Malaysia Airlines Flight 17
 9M-MRD, the aircraft involved, 2011 | |
| Shootdown | |
|---|---|
| Date | 17 July 2014 |
| Summary | Shot down by a surface-to-air missile transported from Russia on the day of the crash[1][2] |
| Site | Near Hrabove, Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine 48°8′17″N 38°38′20″E / 48.13806°N 38.63889°E |
| Aircraft | |
| Aircraft type | Boeing 777-200ER |
| Operator | Malaysia Airlines |
| IATA flight No. | MH17 |
| ICAO flight No. | MAS17 |
| Call sign | MALAYSIAN 17 |
| Registration | 9M-MRD |
| Flight origin | Amsterdam Airport Schiphol, the Netherlands |
| Destination | Kuala Lumpur International Airport, Malaysia |
| Occupants | 298 |
| Passengers | 283 |
| Crew | 15 |
| Fatalities | 298 |
| Survivors | 0 |
Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 (MH17)[a] was a scheduled passenger flight from Amsterdam to Kuala Lumpur that was shot down on 17 July 2014 while flying over eastern Ukraine. All 283 passengers and 15 crew were killed.[3] Contact with the aircraft, a Boeing 777-200ER, was lost when it was about 50 km (31 mi) from the Ukraine–Russia border and wreckage of the aircraft fell near Hrabove in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine, 40 km (25 mi) from the border.[4] The shoot-down occurred in the War in Donbass, during the Battle of Shakhtarsk, in an area controlled by pro-Russian rebels.[5] The crash was Malaysia Airlines' second aircraft loss during 2014 after the disappearance of Flight 370 on 8 March.[6]
The responsibility for investigation was delegated to the Dutch Safety Board (DSB) and the Dutch-led joint investigation team (JIT), who concluded that the airliner was downed by a Buk surface-to-air missile launched from pro-Russian separatist-controlled territory in Ukraine.[7][8] According to the JIT, the Buk that was used originated from the 53rd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade of the Russian Federation,[9][10] and had been transported from Russia on the day of the crash, fired from a field in a rebel-controlled area, and the launcher returned to Russia after it was used to shoot down MH17.[1][2][9] On the basis of the JIT's conclusions, the governments of the Netherlands and Australia hold Russia responsible for the deployment of the Buk installation and are taking steps to hold Russia formally accountable.[11][12]
The DSB and JIT findings confirmed earlier claims by American and German intelligence sources as to the missile type and launch area. In 2014, American intelligence had also said that Russia had supplied the Buk missile to pro-Russian insurgents, and that the insurgents most plausibly shot down MH17 in error, after misidentifying it as a military aircraft.[13][14][15]
Ukrainian Prime Minister Arseniy Yatsenyuk laid the blame on professional soldiers who came from Russia with Ukrainian passports and were coordinated from Russia.[16] As of May 2018[update], the Russian government rejects claims that Russia bears any responsibility for the crash, and denies involvement. The Russian defense ministry said that it had never deployed anti-aircraft missile systems in Ukraine.[10][17] Several conspiracy theories about the crash have since appeared in Russian media, including that the aircraft was followed by a Ukrainian military jet.[14][18] The Russian Government holds Ukraine responsible for the crash,[19][20][21][22] asserting that Ukraine should have redirected the civilian traffic away from the area of conflict.[23]
Several Ukrainian Air Force (UAF) aircraft had been shot down over the rebel-controlled territory, before the MH17 incident. Immediately after the crash, a post appeared on the VKontakte social media profile attributed to Igor Girkin, leader of the Donbass separatist militia, claiming responsibility for shooting down a Ukrainian An-26 military transporter near Torez.[24] This post was removed later the same day, and the separatists then denied shooting down any aircraft.[25][26][27] Russian news agency TASS also reported eyewitness accounts claiming that the Donbass militia had just shot down a Ukrainian An-26 military plane with a missile.[28] In late July 2014, communications intercepts were made public in which, it is claimed, separatists are heard discussing an aircraft that they had downed.[29][30][31][32] A video from the crash site, recorded by the rebels and obtained by News Corp Australia, shows the first rebel soldiers to arrive at the crash site. At first, they assumed that the downed aircraft was a Ukrainian military jet, and were dismayed when they started to realise that it was a civilian airliner.[33]
Aircraft
Flight 17, which was also marketed as KLM Flight 4103 (KL4103) through a codeshare agreement,[34] was operated with a Boeing 777-2H6ER,[b] serial number 28411, registration 9M-MRD.[7]: 30 The 84th Boeing 777 produced, it first flew on 17 July 1997, exactly 17 years before the incident, and was delivered new to Malaysia Airlines on 29 July 1997.[35] Powered by two Rolls-Royce Trent 892 engines and carrying 280 seats (33 business and 247 economy), the aircraft had recorded more than 76,300 hours in 11,430 cycles before the crash.[7]: 30 The aircraft was in an airworthy condition at departure.[7]: 31
The Boeing 777, which entered commercial service on 7 June 1995, has one of the best safety records among commercial aircraft.[36] In June 2014 there were about 1,212 aircraft in service, with 340 more on order.[37]
Passengers and crew
| Nation | Number |
|---|---|
| Australia | 27 |
| Belgium | 4 |
| Canada/Romania (Dual Citizenship) | 1 |
| Germany[c] | 4 |
| Indonesia | 12 |
| Malaysia[d] | 43 |
| Netherlands[e] | 193 |
| New Zealand | 1 |
| Philippines | 3 |
| United Kingdom[f] | 10 |
| Total | 298 |
The incident is the deadliest airliner shootdown incident to date.[39] All 283 passengers and 15 crew died.[7]: 27 By 19 July, the airline had determined the nationalities of all 298 passengers and crew.[6]
The crew were all Malaysian, while over two-thirds (68%) of the passengers were Dutch. Most of the other passengers were Malaysians and Australians, the remainder were citizens of 7 other countries.[7]: 27
Among the passengers were delegates en route to the 20th International AIDS Conference in Melbourne, including Joep Lange, a former president of the International AIDS Society, which organised the conference.[40] Many initial reports had erroneously indicated that around 100 delegates to the conference were aboard, but this was later revised to six.[41] Also on board were Dutch Senator Willem Witteveen,[42] Australian author Liam Davison,[43] and Malaysian actress Shuba Jay.[44]
At least twenty family groups were on the aircraft and eighty passengers were under the age of 18.[45][46]
The flightcrew were captain Eugene Choo Jin Leong and the first officer was Muhd Firdaus Abdul Rahim, the flight also carried a relief crew.[47][g]
Background
An armed conflict in Eastern Ukraine led some airlines to avoid eastern Ukrainian airspace in early March 2014 due to safety concerns.[50][51] Military aircraft were deployed in the conflict, and several were shot down in the months and weeks preceding the MH17 incident. In April, the International Civil Aviation Organization warned governments that there was a risk to commercial passenger flights over south-eastern Ukraine.[7]: 217 The American Federal Aviation Administration issued restrictions on flights over Crimea, to the south of MH17's route, and advised airlines flying over some other parts of Ukraine to "exercise extreme caution". This warning did not include the MH17 crash region.[52][53] 37 airlines continued overflying eastern Ukraine and about 900 flights crossed the Donetsk region in the seven days before the Boeing 777 was shot down.[54]
On 14 June 2014, a Ukrainian Air Force Ilyushin Il-76 military airlifter was shot down on approach to Luhansk International Airport, with loss of nine crew members and forty troops.[7]: 183 On 29 June, Russian news agencies reported that insurgents had obtained a Buk missile system after having taken control of a Ukrainian air defence base (possibly the former location of the 156th Anti-Aircraft Missile Regiment [156 zrp]).[55][56][57] On the same day, the Donetsk People's Republic claimed possession of such a system in a since-deleted tweet.[56][58]
On 14 July 2014, a Ukrainian Air Force An-26 transport plane flying at 6,500 m (21,300 ft) was shot down.[7]: 183 The militia reportedly claimed via social media that a Buk missile launcher had been used to bring down the aircraft.[59] American officials later said evidence suggested the aircraft had been shot down from Russian territory.[60] On 16 July, a Sukhoi Su-25 close air support aircraft was also shot down. The Ukrainian government said that the Russian military had shot down the aircraft with an air-to-air missile fired by a MiG-29 jet in Russia; the Russian defence ministry said that the accusations were false.[61][62] According to the Dutch newspaper De Telegraaf, the Ukrainian government also warned the government of the Netherlands and other European countries about dangers in flying over the East Ukraine three days prior to the shootdown[63][64] due to the downing of the An-26 transport aircraft on 14 July.[65][66]
On 15 July 2014, following his visit to Kiev, Polish Minister of Foreign Affairs Radosław Sikorski warned about the dangers posed by the continued Russian military support for pro-Russian separatists, especially ground-to-air missiles.[67] On 17 July, an Associated Press journalist saw a Buk launcher in Snizhne, a town in Donetsk Oblast, 16 kilometres (10 mi) southeast of the crash site. The reporter also saw seven separatist tanks near the town.[68] Associated Press journalists reported that the Buk M-1 was operated by a man "with unfamiliar fatigues and a distinctive Russian accent" escorted by two civilian vehicles.[69] The battle around Savur-Mohyla has been suggested as the possible context within which the missile that brought down MH17 was fired, as separatists deployed increasingly sophisticated anti-aircraft weaponry in this battle, and had brought down several Ukrainian jets in July.[70]
Ukraine imposed restrictions to air traffic in the airspace of Donetsk Oblast, but did not close it. On 5 June 2014, traffic was restricted to altitudes above 26,000 feet (7,900 m) and on 14 July to above 32,000 feet (9,800 m).[7]: 179–180 This did not prevent commercial overflights as commercial traffic typically travels at altitudes of 33,000 to 44,000 feet.[71] The Russian ATC closed the airspace in the adjacent area over Russia below 53,000 feet (16,000 m), effectively closing it to civilian traffic. The reason given was "armed conflict in Ukraine". The Dutch Safety Board asked, but did not receive, a more detailed explanation for this restriction.[72][73] As with other countries, Ukraine receives overflight fees for commercial aircraft that fly through their borders and this may have contributed to the continued availability of civilian flight paths through the conflict zone over FL 320.[74][75]
On the day of MH17 incident, a Ukrainian An-26 was scheduled to deliver paratroopers to the battle arena.[76]
Crash

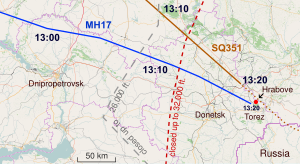
On Thursday, 17 July 2014, Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 departed from Amsterdam Airport Schiphol Gate G3 at 12:13 CEST (10:13 UTC)[7]: 23 and took off at 12:31 local time (10:31 UTC). It was due to arrive at Kuala Lumpur International Airport at 06:10 MYT, Friday, 18 July (22:10 UTC, 17 July).[77]
According to the original flight plan, MH17 was to fly over Ukraine at flight level 330 (33,000 feet or 10,060 metres) and then change to FL 350 around the Ukrainian city of Dnipropetrovsk. When it reached the area as planned, at 15:53 local time (12:53 UTC), Dnipropetrovsk Air Control (Dnipro Control) asked MH17 if they could climb to FL 350 as planned, and also to avoid a potential separation conflict with another flight, Singapore Airlines Flight 351 (SQ351), also at FL 330. The crew asked to remain at FL 330 and the air traffic controller approved this request, moving the other flight to FL 350. At 16:00 local time (13:00 UTC), the crew asked for a deviation of 20 nautical miles (37 km) to the left (north) off course, on airway L980, due to weather conditions. This request was also approved by Dnipro Control ATC. The crew then asked if they could climb to FL 340, which was rejected as this flight level was not available, so MH17 remained at FL 330. At 16:19 local time (13:19 UTC), Dnipro Control noticed that the flight was 3.6 nautical miles (6.7 km) north of the centreline of approved airway and instructed MH17 to return to the track. At 16:19 local time (13:19 UTC), Dnipro Control contacted Russian ATC in Rostov-on-Don (RND Control) by telephone and requested clearance to transfer the flight to Russian airspace. After obtaining the permission, Dnipro Control attempted to contact MH17 for handing them off to RND Control at 16:20 local time (13:20 UTC), but the aircraft did not respond. When MH17 did not respond to several calls, Dnipro Control contacted RND Control again to check if they could see the aircraft on their radar. RND Control confirmed that the plane had disappeared.[3]
The Dutch Safety Board reported a last flight data recording at 16:20 local time (13:20 UTC), located west of the urban-type settlement Rozsypne (Розсипне), near Hrabove heading east-southeast (ESE, 115°) at 494 knots (915 km/h; 568 mph).[3]
At exactly 16:20:03 local time (13:20:03 UTC) a Buk ground-to-air missile, which had been launched from an area east from the aircraft, detonated outside the aircraft just above the cockpit to the left. An explosive decompression occurred, resulting in both the cockpit and tail sections tearing away from the middle portion of the fuselage. All three sections disintegrated as they fell rapidly towards the ground.
