Space Launch System
It has been suggested that Proposed SLS and Orion missions be merged into this article. (Discuss) Proposed since July 2019. |
 Artist's rendering of SLS Block 1/Orion | |
| Function | Super heavy-lift launch vehicle |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | United States |
| Project cost | US$7 billion (2014–18, 2014 estimate),[1] to $35 billion (until 2025, 2011 est.)[2][3][better source needed] |
| Size | |
| Height | 111.25 m (365 ft 0 in), Block 2 Cargo |
| Diameter | 8.4 m (27 ft 7 in), Core Stage |
| Stages | 2 |
| Capacity | |
| Payload to LEO | |
| Mass | |
| Payload to Moon | |
| Mass | |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Under development |
| Launch sites | LC-39B, Kennedy Space Center |
| First flight | Artemis 1 June 2020 (planned)[7] |
| Type of passengers/cargo | Orion MPCV, Europa Clipper, LOP-Gateway Station components |
| Boosters (Block 1, 1B) | |
| No. boosters | 2 five-segment Solid Rocket Boosters |
| Powered by | off |
| Maximum thrust | 16,000 kN (3,600,000 lbf) |
| Total thrust | 32,000 kN (7,200,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 269 seconds (2.64 km/s) (vacuum)[citation needed] |
| Burn time | 126 seconds |
| Propellant | PBAN, APCP |
| First stage (Block 1, 1B, 2) – Core Stage | |
| Height | 64.6 m (211 ft 11 in) |
| Diameter | 8.4 m (27 ft 7 in) |
| Empty mass | 85,270 kg (187,990 lb) |
| Gross mass | 979,452 kg (2,159,322 lb) |
| Powered by | 4 RS-25D/E[8] |
| Maximum thrust | 7,440 kN (1,670,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 363 seconds (3.56 km/s) (sea level), 452 seconds (4.43 km/s) (vacuum) |
| Propellant | LH2 / LOX |
| Second stage (Block 1) – ICPS | |
| Height | 13.7 m (44 ft 11 in) |
| Diameter | 5 m (16 ft 5 in) |
| Empty mass | 3,490 kg (7,690 lb) |
| Gross mass | 30,710 kg (67,700 lb) |
| Powered by | 1 RL10B-2 |
| Maximum thrust | 110.1 kN (24,800 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 462 seconds (4.53 km/s) |
| Burn time | 1125 seconds |
| Propellant | LH2 / LOX |
| Second stage (Block 1B, Block 2) – Exploration Upper Stage | |
| Diameter | 8.4 m (27 ft 7 in) |
| Powered by | 4 RL10 |
| Maximum thrust | 440 kN (99,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | LH2 / LOX |
The Space Launch System (SLS) is a US super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle currently under development. It is the primary launch vehicle of NASA's deep space exploration plans,[9][10] including the planned crewed lunar flights of the Artemis program and a possible follow-on human mission to Mars.[11][12][13]
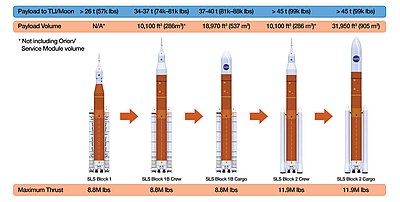
The initial SLS Block 1 is required by the US Congress to lift a payload of 95 metric tons to low Earth orbit (LEO), and will launch Artemis 1, Artemis 2, and Artemis 3 on a circumlunar trajectory. The later Block 1B is intended to debut the Exploration Upper Stage and launch the notional Artemis 4–8.[14] Block 2 is planned to replace the initial Shuttle-derived boosters with advanced boosters and would have a LEO capability of more than 130 metric tons, again as required by Congress.[15] Block 2 is intended to enable crewed launches to Mars.[13] The SLS will launch the Orion Crew and Service Module and use the ground operations and launch facilities at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida.
