyewall replacement cycle shortly thereafter, weakening in intensity as it did so, while turning to the northwest. The typhoon finished its eyewall replacement cycle on February 24 and resumed strengthening; early on February 25, Wutip reached its peak intensity as a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon, with maximum 10-minute sustained winds of 195 km/h (120 mph), 1-minute sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph), and a minimum central pressure of 920 hPa (mbar). On February 26, Wutip entered a hostile environment with moderate wind shear and began to weaken, concurrently making another turn westward. On the next day, Wutip weakened into a tropical depression and lost most of its convection. On February 28, Wutip was given the name "Betty" by the PAGASA, as the storm entered the Philippine Sea. Soon afterward, Wutip entered a more hostile environment, with very high vertical wind shear (40-50 knots (45-60 mph; 75-95 km/h)) and lower sea surface temperatures, and the storm rapidly weakened until it dissipated on March 2.
Preliminary estimates of damage in Guam and Micronesia were at $3.3 million.[26][27]
Tropical Depression 03W (Chedeng)
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | March 14 – March 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | <55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1006 hPa (mbar) |
On March 14, Tropical Depression 03W formed over the Federated States of Micronesia. Over the next couple of days, the system drifted westward while gradually organizing. Early on March 17, the tropical depression entered the PAGASA's area of responsibility in the Philippine Sea, and consequently, the agency assigned the name Chedeng to the storm, shortly before it made landfall on Palau. At 5:30 PST on March 19, Chedeng made landfall on Malita, Davao Occidental.[28] Chedeng rapidly weakened after making landfall in the Philippines, degenerating into a remnant low on March 19. Chedeng's remnants continued weakening while moving westward, dissipating over the southern Sulu Sea on March 20.
Infrastructural damage in Davao Region amounted to Php1.3 million (US$25,000).[29]
Tropical Depression
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Duration | May 7 – May 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | <55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
On May 2, a low-pressure area formed over the Yap Islands. On May 7, the JMA upgraded the low-pressure area to a tropical depression.[citation needed]
Tropical Depression
| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Duration | May 7 – Present |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | <55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
On May 7, a tropical depression formed southwest of the Federated States of Micronesia.[citation needed]
Storm names
Within the Northwest Pacific Ocean, both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assign names to tropical cyclones that develop in the Western Pacific, which can result in a tropical cyclone having two names.[30] The Japan Meteorological Agency's RSMC Tokyo — Typhoon Center assigns international names to tropical cyclones on behalf of the World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee, should they be judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[31] PAGASA names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in their area of responsibility located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N and 25°N even if the cyclone has had an international name assigned to it.[30] The names of significant tropical cyclones are retired, by both PAGASA and the Typhoon Committee.[31] Should the list of names for the Philippine region be exhausted then names will be taken from an auxiliary list of which the first ten are published each season. Unused names are marked in gray.
International names
A tropical cyclone is named when it is judged to have 10-minute sustained windspeeds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[32] The JMA selected the names from a list of 140 names, that had been developed by the 14 members nations and territories of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee.[33] Retired names, if any, will be announced by the WMO in 2020, though replacement names will be announced in 2021. The next 28 names on the naming list are listed here along with their international numeric designation, if they are used.
|
|
|
|
Philippines
This season, PAGASA will use its own naming scheme for tropical cyclones that either develop within or move into their self-defined area of responsibility.[34] The names were taken from a list of names last used during 2015 and are scheduled to be used again during 2023.[34] All of the names are the same except Liwayway and Nimfa, replacing the names Lando and Nona after these were retired.[34]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Season effects
This table summarizes all the systems that developed within or moved into the North Pacific Ocean, to the west of the International Date Line during 2019. The tables also provide an overview of a systems intensity, duration, land areas affected and any deaths or damages associated with the system.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| Pabuk | December 31, 2018 – January 4, 2019 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | Natuna Islands, Vietnam, Malaysia, Thailand, Myanmar | $151 million | 10 | [15][17][18][19] |
| 01W (Amang) | January 4 – 22 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Caroline Islands, Philippines | $4.11 million | 9 | [23][24] |
| Wutip (Betty) | February 18 – March 2 | Typhoon | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) | Caroline Islands, Guam | $3.3 million | None | |
| 03W (Chedeng) | March 14 – 19 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | Caroline Islands, Philippines | $23,000 | None | [29] |
| TD | May 7 – 8 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Yap Islands | None | None | |
| TD | May 7 – Present | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Caroline Islands | None | None | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 6 systems | December 31, 2018 – Season ongoing |
195 km/h (120 mph) | 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) | $159 million | 19 | |||
See also
- Tropical cyclones in 2019
- 2019 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2019 Pacific hurricane season
- 2019 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2018–19, 2019–20
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2018–19, 2019–20