The majority of debris landed near Hrabove, a village located north of Torez in eastern Ukraine's Donetsk Oblast. The debris spread over a 50 square kilometres (19 sq mi) area to the southwest of Hrabove.[7]: 53 The fireball on impact is believed to have been captured on video.[78] Photographs from the site of the crash show scattered pieces of broken fuselage and engine parts, bodies, and passports.[79] Some of the wreckage fell close to houses.[80] Dozens of bodies fell into crop fields, and some fell into houses.[81]
Three other commercial aircraft were in the same area when the Malaysian plane crashed: Air India Flight 113 (AI113), a Boeing 787 en route from Delhi to Birmingham, EVA Air Flight 88 (BR88), a Boeing 777 en route from Paris to Taipei, and the closest aircraft Singapore Airlines Flight 351 (SQ351) was 33 kilometres (21 mi) away, a Boeing 777 en route from Copenhagen to Singapore.[7]: 41
Recovery of bodies

A Ukraine Foreign Ministry representative said that the bodies found at the crash site would be taken to Kharkiv for identification, 270 kilometres (170 mi) to the north. By the day after the crash, 181 of the 298 bodies had been found.[82] Some were observed being placed in body bags and loaded onto trucks.[83][84][85]
Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte complained about the lack of respect shown to the personal belongings of the dead which were reportedly being looted. He initially announced his disgust about the handling of the bodies that were reportedly being "dragged around" and "thrown", but later stated they had been handled with more care than originally thought.[86][87] On 20 July, Ukrainian emergency workers, observed by armed separatists, began loading the remains of the passengers of MH17 into refrigerated railway wagons for transport and identification.[88]
On 21 July, pro-Russian rebels allowed Dutch investigators to examine the bodies. By this time, 272 bodies had been recovered, according to Ukrainian officials.[89] Remains left Torez on a train on the evening of 21 July, en route to Kharkiv to be flown to the Netherlands for identification.[90] On the same day, Malaysian Prime Minister Najib Razak announced that the Malaysian government had reached a tentative agreement to retrieve the remains of the Malaysians who died in the crash, following any necessary forensic work.[91]

It was reported on 21 July that with 282 bodies and 87 body fragments found, there were still 16 bodies missing.[92] An agreement had been reached that the Netherlands would co-ordinate the identification effort. A train carrying the bodies arrived at the Malyshev Factory, Kharkiv on 22 July.[93] Dutch authorities stated that they found 200 bodies on the train when it arrived at Kharkhiv, leaving almost 100 unaccounted for.[94] In late July, the UK Metropolitan Police sent specialist officers to Ukraine to assist with the recovery, identification and repatriation of bodies.[95]
The first remains were flown to Eindhoven in the Netherlands on 23 July,[96] moved there with Dutch air force C-130 and Australian C-17 transport aircraft,[97][98] which landed at Eindhoven Airport just before 16:00 local time.[99] The day after, another 74 bodies arrived.[100] The examination and identification of the bodies was conducted at the Netherlands Army medical regiment training facility in Hilversum and was coordinated by a Dutch forensic team.[101]
On 1 August it was announced that a search and recovery mission, including about 80 forensic police specialists from the Netherlands, Malaysia and Australia, and led by Colonel Cornelis Kuijs of the Royal Marechaussee, would use drones, sniffer dogs, divers and satellite mapping to search for missing body parts at the crash site.[102][103] Australian officials had believed that as many as 80 bodies were still at the site,[104] but after some days of searching the international team had "found remains of only a few victims" and concluded that "the recovery effort undertaken by local authorities immediately after the crash was more thorough than initially thought."[105]
On 6 August the Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte announced that the recovery operation would be temporarily halted due to an upsurge in fighting around the crash site threatening the safety of crash investigators and recovery specialists, and that all international investigators and humanitarian forces conducting searches would leave the country leaving behind a small communications and liaison team.[106]
On 22 August the bodies of 20 Malaysians (of 43 killed in the incident) arrived in Malaysia.[107] The government announced a National Mourning Day, with a ceremony broadcast live on radio and television.[108]
On 9 October a spokesman for the Dutch national prosecutor's office stated that one victim had been found with an oxygen mask around his neck; a forensic investigation of the mask for fingerprints, saliva and DNA did not produce any results and it is therefore not known how or when that mask got around the neck of the victim.[7]: 99
By 5 December 2014, the Dutch-led forensic team had identified the bodies of 292 out of 298 victims of the crash.[109] In February and April 2015 new remains were found on the site,[110][111] after which only 2 victims, both Dutch citizens, had not been identified.[111]
Reporting in the mass media
De Telegraaf, a large-circulation Dutch tabloid, published on 19 July a front-page photo-collage of pro-Russian rebel leaders, including Igor Girkin, under the one-word headline "Murderers" ("Moordenaars").[112]
It was suggested on other media that credit and debit cards may have been looted from the bodies of the victims, and the Dutch Banking Association said it would take "preventative measures" against any possible fraud.[113] There were also accusations that other possessions had been removed and that evidence at the crash site had been destroyed.[114][115] Dutch prime minister Mark Rutte acknowledged on 6 August that early reports of chaos and criminality around the site may have been exaggerated.[105] One eyewitness observed that valuable items like shoes and bottles of alcohol were untouched in the wreckage.[116] On 3 July 1988, the guided missile cruiser USS Vincennes accidentally shot down Iran Air Flight 655, killing 290 passengers.[117] In July 2014, when Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 was shot down in Ukraine, some commentators noted the discrepancy of U.S. official position and media coverage of the two similar incidents.[118][119][120][121]
Aftermath
About 90 minutes after the incident, Ukraine closed all routes in Eastern Ukrainian airspace, at all altitudes.[7]: 101 The incident dramatically heightened fears about airliner shootdowns,[122] leading to some airlines announcing they would avoid overflying conflict zones.
Shortly after the crash, it was announced that Malaysia Airlines would retire flight number MH17 and change the Amsterdam–Kuala Lumpur route to flight number MH19 beginning on 25 July 2014, with the outbound flight unchanged.[123][124] In association with the retirement of the Boeing 777 aircraft type from Malaysia Airlines' fleet, Malaysia Airlines terminated service to Amsterdam, opting to codeshare with KLM on the KUL-AMS route for service beyond 25 January 2016.[125] On 18 July 2014, shares in Malaysia Airlines dropped by nearly 16%.[126]
On 23 July 2014, two Ukrainian military jets were hit by missiles at the altitude of 17,000 feet (5,200 m) close to the area of the MH17 crash. According to the Ukrainian Security Council, preliminary information indicated that the missiles came from Russia.[127]
In July 2015, Malaysia proposed that the United Nations Security Council set up an international tribunal to prosecute those deemed responsible for the downing of the plane. The Malaysian resolution gained a majority on the Security Council, but was vetoed by Russia.[128] Russia had proposed its own rival draft resolution, which pushed for a greater U.N. role in an investigation into what caused the downing of the aircraft and demanded justice, but their proposal would not have set up a tribunal.[129]
On 9 June 2016, a Russian businessman claimed that the shooting down of the plane put an end to hopes of a Russian nation in Ukraine and prolonged the War in Donbass.[130]
Investigation
Two parallel investigations were led by the Dutch, one into the technical cause of the crash, and a separate criminal inquiry.[131] The technical report was released on 13 October 2015,[132] while the criminal investigation reported some of their findings in September 2016.[2][133] According to the Convention on International Civil Aviation, the country in which an aviation incident occurs is responsible for the investigation, but that country may delegate the investigation to another state; Ukraine has delegated the leadership of both investigations to the Netherlands.[134][135][136][137]
On-site investigation
In the hours following the crash, a meeting was convened of the Trilateral Contact Group. After they had held a video conference with representatives of insurgents affiliated with the Donetsk People's Republic (who controlled the area where the aircraft crashed), the rebels promised to "provide safe access and security guarantees" to "the national investigation commission" by co-operating with Ukrainian authorities and OSCE (Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe) monitors.[138] During the first two days of investigation, the militants prevented the OSCE and the workers of Ukrainian Emergencies Ministry from freely working at the crash site. Andrei Purgin, a leader of the Donetsk People's Republic, declared later that "we will guarantee the safety of international experts on the scene as soon as Kiev concludes a ceasefire agreement".[139]

By 18 July 2014, the flight data recorder and the cockpit voice recorder had been recovered by separatists,[140] and three days later were handed over to Malaysian officials in Donetsk.[7]: 44 [141] The voice recorder was damaged but there was no evidence that data had been tampered with.[7]: 45
The National Bureau of Air Accidents Investigation of Ukraine, which led investigations, both off-site and on-site, during the first days after the crash,[142] had by August 2014 delegated the investigation to the DSB because of the large number of Dutch passengers and the flight having originated in Amsterdam.[7]: 14 [143][144]
On 22 July 2014, a Malaysian team of 133 officials, search and recovery personnel, and forensics, technical and medical experts arrived in Ukraine.[145] Also Australia sent a 45-member panel headed by former Air Chief Marshal Angus Houston, who had earlier supervised the MH 370 probe.[146] Approximately 200 special forces soldiers from Australia were also deployed to provide support for the JIT investigators.[147] The United Kingdom sent six investigators from the Air Accidents Investigation Branch (AAIB) and the UK Foreign Office sent extra consular staff to Ukraine.[95] It took until late July before the full international team could start working at the crash site,[148] under the leadership of the Dutch Ministry of Defence.[149]
On 30 July 2014, a Ukrainian representative said that pro-Russian rebels had mined approaches to the crash site and moved heavy artillery.[150]
On 6 August 2014, the experts left the crash site due to concerns about their safety.[151] In mid-September they unsuccessfully attempted to regain access to the site.[152][153] On 13 October 2014, a Dutch-Ukrainian team resumed recovery of victims' personal belongings.[154] In mid-November 2014, work was undertaken to remove part of the wreckage from the crash site. Earlier efforts by the recovery team to salvage the MH17 wreckage had been frustrated by disagreements with the local rebels.[155][156] The recovery operation took one week to complete. The debris was transported to the Netherlands where investigators reconstructed parts of the plane.[157]
In August 2015, possible Buk missile launcher parts were found at the crash site by the Dutch led joint investigation team (JIT).[158][159]
Cause of crash

| External audio | |
|---|---|
Soon after the crash both American and Ukrainian officials said that a 9M38 series surface-to-air missile strike was the most likely cause,[160] and if so, then the missile was fired from a mobile Soviet-designed Buk missile system (NATO reporting name: SA-11 "Gadfly") as this was the only surface-to-air missile system in the region capable of reaching the cruising altitude of commercial air traffic.[60][161][162][163][164][165] According to defence analyst Reed Foster (from Jane's Information Group), the contour of the aluminium and the blistering of the paint around many of the holes on the aircraft fragments indicate that small, high-velocity fragments entered the aircraft externally, a damage pattern indicative of an SA-11.[166] Ballistics specialist Stephan Fruhling of the Australian National University's Strategic and Defence Studies Centre concurred with this, explaining that since it struck the cockpit rather than an engine it was probably a radar guided, rather than heat seeking, missile equipped with a proximity fuzed warhead such as an SA-11.[167]