Vehicle description

The SLS is a Shuttle-Derived Launch Vehicle and will have the ability to tolerate a minimum of 13 tanking cycles due to launch scrubs and other launch delays before launch. The assembled rocket is to be able to remain at the launch pad for a minimum of 180 days and can remain in stacked configuration for at least 200 days.[16]
Core Stage
The Space Launch System's Core Stage will be 8.4 meters (28 ft) in diameter and mount a Main Propulsion System (MPS) incorporating four RS-25 engines.[8][17] The core stage will be structurally similar to the Space Shuttle external tank,[18][19] and initial flights will use modified RS-25D engines left over from the Space Shuttle program.[20] Later flights will switch to a cheaper version of the engine not intended for reuse.[21]
The core stage will be fabricated at the Michoud Assembly Facility[22] and is common across all currently planned evolutions of the SLS to avoid the need for substantial redesigns to meet various payload mandates.[23][24][17][25]
Boosters
Block 1 and 1B boosters
Blocks 1 and 1B of the SLS will use two five-segment Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs) based on the four-segment Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Boosters. Modifications to the five-segment boosters included the addition of a center booster segment, new avionics, and lighter insulation. The five-segment SRBs provide approximately 25% more total impulse than the Shuttle SRB and will not be recovered after use.[26][27]
Block 2 advanced boosters (late 2020s)
The advanced boosters for Block 2[28] were intended to be selected through the Advanced Booster Competition, which was to be held in 2015.[8][29]
Several companies proposed boosters for this competition:
- Aerojet, in partnership with Teledyne Brown, offered a booster powered by three new AJ1E6 LOX/RP-1 oxidizer-rich staged combustion engines, each producing 4,900 kN (1,100,000 lbf) thrust using a single turbopump to supply dual combustion chambers.[30] On 14 February 2013, Aerojet was awarded a $23.3 million, 30-month contract to build a 2,400 kN (550,000 lbf) main injector and thrust chamber.[31]
- Alliant Techsystems (ATK) proposed an advanced SRB nicknamed "Dark Knight", which would switch to a lighter composite case, use a more energetic propellant, and reduce the number of segments from five to four.[32]
- Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne and Dynetics proposed a liquid-fueled booster named Pyrios.[33]
In 2013, the manager of NASA's SLS advanced development office indicated that all three approaches were viable.[34]
However, the 2015 competition was planned in support of Block 1A. A later study found that the advanced booster would have resulted in unsuitably high acceleration,[35] and NASA cancelled Block 1A and the planned competition in 2014.[36][37] In February 2015, it was reported that SLS is expected to fly with the five-segment SRB until at least the late 2020s, and modifications to Launch Pad 39B, its flame trench, and SLS's Mobile Launcher Platform were being evaluated.[36]
Upper Stage

ICPS - Block 1
Block 1, scheduled to fly Artemis 1 in June 2020,[7] will use the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS), a modified Delta IV 5–meter Delta Cryogenic Second Stage (DCSS) powered by a single RL10B-2.[38] Block 1 will be capable of lifting 95 t to LEO in this configuration if the ICPS is considered part of the payload.[4] Artemis 1 will be launched into an initial 1,800 km by −93 km suborbital trajectory to ensure safe disposal of the core stage. ICPS will then perform an orbital insertion burn at apogee and a subsequent translunar injection burn to send Orion towards the moon.[39]
EUS - Block 1B and 2
The Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) was scheduled to fly initially on Artemis 2. Similar to the S-IVB, the EUS would have completed the SLS ascent phase and then re-ignited to send its payload to destinations beyond low-Earth orbit.[40] It was expected to be used by Block 1B and Block 2, share the core stage diameter of 8.4 meters, and be powered by four RL10 engines.[41]
The Artemis 2 flight may fly earlier than planned. In this case it will launch on the less-capable ICPS.[42]
Payload carrying capacity
| SLS variant | Payload mass to ... (metric tons) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| low Earth orbit (LEO) | trans-lunar injection (TLI) | heliocentric orbit (HCO) | |
| Block 1 | 95 t[4] | 26 t[4] | |
| Block 1B | 105 t[43] | 37 t[4] | |
| Block 2 | 130 t[5] | 45 t[4] | |
Development history
SLS is to replace the retired Space Shuttle as NASA's flagship vehicle. Following the cancellation of the Constellation program, the NASA Authorization Act of 2010 envisioned a single launch vehicle usable for both crew and cargo. SLS is to have the world's highest ever total thrust at launch,[44][45] but not the world's highest ever payload mass.[46][47][48] However, with modern technology the SLS is arguably the most capable heavy lift vehicle built.[18][49]
Program history
During the joint Senate-NASA presentation in September 2011, it was stated that the SLS program had a projected development cost of $18 billion through 2017, with $10 billion for the SLS rocket, $6 billion for the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and $2 billion for upgrades to the launch pad and other facilities at Kennedy Space Center.[50][51] These costs and schedule were considered optimistic in an independent 2011 cost assessment report by Booz Allen Hamilton for NASA.[52]
An unofficial 2011 NASA document estimated the cost of the program through 2025 to total at least $41bn for four 95 t launches (1 uncrewed, 3 crewed),[2][3] with the 130 t version ready no earlier than 2030.[53]
The Human Exploration Framework Team (HEFT) estimated unit costs for Block 0 at $1.6bn and Block 1 at $1.86bn in 2010.[54] However, since these estimates were made the Block 0 SLS vehicle was dropped in late 2011, and the design was not completed.[55] The Space Review estimated the cost per launch at $5 billion, depending on the rate of launches.[56][57] NASA announced in 2013 that the European Space Agency will build the Orion Service Module.[58]
In September 2012, an SLS deputy project manager stated that $500 million per launch is a reasonable target cost for SLS.[59] By comparison, a Saturn V launch cost roughly $1.23 billion in 2016 dollars.[60][61]
In August 2014, as the SLS program passed its Key Decision Point C review and entered full development, costs from February 2014 until its planned launch in September 2018 were estimated at $7.021 billion.[62] Ground systems modifications and construction would require an additional $1.8 billion over the same time period.[63]
