Differential amplifier

A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input voltages but suppresses any voltage common to the two inputs.[1] It is an analog circuit with two inputs and and one output in which the output is ideally proportional to the difference between the two voltages
where is the gain of the amplifier.
Theory
The output of an ideal differential amplifier is given by:
Where and are the input voltages and is the differential gain.
In practice, however, the gain is not quite equal for the two inputs. This means, for instance, that if and are equal, the output will not be zero, as it would be in the ideal case. A more realistic expression for the output of a differential amplifier thus includes a second term.
is called the common-mode gain of the amplifier.
As differential amplifiers are often used to null out noise or bias-voltages that appear at both inputs, a low common-mode gain is usually desired.
The common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), usually defined as the ratio between differential-mode gain and common-mode gain, indicates the ability of the amplifier to accurately cancel voltages that are common to both inputs. The common-mode rejection ratio is defined as:
In a perfectly symmetric differential amplifier, is zero and the CMRR is infinite. Note that a differential amplifier is a more general form of amplifier than one with a single input; by grounding one input of a differential amplifier, a single-ended amplifier results.
Long-tailed pair
Historical background
Modern differential amplifiers are usually implemented with a basic two-transistor circuit called a “long-tailed” pair or differential pair. This circuit was originally implemented using a pair of vacuum tubes. The circuit works the same way for all three-terminal devices with current gain. The “long tail” resistor circuit bias points are largely determined by Ohm's Law and less so by active component characteristics.
The long-tailed pair was developed from earlier knowledge of push-pull circuit techniques and measurement bridges.[2] An early circuit which closely resembles a long-tailed pair was published by British neurologist Bryan Matthews in 1934,[3] and it seems likely that this was intended to be a true long-tailed pair but was published with a drawing error. The earliest definite long-tailed pair circuit appears in a patent submitted by Alan Blumlein in 1936.[4] By the end of the 1930s the topology was well established and had been described by various authors including Frank Offner (1937),[5] Otto Schmitt (1937)[6] and Jan Friedrich Toennies (1938) [7] and it was particularly used for detection and measurement of physiological impulses.[8]
The long-tailed pair was very successfully used in early British computing, most notably the Pilot ACE model and descendants,[nb 1] Maurice Wilkes’ EDSAC, and probably others designed by people who worked with Blumlein or his peers. The long-tailed pair has many favorable attributes if used as a switch: largely immune to tube (transistor) variations (of great importance when machines contained 1,000 tubes or more), high gain, gain stability, high input impedance, medium/low output impedance, good clipper (with a not-too-long tail), non-inverting (EDSAC contained no inverters!) and large output voltage swings. One disadvantage is that the output voltage swing (typically ±10–20 V) was imposed upon a high DC voltage (200 V or so), requiring care in signal coupling, usually some form of wide-band DC coupling. Many computers of this time tried to avoid this problem by using only AC-coupled pulse logic, which made them very large and overly complex (ENIAC: 18,000 tubes for a 20 digit calculator) or unreliable. DC-coupled circuitry became the norm after the first generation of vacuum tube computers.
Configurations
A differential (long-tailed,[nb 2] emitter-coupled) pair amplifier consists of two amplifying stages with common (emitter, source or cathode) degeneration.
Differential output

With two inputs and two outputs, this forms a differential amplifier stage (Figure 2). The two bases (or grids or gates) are inputs which are differentially amplified (subtracted and multiplied) by the transistor pair; they can be fed with a differential (balanced) input signal, or one input could be grounded to form a phase splitter circuit. An amplifier with differential output can drive a floating load or another stage with differential input.
Single-ended output
If the differential output is not desired, then only one output can be used (taken from just one of the collectors (or anodes or drains), disregarding the other output; this configuration is referred to as single-ended output. The gain is half that f the stage with differential output. To avoid sacrificing gain, a differential to single-ended converter can be utilized. This is often implemented as a current mirror (Figure 3, below).
Single-ended input
The differential pair can be used as an amplifier with a single-ended input if one of the inputs is grounded or fixed to a reference voltage (usually, the other collector is used as a single-ended output) This arrangement can be thought of as cascaded common-collector and common-base stages or as a buffered common-base stage.[nb 3]
The emitter-coupled amplifier is compensated for temperature drifts, VBE is cancelled, and the Miller effect and transistor saturation are avoided. That is why it is used to form emitter-coupled amplifiers (avoiding Miller effect), phase splitter circuits (obtaining two inverse voltages), ECL gates and switches (avoiding transistor saturation), etc.
