Atapuerca Mountains
Sierra de Atapuerca | |
 Atapuerca Mountains panorama | |
| Location | near Atapuerca, Ibeas de Juarros |
|---|---|
| Region | Burgos, Castile and León |
| Coordinates | 42°22′0″N 3°31′20″W / 42.36667°N 3.52222°W |
| History | |
| Periods | Paleolithic |
| Associated with | Homo antecessor, Homo heidelbergensis, Homo neanderthalensis |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | since 1964 |
| Archaeologists | Francisco Jordá Cerdá |
| Website | http://www.atapuerca.org/ |
| Official name | Archaeological Site of Atapuerca |
| Criteria | Cultural: (iii)(v) |
| Reference | 989 |
| Inscription | 2000 (24th Session) |
| Area | 284.119 ha (702.07 acres) |
The Atapuerca Mountains (Template:Lang-es) is a karstic hill formation near the village of Atapuerca, in the Province of Burgos (autonomous community of Castile and Leon), northern Spain. In a still ongoing excavation campaign, rich fossil deposits and stone tool assemblages were discovered which are attributed to the earliest known hominin residents in Western Europe.[1] This "exceptional reserve of data" has been deposited during extensive Lower Paleolithic presence, as the Atapuerca Mountains served as the preferred occupation site of Homo erectus, Homo antecessor (or Homo erectus antecessor), Homo heidelbergensis and Homo neanderthalensis[2] communities. The earliest specimen so far unearthed and reliably dated confirm an age between 1.2 Million and 630,000 years. Some finds are exhibited in the nearby Museum of Human Evolution, in Burgos. The site was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site, under the name, Archaeological Site of Atapuerca.[3][4]
Regional geography
Encompassing 284,119 ha (702,070 acres) or over 1000 square miles, the Atapuerca Mountains are a mid-altitude karstic range of small foothills around 1,080 m (3,540 ft) above sea level. They are located at the north-east corner of the Douro basin, to the south of the Cantabrian Mountains that run across northern Spain,[5] and stretch alongside the Bureba corridor, a mountain pass that connects the Ebro river valley with the Mediterranean Sea and the Duero basin. This conjunction[clarification needed] constitutes an ecotone, which is rich in species of both ecosystems. The mountain pass was part of a causeway built by the Romans, as well as part of the pilgrimage route of Saint James; it is now traversed by the N-I and AP-1 highways. The mountains are strategically located between two major drainage divides and near the mountain pass; this location is assumed to have been a factor in the area's successful and prolonged hominid habitation.[6][7]
Fauna
In 2008 scholars identified a new genus and species of red-toothed shrew from the Pleistocene layers of the Gran Dolina cave. Until this discovery, researchers had believed that the fossils found in this area were of the Beremendia fissidens type, but recent research has been published to support an Asiatic type called Dolinasorex glyphodon that might be endemic and is the earliest known type of soricid in the Iberian peninsula.[8]
Archaeological site

The archaeological significance of the area became increasingly apparent during the construction of a railway line as deep trenches were cut through the rocks and sediments of the Gran Dolina site, the Galería Elefante and at Sima de los Huesos. The subsequent excavation of 1964 under the direction of Francisco Jordá Cerdá succeeded with the discovery of anthropogenic artifacts and human fossils from a broad time range of early humans, hunter-gatherer groups to Bronze Age occupants and modern human settlers. Further campaigns expanded and interdisciplinary work has been undertaken by several teams, led by Emiliano Aguirre from 1978 to 1990 and later jointly by Eudald Carbonell, José María Bermúdez de Castro and Juan Luis Arsuaga.
The government of Castile and León has designated the site an Espacio cultural and under the title Zona Arqueológica sierra de Atapuerca the site is protected under Spanish law as it was induced into the Bien de Interés Cultural heritage register.[9]




Portalón (1910 to present)
The combined work of archaeologists Jesús Carballo (1910 to 1911), Geoffrey Clark (1971), José María Apellániz (1973 to 1983) and the current team of Juan Luis Arsuaga account for the documentation of the excavation sequence of ceramic objects from all relevant sediment layers since the Neolithic.
Galería de la Eduarda y el Kolora (1972)
The Galería de la Eduarda y el Kolora is a local cave that contains parietal rock paintings, only discovered in 1972 by a group of local speleologists.