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2018–19, 2019–20
References
- ^ a b Kristina Pydynowski; Robert Richards (23 February 2019). "Wutip becomes strongest super typhoon in February as it lashes Guam with rain, wind". Accuweather. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- ^ Saunders, Mark; Lea, Adam (May 11, 2018). Extended Range Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2018 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Malano, Vicente B (February 7, 2019). January–June 2019 (PDF) (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Retrieved February 7, 2019.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "97W INVEST". United States Naval Research Laboratory. 28 December 2018. Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Tropical Depression 35W (Thirtyfive) Warning Nr 023". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 30 December 2018. Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "WTPQ20 RJTD 310600 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Japan Meteorological Agency. 31 December 2018. Archived from the original on 2019-01-01. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 36W (Thirtysix) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 31 December 2018. Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "WTPQ20 RJTD 010600 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Japan Meteorological Agency. 1 January 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-01-01. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 36W (Thirtysix) Warning Nr 005". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 1 January 2019. Archived from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "JTWC/36W/#16/01-04 00Z Prognostic Reasoning". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 4 January 2019. Archived from the original on 4 January 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- ^ "Weather Warning "Tropical Storm "PABUK"" No. 18 Time Issued January 4, 2019". Thai Meteorological Department. 4 January 2019. Archived from the original on 6 January 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- ^ "WTPQ20 RJTD 041200 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory". Japan Meteorological Agency. 4 January 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-01-06. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "WTPQ30 RJTD 041200 RSMC Tropical Cyclone Prognostic Reasoning Reasoning No.18 for TS 1901 Pabuk (1901)". Japan Meteorological Agency. 4 January 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-01-06. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Tropical Storm Pabuk hits Thailand's beaches with rain and surging seas (Report). telegraph. January 5, 2019. Retrieved January 9, 2019.
- ^ a b "Bão số 1 áp sát miền Tây: Sập nhà, 1 người chết" (in Vietnamese). VietNamNet. January 4, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ Trương, Huyền (January 6, 2019). "Hậu quả do bão số 1: Còn 2 người mất tích, thiệt hại ước tính 30 tỷ đồng" (in Vietnamese). Báo Kinh Tế Đô Thị. Retrieved January 6, 2019.
- ^ a b Panpetch, Sumeth (January 3, 2019). "Thailand braces for powerful storm at southern beach towns". Associated Press. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ a b "Thai preparedness limits Pabuk damage". The Thaiger. January 11, 2019. Retrieved January 11, 2019.
- ^ a b "罔顧「帕布」風暴來襲警報2男子冒險出海遇巨浪釀1死" (in Chinese). Oriental Daily News. January 4, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ "Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 001". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 4 January 2019. Archived from the original on 8 January 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning Nr 008". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 6 January 2019. Archived from the original on 8 January 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "WWJP25 RJTD 190600". Japan Meteorological Agency. 19 January 2019. Archived from the original on 19 January 2019. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- ^ a b Dalizon, Alfred P. (January 24, 2019). "Landslide buries 7 treasure hunters in Agusan del Norte". People's Journal. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- ^ a b NDRRMC Update: Sitrep No. 03 re Flashflood and Landslide Incidents in Davao Oriental Province (Region XI) (pdf) (Report). NDRRMC. January 26, 2019. Retrieved January 26, 2019.
- ^ Comilang, Randie J. (February 5, 2019). "Agriculture damages at P216M". SunStar Davao. Retrieved February 6, 2019.
- ^ "Preliminary cost estimate of Wutip: More than $1.3 million". Guam Pacific Daily News. March 1, 2019. Retrieved March 2, 2019.
- ^ Losinio, Louella (April 12, 2019). "Post-Wutip damages to FSM cost at least $2M". Pacific News Center. Retrieved April 22, 2019.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #11" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b NDRRMC Update: SitRep No. 05 re Preparedness Measures for TD CHEDENG (pdf) (Report). NDRRMC. March 21, 2019. Retrieved March 25, 2019.
- ^ a b Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary December 1999". Australian Severe Weather. Archived from the original on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b The Typhoon Committee (February 21, 2013). "Typhoon Committee Operational Manual 2013" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. pp. 37–38. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 28, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "REVIEW OF THE 2015 TYPHOON SEASON (submitted by the RSMC Tokyo – Typhoon Center)" (PDF). Typhooncommittee.org. Retrieved 13 December 2018.
- ^ Zhou, Xiao; Lei, Xiaotu (2012). "Summary of retired typhoons within the Western North Pacific Ocean". Tropical Cyclone Research and Review. 1 (1). The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific/World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee: 23–32. doi:10.6057/2012TCRR01.03. ISSN 2225-6032. Retrieved December 21, 2014.
- ^ a b c "Philippine Tropical Cyclone Names". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
External links
- China Meteorological Agency
- Digital Typhoon
- Hong Kong Observatory
- Japan Meteorological Agency
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center
- Korea Meteorological Administration
- Malaysian Meteorological Department
- National Weather Service Guam
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
- Taiwan Central Weather Bureau
- TCWC Jakarta
- Thai Meteorological Department
- Typhoon2000
- Vietnam's National Hydro-Meteorological Service