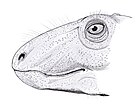
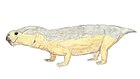
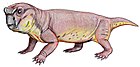
Dicynodontia
| Dicynodontia Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Skull of the dicynodont Endothiodon angusticeps in the American Museum of Natural History | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | †Anomodontia |
| Clade: | †Chainosauria |
| Clade: | †Dicynodontia Owen, 1859 |
| Clades & genera | |
|
see "Taxonomy" | |
Dicynodontia is a taxon of anomodont therapsids with beginnings in the mid-Permian, which were dominant in the Late Permian and continued throughout the Triassic, with a few possibly surviving into the Early Cretaceous. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with two tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. They are also the most successful and diverse of the non-mammalian therapsids, with over 70 genera known, varying from rat- to elephant-sized.
Characteristics


The dicynodont skull is highly specialised, light but strong, with the synapsid temporal openings at the rear of the skull greatly enlarged to accommodate larger jaw muscles. The front of the skull and the lower jaw are generally narrow and, in all but a number of primitive forms, toothless. Instead, the front of the mouth is equipped with a horny beak, as in turtles and ceratopsian dinosaurs. Food was processed by the retraction of the lower jaw when the mouth closed, producing a powerful shearing action,[3] which would have enabled dicynodonts to cope with tough plant material. Many genera also have a pair of tusks, which it is thought may have been an example of sexual dimorphism.[4]
The body is short, strong and barrel-shaped, with strong limbs. In large genera (such as Dinodontosaurus) the hindlimbs were held erect, but the forelimbs bent at the elbow. Both the pectoral girdle and the ilium are large and strong. The tail is short.
Endothermy and hair
Dicynodonts have long been suspected of being warm-blooded animals. Their bones are highly vascularised and possess Haversian canals, and their bodily proportions are conducive to heat preservation.[5] In young specimens, the bones are so highly vascularised that they exhibit higher channel densities than most other therapsids.[6] Yet, studies on Late Triassic dicynodont coprolites paradoxically showcase digestive patterns more typical of animals with slow metabolisms.[7]
More recently, the discovery of hair remnants in Permian coprolites possibly vindicates the status of dicynodonts as endothermic animals. As these coprolites come from carnivorous species and digested dicynodont bones are abundant, it has been suggested that at least some of these hair remnants come from dicynodont prey.[8] A new chemical study seemed to suggest that cynodonts and dicynodonts both developed warm blood independently before the Permian extinction using chemical analysis.[9]
Feet
Pentasauropus dicynodont tracks suggest that dicynodonts had fleshy pads on their feet.[10]
History
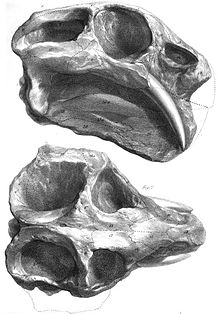
Dicynodonts have been known since the mid-1800s. The South African geologist Andrew Geddes Bain gave the first description of dicynodonts in 1845. At the time, Bain was a supervisor for the construction of military roads under the Corps of Royal Engineers and had found many reptilian fossils during his surveys of South Africa. Bain described these fossils in an 1845 letter published in Transactions of the Geological Society of London, calling them "bidentals" for their two prominent tusks.[11] In that same year, the English paleontologist Richard Owen named two species of dicynodonts from South Africa: Dicynodon lacerticeps and Dicynodon bainii. Since Bain was preoccupied with the Corps of Royal Engineers, he wanted Owen to describe his fossils more extensively. Owen did not publish a description until 1876 in his Descriptive and Illustrated Catalogue of the Fossil Reptilia of South Africa in the Collection of the British Museum.[12] By this time, many more dicynodonts had been described. In 1859, another important species called Ptychognathus declivis was named from South Africa. A year later, in 1860, Owen named the group Dicynodontia.[13] In his Descriptive and Illustrated Catalogue, Owen honored Bain by erecting Bidentalia as a replacement name for his Dicynodontia.[12] The name Bidentalia quickly fell out of use in the following years, replaced by popularity of Owen's Dicynodontia.[14]
Evolutionary history

Dicynodonts first appear during Middle Permian, and underwent a rapid evolutionary radiation, becoming the most successful and abundant land vertebrates of the Late Permian. During this time, they included a large variety of ecotypes, including large, medium-sized, and small herbivores and short-limbed mole-like burrowers.