In October 2018, NASA's inspector general reported that the Boeing core stage contract had made up 40 percent of the $11.9 billion spent on SLS as of August 2018. By 2021, core stages were expected to have cost a total of US$8.9 billion, which is twice the initial planned amount.[64]
In December 2018, NASA estimated that yearly budgets for SLS will range from US$2.1 to US$2.3B between 2019 to 2023.[65]
In March 2019, the Trump Administration released its Fiscal Year 2020 Budget Request for NASA. This budget did not include any money for the Block 1B and Block 2 variants of SLS. It is uncertain whether these future variants of SLS will be developed.[66] Several launches previously planned for the SLS Block 1B are now expected to fly on commercial launcher vehicles such as Falcon Heavy, New Glenn, Omega, and Vulcan.[67] However, the request for a budget increase of 1.6 billion dollars towards SLS, Orion, and crewed landers along with the launch manifest seem to indicate support of the development of Block 1B, debuting Artemis 3. The Block 1B will be used mainly for co manifested crew transfers and logistic rather than constructing the Gateway. An uncrewed Block 1B is planned to launch the Lunar Surface Asset in 2028, the first lunar outpost of the Artemis program. Block 2 development will most likely start in the late 2020s, after NASA is regularly visiting the lunar surface and shifts focus towards Mars.[68]
Funding history
For fiscal years 2011 through 2018, the SLS program had expended funding totaling $13,999 million in nominal dollars. This is equivalent to $15,109 million adjusting to 2018 dollars using the NASA New Start Inflation Indices.[69]
| Fiscal Year | Funding ($millions) | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | $1,536.1 | Actual[70] (Formal SLS Program reporting excludes the Fiscal 2011 budget.)[71] |
| 2012 | $1,497.5 | Actual[72] |
| 2013 | $1,414.9 | Actual[73] |
| 2014 | $1,600.0 | Actual[74] |
| 2015 | $1,678.6 | Actual[75] |
| 2016 | $1,971.9 | Enacted[75] |
| 2017 | $2,150.0 | Appropriated[76] |
| 2018 | $2,150.0 | Appropriated[77] |
| 2011–2018 | Total: $13,999M |
Excluded from the prior SLS costs are:
- Costs of the predecessor Ares V / Cargo Launch Vehicle (funded from 2008 to 2010)[78]
- Costs for the Ares 1 / Crew Launch Vehicle (funded from 2006 to 2010, a total of $4.8 billion[78][79] in development that included the 5-segment Solid Rocket Boosters that will be used on the SLS)
- Costs to assemble, integrate, prepare and launch the SLS and its payloads such as Orion (funded under the NASA Ground Operations Project,[80] currently about $400M[74] per year)
- Costs of payloads for the SLS (such as Orion)
Included in the prior SLS costs are:
- Costs of the interim Upper Stage for the SLS, the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS) for SLS, which includes a $412M contract[81]
- Costs of the final Upper Stage for the SLS, the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) (funded at $85M in 2016,[82] $300M in 2017[83] and $300M in 2018[84])
There are no current NASA estimates for the average costs per flight of SLS, nor for the SLS program recurring yearly costs once operational. In 2016, the projected annual cost for Orion, SLS, and ground systems was $2 billion or less.[85] NASA associate administrator William H. Gerstenmaier has said that per flight cost estimates will not be provided by NASA.[86]
Constellation
From 2009 to 2011, three full-duration static fire tests of five-segment SRBs were conducted under the Constellation Program, including tests at low and high core temperatures to validate performance at extreme temperatures.[87][88][89]
Early SLS
During the early development of the SLS a number of configurations were considered, including a Block 0 variant with three main engines,[17] a Block 1A variant with upgraded the vehicle's boosters instead of improved second stage,[17] and a Block 2 with five main engines and the Earth Departure Stage, with up to three J-2X engines.[25] In February 2015, it was determined that these concepts would exceed the congressionally mandated Block 1 and Block 1B baseline payloads.[36]
On 14 September 2011, NASA announced the new launch system,[90] which is intended to take the agency's astronauts farther into space than ever before and provide the cornerstone for future US human space exploration efforts in combination with the Orion spacecraft[91][92][93]
On 31 July 2013, the SLS passed the Preliminary Design Review (PDR). The review included not only the rocket and boosters but also ground support and logistical arrangements.[94] On August 7, 2014 the SLS Block 1 passed a milestone known as Key Decision Point C and entered full-scale development, with an estimated launch date of November 2018.[95][62]
In 2013, NASA and Boeing analyzed the performance of several EUS engine options. The analysis was based on a second stage usable propellant load of 105 metric tons, and compared stages with four RL10 engines, two RL60 engines, or one J-2X engine.[96]
In 2014, NASA also considered using the European Vinci instead of the RL10. The Vinci offers the same specific impulse but with 64% greater thrust, which would allow for the same performance at lower cost.[97][98]
Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems has completed full-duration static fire tests of the five-segment SRBs. Qualification Motor 1 (QM-1) was tested on March 10, 2015.[99] Qualification Motor 2 (QM-2) was successfully tested on June 28, 2016.
Current SLS
Currently three SLS versions are planned: Block 1, Block 1B, and Block 2. Each will use the same core stage with four main engines, but Block 1B will feature the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and Block 2 will combine the EUS with upgraded boosters.[43][15][100]
In mid-November 2014, construction of the first core stage hardware began using a new welding system in the South Vertical Assembly Building at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility.[101] Between 2015 and 2017 NASA test fired RS-25 engines in preparation for use on SLS.[21]
As of late 2015, the SLS program was stated to have a 70% confidence level for the first crewed Orion flight by 2023.[102][103][104]
Confidence article builds for the core stage began on January 5, 2016 and were expected to be completed in late January of that year. Once completed the test articles will be sent to ensure structural integrity at Marshall Spaceflight Center. A structural test article of the ICPS was delivered in 2015, with the stage for Artemis 1 was slated for assembly in late January 2016.[105][needs update]
The first flight of SLS has slipped multiple times, first to 2019,[106] then to June 2020.[7]
Criticism
The main criticisms of SLS are program cost, lack of commercial involvement, and the non-competitive nature of a vehicle that is legislated to use Space Transportation System components.