Shortly after the crash, Igor Girkin, leader of the Donbass separatists, was reported to have posted on social media network VKontakte, taking credit for downing a Ukrainian An-26.[24][168][169] This news was repeated by channels in Russia, with LifeNews reporting "a new victory of Donetsk self-defence who shot down yet another Ukrainian airplane".[170] Russian news agency TASS also reported eyewitness accounts claiming that the Donbass militia had just shot down a Ukrainian An-26 military plane with a missile.[28] The separatists later denied involvement, saying they did not have the equipment or training to hit a target at that altitude.[171][172][173] Russian media also reported that Alexander Borodai called one of the Moscow media managers 40 minutes after the crash, saying that "likely we shot down a civilian airliner".[169]
Witnesses in Torez reported sightings on the day of the incident of what appeared to be a Buk missile launcher,[174] and AP journalists reported sightings of a Buk system in separatist controlled Snizhne.[69] The witness reports backed up photographs and videos which had been posted online, of the Buk launcher in rebel-held territory.[174]
On 19 July 2014, Vitaly Nayda, the chief of the Counter Intelligence Department of the Security Service of Ukraine (SBU), told a news conference, "We have compelling evidence that this terrorist act was committed with the help of the Russian Federation. We know clearly that the crew of this system were Russian citizens."[175][176][177] He cited what he said were recorded conversations in which separatists expressed satisfaction to Russian intelligence agents that they brought down an aircraft.[178][179] While one of the involved persons acknowledged that these conversations took place, the separatists denied that they were related to the crash of MH17 and blamed the Ukrainian government for shooting it down.[77][180][181][182] According to Nayda, a Buk launcher used in the shootdown was moved back into Russia the night after the attack.[69] The SBU released another recording, which they said was of pro-Russian-separatist leader Igor Bezler being told of an approaching aircraft two minutes before MH17 was shot down. Bezler said the recording was real, but referred to a different incident.[183] The head of the SBU, Valentyn Nalyvaichenko, later concluded that rebels intended to shoot down a Russian airliner in a false flag operation to give Russia a pretext to invade Ukraine, but shot down MH17 by mistake.[184][185][186]
Journalists from the Associated Press in Snizhne, Ukraine reported seeing a Buk M-1 enter the town operated by a man "with unfamiliar fatigues and a distinctive Russian accent" escorted by two civilian vehicles, which then moved off in the direction where the shootdown later occurred. According to Ukrainian counterterrorism chief, Vitaly Nayda, after downing the plane under separatist direction, the launcher's Russian crew quickly moved it back across the border into Russia.[69]
On 22 July 2014, a rebel fighter revealed to an Italian reporter that fellow separatists had told his unit the aircraft had been shot down under the assumption that it was Ukrainian.[187] This information was verified and confirmed on the same day by a German newspaper.[188] Unnamed American intelligence officials stated that sensors that traced the path of the missile, shrapnel patterns in the wreckage, voice print analysis of separatists' conversations in which they claimed credit for the strike, and photos and other data from social media sites all indicated that Russian-backed separatists had fired the missile.[14]
American officials said that satellite data from infrared sensors detected the explosion of Flight MH17.[189] American intelligence agencies said that analysis of the launch plume and trajectory suggested the missile was fired from an area near Torez and Snizhne.[60][162] The British Daily Telegraph said: "The Telegraph's own inquiries suggest the missile, an SA-11 from a Buk mobile rocket launcher, was possibly fired from a cornfield about 19 kilometres (12 mi) to the south of the epicentre of the crash site."[163] Other sources suggest the missile was launched from the separatist-controlled town of Chernukhino.[190] Several other media outlets including The Guardian, The Washington Post and the Sydney Morning Herald reported that the aeroplane is believed to have been downed by a rebel-fired missile.[104][191][192]
An unnamed American intelligence official stated that Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 may have been shot down in error by pro-Russian separatists, citing evidence that separatists launched an SA-11 surface-to-air missile that blew up the Malaysian airliner. They said it was possible the rebel was a former member of the Armed Forces of Ukraine who had defected to the pro-Russian separatists.[13] The official dismissed Russian allegations that MH17 took evasive action and said the claim that the Ukrainian government had shot down MH17 was not realistic, as Kiev had no such missile systems in that area, which was rebel-controlled.[164] American intelligence officials also said that Russia was attempting to disguise the flow of weaponry it was delivering to the rebels by sending older weapons that matched Ukraine's inventory.[14] The British Foreign Office stated that it was "highly likely" that the missile was fired from an area controlled by Russian-backed separatists.[193]
The Russian Ministry of Defence has maintained that American claims of separatist responsibility were "unfounded", and said that the American intelligence agencies have not released any of the data on which they based their conclusions.[194] According to the Russian military, in what the New York Magazine called "Russia's Conspiracy Theory", MH17 was shot down by the Ukrainians, using either a surface-to-air missile or a fighter plane.[18][195]
On 21 July 2014, the Russian Ministry of Defence (MoD) held a press conference and said that while the Boeing 777 was crashing, a Ukrainian Su-25 ground-attack aircraft approached to within 3 to 5 kilometres (1.9 to 3.1 mi) of the Malaysian airliner. The MoD also claimed that satellite photographs showed that the Ukrainian army moved a Buk SAM battery to the area close to the territory controlled by the rebels on the morning of 17 July, hours before the crash. They said the installation was then moved away again by 18 July.[196] Promoted by Russian media, the idea that a Su-25 could have downed the Boeing 777 with an air-to-air missile was dismissed by chief designer of the Su-25, Vladimir Babak.[197] In 2015 Bellingcat purchased satellite photos from the same area and time as used by the MoD and demonstrated that they had used older photos (May and June 2014) in their presentation that were edited to make a Ukrainian Buk launcher appear as if it was removed after the attack.[198] In the report published by the Dutch Safety Board, an air-to-air missile strike was ruled out.[8]
In an interview with Reuters on 23 July 2014, Alexander Khodakovsky, the commander of the pro-Russian Vostok Battalion, acknowledged that the separatists had an anti-aircraft missile of the type the Americans had said was used to shoot down the aircraft, and said that it could have been sent back to Russia to remove proof of its presence;[199][200][201] he later retracted his comments, saying that he had been misquoted and stating that rebels never had a Buk.[202] In November 2014 he repeated that the separatists had a Buk launcher at the time, but stated that the vehicle, under control of fighters from Luhansk, had still been on its way to Donetsk when MH17 crashed. It was then withdrawn to avoid being blamed.[203]
On 28 July 2014, Ukrainian security official Andriy Lysenko announced, at a press conference, that black box recorder analysis had revealed that the aircraft had been brought down by shrapnel that caused "massive explosive decompression." Dutch officials were reported to be "stunned" by what they saw as a "premature announcement" and said that they had not provided this information.[204]
On 8 September 2014, the BBC released new material by John Sweeney who cited three civilian witnesses from Donbass who saw the Buk launcher in the rebel-controlled territory on the day when MH17 crashed. Two witnesses said the crew of the launcher and a military vehicle escorting it did not have local accents and spoke with Muscovite accents.[205] On the same day Ignat Ostanin, a Russian journalist, published an analysis of photos and films of Buk units moving in Russia and Ukraine in the days before and after the MH17 crash. According to Ostanin, the markings on the specific launcher suspected of being used to shoot MH17, together with the number plates of the large goods vehicle that carried the launcher, suggested that it belonged to the 53rd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade of the Air Defence Forces of the Russian Ground Forces.[206][207]
On 8 October 2014 the president of the German Federal Intelligence Service (BND) gave a presentation about MH17 to a German parliamentary committee overseeing intelligence activities. According to Der Spiegel, the report contained a detailed analysis which concluded that pro-Russian separatists had used a captured Ukrainian Buk system to shoot down Flight MH17. The report also noted that "Russian claims the missile had been fired by Ukrainian soldiers and that a Ukrainian fighter jet had been flying close to the passenger jet were false".[208][209] The Attorney General of Germany opened an investigation against unknown persons due to a suspected war crime.[210]
Between November 2014 and May 2016, UK-based investigative collective Bellingcat made a series of conclusions, based on their examination of photos in social media and other open-source information. Bellingcat said that the launcher used to shoot down the aircraft was a Buk 332 of the Russian 53rd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade based in Kursk, Russia, which had been transported from Donetsk to Snizhne and was controlled by separatists in Ukraine on the day of the attack.[211][212][213][214][215]
On 22 December 2014 the Dutch news service RTL Nieuws published a statement of an unnamed local resident who witnessed the shooting down of MH17, indicating that the plane was shot down by a missile from rebel territory. He took photographs of what appeared to be the vapour trail of a ground-launched missile which he passed to the SBU.[216][217] On 24 December Russia's state-operated domestic news agency RIA Novosti quoted the leader of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic, Alexander Zakharchenko, saying he saw MH17 shot out of the sky by two Ukrainian jets.[218][219]
In January 2015 a report produced by the German investigative team CORRECT!V concluded a Buk surface-to-air missile launcher operated by the 53rd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade shot down MH17.[220] Large amounts of other circumstantial evidence were presented separately by various parties that supports this version, identifying specific launcher vehicle, operator name, truck transporting it and its alleged route through Russia and Ukraine.[221]
In March 2015 Reuters published statements from named witnesses from Chervonyi Zhovten (Template:Lang-uk), a village close to Torez and Snizhne, who said they saw the Buk rocket passing over the village when it was fired from a field around 1.5 km away. It also published a statement from a witness who was said to be a separatist fighter (referred to by first name only) who confirmed that the launcher was placed in that area on the day of the Boeing crash to prevent Ukrainian airstrikes.[222]
In July 2015, News Corp Australia published the transcript of a 17-minute video recorded at the scene shortly after the crash. The transcript and published segments of the video indicated that Russian-backed rebels arrived at the crash site in the expectation of finding the wreckage of a military aircraft and of locating crew that had parachuted from the aircraft.[223]
In May 2016, Stratfor released satellite imagery taken 5 hours before the crash which showed a Russian Buk system travelling on a flatbed truck east through the town of Makiivka, 40 km away from Snizhne. Stratfor's concluded that a Buk system had moved from the Russian border toward Donetsk on 15 July 2014, and then moved back to the east on the afternoon of 17 July 2014, hours before Flight MH17 was shot down.[224]
Dutch Safety Board reports
Preliminary report
On 9 September 2014, the preliminary report was released by the Dutch Safety Board (DSB).[3][225]: 16 This preliminary report concluded that there was no evidence of any technical or operational failure in the aircraft or from the crew prior to the ending of the CVR and FDR recordings at 13.20:03 hrs (UTC). The report also said that "damage observed on the forward fuselage and cockpit section of the aircraft appears to indicate that there were impacts from a large number of high-energy objects from outside the aircraft". According to the investigators, this damage probably led to a loss of structural integrity that caused an in-flight break-up first of the forward parts of the aircraft and then of the remainder with an expansive geographic spread of the aircraft's pieces.