Only four lineages are known to have survived the end of Permian extinction; the first three represented with a single genus each: Myosaurus, Kombuisia, and Lystrosaurus, the latter being the most common and widespread herbivores of the Induan (earliest Triassic). None of these survived long into the Triassic. The fourth group was the Kannemeyeriiformes, the only dicynodonts who diversified during the Triassic.[15] These stocky, pig- to ox-sized animals were the most abundant herbivores worldwide from the Olenekian to the Ladinian age. By the Carnian they had been supplanted by traversodont cynodonts and rhynchosaur reptiles. During the Norian (middle of the Late Triassic), perhaps due to increasing aridity, they drastically declined, and the role of large herbivores was taken over by sauropodomorph dinosaurs.
Fossils of an Asian elephant-sized dicynodont Lisowicia bojani discovered in Poland indicate that dicynodonts survived at least until the late Norian or earliest Rhaetian (latest Triassic); this animal was also the largest known dicynodont species.[16][17] Six fragments of fossil bone interpreted as remains of a skull discovered in Australia (Queensland) might indicate that dicynodonts survived into the Cretaceous in southern Gondwana.[2] However, Agnolin et al. (2010) considered the affinities of the specimen from Australia to be uncertain, and noted its similarity to the skull bones of some baurusuchian crocodyliforms, such as Baurusuchus pachecoi.[18]

With the decline and extinction of the kannemeyerids, there were to be no more dominant large synapsid herbivores until the middle Paleocene epoch (60 Ma) when mammals, descendants of cynodonts, began to diversify after the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs.
Systematics
Taxonomy
Dicynodontia was originally named by the English paleontologist Richard Owen. It was erected as a family of the order Anomodontia and included the genera Dicynodon and Ptychognathus. Other groups of Anomodontia included Gnathodontia, which included Rhynchosaurus (now known to be an archosauromorph) and Cryptodontia, which included Oudenodon. Cryptodonts were distinguished from dicynodonts from their absence of tusks. Although it lacks tusks, Oudenodon is now classified as a dicynodont, and the name Cryptodontia is no longer used. Thomas Henry Huxley revised Owen's Dicynodontia as an order that included Dicynodon and Oudenodon.[19] Dicynodontia was later ranked as a suborder or infraorder with the larger group Anomodontia, which is classified as an order. The ranking of Dicynodontia has varied in recent studies, with Ivakhnenko (2008) considering it a suborder, Ivanchnenko (2008) considering it an infraorder, and Kurkin (2010) considering it an order.[20]
Many higher taxa, including infraorders and families, have been erected as a means of classifying the large number of dicynodont species. Cluver and King (1983) recognised several main groups within Dicynodontia, including Diictodontia, Endothiodontia, Eodicynodontia, Kingoriamorpha, Pristerodontia, and Venyukoviamorpha.[21] Many families have been proposed, including Cistecephalidae, Diictodontidae, Dicynodontae, Emydopidae, Endothiodontidae, Kannemeyeriidae, Kingoriidae, Lystrosauridae, Myosauridae, Oudenodontidae, Pristerodontidae, and Robertiidae. However, with the rise of phylogenetics, most of these taxa are no longer considered valid. Kammerer and Angielczyk (2009) suggested that the problematic taxonomy and nomenclature of Dicynodontia and other groups results from the large number of conflicting studies and the tendency for invalid names to be mistakenly established.[14]