In 2009, the Augustine commission proposed a commercial 75-metric-ton (165,000 lb) launcher with lower operating costs, and noted that a 40–60 t (88,000–132,000 lb) launcher was the minimum required to support lunar exploration.[107]
In 2011–2012, the Space Access Society, Space Frontier Foundation and The Planetary Society called for cancellation of the project, arguing that SLS will consume the funds for other projects from the NASA budget.[108][109][110] U.S. Representative Dana Rohrabacher and others proposed that an orbital propellant depot should be developed and the Commercial Crew Development program accelerated instead.[108][111][112][113][114] A NASA study that was not publicly released[115][116] and another from the Georgia Institute of Technology that was show this option to be possibly cheaper.[117][118] In 2012, the United Launch Alliance also suggested using existing rockets with on-orbit assembly and propellant depots as needed. The lack of competition in the SLS design was highlighted.[119][120][121][122][123]
In 2011, Mars Society/Mars Direct founder Robert Zubrin suggested that a heavy lift vehicle could be developed for $5 billion on fixed-price requests for proposal.[124]
In 2010, SpaceX's CEO Elon Musk claimed that his company could build a launch vehicle in the 140–150 t payload range for $2.5 billion, or $300 million (in 2010 dollars) per launch, not including a potential upper-stage upgrade.[125][126] In the early 2010s, SpaceX went on to start development of BFR, a planned fully reusable super-heavy launch system. Reusability is claimed to allow the lowest cost super-heavy launcher ever made.[127] If the price per launch and payload capabilities for the BFR are anywhere near Musk's claimed capabilities, the rocket will be substantially cheaper than the SLS.[128]
In 2011, Rep. Tom McClintock and other groups called on the Government Accountability Office (GAO) to investigate possible violations of the Competition in Contracting Act (CICA), arguing that Congressional mandates forcing NASA to use Space Shuttle components for SLS are de facto non-competitive, single source requirements assuring contracts to existing shuttle suppliers.[109][129][130] Opponents of the heavy launch vehicle have critically used the name "Senate launch system".[38] The Competitive Space Task Force, in September 2011, said that the new government launcher directly violates NASA's charter, the Space Act, and the 1998 Commercial Space Act requirements for NASA to pursue the "fullest possible engagement of commercial providers" and to "seek and encourage, to the maximum extent possible, the fullest commercial use of space".[108]
In 2013, Chris Kraft, the NASA mission control leader from the Apollo era, expressed his criticism of the system as well.[131] Lori Garver, former NASA Deputy Administrator, has called for cancelling the program.[132] Phil Plait has voiced his criticism of SLS in light of ongoing budget tradeoffs between Commercial Crew Development and SLS budget, also referring to earlier critique by Garver.[133]
In 2015, The Planetary Society claimed that a Mars mission could be conducted within existing budgets.[134]}}
In 2019, the [Government Accounting Office] found that NASA had been awarding Boeing over $200 million dollars for excellent service despite cost overruns and delays. [135] [136]
Proposed SLS flights
The list below includes NASA planned missions as of May 2019.
| Name | SLS Block |
Crew size |
Launch date |
Status | Duration | Destination | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artemis 1 | 1 | — | TBD[137] | Planned | 25.5 days[138] | Distant retrograde lunar orbit | Uncrewed lunar orbital test flight of Orion.[139] |
| Artemis 2 | 1 | 4 | June 2022[140] | Planned | 9 days[141] | Lunar flyby | Crewed free-return cislunar test flight of Orion.[142] |
| Europa Clipper | 1 Cargo | — | 2023[143] | Planned | 6 years | Jovian orbit | Flagship robotic orbiter to explore Europa[144][145] |
| Artemis 3 | 1B[146] | 4 | 2024[143] | Planned | 30 days[143] | L2 Southern Near Rectilinear Halo Orbit (NRHO) | Crewed flight to the Lunar Orbital Platform-Gateway and landing at the South Pole–Aitken basin.[83] |
| Artemis 4 | 1B | 4 | 2025[13] | Proposed | 26–42 days[140] | L2 Southern NRHO | Crewed flight to the Gateway to deliver the U.S. Habitation module; lunar landing to test ISRU and Nuclear surface power.[84] |
| Artemis 5 | 1B | 4 | 2026[13] | Proposed | 26–42 days[140] | L2 Southern NRHO | Crewed flight to the Gateway to deliver a logistics module; first lunar landing with reusable ascent and transfer stages and further ISRU tests.[84] |
| Artemis 6 | 1B | 4 | 2027 | Proposed | 26–42 days[140] | L2 Southern NRHO | Crewed flight to the Gateway to deliver a logistics module and Canadarm-3; second landing with reusable lander and deployment of Lunar Surface Assets.[84] |
| Artemis 7 | 1B Cargo | — | 2028 | Proposed | L2 Southern NRHO | Uncrewed lunar landing of the Lunar Surface Asset.[84] | |
| Artemis 8 | 1B | 4 | 2028 | Proposed | 191–221 days | L2 Southern NRHO | Crewed flight to the Gateway to deliver a logistics module; extended surface mission at the Lunar Surface Asset.[84] |
Gallery
-
RS-25D engine testing at Stennis Space Center
-
SLS core stage segment at Michoud Assembly Facility
-
SLS Mobile Launcher
-
SRB segment
-
SLS vehicle adapter
-
SLS Core Stage being assembled
-
Orion launch abort motor
-
SLS liquid oxygen tank
-
SLS ICPS
-
ICPS on the move
See also
- Artemis program, a NASA proposal to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024
- Human mission to Mars
- Austere Human Missions to Mars
- Comparison of orbital launchers families
- Comparison of orbital launch systems
- DIRECT
- Shuttle-Derived Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle, a 2009 concept launch vehicle
- Ares V, a 2000s cargo vehicle design for the Constellation Program
- National Launch System, 1990s
- Magnum (rocket), a 1990s concept
- Saturn (rocket family), 1960s
References
- ^ "NASA commits to $7 billion mega rocket, 2018 debut". CBS News. August 27, 2014. Retrieved March 13, 2015.