Operation
To explain the circuit operation, four particular modes are isolated below although, in practice, some of them act simultaneously and their effects are superimposed.
Biasing
In contrast with classic amplifying stages that are biased from the side of the base (and so they are highly β-dependent), the differential pair is directly biased from the side of the emitters by sinking/injecting the total quiescent current. The series negative feedback (the emitter degeneration) makes the transistors act as voltage stabilizers; it forces them to adjust their VBE voltages (base currents) to pass the quiescent current through their collector-emitter junctions.[nb 4] So, due to the negative feedback, the quiescent current depends only slightly on the transistor's β.
The biasing base currents needed to evoke the quiescent collector currents usually come from the ground, pass through the input sources and enter the bases. So, the sources have to be galvanic (DC) to ensure paths for the biasing current and low resistive enough to not create significant voltage drops across them. Otherwise, additional DC elements should be connected between the bases and the ground (or the positive power supply).
Common mode
At common mode (the two input voltages change in the same directions), the two voltage (emitter) followers cooperate with each other working together on the common high-resistive emitter load (the "long tail"). They all together increase or decrease the voltage of the common emitter point (figuratively speaking, they together "pull up" or "pull down" it so that it moves). In addition, the dynamic load "helps" them by changing its instant ohmic resistance in the same direction as the input voltages (it increases when the voltage increases and vice versa.) thus keeping up constant total resistance between the two supply rails. There is a full (100%) negative feedback; the two input base voltages and the emitter voltage change simultaneously while the collector currents and the total current do not change. As a result, the output collector voltages do not change as well.
Differential mode
Normal. At differential mode (the two input voltages change in opposite directions), the two voltage (emitter) followers oppose each other - while one of them tries to increase the voltage of the common emitter point, the other tries to decrease it (figuratively speaking, one of them "pulls up" the common point while the other "pulls down" it so that it stays immovable) and v.v. So, the common point does not change its voltage; it behaves like a virtual ground with a magnitude determined by the common-mode input voltages. The high-resistive emitter element does not play any role it is shunted by the other low-resistive emitter follower. There is no negative feedback since the emitter voltage does not change at all when the input base voltages change. The common quiescent current vigorously steers between the two transistors and the output collector voltages vigorously change. The two transistors mutually ground their emitters; so, although they are common-collector stages, they actually act as common-emitter stages with maximum gain. Bias stability and independence from variations in device parameters can be improved by negative feedback introduced via cathode/emitter resistors with relatively small resistances.
Overdriven. If the input differential voltage changes significantly (more than about a hundred millivolts), the transistor driven by the lower input voltage turns off and its collector voltage reaches the positive supply rail. At high overdrive the base-emitter junction gets reversed. The other transistor (driven by the higher input voltage) drives all the current. If the resistor at the collector is relatively large, the transistor will saturate. With relatively small collector resistor and moderate overdrive, the emitter can still follow the input signal without saturation. This mode is used in differential switches and ECL gates.
Breakdown. If the input voltage continues increasing and exceeds the base-emitter breakdown voltage, the base-emitter junction of the transistor driven by the lower input voltage breaks down. If the input sources are low resistive, an unlimited current will flow directly through the "diode bridge" between the two input sources and will damage them.
At common mode, the emitter voltage follows the input voltage variations; there is a full negative feedback and the gain is minimum. At differential mode, the emitter voltage is fixed (equal to the instant common input voltage); there is no negative feedback and the gain is maximum.
Differential Amplifier Improvements
Emitter constant current source

The quiescent current has to be constant to ensure constant collector voltages at common mode. This requirement is not so important in the case of a differential output since the two collector voltages will vary simultaneously but their difference (the output voltage) will not vary. But in the case of a single-ended output, it is extremely important to keep a constant current since the output collector voltage will vary. Thus the higher the resistance of the current source , the lower (better) is the common-mode gain . The constant current needed can be produced by connecting an element (resistor) with very high resistance between the shared emitter node and the supply rail (negative for NPN and positive for PNP transistors) but this will require high supply voltage. That is why, in more sophisticated designs, an element with high differential (dynamic) resistance approximating a constant current source/sink is substituted for the “long tail” (Figure 3). It is usually implemented by a current mirror because of its high compliance voltage (small voltage drop across the output transistor).