- Infraorder Dicynodontia
- Genus Angonisaurus
- Genus Colobodectes
- Superfamily Eodicynodontoidea
- Family Eodicynodontidae
- Superfamily Kingorioidea
- Family Kingoriidae
- Clade Diictodontia
- Superfamily Emydopoidea
- Family Cistecephalidae
- Family Emydopidae
- Genus Myosauroides
- Genus Myosaurus
- Genus Palemydops
- Superfamily Robertoidea
- Family Diictodontidae
- Family Robertiidae
- Genus Robertia
- Superfamily Emydopoidea
- Clade Pristerodontia
- Genus Dinanomodon
- Genus Odontocyclops
- Genus Propelanomodon
- Family Aulacocephalodontidae
- Family Dicynodontidae
- Genus Dicynodon
- Family Lystrosauridae
- Genus Kwazulusaurus
- Genus Lystrosaurus
- Family Oudenodontidae
- Genus Cteniosaurus
- Genus Oudenodon
- Genus Tropidostoma
- Genus Rhachiocephalus
- Family Pristerodontidae
- Superfamily Kannemeyeriiformes
- Family Kannemeyeriidae
- Genus Dinodontosaurus
- Genus Dolichuranus
- Genus Ischigualastia
- Genus Kannemeyeria
- Genus Rabidosaurus
- Genus Sinokannemeyeria
- Family Shansiodontidae
- Family Stahleckeriidae
- Family Kannemeyeriidae
Unknown placement:
- Genus Counillonia
- Genus Moghreberia
- Genus Wadiasaurus
Phylogeny
Below is a cladogram modified from Angielczyk and Rubidge (2010) showing the phylogenetic relationships of Dicynodontia:[22]
| Dicynodontia | |
See also
References
- ^ Racki, Grzegorz; Lucas, Spencer G. (2018). "Timing of dicynodont extinction in light of an unusual Late Triassic Polish fauna and Cuvier's approach to extinction". Historical Biology: 1–11. doi:10.1080/08912963.2018.1499734.
- ^ a b Thulborn, T.; Turner, S. (2003). "The last dicynodont: an Australian Cretaceous relict". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 270 (1518): 985–993. doi:10.1098/rspb.2002.2296. JSTOR 3558635. PMC 1691326. PMID 12803915.
- ^ Crompton, A. W; Hotton, N. (1967). "Functional morphology of the masticatory apparatus of two dicynodonts (Reptilia, Therapsida)". Postilla. 109: 1–51.
- ^ Colbert, E. H., (1969), Evolution of the Vertebrates, John Wiley & Sons Inc (2nd ed.), p. 137
- ^ Bakker, Robert T. (April 1975). "Dinosaur renaissance". Scientific American. 232 (4): 58–79. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0475-58.
- ^ Botha-Brink, Jennifer; Angielczyk, Kenneth D. (2010). "Do extraordinarily high growth rates in Permo-Triassic dicynodonts (Therapsida, Anomodontia) explain their success before and after the end-Permian extinction?". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 160 (2): 341–365. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2009.00601.x.
- ^ Bajdek, Piotr; Owocki, Krzysztof; Niedźwiedzki, Grzegorz (2014). "Putative dicynodont coprolites from the Upper Triassic of Poland". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 411: 1–17. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.06.013.
- ^ Bajdek, Piotr; Qvarnström, Martin; Owocki, Krzysztof; Sulej, Tomasz; Sennikov, Andrey G.; Golubev, Valeriy K.; Niedźwiedzki, Grzegorz (2016). "Microbiota and food residues including possible evidence of pre-mammalian hair in Upper Permian coprolites from Russia". Lethaia. 49 (4): 455–477. doi:10.1111/let.12156.