- ^ a b Andy Paszior (September 7, 2011). "White House Experiences Sticker Shock Over NASA's Plans". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 22, 2015.
- ^ a b "ESD Integration, Budget Availability Scenarios" (PDF). Space Policy Online. August 19, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f Harbaugh, Jennifer (July 9, 2018). "The Great Escape: SLS Provides Power for Missions to the Moon". NASA. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
- ^ a b Creech, Stephen (April 2014). "NASA's Space Launch System: A Capability for Deep Space Exploration" (PDF). NASA. p. 2. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Mohon, Lee (March 16, 2015). "Space Launch System (SLS) Overview". NASA. Retrieved July 6, 2019.
- ^ a b c Clark, Stephen (November 20, 2017). "NASA expects first Space Launch System flight to slip into 2020". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ a b c "space launch system" (PDF). NASAfacts. 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 13, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Siceloff, Steven (April 12, 2015). "SLS Carries Deep Space Potential". Nasa.gov. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ^ "World's Most Powerful Deep Space Rocket Set To Launch In 2018". Iflscience.com. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ^ Chiles, James R. "Bigger Than Saturn, Bound for Deep Space". Airspacemag.com. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ^ "Finally, some details about how NASA actually plans to get to Mars". Arstechnica.com. Retrieved January 2, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Gebhardt, Chris (April 6, 2017). "NASA finally sets goals, missions for SLS – eyes multi-step plan to Mars". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved August 21, 2017.
- ^ "Space Launch System". aerospaceguide.net.
- ^ a b "The NASA Authorization Act of 2010". Featured Legislation. Washington DC, United States: United States Senate. July 15, 2010. Retrieved May 26, 2011.
- ^ "SLS to be robust in the face of scrubs, launch delays and pad stays". NASASpaceFlight.com. April 4, 2012. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ a b c d Chris Bergin (October 4, 2011). "SLS trades lean towards opening with four RS-25s on the core stage". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ a b Stephen Clark (March 31, 2011). "NASA to set exploration architecture this summer". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved May 26, 2011.
- ^ Chris Bergin (September 14, 2011). "SLS finally announced by NASA – Forward path taking shape". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ Sloss, Philip. "NASA ready to power up the RS-25 engines for SLS". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved March 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Campbell, Lloyd (March 25, 2017). "NASA conducts 13th test of Space Launch System RS-25 engine". SpaceflightInsider.com. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ "NASA's Space Launch System Core Stage Passes Major Milestone, Ready to Start Construction". Space Travel. December 27, 2012.
- ^ Chris Bergin (April 25, 2011). "SLS planning focuses on dual phase approach opening with SD HLV". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (June 16, 2011). "Managers SLS announcement after SD HLV victory". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ a b Bergin, Chris (February 23, 2012). "Acronyms to Ascent – SLS managers create development milestone roadmap". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ Priskos, Alex. "Five-segment Solid Rocket Motor Development Status" (PDF). ntrs.nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved March 11, 2015.
- ^ "Space Launch System: How to launch NASA's new monster rocket". NASASpaceflight.com. February 20, 2012. Retrieved April 9, 2012.
- ^ Keith Cowing (September 14, 2011). "NASA's New Space Launch System Announced – Destination TBD". SpaceRef. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ Frank Morring (June 17, 2011). "NASA Will Compete Space Launch System Boosters". Aviation Week. Retrieved June 20, 2011.
- ^ "NASA's Space Launch System: Partnering For Tomorrow" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved March 12, 2013.
- ^ Rachel Kraft (February 14, 2013). "NASA Awards Final Space Launch System Advanced Booster Contract". NASA. Retrieved February 19, 2013.
- ^ "The Dark Knights – ATK's Advanced Boosters for SLS revealed". NASASpaceFlight.com. January 14, 2013.
- ^ Lee Hutchinson (April 15, 2013). "New F-1B rocket engine upgrades Apollo-era design with 1.8M lbs of thrust". Ars Technica. Retrieved April 15, 2013.