Collector current mirror
The collector resistors can be replaced by a current mirror, whose output part acts as an active load (Fig. 3). Thus the differential collector current signal is converted to a single ended voltage signal without the intrinsic 50% losses and the gain is extremely increased. This is achieved by copying the input collector current from the left to the right side where the magnitudes of the two input signals add. For this purpose, the input of the current mirror is connected to the left output and the output of the current mirror is connected to the right output of the differential amplifier.

The current mirror copies the left collector current and passes it through the right transistor that produces the right collector current. At this right output of the differential amplifier, the two signal currents (pos. and neg. current changes) are subtracted. In this case (differential input signal), they are equal and opposite. Thus, the difference is twice the individual signal currents (ΔI - (-ΔI) = 2ΔI) and the differential to single ended conversion is completed without gain losses. Fig. 4 shows the transmission characteristic of this circuit.
Interfacing considerations
Floating input source
It is possible to connect a floating source between the two bases, but it is necessary to ensure paths for the biasing base currents. In the case of galvanic source, only one resistor has to be connected between one of the bases and the ground. The biasing current will enter directly this base and indirectly (through the input source) the other one. If the source is capacitive, two resistors have to be connected between the two bases and the ground to ensure different paths for the base currents.
Input/output impedance
The input impedance of the differential pair highly depends on the input mode. At common mode, the two parts behave as common-collector stages with high emitter loads; so, the input impedances are extremely high. At differential mode, they behave as common-emitter stages with grounded emitters; so, the input impedances are low.
The output impedance of the differential pair is high (especially for the improved differential pair with a current mirror as shown in Figure 3).
Input/output range
The common-mode input voltage can vary between the two supply rails but cannot closely reach them since some voltage drops (minimum 1 volt) have to remain across the output transistors of the two current mirrors.
Operational amplifier as differential amplifier
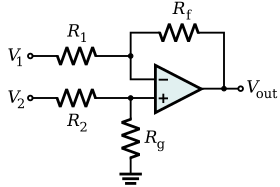
An operational amplifier, or op-amp, is a differential amplifier with very high differential-mode gain, very high input impedance, and low output impedance. An op-amp differential amplifier can be built with predictable and stable gain by applying negative feedback (Figure 5).[nb 5] Some kinds of differential amplifier usually include several simpler differential amplifiers. For example, a fully differential amplifier, an instrumentation amplifier, or an isolation amplifier are often built from a combination of several op-amps.
Applications
Differential amplifiers are found in many circuits that utilize series negative feedback (op-amp follower, non-inverting amplifier, etc.), where one input is used for the input signal, the other for the feedback signal (usually implemented by operational amplifiers). For comparison, the old-fashioned inverting single-ended op-amps from the early 1940s could realize only parallel negative feedback by connecting additional resistor networks (an op-amp inverting amplifier is the most popular example). A common application is for the control of motors or servos, as well as for signal amplification applications. In discrete electronics, a common arrangement for implementing a differential amplifier is the long-tailed pair, which is also usually found as the differential element in most op-amp integrated circuits. A long-tailed pair can be used as an analog multiplier with the differential voltage as one input and the biasing current as another.
A differential amplifier is used as the input stage emitter coupled logic gates and as switch. When used as a switch, the "left" base/grid is used as signal input and the "right" base/grid is grounded; output is taken from the right collector/plate. When the input is zero or negative, the output is close to zero (but can be not saturated); when the input is positive, the output is most-positive, dynamic operation being the same as the amplifier use described above.
Symmetrical feedback network eliminates common-mode gain and common-mode bias

In case the operational amplifier's (non-ideal) input bias current or differential input impedance are a significant effect, one can select a feedback network that improves the effect of common-mode input signal and bias. In Figure 6, current generators model the input bias current at each terminal; I+b and I−b represent the input bias current at terminals V+ and V−, respectively.
The Thévenin equivalent for the network driving the V+ terminal has a voltage V+' and impedance R+':
while for the network driving the V− terminal,
The output of the op amp is just the open-loop gain Aol times the differential input current i times the differential input impedance 2Rd, therefore
where R// is the average of R+// and R−//.