Galería (1978 to present)
Among numerous faunal and floral fossils a jaw fragment was found during the 1970s and a skull fragment in 1995, which both belong to Homo heidelbergensis. They date to between 600,000 and 400,000 years BP.
Trinchera Dolina (1981 to present)
The Gran Dolina (also Trinchera Dolina, En: Dolina trench) site is a huge cavern, which is being excavated since September 1981. Its sediments were divided into eleven stratae (TD-1 to TD-11)
- TD-11: Mousterian tools found
- Level TD-10 presumed to have been a Homo heidelbergensis camp with tools and bison fossils.
- Level TD-8, accessible since 1994, it contained remarkable carnivore fossils.
- In level TD-7, a bovine leg in anatomical position was recovered in 1994
- TD-6 (Aurora stratum): In 1994 and 1995, over 80 bone fragments of five or six hominids found, between 850,000 and 780,000 years old, being at least 250,000 years older than any other hominid yet discovered in western Europe. About 25% of the bones have manipulation marks that suggest cannibalism. Classification of these remains is still being debated, suggestions range from Homo erectus to Homo heidelbergensis and Homo antecessor. Some researchers, who are familiar with the stratigraphic material of Gran Dolina argue that Homo antecessor may be the ancestor of Homo heidelbergensis, who in turn gave rise to Homo neandertalensis. The Homo erectus-like fossils were also found with retouched flake and core stone tools.
- Level TD-5 is assumed to have been a carnivore den.
- In TD-4 (dated to 780,000 BP), four lithic pieces were found during the 1991 excavation and several remnants of Ursus dolinensis, a sparsely described bear species.
- At the lowest levels (TD-1 and TD-2) no fossils
Sima de los Huesos (1983 to present)
Sima de los Huesos (Pit of Bones) accounts for the greatest number of valuable scientific discoveries and knowledge acquired with far-reaching implications. This site is located at the bottom of a 13 m (43 ft) deep shaft, or "chimney" accessible via the narrow corridors of the Cueva Mayor.[10]
Since 1997 the excavators have located more than 5,500 human skeletal remains deposited during the Middle Pleistocene period, at least 350,000 years old, which represent 28 individuals of Homo heidelbergensis.[11] Associated finds include Ursus deningeri fossils and a hand axe called Excalibur. Having received a surprisingly high degree of attention, a number of experts support the hypothesis that this particular Acheulean tool made of red quartzite seems to have served as a ritual offering, most likely for a funeral. The idea sparked a renewal of the disputed evolutionary progress and the stages of human cognitive, intellectual and conceptual development.[12] Ninety percent of the known Homo heidelbergensis fossil record have been obtained at the site. The fossil bone pit includes:
- The complete cranium, Skull 5, nicknamed Miguelón, the fragmented cranial remains of Skull 4, nicknamed Agamenón and Skull 6, nicknamed Rui (a reference to the medieval military leader El Cid).
- A complete pelvis (Pelvis 1), humorously nicknamed Elvis
- Mandibles, teeth, a lot of postcranial bones (femora, hand and foot bones, vertebrae, ribs, etc.)
- Remains of a child with craniosynostosis were found and dated to 530,000 BP. The find was considered to provide evidence for food sharing in early human populations.[13]
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from a 400,000 year old femur has been sequenced, the oldest hominin mtDNA recovered as of 2013. The mtDNA was found to be closer to the mtDNA of Denisova hominins than to the mtDNA of Neanderthals.[14]
- In 2016, nuclear DNA analysis results determined the Sima hominins to be Neanderthals and not Denisova hominins, and the divergence between Neanderthals and Denisovans predates 430,000 years.[15][16]
- In 2019, analysis of Neandertal teeth found at Sima de los Huesos indicates that modern humans and Neandertals separated from a common ancestor more than 800,000 years ago.[17]
Some excavators have stated that the concentration of bones in the pit allows the suggestion of a traditional burial culture among the cave's inhabitants. A competing theory cites the lack of small bones in the assemblage and suggests that the fossils were washed into the pit by non-human agents.
Sima del Elefante (1996 to present)
According to José María Bermúdez de Castro, co-director of research at Atapuerca, the Sima del Elefante findings support "anatomical evidence of the hominids that fabricated tools more than one million years ago", which may have been the earliest among Western European hominids. The first discovery in June 2007 was a tooth[18] followed by a fragment of a jawbone and a proximal phalanx in 2008.[19]
Cueva del Mirador (1999 to present)
This site provides information on earliest local farmers and herders of the late Neolithic and Bronze Age.