- ^ "SLS Block II drives hydrocarbon engine research". thespacereview.com. January 14, 2013.
- ^ "Wind Tunnel testing conducted on SLS configurations, including Block 1B". NASASpaceFlight.com.
- ^ a b c Bergin, Chris. "Advanced Boosters progress towards a solid future for SLS". NasaSpaceFlight.com. Retrieved February 25, 2015.
- ^ "Second SLS Mission Might Not Carry Crew". spacenews.com. May 21, 2014. Retrieved July 25, 2014.
- ^ a b Rosenberg, Zach. "Delta second stage chosen as SLS interim". Flight International, May 8, 2012.
- ^ "Space Launch System Data Sheet". SpaceLaunchReport.com. Retrieved July 25, 2014.
- ^ "SLS prepares for PDR – Evolution eyes Dual-Use Upper Stage". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ "NASA confirms EUS for SLS Block 1B design and EM-2 flight". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ^ NASA may fly crew into deep space sooner, but there’s a price. Eric Berger. Ars Technica. 12 April 2018. Quote: "Without the Exploration Upper Stage, NASA will not be able to fly, in a single flight, crew members and pieces of a deep space gateway it hopes to build near the Moon in the 2020s."
- ^ a b "Space Launch System" (PDF). NASA Facts. NASA. October 11, 2017. FS-2017-09-92-MSFC. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
- ^ Harbaugh, Jennifer (May 12, 2017). "NASA Continues Testing, Manufacturing World's Most Powerful Rocket". Nasa.gov.
- ^ Wall, Mike (August 16, 2016). "Yes, NASA's New Megarocket Will Be More Powerful Than the Saturn V". Space.com. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- ^ The Congress of the United States. Congressional Budget Office, October 2006, pp. X,1,4,9. "The Apollo Saturn V launch vehicle had a lift capability of 140 metric tons to low Earth orbit."
- ^ Wells, Jane (January 26, 2016). "Boeing builds the most powerful rocket ever made". cnbc.com.
- ^ Wood, Anthony (July 25, 2015). "Most powerful rocket ever edges closer to lift-off". New Atlas. Retrieved September 13, 2018.
- ^ Dwayne Day (November 25, 2013). "Burning thunder".
- ^ Marcia Smith (September 14, 2011). "New NASA Crew Transportation System to Cost $18 Billion Through 2017". Space Policy Online. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ Bill Nelson, Kay Bailey Hutchison, Charles F. Bolden (September 14, 2011). Future of NASA Space Program. Washington, D.C.: Cspan.org.
- ^ Booz Allen Hamilton (August 19, 2011). "Independent Cost Assessment of the Space Launch System, Multi-purpose Crew Vehicle and 21st Century Ground Systems Programs: Executive Summary of Final Report" (PDF). NASA.
- ^ Marcia Smith (September 9, 2011). "The NASA Numbers Behind That WSJ Article". Space Policy Online. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ "HEFT Phase I Closeout" (PDF). nasawatch.com. September 2010. p. 69.
- ^ Chris Bergin (October 4, 2011). "SLS trades lean towards opening with four RS-25s on the core stage". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved September 16, 2013.
- ^ Lee Roop (July 29, 2013). "NASA defends Space Launch System against charge it 'is draining the lifeblood' of space program". AL.com. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ^ John Strickland (July 15, 2013). "Revisiting SLS/Orion launch costs". The Space Review. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ^ NASA Content Administrator, ed. (April 12, 2015) [January 16, 2013]. "NASA Signs Agreement for a European-Provided Orion Service Module". NASA. Archived from the original on January 18, 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "NASA's huge new rocket may cost $500 million per launch". MSNBC. September 12, 2012.
- ^ "SP-4221 The Space Shuttle Decision- Chapter 6: ECONOMICS AND THE SHUTTLE". NASA. Retrieved January 15, 2011.
- ^ "Apollo Program Budget Appropriations". NASA.
- ^ a b Foust, Jeff (August 27, 2014). "SLS Debut Likely To Slip to 2018". SpaceNews.com. Retrieved March 12, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Jason. "NASA Budget Lists Timelines, Costs and Risks for First SLS Flight". The Planetary Society. Retrieved March 11, 2015.
- ^ "NASA'S MANAGEMENT OF THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM STAGES CONTRACT" (PDF). NASA OIG. NASA Office of Inspector General Office of Audits. October 10, 2018. Retrieved October 14, 2018.
- ^ "NASA FY 2019 Budget Estimates" (PDF). nasa.gov. p. BUD-2. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Smith, Rich (March 26, 2019). "Is NASA Preparing to Cancel Its Space Launch System? -". The Motley Fool. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- ^ "NASA FY 2019 Budget Overview" (PDF). Quote: "Supports launch of the Power and Propulsion Element on a commercial launch vehicle as the first component of the LOP – Gateway, (page 14)
- ^ "Space Launch Report". www.spacelaunchreport.com. Retrieved May 22, 2019.