Tjibbe Joustra, Chairman of the Dutch Safety Board, explained that the investigation thus far pointed "towards an external cause of the MH17 crash", but determining the exact cause required further investigation. They also said that they aimed to publish the final report within a year of the crash date.[226]
Final report
The Dutch Safety Board (DSB) issued its final report on the crash on 13 October 2015. The report concluded that the crash was caused by a Buk 9M38-series surface-to-air missile with a 9N314M warhead. The warhead detonated outside and above the left-hand side of the cockpit. The impact killed the three people in the cockpit and caused structural damage to the airplane leading to an in-flight break-up resulting in a wreckage area of 50 square kilometres and loss of the lives of all 298 occupants.[7] Based on evidence they were able to exclude meteor strikes, the plane having technical defects, a bomb, and an air-to-air attack as causes of the crash. The DSB calculated the trajectory of the missile and found it was fired within a 320-square-kilometre (120 sq mi) area southeast of Torez. Narrowing down a specific launch site was outside the DSB's mandate.[7]: 147 The findings do not specify who launched the Buk missile but according to Al Jazeera, the area identified by the DSB was controlled by separatists at the time of the downing.[227]
In addition to the technical investigation, the selection of the flight route was also investigated by the DSB.[228] Many airlines had avoided the Eastern Ukrainian airspace for months prior to the MH17 disaster. Many others, including 62 operators from 32 countries, continued to use this route.[7]: 224 [229] The DSB stated that authorities should have closed the airspace above eastern Ukraine prior to the incident due to the ongoing conflict.[230] It recommended that states involved in armed conflicts should exercise more caution when evaluating their airspace, and operators should more thoroughly assess the risks when selecting routes over conflict areas.[231]
Criminal investigation
The criminal investigation into the downing of MH17 is being led by the Public Prosecution Service of the Dutch Ministry of Justice, and is the largest in Dutch history, involving dozens of prosecutors and 200 investigators.[232] Investigators interviewed witnesses and examined forensic samples, satellite data, intercepted communications, and information on the Web.[233] Participating in the investigation along with the Netherlands, are the four other members of the joint investigation team (JIT),[234] Belgium, Ukraine, Australia, and lastly, Malaysia,[235] which joined in November 2014.[234] Early in the investigation, the JIT eliminated accident, internal terrorist attack or air-to-air attack from another aircraft as the cause of the crash.[1]
In December 2014, in a letter to the Security Council, the Netherlands UN representative wrote that "The Dutch government is deliberately refraining from any speculation or accusations regarding legal responsibility for the downing of MH17."[236] Also in December, the assistant secretary of the United States Department of State's European and Eurasian Affairs said America had given all of its information, including classified information to the Dutch investigators and to the ICAO.[237]
On 30 March 2015, the JIT released a Russian-language video calling for witnesses in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions who might have seen a Buk missile system.[238] The video included some previously undisclosed recordings allegedly of tapped phone conversations between rebel fighters about the Buk. In one recording, of a conversation a few hours after the shoot down, a fighter says that a member of the Buk's accompanying crew had been left behind at a checkpoint. In another recording, dated the day after the shootdown, a rebel allegedly says the Buk system and its crew had been brought from Russia by "the Librarian." The video presents a "scenario" whereby a Buk missile was transported on a Volvo low loader truck from Sievernyi (Сєверний), a town located within a kilometre of the Russian border (near Krasnodon), to Donetsk during the night of 16/17 July.[239] In the week following the public appeal, the JIT received more than 300 responses resulting in dozens of "serious witnesses".[240][241] In 2016 the presence of the transloader of matching color with a Buk missile was confirmed on a satellite photo of the area taken just a few hours before the downing of the plane, which was described as "correlating with other evidence" by Stratfor who found the photo in DigitalGlobe archive.[242][243]
On 9 April 2015 Dutch authorities made available 569 documents concerning the shoot-down. Personal information and official interviews had been redacted. A further 147 documents were not made public.[244]
Findings of the joint investigation team (JIT)
On 28 September 2016, the JIT gave a press conference in which it concluded that the aircraft was shot down with a 9M38 Buk missile fired from a rebel-controlled field near Pervomaisky (Первомайський), a town 6 km (3.7 mi) south of Snizhne.[133] It also found the Buk missile system used had been transported from Russia into Ukraine on the day of the crash, and then back into Russia after the crash, with one missile less than it arrived with.[1][2] The JIT said they had identified 100 people, witnesses as well as suspects, who were involved in the movement of the Buk launcher, though they had not yet identified a clear chain of command to assess culpability, which was a matter for ongoing investigation. The Dutch chief prosecutor said "the evidence must stand before a court" which would render final judgement.[1] During the investigation, the JIT recorded and assessed five billion internet pages, interviewed 200 witnesses, collected half a million photos and videos, and analysed 150,000 intercepted phone calls.[133][245] According to JIT head prosecutor Fred Westerbeke the criminal investigation is based on "immense body of evidence," including testimonies of live witnesses who saw the "Buk" launcher, primary radar data, original photos and videos.[246]

On 24 May 2018, after extensive comparative research, the JIT concluded that the Buk that shot down the flight came from the Russian 53rd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade in Kursk.[247] The head of the National Investigation Service of the Dutch police asked the eyewitnesses and insiders to share information about the identities of the Buk crew members, the instruction the crew members followed and persons responsible for the operational deployment of the involved Buk on 17 July 2014.[247] According to Dutch Public Prosecution Service, by 24 May 2018 "the authorities of the Russian Federation have ... not reported to the JIT that a Buk of the 53rd Brigade was deployed in Eastern Ukraine and that this Buk downed flight MH17."[247] In response, Russian President Vladimir Putin stated that Russia will analyze the JIT conclusion, but will acknowledge it only if it becomes a party in the investigation.[248] The Russian Ministry of Defence in turn stated that no Russian Buk crossed the border with Ukraine.[248]
On 25 May 2018 the governments of the Netherlands and Australia issued a joint statement in which they laid responsibility on Russia "for its part" in the crash.[11] The Netherlands and Australian foreign ministers stated that they would hold Russia legally responsible for shooting the airliner down. Netherlands Foreign Minister Stef Blok stated that "the government is now taking the next step by formally holding Russia accountable," and, "The Netherlands and Australia today asked Russia to enter into talks aimed at finding a solution that would do justice to the tremendous suffering and damage caused by the downing of MH17. A possible next step is to present the case to an international court or organization for their judgment."[249]
Several other countries and international organisations expressed their support for the JIT's conclusions and the joint statement by the Netherlands and Australia.[250] UK Foreign Secretary Boris Johnson said the United Kingdom "fully supports Australia and the Netherlands," calling on Russia to cooperate.[251] High Representative Federica Mogherini of the EU stated that the European Union "calls on the Russian Federation to accept its responsibility" and to cooperate as well.[252] The German government called on Russia to "fully explain the tragedy."[253] The US Department of State issued a statement saying that the United States "strongly support the decisions by the Netherlands and Australia," requesting Russia to acknowledge its involvement and to "cease its callous disinformation campaign."[254] NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg called on Russia to "accept responsibility and fully cooperate ... in line with United Nations Security Council Resolution 2166."[255]
In response to the JIT's conclusions, Russian President Vladimir Putin reiterated that the Russians are "not involved in it."[256] Following release of the JIT report, Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir said the JIT was making Russia a "scapegoat" and that he did not believe the Russians whom the JIT had charged were involved. Conversely the Malaysian prosecutor supported the investigation by saying the findings "are based on extensive investigations and also legal research".[257]
Proposed international tribunal
In June 2015, the Netherlands, supported by the other JIT members, sought to create an international tribunal to prosecute those suspected of downing the Malaysian airliner, which would take up the case after the closing of the criminal investigation. The Dutch hoped that an international tribunal would induce Russian cooperation, which was considered critical.[258] In late June 2015, the Russian government rejected a request by the five countries on the investigative committee to form a UN tribunal which would try those responsible for the shooting down of the aircraft, calling it "not timely and counterproductive."[259] On 8 July 2015, Malaysia, a member of the UN Security Council, distributed a draft resolution to establish such a tribunal. This resolution was jointly proposed by the five JIT member countries. Russian UN Ambassador Vitaly Churkin responded, "I don't see any future for this resolution. Unfortunately, it seems that this is an attempt to organize a grandiose, political show, which only damages efforts to find the guilty parties."[128] Russia later circulated a rival resolution which criticised the international investigation's lack of "due transparency" and demanded those responsible be brought to justice, but which did not call for a tribunal.[260] In a vote, Malaysia's resolution gained majority support of the UNSC, but was vetoed by Russia.[129]
Criminal prosecution
In a statement made on 5 July 2017 by the Dutch Minister of Foreign Affairs Bert Koenders, it was announced that the JIT countries would prosecute any suspects identified in the downing of flight MH17 in the Netherlands and under Dutch law.[261] A treaty between the Netherlands and Ukraine made it possible for the Netherlands to prosecute in the cases of all 298 victims, regardless of their nationality. This treaty was signed on 7 July 2017,[262] and went into force on 28 August 2018.[263] On 21 March 2018, the Dutch government sent legislation to the parliament, allowing the suspects involved to be prosecuted in the Netherlands under Dutch law.[264][265]
A joint investigation between Bellingcat, The Insider and McClatchy DC Bureau identified another person of interest to the investigation. The person known as 'Andrey Ivanovich', or by the call sign 'Orion', according to Bellingcat, is a Russian GRU officer named Oleg Vladimirovich Ivannikov.[266] Ivannikov has a distinct, high-pitched voice. The Kremlin denied this allegation.[267]