These equations undergo a great simplification if
resulting in the relation,
which implies that the closed-loop gain for the differential signal is V+in - V−in, but the common-mode gain is identically zero. It also implies that the common-mode input bias current has cancelled out, leaving only the input offset current IΔb = 'I+b - 'I−b still present, and with a coefficient of Ri. It is as if the input offset current is equivalent to an input offset voltage acting across an input resistance Ri, which is the source resistance of the feedback network into the input terminals. Finally, as long as the open-loop voltage gain Aol is much larger than unity, the closed-loop voltage gain is Rf / Ri, the value one would obtain through the rule-of-thumb analysis known as "virtual ground".[nb 6]
Footnotes
- ^ Details of the long-tailed pair circuitry used in early computing can be found in Alan Turing’s Automatic Computing Engine (Oxford University Press, 2005, ISBN 0-19-856593-3) in Part IV, ‘ELECTRONICS’
- ^ Long-tail is a figurative name of high resistance that represents the high emitter resistance at common mode with a common long tail with a proportional length (at differential mode this tail shortens up to zero). If additional emitter resistors with small resistances are included between the emitters and the common node (to introduce a small negative feedback at differential mode), they can be figuratively represented by short tails.
- ^ More generally, this arrangement can be considered as two interacting voltage followers with negative feedback: the output part of the differential pair acts as a voltage follower with constant input voltage (a voltage stabilizer) producing constant output voltage; the input part acts as a voltage follower with varying input voltage trying to change the steady output voltage of the stabilizer. The stabilizer reacts to this intervention by changing its output quantity (current, respectively voltage) that serves as a circuit output.
- ^ It is interesting fact that the negative feedback as though has reversed the transistor behavior - the collector current has become an input quantity while the base current serves as an output one.
- ^ In this arrangement it seems strange that a high-gain differential amplifier (op-amp) is used as a component of a low-gain differential amplifier, in the way that a high-gain inverting amplifier (op-amp) serves as a component in a low-gain inverting amplifier. This paradox of negative-feedback amplifiers impeded Harold Black obtaining his patent.
- ^ For the closed-loop common-mode gain to be zero only requires that the ratio of resistances Rf / Ri be matched in the inverting and non-inverting legs. For the input bias currents to cancel, the stricter relation given here must obtain.
See also
References
- ^ Laplante, Philip A. (2005). Comprehensive Dictionary of Electrical Engineering, 2nd Ed. CRC Press. p. 190. ISBN 978-1420037807.
- ^ Eglin, J. M. (1 May 1929). "A Direct-Current Amplifier for Measuring Small Currents". Journal of the Optical Society of America. 18 (5): 393–402. doi:10.1364/JOSA.18.000393.
- ^ Matthews, Bryan H. C. (1 December 1934). "PROCEEDINGS OF THE PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY". The Journal of Physiology. 81 (suppl): 28–29. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003151.
- ^ "US Patent 2185367" (PDF). Freepatensonline.com. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ Offner, Franklin (1937). "Push-Pull Resistance Coupled Amplifiers". Review of Scientific Instruments. 8 (1): 20–21. doi:10.1063/1.1752180.
- ^ Schmitt, Otto H. (1941). "Cathode Phase Inversion" (PDF). Review of Scientific Instruments. 12 (11): 548–551. doi:10.1063/1.1769796. Retrieved 15 February 2016.
- ^ "US Patent 2147940" (PDF). Google Inc. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ^ Geddes, L. A. Who Invented the Differential Amplifier?. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, May/June 1996, p.116-117.
External links
- BJT Differential Amplifier — Circuit and explanation
- A testbench for differential circuits
- Application Note: Analog Devices - AN-0990 : Terminating a Differential Amplifier in Single-Ended Input Applications
- A discrete OpAmp with complimentary differential amplifier (in German)


















![{\displaystyle V_{\text{in}}^{+}-V_{\text{in}}^{-}-R_{\text{i}}*I_{\text{b}}^{\Delta }=V_{\text{out}}\left[{\frac {R_{\text{i}}}{R_{\text{f}}}}+{\frac {1}{A_{\text{ol}}*{\frac {R_{\text{i}}}{R_{\text{i}}/\!\!/R_{\text{f}}/\!\!/R_{\text{d}}}}}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9437271f9ed0c9a605ffafb543f499b0ea472677)