Orchids Valley (2000 to 2001) and Hundidero (2004 to 2005)
Stone tools of the Upper Paleolithic have been extracted from this locality.
Recorded history
Piedrahita ("standing stone") in the Atapuerca valley is according to records site of the Battle of Atapuerca, which took place in 1054 between the forces of Ferdinand I of Castile and his brother García V of Navarre.
Economic and demographic development
Apart from the typical dryland farming of the region, the municipality has grown significantly in economic, demographic and social level with the impact generated by the presence of the archaeological site and its associated services. 15% of the active population owns a job related to tourism. This "tertiarization" of their economy has reversed depopulation by growing and rejuvenating it (with the average age at 42 years).[20]
Gallery
-
Model of a female Homo antecessor of Atapuerca mountains practicing cannibalism (Ibeas Museum, Burgos, Spain)
-
Lithic core in flint, section TD-11 of "Galería", Atapuerca
-
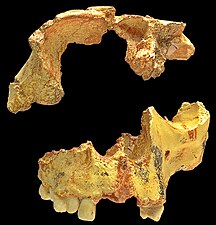
Homo antecessor, incomplete skull found in "Gran Dolina", Atapuerca
-
Carnivore skull
-
The railroad trench in which the first discoveries were made
See also
References
- ^ "Homo heidelbergensis: Evolutionary Tree information". Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ https://www.nature.com/news/oldest-ancient-human-dna-details-dawn-of-neanderthals-1.19557
- ^ "Archaeological Site of Atapuerca - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". Whc.unesco.org. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ "Landforms And Geomorphological Processes In The Duero Basin. Pleistocene Geoarcheology Of Ambrona And Atapuerca Sites" (PDF). Geomorfologia.es. Retrieved January 27, 2017.
- ^ Arsuaga, Juan (2009). The Neanderthal's Necklace: In Search of the First Thinkers. Basic Books. ISBN 9780786740734.
- ^ ". Geographic setting of the Sierra de Atapuerca and map of the... - Figure 1 of 14". researchgate.net. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ "No. 2516: Atapuerca". Uh.edu. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ ROFES, J. and CUENCA‐BESCÓS, G. (2009), A new genus of red‐toothed shrew (Mammalia, Soricidae) from the Early Pleistocene of Gran Dolina (Atapuerca, Burgos, Spain), and a phylogenetic approach to the Eurasiatic Soricinae. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 155: 904-925. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2008.00470.x
- ^ "MEMORIA del Espacio Cultural "Sierra de Atapuerca"" (PDF). Jcyl.es. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ "Prehistoric skull with puncture wounds could be world's first murder mystery". Msn.com. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ Greenspan, Stanley (2006-02-07). How Symbols, Language, and Intelligence Evolved from Early Primates to Modern Human. ISBN 978-0-306-81449-5.
- ^ "Excalibur, the rock that may mark a new dawn for man". The Guardian. January 9, 2003. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ "Craniosynostosis in the Middle Pleistocene human Cranium 14 from the Sima de los Huesos, Atapuerca, Spain". Pnas.org. Retrieved January 26, 2017.
- ^ Callaway, Ewen. "Hominin DNA baffles experts". Nature.com. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ magazine, Ewen Callaway,Nature. "Oldest Ancient-Human DNA Details Dawn of Neandertals". Scientific American. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Meyer, Matthias; Arsuaga, Juan-Luis; de Filippo, Cesare; Nagel, Sarah; Aximu-Petri, Ayinuer; Nickel, Birgit; Martínez, Ignacio; Gracia, Ana; de Castro, José María Bermúdez (2016-03-14). "Nuclear DNA sequences from the Middle Pleistocene Sima de los Huesos hominins". Nature. 531 (7595): 504–507. doi:10.1038/nature17405. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 26976447.
- ^ Gómez-Robles, Aida (2019-05-15). "Dental evolutionary rates and its implications for the Neanderthal–modern human divergence". Science Advances. 5. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw1268.
- ^ "'First west Europe tooth' found". BBC News. 2007-06-30.
- ^ "'Fossil find is oldest European yet'". Nature News. 2008-03-26.
- ^ "Creation of economic and demographic development [Social Impact]. ATAPUERCA project". SIOR. Social Impact Open Repository.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help)