On 19 June 2019, the Dutch Public Prosecution Service charged four people with murder in connection with the shooting down of the aircraft: three Russians, Igor Girkin, Sergey Dubinsky, and Igor Pulatov, and one Ukrainian, Leonid Kharchenko. International arrest warrants were issued in respect of each of the accused.[268] Their trial in absentia is scheduled to be held on 9 March 2020 in the District Court of The Hague.[269]
In July 2019 SBU arrested Vladimir Tsemakh, head of air-defence in DPR-controlled Snizhne during the attack on MH17. Bellingcat described him as an important eye-witness to the events surrounding the downing of flight MH17. Bellingcat analysed his possible role and said that a video showed Tsemakh making "what appears to be a damning admission to his personal involvement in hiding the Buk missile launcher in the aftermath of its use on 17 July 2014".[270] In August 2019 Russia reportedly added Tsemakh to its list in a previoulsy agreed exchange of prisoners of war with Ukraine. In an article, The Insider website commented on Russia's motives in requesting the exchange of a Ukrainian citizen.[271] On 4 September 2019, an appeals court in Kiev ruled to release Tsemakh.[272] On 7 September 2019, Volodymyr Tsemakh was released during a Ukraine-Russia prisoner exchange.[273] According to the Dutch Foreign Minister Stef Blok, the exchange had been delayed for a week so that Vladimir Tsemakh could be questioned by the Dutch Public Prosecution Service as a witness about the events surrounding the downing of flight MH17.[273] The Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte, the Minister of Justice and Security Ferd Grapperhaus, the JIT, and Blok added that the Netherlands regretted Tsemakh, who is a 'person of interest', being included in the exchange due to pressure on Ukraine from Russia.[272][273][274][275][276] Others including Chairman Piet Ploeg of Stichting Vliegramp MH17 which is the organization of the victims' relatives called the release of Tsemach "unacceptable".[275] The Dutch Public Prosecution Service (OM) requested that Tsemach, who is not a Russian citizen, be extradited from Russia to the Netherlands.[275] On 14 November 2019 the JIT published a new witnesses appeal and simultaneously released a number of recorded conversations of rebel leaders. JIT was particularly interested in "the command structure and the role that Russian government officials may have played."[277][278]
British ISC report
On 20 December 2017, the Intelligence and Security Committee of the UK Parliament published its annual report. It contains a short section entitled "Russian objectives and activity against UK and allied interests" which quotes MI6 as stating: "Russia conducts information warfare on a massive scale... An early example of this was a hugely intensive, multichannel propaganda effort to persuade the world that Russia bore no responsibility for the shooting down of [Malaysian Airlines flight] MH-17 (an outright falsehood: we know beyond any reasonable doubt that the Russian military supplied and subsequently recovered the missile launcher)".[279][280]
Civil cases
In July 2015 a writ was filed in an American court by families of 18 victims accusing the separatist leader Igor Girkin of "orchestrating the shootdown" and the Russian government of being complicit in the act. The writ was brought under the Torture Victim Protection Act of 1991.[281] In May 2016 families of 33 victims of the crash filed a claim against Russia and president Vladimir Putin in the European Court of Human Rights, arguing Russian actions violated the passengers' right to life.[282][283] A group of 270 relatives of Dutch victims joined the claim in May 2018 after the JIT concluded that Russia was involved.[284] In July 2016, Malaysia Airlines was sued in Malaysia by 15 passengers' families in two separate writs, each brought under the Montreal Convention, arguing that the airline should not have chosen that route.[285] A month earlier, a separate lawsuit was brought by the families of 6 crew members who alleged negligence and breach of contract by the airline.[286]
Reactions
Countries
Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko called the crash the result of an act of terrorism, and also called for an international investigation into the crash.[287]
Malaysian Deputy Foreign Minister Hamzah Zainuddin said that the foreign ministry would be working with the Russian and Ukrainian governments with regard to the incident.[288] Prime Minister Najib Razak said that Malaysia was unable yet to verify the cause of the crash but that, if the plane was shot down, the perpetrators should be swiftly punished.[289] The Malaysian government flew the national flag at half-mast from 18 July until 21 July.[290]

Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte and King Willem-Alexander voiced their shock at the crash,[291][292] and Minister of Foreign Affairs Frans Timmermans joined the Dutch investigation team sent to Ukraine.[293] Dutch government buildings flew the flag at half-mast on 18 July.[294] Music was cancelled and festivities were toned down on the last day of the Nijmegen Marches.[295] On 21 July the Netherlands opened a war crimes investigation on the downing of the aircraft and a Netherlands public prosecutor went to Ukraine as part of this investigation. Rutte threatened tough action against Russia if it did not help in the investigation.[296] On the same day, Timmermans spoke at the UN Security Council Meeting, after the Council had unanimously condemned the shooting down of MH17.[297] An increase in negative emotions and somatic complaints was observed in the Dutch population during the first four days after the MH17 crash.[298]
Australian Prime Minister Tony Abbott said in an address to parliament that the aircraft was downed by a missile which seemed to have been launched by Russian-backed rebels.[299] Julie Bishop, the Australian Minister for Foreign Affairs, said in an interview on an Australian television programme that it was "extraordinary" that her Russian counterparts had refused to speak to her over the shootdown after the Russian ambassador was summoned to meet her.[299] The Russian government was critical of Abbott's response; Abbott was one of the first world leaders to publicly connect the shootdown to Russia.[300] Abbott later criticised the recovery efforts as "shambolic", and "more like a garden clean-up than a forensic investigation"; Bishop publicly warned separatist forces against treating the victims' bodies as hostages.[301] Abbott also said in an interview on 13 October 2014, in anticipation of Russia's President Vladimir Putin's attendance at the 2014 G20 summit, scheduled for mid-November 2014 in Brisbane, Australia: "Australians were murdered. They were murdered by Russian-backed rebels using Russian-supplied equipment. We are very unhappy about this."[302]
Russian President Putin said that Ukraine bore responsibility for the incident which happened in its territory, which he said would not have happened if hostilities had not resumed in the south-east of Ukraine.[4][303][304] He also said that it was important to refrain from reaching hasty conclusions and politicised statements before the end of the investigation. He said that Russia would help an international inquiry led by the ICAO.[305] At the end of July a Duma deputy Ilya Ponomarev said in an interview for Die Welt that the separatists had shot down the plane by mistake and that Putin now realised he had supplied the weapon to the "wrong people".[306] The Danish Institute for International Studies has pointed out to the similarities of Russian reaction to the downing of Korean Airlines flight KAL-007 in 1983 where the USSR initially denied any involvement.[307]
United States President Barack Obama said the United States would help determine the cause.[4] In a press statement, White House spokesman Josh Earnest called for an immediate ceasefire in Ukraine to allow for a full investigation.[308] Vice-President Joe Biden said the plane appeared to have been deliberately shot down, and offered American assistance for the investigation into the crash.[304] American Ambassador to the United Nations Samantha Power called on Russia to end the war.[309] The British government requested an emergency meeting of the United Nations Security Council and called an emergency Cobra meeting after the incident.[310][311] Chairman of the US Joint Chiefs of Staff Martin E. Dempsey said that instead of backing away from supporting the rebels in the wake of the airliner shootdown, Putin had "taken a decision to escalate."[312]

On 17 July 2017, exactly three years after the crash, a memorial in memory of the victims was unveiled in Vijfhuizen, the Netherlands. The opening of the memorial, which is located just outside Schiphol Airport, was attended by more than 2000 relatives of victims, King Willem-Alexander and his wife Queen Máxima, Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte, Minister of Security and Justice Stef Blok and the speakers of the Dutch Senate and House of Representatives. The memorial includes 298 trees, one tree for each victim.[313]
Organisations
On 17 July the European Union's representatives José Manuel Barroso and Herman Van Rompuy released a joint statement calling for an immediate and thorough investigation.[314] The EU officials also said that Ukraine has first claim on the plane's black boxes.[315]
The International Civil Aviation Organization announced, on 18 July, that it was sending its team of experts to assist the National Bureau of Air Accidents Investigation of Ukraine (NBAAI), under Article 26 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation.[316] The United Nations Security Council adopted Resolution 2166 on 21 July, regarding an official crime investigation into the incident. On 24 July 2014 the ICAO issued a State Letter reminding signatory states of their responsibilities with respect to the safety and security of civil aircraft operating in airspace affected by conflict.[317]

After the crash, memorial services were held in Australia[318] and in the Netherlands, which declared 23 July, the day when the first victims arrived in the country, a national day of mourning, the first since 1962.[319][320] The opening ceremony of the AIDS 2014 conference, on 20 July, of which several delegates had been on board Flight MH17, began with a tribute to the victims of the crash.[321] In Malaysia, makeshift memorials were created in the capital city of Kuala Lumpur.[322]
Russian media coverage
In July 2014, shortly after the crash, the liberal Russian opposition newspaper Novaya Gazeta published a headline in Dutch that read "Vergeef ons, Nederland" ("Forgive Us, Netherlands").[323][324]
Coverage by official media and bodies has however differed from coverage in most other countries and significantly changed over time[325][326] usually in response to new evidence published by DSB and the investigation team.[327]
According to the poll conducted by the Levada Center between 18 and 24 July in 2014, 80% of Russians surveyed believed that the crash of MH17 was caused by the Ukrainian military. Only 3% of respondents to the poll blamed the disaster on pro-Russian separatists in eastern Ukraine.[328][329][330]
In December 2017 the Russian portal The Insider, the news agency McClatchyDC, and Bellingcat performed a joint investigation that confirmed the identity of a high-rank military officer using a call-sign "Dolphin" to be colonel general Nikolai Fedorovich Tkachev. Tkachev is frequently heard in the wiretaps acquired by JIT supervising the operation of "Buk" delivery and set-up.[331][332]
Initial reactions and "An-26 downing" version
On the evening of the crash, the LifeNews portal released a statement from the separatists saying that a "Ukrainian Air Force An-26 transport plane" had been shot down by a missile and crashed.[333] ITAR-TASS and RIA Novosti also reported that an An-26 had been shot down by the separatist militia near Torez at around 16:00 local time in what it described as "yet another victory of DPR self-defence".[28][334] There was no evidence about altitude and weapons used.