- ^ Rey, Kévin; Amiot, Romain; Fourel, François; Abdala, Fernando; Fluteau, Frédéric; Jalil, Nour-Eddine; Liu, Jun; Rubidge, Bruce S; Smith, Roger MH; Steyer, J Sébastien; Viglietti, Pia A; Wang, Xu; Lécuyer, Christophe (2017). "Oxygen isotopes suggest elevated thermometabolism within multiple Permo-Triassic therapsid clades". eLife. 6: e28589. doi:10.7554/eLife.28589.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Citton, Paolo; Díaz-Martínez, Ignacio; de Valais, Silvina; Cónsole-Gonella, Carlos (7 August 2018). "Triassic pentadactyl tracks from the Los Menucos Group (Río Negro province, Patagonia Argentina): possible constraints on the autopodial posture of Gondwanan trackmakers". PeerJ. 6: e5358. doi:10.7717/peerj.5358. PMC 6086091. PMID 30123702. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bain, A.G. (1845). "On the discovery of fossil remains of bidental and other reptiles in South Africa". Transactions of the Geological Society of London. 1: 53–59. doi:10.1144/GSL.JGS.1845.001.01.72.
- ^ a b Owen, R. (1876). Descriptive and Illustrated Catalogue of the Fossil Reptilia of South Africa in the Collection of the British Museum. London: British Museum. p. 88.
- ^ Owen, R. (1860). "On the orders of fossil and recent Reptilia, and their distribution in time". Report of the Twenty-Ninth Meeting of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. 1859: 153–166.
- ^ a b Kammerer, C.F.; Angielczyk, K.D. (2009). "A proposed higher taxonomy of anomodont therapsids" (PDF). Zootaxa. 2018: 1–24.
- ^ Kammerer, Christian F.; Fröbisch, Jörg; Angielczyk, Kenneth D. (31 May 2013). "On the validity and phylogenetic position of Eubrachiosaurus browni, a kannemeyeriiform dicynodont (Anomodontia) from Triassic North America". PLoS ONE. 8 (5): e64203. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064203. PMC 3669350. PMID 23741307.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Tomasz Sulej; Grzegorz Niedźwiedzki (2019). "An elephant-sized Late Triassic synapsid with erect limbs". Science. 363 (6422): 78–80. doi:10.1126/science.aal4853. PMID 30467179.
- ^ St. Fleur, Nicholas (4 January 2019). "An Elephant-Size Relative of Mammals That Grazed Alongside Dinosaurs". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- ^ Agnolin, F. L.; Ezcurra, M. D.; Pais, D. F.; Salisbury, S. W. (2010). "A reappraisal of the Cretaceous non-avian dinosaur faunas from Australia and New Zealand: Evidence for their Gondwanan affinities". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 8 (2): 257–300. doi:10.1080/14772011003594870.
- ^ Osborn, H.F. (1904). "Reclassification of the Reptilia". The American Naturalist. 38 (446): 93–115. doi:10.1086/278383.
- ^ Kurkin, A.A. (2010). "Late Permian dicynodonts of Eastern Europe". Paleontological Journal. 44 (6): 72–80. doi:10.1134/S0031030110060092.
- ^ Cluver, M.A.; King, G.M. (1983). "A reassessment of the relationships of Permian Dicynodontia (Reptilia, Therapsida) and a new classification of dicynodont". Annals of the South African Museum. 91: 195–273.
- ^ Kenneth D. Angielczyk; Bruce S. Rubidge (2010). "A new pylaecephalid dicynodont (Therapsida, Anomodontia) from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, Karoo Basin, Middle Permian of South Africa". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (5): 1396–1409. doi:10.1080/02724634.2010.501447.
Further reading
- Carroll, R. L. (1988), Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution, WH Freeman & Co.
- Cox, B., Savage, R.J.G., Gardiner, B., Harrison, C. and Palmer, D. (1988) The Marshall illustrated encyclopedia of dinosaurs & prehistoric animals, 2nd Edition, Marshall Publishing
- King, Gillian M., "Anomodontia" Part 17 C, Encyclopedia of Paleoherpetology, Gutsav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart and New York, 1988
- -- --, 1990, the Dicynodonts: A Study in Palaeobiology, Chapman and Hall, London and New York