- ^ "NASA New Start Inflation Indices". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "FY 2013 Presidents Budget Request Summary" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. BUD-4. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "NASA, Assessments of Major Projects" (PDF). General Accounting Office. March 2016. p. 63. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "FY 2014 Presidents Budget Request Summary" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. BUD-8. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "FY 2015 Presidents Budget Request Summary" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. BUD-5. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ a b "FY 2016 Presidents Budget Request Summary" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. BUD-5. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ a b "FY 2018 Budget Estimates" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. BUD-3. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "H.R.244 – Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2017". congress.gov. 2017. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2018". govinfo.gov. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b "Fiscal Year 2010 Budget Estimates" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. v. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "FY 2008 Budget Estimates" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. p. ESMD-14. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations Program Completes Preliminary Design Review". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "Definitive Contract NNM12AA82C". govtribe.com. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "Consolidated Appropriations Act 2016" (PDF). house.gov. p. 183. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b "NASA outlines plan for 2024 lunar landing". SpaceNews.com. May 1, 2019. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ a b c d e f Berger, Eric (May 20, 2019). "NASA's full Artemis plan revealed: 37 launches and a lunar outpost". Ars Technica. Retrieved May 20, 2019.
- ^ Berger, Eric (August 19, 2016). "How much will SLS and Orion cost to fly? Finally some answers". arstechnica.com. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ Berger, Eric (October 20, 2017). "NASA chooses not to tell Congress how much deep space missions cost". arstechnica.com. Retrieved December 16, 2018.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help) - ^ "NASA and ATK Successfully Test Ares First Stage Motor". NASA. September 10, 2009. Retrieved January 30, 2012.
- ^ "NASA and ATK Successfully Test Five-Segment Solid Rocket Motor". NASA. August 31, 2010. Retrieved January 30, 2012.
- ^ "NASA Successfully Tests Five-Segment Solid Rocket Motor". NASA. August 31, 2010. Retrieved September 8, 2011.
- ^ "NASA Announces Key Decision For Next Deep Space Transportation System". NASA. May 24, 2011. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ "NASA Announces Design For New Deep Space Exploration System". NASA. September 14, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
- ^ "Press Conference on the Future of NASA Space Program". C-Span. September 14, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
- ^ Kenneth Chang (September 14, 2011). "NASA Unveils New Rocket Design". New York Times. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
- ^ "NASA's Space Launch System Program PDR: Answers to the Acronym". NASA. August 1, 2013. Retrieved August 3, 2013.
- ^ "NASA Completes Key Review of World's Most Powerful Rocket in Support". NASA. Retrieved October 26, 2015.
- ^ Chris Gebhardt (November 13, 2013). "SLS upper stage proposals reveal increasing payload-to-destination options". NASASpaceFlight.com.
- ^ David Todd (June 3, 2013). "SLS design may ditch J-2X upper stage engine for four RL-10 engines". Seradata. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016.
- ^ David Todd (November 7, 2014). "Next Steps for SLS: Europe's Vinci is a contender for Exploration Upper-Stage Engine". Seradata. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (March 10, 2015). "QM-1 shakes Utah with two minutes of thunder". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved March 10, 2015.
- ^ Karl Tate (September 16, 2011). "Space Launch System: NASA's Giant Rocket Explained". Space.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ "SLS Engine Section Barrel Hot off the Vertical Weld Center at Michoud". NASA.
- ^ Foust, Jeff (September 16, 2015). "First Crewed Orion Mission May Slip to 2023". SpaceNews.com. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (September 16, 2015). "Orion spacecraft may not fly with astronauts until 2023". spaceflightnow.com. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ Clark, Smith (May 1, 2014). "Mikulski "Deeply Troubled" by NASA's Budget Request; SLS Won't Use 70 Percent JCL". spacepolicyonline.com. Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ^ "NASA facilities, teams ramp up SLS flight production for 2018 maiden flight". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved January 26, 2016.
- ^ Clark, Stephen (April 28, 2017). "NASA confirms first flight of Space Launch System will slip to 2019". Spaceflight Now. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Review of U.S. Human Space Flight Plans Committee; Augustine, Austin; Chyba, Kennel; Bejmuk, Crawley; Lyles, Chiao; Greason, Ride (October 2009). "Seeking A Human Spaceflight Program Worthy of A Great Nation" (PDF). NASA. Retrieved April 15, 2010.
- ^ a b c Henry Vanderbilt (September 15, 2011). "Impossibly High NASA Development Costs Are Heart of the Matter". moonandback.com. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
- ^ a b Ferris Valyn (September 15, 2011). "Monster Rocket Will Eat America's Space Program". Space Frontier Foundation. Archived from the original on October 6, 2011. Retrieved September 16, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Statement before the Committee on Science, Space, and Technology US House of Representatives Hearing: A Review of the NASA's Space Launch System" (PDF). The Planetary Society. July 12, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 29, 2012. Retrieved January 26, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rohrabacher, Dana (September 14, 2011). "Nothing New or Innovative, Including It's Astronomical Price Tag". Archived from the original on September 24, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Rohrabacher calls for "emergency" funding for CCDev". parabolicarc.com. August 24, 2011. Retrieved September 15, 2011.
- ^ Jeff Foust (September 15, 2011). "A monster rocket, or just a monster?". The Space Review.
- ^ Jeff Foust (November 1, 2011). "Can NASA develop a heavy-lift rocket?". The Space Review.