Shortly after it became evident that the plane was a civilian one, the separatist media denied any involvement in the crash and possession of anti-aircraft missiles capable of reaching this altitude.[25][26][27]
Conspiracy theories
On 18 July Commander of the Donbass People's Militia Igor Girkin was quoted as stating that "a significant number of the bodies weren't fresh". He followed up by saying "Ukrainian authorities are capable of any baseness"; and also claimed that blood serum and medications were found in the plane's wreckage in large quantities.[335] Girkin also claimed that some of the passengers had died a few days before the crash.[336]
The Russian government-funded[337] outlet RT initially said that the plane may have been shot down by Ukraine in a failed attempt to assassinate Vladimir Putin, in a plot which was organised by Ukraine's "Western backers". This was quickly dismissed as Putin's flight route was going hundreds of kilometres north of Ukraine.[338][339]
Other conspiracy theories propagated by Russian media included that the Ukrainians shot down the plane by mistake, drawing parallels to downing Siberia Airlines Flight 1812 in 2001 (reported in July[citation needed] and in December 2014[340]); that Ukrainian air traffic controllers purposefully redirected the flight to fly over the war zone (proven false by the DSB investigation); and that the Ukrainian government organised the attack on the plane to bring infamy upon the pro-Russian rebels.[341]
The number of alternative theories disseminated in Russian mass media started growing as the DSB and JIT investigations increasingly pointed towards the separatists.[342] On 15 November 2014, Russia's Channel One reported on a supposedly leaked spy satellite photo which showed the plane being shot from behind by a Ukrainian Su-25 fighter jet.[343][344] Many other Russian media reprinted the photo but its authenticity was immediately dismissed as the airplanes were out of scale which indicated poor copy-and-paste.[345] Later it was disclosed, that the photo had been initially emailed to the Vice-President of the Russian Union of Engineers by a self-described aviation expert who had found it on a Russian online forum.[346] The aviation expert later apologised, saying that he was unhappy with how the information had been used.[346] In a later interview by magazine The New Yorker, Channel One CEO Konstantin Ernst admitted that reporting on the satellite photo was a "simple error", saying that it was a human mistake not made on purpose.[347]
In July 2014, Sara Firth, who had worked as a correspondent with RT for the previous five years, resigned in protest at the channel's coverage of the crash, which she described as "lies".[348] RT said Firth had left to take another job.[349]
In 2017 Dutch newspaper NRC Handelsblad described how false stories about the MH17 crash had been propagated with the support of Christian Democratic Appeal politician Pieter Omtzigt, who introduced a Russian-speaking Ukrainian man as an "eyewitness" to the crash on a public expert debate in May 2017. The man, who was an asylum-seeker from Ukraine, did not witness the crash and his speech, texted to him by Omtzigt prior to the interview, repeated the Russian-promoted version that Ukrainian jets downed the Boeing.[350]
The "Ukrainian Buk" version
In May 2015 Novaya Gazeta published a report by "a group of Russian military engineers" that came to the conclusion that the airplane was shot down by a Buk-M1 launcher with 9M38M1 missile. The authors also analysed the visible impact traces on the surface of the airplane and suggested that the missile couldn't have been fired from Snizhne, but was instead fired from Zaroshchenske and claimed that a Ukrainian anti-air unit was located there at that time.[351] In June 2015 the report was the subject of a press conference and was attributed to Mikhail Malisevskiy, chief engineer at Moscow-headquartered Almaz-Antey, the Buk missile manufacturer.[352] The Security Service of Ukraine said that there were inaccuracies in this version, and called part of the report a fake.[353] Russian military expert Vadim Lukashevich argued on TV Rain that the spatial orientation of the rocket at the moment of explosion did not exclude the possibility that it was launched from Snizhne, as the report claimed. Lukashevich also noted that the report admitted a Buk missile as the cause of the crash, discrediting the previous theories about the crash (Su-25 etc.) circulated in Russian media.[354] Ukrainska Pravda questioned claims about the Ukrainian anti-aircraft unit and stated that Zaroshchenske was under control of pro-Russian forces on the day of shootdown.[355] Novaya Gazeta published a long analysis by Mark Solonin, also denying the Almaz-Antey version,[356] interviewed inhabitants of Zaroshchenske who denied claims that Ukrainian forces and Buk launchers were present in the village at that time.[357][358] According to Bellingcat, Russia's satellite images were from June and showed signs of editing.[359][360] Bild described the Russian satellite image as "fake".[361]
On 17 September 2018, Russia's Ministry of Defense held a press conference that aimed to cast doubt on Moscow's culpability for the tragedy. Lt. Gen. Nikolai Parshin, chief of the Missile and Artillery Directorate, told that after Dutch investigators displayed parts of the missile and their serial numbers, they studied and declassified archives at the research center that produced the Buk missiles. Parshin said the Russian archives show that the missile that was made of these parts was transported to a military unit in western Ukraine in 1986, and to Russia's knowledge never left Ukraine. Officials also claim that video evidence presented by Joint Investigation Team (JIT), in which the missile that allegedly shot down the plane being moved from Russia into Ukraine, were fabricated.[362]
JIT responded that it had requested Russia in May 2018 on the issue of details about recovered missile parts, but had received no answer. Information from the Russian Ministry of Defense will be carefully studied as soon as the documents were made available, as requested in May 2018 and required by UNSC in 2016. JIT stated it had always carefully analysed information provided by Russia, but information presented to the public was inaccurate on several points. Russia has given differing accounts over time of how MH17 was shot down; for example they also claimed to have evidence (radar image) of Ukrainian fighter fired an air-to-air missile to MH17.[363][364]
Oleksandr Turchynov, secretary of National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine, said in September 2018 that Russia's claim is "yet another failed fake report that the Kremlin made up in order to cover up their crime that has been proven by the official investigation as well as independent experts."[365]
Maps

See also
- List of airliner shootdown incidents
- List of aircraft accidents and incidents resulting in at least 50 fatalities
Notes
- ^ MH is the IATA designator. The flight was also marketed as KLM Flight 4103 (KLM4103) through a codeshare, and has been commonly referred to as "MH17", "Flight 17" or "Flight MH17".
- ^ The aircraft is a Boeing 777-200ER (for Extended Range) model; Boeing assigns a unique customer code for each company that buys one of its aircraft, which is applied as an infix in the model number at the time the aircraft is built. The code for Malaysia Airlines is "H6", hence "777-2H6ER".
- ^ Including:
- 1 dual German-Dutch citizen
- ^ 28 passengers and 15 crew
- ^ Including:
- 1 dual Dutch-Belgian citizen;
- 1 dual Dutch-Israeli citizen;
- 1 dual Dutch-Italian citizen;
- 1 dual Dutch-American citizen;
- 1 dual Dutch-Malaysian citizen[38]
- ^ Including:
- 1 dual British-South African citizen; and
- 1 dual British-New Zealand citizen.
- ^ The family name is Choo, as the Chinese name is Choo Jin Leong (Chinese: 朱仁隆; pinyin: Zhū Rénlóng[48] and Muhd Firdaus note that Ethnic Malays do not have family names.[7][49]
- ^ "A United States official said the missile that shot down the plane was launched from a region near the towns of Torez and Snizhne"[309]
References
- ^ a b c d e Miller, Nick (29 September 2016). "Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 was shot down from pro-Russian rebel controlled territory, investigation finds". Sydney Morning Herald.
- ^ a b c d "MH17 missile 'came from Russia', Dutch-led investigators say". BBC News Online. BBC. 28 September 2016. Retrieved 2 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d "Report: MH17 hit by burst of 'high-energy objects' from outside". CNN. 9 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2014.
- ^ a b c Alexander, Harriet (17 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines plane crashes on Ukraine-Russia border – live". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Higgins, Andrew; Clark, Nicola (9 September 2014). "Malaysian Jet Over Ukraine Was Downed by 'High-Energy Objects,' Dutch Investigators Say". The New York Times.
- ^ a b "Saturday, July 19, 07:30 pm GMT +0800 Media Statement 7 : MH17 Incident". Malaysia Airlines. 19 July 2014. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Crash of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 (PDF) (Report). Dutch Safety Board. 13 October 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 October 2015.
- ^ a b Weaver, Matthew (13 October 2015). "MH17 crash report: Dutch investigators confirm Buk missile hit plane – live updates". the Guardian. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ a b "MH17 missile owned by Russian brigade, investigators say". BBC News. 24 May 2018.
- ^ a b Smith-Spark, Laura; Masters, James (24 May 2018). "Missile that downed MH17 'owned by Russian brigade'". CNN.
- ^ a b Algemene Zaken, Ministerie van; Buitenlandse Zaken, Ministerie van (25 May 2018). "MH17: The Netherlands and Australia hold Russia responsible". www.government.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "MH17 evidence points to 'rogue state' Russia, Tony Abbott says". The Australian.
- ^ a b "U.S. officials believe attack against Malaysian plane was mistake". Los Angeles Times. 22 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d Greg Miller (22 July 2014), U.S. discloses intelligence on downing of Malaysian jet The Washington Post
- ^ "The evidence that may prove pro-Russian separatists shot down MH17". The Washington Post. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "Yatsenyuk: 'We need to survive first'". Kyiv Post. 22 August 2014.
- ^ "No Russian air defense missile systems crossed Russia-Ukraine border – top brass". TASS (in Russian). Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ a b Hartmann, Margaret (22 July 2014), "Russia's 'Conspiracy Theory': MH17 Shot Down by Ukrainian Fighter Jet or Missile", New York, retrieved 20 September 2014
- ^ "Ukraine crisis: Poroshenko offers rebels more autonomy". BBC News. 10 September 2014. Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ Nick Miller (15 July 2015). "MH17 anniversary: In Russia, conspiracy theories on downed plane still find believers".
- ^ "Internet dipenuhi berita konspirasi penembakan MH17".
- ^ "Flight MH17's weirdest conspiracy".
- ^ Sipalan, Joseph (21 June 2019). "Russians made a 'scapegoat' after MH17 report released, says Malaysia PM". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- ^ a b "Wall – VK". archive.org. 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 22 October 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ a b "Сводки от Стрелкова Игоря Ивановича". VKontakte. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ a b Arthur Bright (17 July 2014). "Web evidence points to pro-Russia rebels in downing of MH17 (+video)". The Christian Science Monitor.
- ^ a b Alec Luhn (20 July 2014). "The Guardian 20 July 2014". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ a b c "Donetsk People's Republic militia downs another Ukraine's An-26 plane – eyewitnesses". Information Telegraph Agency of Russia. 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ a b Landay, Jonathan S. "WASHINGTON: U.S. officials still don't know who shot down Malaysian airliner | World". The Bellingham Herald. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ a b "Militants admit to shooting down MH17 – reports". ONE News. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ a b Demirjian, Karoun. "Watch: Ukraine's pro-Russian rebels discuss MH17′s black box in secret recording". The Washington Post. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "'I'm Nearby The Place Where The Bodies Started Falling': Chilling Transcript of Militants Realizing They Shot Down An Airliner With Nearly 300 People Aboard". Business Insider. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ Miranda, Charles (17 July 2015). "The shocking aftermath of MH17". News.com.au. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- ^ "Statement Malaysia Airlines MH17". KLM. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines 9M-MRD (Boeing 777 – MSN 28411) | Airfleets aviation". Airfleets.net. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Larry Copeland (17 July 2014). "Boeing 777 has excellent track record, experts say". Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ "777 Model Orders and Deliveries summary". Boeing. June 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Remains of Shell worker and baby coming home". The Star. 9 September 2014. Retrieved 25 September 2017.
The 35, he added, included restaurateur Jenny Loh Yan Hwa, a passenger with dual citizenship, along with Dutch citizens Fan Shun Po and Paul Goes.
– The Dutch-Malaysian is counted as Dutch on the manifest - ^ "Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17: Top 5 deadliest airliner shootdowns". Reuters. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Lillebuen, Steve (18 July 2014). "Crash claims top AIDS researchers heading to Melbourne". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Robin, Myriam (23 July 2014). "100 AIDS researchers on MH17? Why and how the media got it wrong". Crikey. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ "Senator Witteveen (PvdA) omgekomen bij crash – Binnenland – VK". De Volkskrant. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Victorians among those killed in MH17 crash: Premier". Bendigo Advertiser. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysian actress, Dutch hubby and baby die with MH17". The Malaysian Insider. Archived from the original on 22 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines MH17 crash: 20 families gone in one shot". The Straits Times. 21 July 2014. Archived from the original on 21 July 2014.
- ^ Miranda, Charles; Wockner, Cindy; McPhedran, Ian; Magnay, Jacquelin (22 July 2014). "MH17 train in Kharkiv as Tony Abbott says MH17 aftermath is evidence tampering on industrial scale". News Corp Australia. Archived from the original on 24 July 2015. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "The crew of MH17" (Archive). The Star. 22 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ MH17航班华裔机长父妻均曾就职马航 (in Simplified Chinese). Sina News. 18 July 2014. - The reference contains Choo's name in Chinese characters.
- ^ https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2014/08/22/the-crew-of-mh17
- ^ "MH17 crash: Airlines divert flights from eastern Ukraine". BBC. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Neate, Rupert; Glenza, Jessica (18 July 2014). "Many airlines have avoided Ukrainian airspace for months". the Guardian. Retrieved 12 June 2018.
- ^ "U.S. air carriers to avoid Russia-Ukraine border airspace". Reuters. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ Whitehead, Tom (17 July 2014). "Air operators belatedly avoid Ukraine war zone". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Absturz von Flug MH17: Lufthansa flog zuletzt 56-mal über Kriegsgebiet" [Crash of Flight MH17: Lufthansa lately flew 56 times over crisis region]. Der Spiegel (in German). 18 July 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Donetsk militia takes control of Ukrainian anti-air installation". Voice of Russia. 29 June 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ a b Ополченцы ДНР взяли под контроль воинскую часть ПВО с зенитно-ракетными комплексами "Бук" [DNR militias seized an air defence base with anti-aircraft missile systems "Buk"] (in Russian). Information Telegraph Agency of Russia. 29 June 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Донецкие ополченцы обзавелись зенитно-ракетными комплексами "Бук" [Donetsk militias acquired anti-aircraft missile systems "Buk"]. NTV News (in Russian). NTV. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Panda, Ankit (17 July 2014). "Malaysian Airlines Flight MH17 Shot Down Over Donetsk, Ukraine". The Diplomat. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Ополченцы сообщили, из чего сбили украинский Ан-26". Vzglyad. 14 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
Today the self-defence destroyed An-26 airplane using SAM "9К37М1" (better known as 'Buk') ... said the militia, distributed in social networks [translation after ellipsis from Google translate]
- ^ a b c Peter Baker (18 July 2014), U.S. Sees Evidence of Russian Links to Jet's Downing The New York Times
- ^ "Ukraine conflict: Russia accused of shooting down jet". BBC News. London. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Russia Rejects 'Absurd' Accusation Over Downed Ukrainian Jet". RFE/RL. Prague: RFE/RL. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Netherlands knew about dangers of flying over Donbas prior to the MH17 tragedy. Ukrayinska Pravda. 24 January 2015
- ^ Vertrouwelijkheid MH17 is onzin. De Telegraaf. 23 January 2015
- ^ Communication was lost with the plane AN26 of ATO forces in the Luhansk region. LIGANews. 14 July 2014
- ^ In Luhansk Oblast militants downed Ukrainian plane, pilot was ejected – witnesses. Ukrainian Independent Information Agency. 14 July 2014
- ^ "Polish politics: Where is Radek?". The Economist. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Peter Leonard (17 July 2014). "Ukraine: Air Force jet downed by Russian missile". ABC News. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 13 January 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d Yuras Karmanau; Peter Leonard (25 July 2014). "What happened? The day Flight 17 was downed". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 9 October 2014. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Daily Telegraph, 14 November 2014,the unlikely pilgrimage site of saur mogila
- ^ "What Is the Altitude of a Plane in Flight?". traveltips.usatoday.com. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ "MH17 Crash" (PDF). Dutch Safety Board. p. 180. Retrieved 16 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Maps of the Crash of Malaysia Airlines Flight 17". The New York Times. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ Freed, Jamie (20 July 2014). "Ukraine responsible for airspace safety: IATA". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Tom Whitehead; Nick Collins; Martin Evans (18 July 2014). "MH17 disaster: Flights over war zones 'because it's cheaper". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "17 июля в зону АТО должен был вылететь транспортный Ан-26 с украинскими десантниками" [On 17 July an An-26 transport was to fly with Ukrainian paratroopers] (in Russian). 10 June 2015. Retrieved 10 June 2015.
- ^ a b "MH17 Malaysia plane crash in Ukraine: What we know". BBC News. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines crash: video believed to show moment of plane's impact". The Telegraph. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Nelson, Sara C (17 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 'Shot Down in Ukraine Near Russian Border'". The Huffington Post. United Kingdom. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Maleisisch passagiersvliegtuig in Oekraïne neergestort" [Malaysian passenger aircraft shot down in Ukraine]. De Telegraaf (in Dutch). 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Cahal Milmo (19 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines MH17 crash: No forensic investigators, co-ordination or body bags as Ukraine locals are left to scour gruesome scene". The Independent. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Official: 181 bodies found at MH17 crash site". The Hindu. Associated Press. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Raw: Crews begin moving bodies at jet crash site". USA Today. Associated Press. 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Miller, Nick (19 July 2014). "MH17: 'Unknown groups' use body bags". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Grytsenko, Oksana. "MH17: armed rebels fuel chaos as rotting corpses pile up on the roadside". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Rutte geschokt over 'respectloos gedrag' op rampplek" (in Dutch). Nu.nl. 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Laura de Jong (21 July 2014). "Rutte: 'Zorgvuldiger met lichamen omgegaan dan werd gevreesd'". de Volkskrant (in Dutch).
- ^ Sonne, Paul; Alexander Kolyandr, Margaret Coker (20 July 2014). "Bodies Removed From MH17 Crash Site Human Remains Moved to Railcars at Torez Station". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17 plane crash: Dutch experts examine bodies". BBC. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17 plane crash: Train with bodies leaves Ukraine station". BBC News. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Marlow, Iain (21 July 2014). "MH17: Malaysia reaches 'behind the scenes' deal to recover bodies". The Globe and Mail. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Obama calls for Russia 'pivot' on Ukraine as MH17 investigation begins". Al Jazeera. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Higgins, Andrew (22 July 2014). "Bodies of Crash Victims Safely Moved Out of Combat Area". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ McGeough, Paul (23 July 2014). "MH17 crash: families' worst fears realised as bodies go missing". The Age. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ a b "Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17: British Investigators Join Probe in Ukraine Amid Fears of Evidence Tampering". The Huffington Post. 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17 bodies leave Ukraine rebel area and reach Kharkiv". BBC News. 22 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "Netherlands to coordinate MH17 victim identification efforts | Business Standard News". Business Standard. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Tony Abbott announces Operation Bring Them Home to secure and identify victims of Malaysia Airlines disaster – ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Heather Saul (23 July 2014). "MH17 crash victims: First bodies arrive in Netherlands from Ukraine". The Independent.
- ^ "Weer 74 kisten naar Hilversum". NOS (in Dutch). 24 July 2014.
- ^ "Hilversum treft voorbereidingen voor lichamen MH17". Nieuws.nl. 22 July 2014. Archived from the original on 23 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Parfitt, Tom (1 August 2014). "Dutch and Australian police to use drones, divers and sniffer dogs in perilous search for victims". The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ "MH17 investigators frustrated at limited access due to fighting". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ a b "Australia says all MH17 bodies should be retrieved from crash site within days". The Guardian. Australian Associated Press. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- ^ a b Toby Sterling, "Dutch premier halts search for Ukraine victims," Associated Press, 6 August 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2014. Archived 18 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Helen Davidson and agencies (6 August 2014). "MH17 crash: search for remains halted as Australia begins day of mourning". The Guardian. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "MH17 bodies arrive in Malaysia". Agence France-Presse in Kuala Lumpur. 21 August 2014. Retrieved 22 August 2014.
- ^ TheStar (22 August 2014). "MH17 day of mourning: White hearses arrive at KLIA".
- ^ Grindstad, Ingrid (5 December 2014). "Six MH17 victims remain unidentified". NL Times. Retrieved 6 December 2014.
- ^ Anthony Deutsch (2 February 2015). "Dutch search team recovers remains, MH17 wreckage in Ukraine". Reuters. Retrieved 16 April 2015.
- ^ a b "Dutch investigators recover human remains from MH17 crash site". Agence France-Presse. 21 April 2015. Retrieved 23 April 2015.
- ^ Adam Withnall (21 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines MH17 crash: Dutch newspapers respond with anger and despair as wait for return of bodies continues – Europe – World". The Independent. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "Dutch Banks Respond to Reports of MH17 Victims' Looted Credit Cards". NBC News. 19 July 2014. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Mendick, Robert; Sawer, Patrick; Ross, Time (19 July 2014). "MH17: Malaysia Airlines crash victims robbed of their dignity by rebels". The Telegraph. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Wagner, Meg (18 July 2014). "Heartless looters raid Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 crash site, swipe victims' luggage, personal items". Daily News. New York. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Shaun Walker with Harriet Salem and Josh Halliday, "MH17: world's anger at Russia grows as bodies pile on to train at crash site," The Guardian, 21 July 2014. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- ^ Hammond, Jeremy (3 July 2017). "The 'Forgotten' US Shootdown of Iranian Airliner Flight 655". Foreign Policy.
- ^ Kaplan, Fred. "America's Flight 17: The time the United States blew up a passenger plane—and tried to cover it up". Slate.
- ^ Gusterson, Hugh (27 July 2014). "In Malaysia Airlines tragedy, echoes of a US act". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists.
- ^ Gupta, Samarth (28 July 2014). "Hidden Hypocrisy". Harvard Political Review. Archived from the original on 27 September 2016.
- ^ Pillar, Paul R. (24 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 and Iran Air Flight 655". The National Interest. Archived from the original on 13 October 2015.
- ^ "Air India flight with 126 on board was right behind MH 17". The Times of India. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 12 November 2014.
- ^ Jansen, Bart (18 July 2014). "Malaysia will stop using No. 17 next week". USA Today. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Malaysia Airlines retires flight number after Ukraine crash". 21 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines Cancels Amsterdam / Paris Routes from late-Jan 2016". Airlineroute.net. 3 December 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines Shares Tank". Business Insider. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Ukraine: missiles that brought down jets may have been fired from Russia". Retrieved 19 September 2014.
- ^ a b "Malaysia Airlines MH17: Russia rebukes push for UN tribunal". CBC News. 10 July 2015. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- ^ a b Michelle Nichols (29 July 2015). "Russia vetoes bid to set up tribunal for downed Flight MH17". Reuters.
- ^ Loiko, Sergei. "The Unraveling of Moscow's 'Novorossia' Dream". Radio Free Liberty.
- ^ Anthony Deutsch (11 November 2014). "Where are the bodies, MH17 families ask". Reuters. Retrieved 11 November 2014.
- ^ Wall, Robert (27 August 2015). "Final Report on Downing of Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 Due October". The Wall Street Journal.
- ^ a b c "JIT: MH17 shot down with missile fired from pro-Russian rebel controlled field".
- ^ Lévesque, Julie (3 December 2014). "MH17 investigation – why is Malaysia excluded?". eTN Global Travel Industry News. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ^ Parker, Andrew; Olearchyk, Roman (21 July 2014). "Netherlands to lead MH17 investigation". Financial Times. Financial Times Ltd. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Bewerkt door: redactie. "Nederlandse leidersrol krijgt juridische basis −0 Vliegtuigcrash in Oekraïne – VK". De Volkskrant. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ "Dutch Safety Board heads investigation: investigation effort in full swing, black boxes currently being read out" (PDF). onderzoeksraad.nl. Dutch Safety Board, The Hague. 23 July 2014. Archived from the original on 19 September 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) () - ^ "Press statement by the Trilateral Contact Group". Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. 18 July 2014. Archived from the original on 8 September 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Walker, Shaun. "MH17: pro-Russia rebels will allow access to crash site if ceasefire agreed". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines MH17 black boxes reportedly recovered, Russia denies it will take them from rebels". National Post. 22 May 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Walker, Shaun; Salem, Harriet. "Ukraine rebels hand over MH17 black boxes and let train carrying bodies leave". The Guardian. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ "Розслідування катастрофи літака Boeing 777". NBAAI. 18–25 August 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Investigation crash MH17, 17 July 2014." Dutch Safety Board. Retrieved 22 August 2014. "Ukraine has transferred responsibility for investigating the cause of the crash to the Dutch Safety Board. The request came from Ukraine. This request was made because the flight departed from the Netherlands, and due to the large number of Dutch nationals who died in the crash"
- ^ "MH17 misbruikt voor opvoeren spanning met Rusland". NOS (in Dutch). 26 October 2016. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ^ "MH17 plane crash: Dutch experts examine bodies". BBC. 21 July 2014. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "MH370 search coordinator to lead Australia's MH17 probe Panel". news.biharprabha.com. Indo-Asian News Service. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Wroe, David (13 June 2017). "Tony Abbott's office floated sending Australian troops into Ukraine conflict, defence expert claims". The Sydney Morning Herald. Fairfax Media. Retrieved 13 October 2017.