- ^ Mohney, Doug (October 21, 2011). "Did NASA Hide In-space Fuel Depots To Get a Heavy Lift Rocket?". Satellite Spotlight. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- ^ "Propellant Depot Requirements Study" (PDF). HAT Technical Interchange Meeting. July 21, 2011.
- ^ Cowing, Keith (October 12, 2011). "Internal NASA Studies Show Cheaper and Faster Alternatives to the Space Launch System". SpaceRef.com. Retrieved November 10, 2011.
- ^ "Near Term Space Exploration with Commercial Launch Vehicles Plus Propellant Depot" (PDF). Georgia Institute of Technology / National Institute of Aerospace. 2011.
- ^ "Affordable Exploration Architecture" (PDF). United Launch Alliance. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 21, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Grant Bonin (June 6, 2011). "Human spaceflight for less: the case for smaller launch vehicles, revisited". The Space Review.
- ^ Robert Zubrin (May 14, 2011). "How We Can Fly to Mars in This Decade—And on the Cheap". Mars Society. Archived from the original on March 19, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Rick Tumlinson (September 15, 2011). "The Senate Launch System – Destiny, Decision, and Disaster". Huffington Post.
- ^ Andrew Gasser (October 24, 2011). "Propellant depots: the fiscally responsible and feasible alternative to SLS". The Space Review.
- ^ Alan Boyle (December 7, 2011). "Is the case for Mars facing a crisis?". MSNBC. Archived from the original on January 7, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ John K. Strickland, Jr. "The SpaceX Falcon Heavy Booster: Why Is It Important?". National Space Society. Retrieved January 4, 2012.
- ^ "NASA Studies Scaled-Up Falcon, Merlin". Aviation Week. December 2, 2010. Archived from the original on July 27, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Spacex BFR to be lower cost than Falcon 1 at $7 million per launch". nextbigfuture.com. Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- ^ Bergin, Chris (August 29, 2014). "Battle of the Heavyweight Rockets – SLS could face Exploration Class rival". NASAspaceflight.com. Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ "Congressman, Space Frontier Foundation, And Tea Party In Space Call For NASA SLS Investigation". moonandback.com. October 4, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "The Senate Launch System". Competitive Space. October 4, 2011. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ "NASA veteran Chris Kraft upfront with criticism". August 2013.
- ^ "Garver: NASA Should Cancel SLS and Mars 2020 Rover". Space News. January 2014.
- ^ "Why NASA Still Can't Put Humans in Space: Congress Is Starving It of Needed Funds". 2015.
- ^ "The Space Review: Doing humans to Mars on—and within—a budget". thespacereview.com. April 2015.
- ^ . 2019.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help); Text "https://arstechnica.com/science/2019/06/new-report-finds-nasa-awarded-boeing-large-fees-despite-sls-launch-slips/" ignored (help); Unknown parameter|Title=ignored (|title=suggested) (help) - ^ . 2019.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help); Text "https://spacenews.com/contractors-continue-to-win-award-fees-despite-sls-and-orion-delays/" ignored (help); Unknown parameter|Title=ignored (|title=suggested) (help) - ^ "NASA administrator on recent personnel shakeup: 'There's no turmoil at all'". July 12, 2019.
- ^ Hambleton, Kathryn. "Exploration Mission-1 Map". nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved September 16, 2018.
- ^ Hill 2018, Page 2, "The first uncrewed, integrated flight test of NASA's Orion spacecraft [...] Enter Distant Retrograde Orbit for next 6–10 days [...] 37,000 miles from the surface of the Moon [...] Mission duration: 25.5 days"
- ^ a b c d Gebhardt, Chris (September 22, 2017). "SLS EM-1 & -2 launch dates realign; EM-3 gains notional mission outline". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved September 23, 2017.
- ^ Hambleton, Kathryn. "NASA's First Flight With Crew Important Step on Long-term Return to the Moon, Missions to Mars". nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved September 16, 2018.
- ^ Hill 2018, Page 3, "Crewed Hybrid Free Return Trajectory, demonstrating crewed flight and spacecraft systems performance beyond Low Earth orbit (LEO) [...] lunar fly-by 4,800 nmi [...] 4 astronauts [...] Mission duration: 9 days"
- ^ a b c Sloss, Philip (September 11, 2018). "NASA updates Lunar Gateway plans". NASASpaceFlight.com. Retrieved September 17, 2018.
- ^ "Additional $1.3 billion for NASA to fund next Mars rover, Europa mission –". thespacereporter.com. Archived from the original on January 18, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "A Lander for NASA's Europa Mission". planetary.org.
- ^ Boeing Space (July 31, 2019). "Farther and faster: The next stage of America's Moon rocket is taking shape to dramatically reduce travel time in space and carry more on a single flight. The Boeing-built @NASA_SLS Exploration Upper Stage will fly on Artemis-3.pic.twitter.com/pNye8izfiE". Twitter. Retrieved July 31, 2019.
External links
- Space Launch System and Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle page on NASA.gov
- "Preliminary Report on Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle and Space Launch System" (PDF), NASA.
- SLS Future Frontiers video
- Video animations of mission to asteroid, the Moon, and Mars, beyondearth.com
- "NASA Continues Journey to Mars Planning", spacepolicyonline.com