In the end, Australia quietly deployed about 200 special forces soldiers in a low-key role supporting police investigators.
- ^ "MH17 investigators reach crash site two weeks after plane brought down". The Guardian. 1 August 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Summary Report of a Briefing at Civil Service Level". House of Representatives. 28 July 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ Kolyandr, Alexander; Steinhauser, Gabriele (30 July 2014). "Still No Safe Passage to Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 Crash Site in Eastern Ukraine". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ^ "21 More MH17 Crash Victims Identified, Experts Leave Site". Outlook India. Press Trust of India. 8 August 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2014.
- ^ "Netherlands deploys more experts to probe MH17 crash". CNN-IBNLive. Press Trust of India. 13 September 2014. Retrieved 14 September 2014.
- ^ "Additional MH17 crash investigators return to Netherlands". Oneindia.in. 20 September 2014. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ "Dutch Experts Help Recover MH17 Crash Items Despite Nearby Clashes". Newsweek. 13 October 2014. Retrieved 13 October 2014.
- ^ "MH17 crash: Dutch salvage team 'unable to start'". BBC. 11 November 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2014.
- ^ "Ukraine crisis: Timeline". BBC. 13 November 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Dutch complete recovery of Malaysia Airlines wreckage in eastern Ukraine". ABC News. Agence France-Presse. 24 November 2014. Retrieved 24 November 2014.
- ^ Dearden, Lizzie (11 August 2015). "MH17 crash: Investigators find possible parts of Buk missile used to shoot plane down". The Independent. Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ "Investigation into possible Buk-missile-parts". Landelijk Parket. Openbaar Ministerie (Dutch public prosecution service). Retrieved 11 August 2015.
- ^ Ensor, Josie (19 July 2014). "MH17: what we know two days after Malaysia Airlines crash over Ukraine". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Thijssen, Wil (19 July 2014). "De bewijsstukken: Wie schoot MH17 neer?". de Volkskrant (in Dutch). Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ a b Vartabedian, Ralph; Hennigan, W.J. (17 July 2014). "High-tech spycraft tracked missile's path to Malaysia Airlines jet". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ a b Robert Mendick (27 July 2014) MH17: why the culprits may never be caught The Daily Telegraph
- ^ a b "MH17 likely shot down by mistake by Russian separatists, US intelligence official says". ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation). 23 July 2014. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ "SBU releases more conversations implicating Russia in shooting down Malaysia Airlines flight (VIDEO, TRANSCRIPT)". Kyiv Post. 14 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Wreckage Offers Clues on Why Flight 17 Went Down". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ Rose Powell (22 July 2014). "Photo of MH17 wreckage proves missile attack, claims report". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ Catherine A. Fitzpatrick (27 July 2014). "Evidence of Separatists' Possession of Buk System Before Downing of MH17". The Interpreter Magazine. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- ^ a b Catherine A. Fitzpatrick (13 August 2014). "Novaya Gazeta Editor: Boroday Called Moscow Press About Downing of Civilian Airliner". The Interpreter Magazine. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- ^ Бугоркова, Ольга (28 September 2016). "Катастрофа MH17: как менялись версии российских СМИ". BBC Русская служба. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ Rick Feneley. "Attack on Flight MH17: After the tragedy, the accusations rain down". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Ultimate responsibility lies with Putin". The Age. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ "Web evidence points to pro-Russia rebels in downing of MH17 (+video)". The Christian Science Monitor. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ a b Walker, Shaun. "Ukrainians report sightings of missile launcher on day of MH17 crash". The Guardian. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ Polityuk, Pavel; Piper, Elizabeth (19 July 2014). Ireland, Louise (ed.). "Ukraine says has 'compelling evidence' Russian crew shot down Malaysian plane". Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Ракетним комплексом "Бук", який збив Boeing-777 керували росіяни, – СБУ (Missile complex "BUK", that shot Boeing-777 was managed by Russian citizens) – Espreso.tv (leading Ukrainian news agency)". Espreso.tv. 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Schofield, Matthew. "Ukraine video claims proof of Russia-supplied anti-aircraft system". Mcclatchydc.com. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ Gregory, Paul Roderick (18 July 2014). "Smoking Guns: Russian Separatists Shot Down Malaysian Flight MH17; Putin Must Be Held Responsible". Forbes.
- ^ Gregory, Paul Roderick (19 July 2014). "Here Are The Intercepted Transcripts Indicating Russian Rebels Shot Down Malaysian Flight MH17". Forbes. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "Бес отверг обвинения в уничтожении "Боинга"". Lenta.ru. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2014.
- ^ Leonard, Peter; Chernov, Mstyslav. "Both sides in Ukraine deny shooting down plane". Associated Press. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysian plane was shot down by rebels, intercepted phone calls prove, Ukraine's president says". National Post. Associated Press via Postmedia Network. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "The Guardian 29 July 2014". The Guardian. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "Separatists planned terrorist attacks against Aeroflot aircraft on day of MH17 crash as pretext for Russian invasion into Ukraine- SBU chief", Radio Ukraine International, 7 August 2014, archived from the original on 29 November 2014, retrieved 21 November 2014
- ^ Dolgov, Anna (8 August 2014). "Ukraine Says Rebels Mistook Doomed Flight MH17 for Aeroflot Plane". Moscow Times. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ^ "Terrorists and militants planned cynical terrorist attack at Aeroflot civil aircraft", Security Service of Ukraine, 7 August 2014, archived from the original on 21 July 2015, retrieved 7 June 2015
- ^ Cremonesi, Lorenzo (22 July 2014). "Così è stato colpito l'aereo" [So the plane was struck]. Corriere della Sera (in Italian). Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ Konrad Schuller (22 July 2014). "Separatisten am Abschussort sollten Piloten festnehmen" [Separatists at the crash site should capture pilots]. Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. Retrieved 2 October 2014.
- ^ Stewart, Phil; Hosenball, Mark (19 July 2014). "U.S scrambles to determine who fired Russian-made missile at jet". Reuters. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ M.J.S. (18 July 2014). "Flight MH17: The Evidence". The Economist. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- ^ Ishaan Tharoor – The evidence that may prove pro-Russian separatists shot down MH17 – The Washington Post – 20 July 2014. Retrieved 3 August 2014.
- ^ Paul McGeough (14 June 2012). "Ukraine war zone tempers Federal Police attempts to access MH17 crash site". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- ^ "Britain says highly likely MH17 shot down by Russian-supplied missile". Reuters. 26 July 2014. Retrieved 4 August 2014.
- ^ "US Claims of Flight MH17 Downing by Militia Remain Unfounded – Russia's Defense Ministry". RIA Novosti. 24 July 2014.
The United States has not yet provided any documented evidence to prove that the rocket that brought down the Malaysia Airlines Boeing 777 was launched from militia-controlled territory, Russian Deputy Defence Minister Anatoly Antonov said on Thursday.
- ^ Razumovskaya, Olga (21 July 2014), "Russia Presents Its Account of Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 Crash", The Wall Street Journal, retrieved 20 September 2014
- ^ Razumovskaya, Olga (22 July 2014). "Russia Presents Its Account of Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 Crash". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "General designer of Su-25 says aircraft couldn't have shot down MH17". Ukraine Today. 11 March 2015. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ "MH17-Absturz kontert Kritik mit neuen Satellitenbildern". De Zeit (in German). 12 June 2015. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- ^ Anton Zverev (23 July 2014). "Ukraine rebel commander acknowledges fighters had Buk missile". Reuters.
- ^ Shaun Walker in Donetsk. "MH17: Ukraine separatist commander 'admits' rebels had Buk missile system". The Guardian. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Buckley, Neil (4 July 2014). "Separatist leader admits Ukraine rebels held Buk missile system". Financial Times. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Walker, Shaun. "MH17: Ukraine separatist commander 'admits' rebels had Buk missile system". The Guardian. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Lanting, Bert (4 November 2014). "Wij hadden raket, maar haalden MH17 niet neer". de Volkskrant (in Dutch). Retrieved 4 November 2014.
- ^ Natasha Culzac (28 July 2014). "MH17 crash: Black boxes show plane suffered 'massive explosive decompression' following shrapnel hit – Europe – World". The Independent. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
- ^ Sweeney, John (8 September 2014). "MH17 disaster: Russians 'controlled Buk missile system'". BBC News. Retrieved 9 September 2014.
- ^ "Is The MH17 Joint Investigation Team Avoiding The Question of Kremlin Guilt?". Forbes. 2 April 2015. Retrieved 3 April 2015.
- ^ Ostanin, Iggy (8 September 2014). "Images Show the Buk that Downed Flight MH17, Inside Russia, Controlled by Russian Troops". Bellingcat. Retrieved 9 September 2014.
- ^ "Ostukraine: BND macht Separatisten für MH17-Absturz verantwortlich" [Eastern Ukraine: BND says separatists are responsible for MH17 crash]. Der Spiegel (in German). 19 October 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- ^ "Germany says Ukraine rebels downed MH17 with seized missiles: report". Agence France-Presse. 20 October 2014. Retrieved 20 October 2014. "He also said Ukrainian photos had been "manipulated", the magazine reported but did not elaborate on what the pictures showed, who had provided them or altered them."
- ^ "Deadly Ukraine Crash: German Intelligence Claims Pro-Russian Separatists Downed MH17". Der Spiegel. 19 October 2014. Retrieved 19 October 2014.
- ^ Bellingcat MH17 Investigation Team (8 November 2014). "MH17: Source of the Separatists' Buk" (PDF). Bellingcat. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 16 May 2015.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Gorchinskaya, Katya; Lavrov, Vlad (9 November 2014). "Journalists find 'solid' Russian ties to missile that hit MH17". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
- ^ Tucker, Maxim (22 June 2015). "Meet Eliot Higgins, Putin's MH17 Nemesis". Newsweek. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- ^ "Bellingcat: New evidence against Russian soldiers on MH17". DW.COM. Retrieved 4 May 2016.
- ^ "bellingcat – The Lost Digit: Buk 3x2 – bellingcat". bellingcat. Retrieved 4 May 2016.
- ^ "Ooggetuige MH17: 'Mijn doel is rechtvaardigheid'" [Eyewitness of MH17: "My goal is justice"]. RTL News (in Dutch). 22 December 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ^ "New Competing Claims on Downing of MH17". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 24 December 2014.
- ^ "Глава ДНР о крушении MH17: "Я видел, как это происходило"" [Head of the DPR about the crash of MH17: "I saw how it happened"]. RIA News (in Russian). 25 December 2014. Retrieved 26 December 2014.
- ^ "Kremlin-backed insurgent leader claims personally witnessing Ukrainian aircraft shooting down MH17". Ukraine Today. 25 December 2014.
- ^ Tucker, Maxim (10 January 2015). "New report says it proves Russian forces downed flight MH17". Kyiv Post. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Robert Coalson (13 May 2015). "Evidence mounts that Russia supplied the missiles that shot down MH17 in Ukraine". Business Insider. Retrieved 13 June 2015.
- ^ Anton Zverev. "Exclusive: From 'Red October' village, new evidence on downing of Malaysian plane over Ukraine". Reuters. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ "Full transcript: Russian-backed rebels ransack the wreckage of MH17 in shocking 17-minute video". news.com.au. 17 July 2015. Archived from the original on 17 July 2015. Retrieved 17 July 2015.
- ^ "Examining the Evidence of Russia's Involvement in a Malaysia Airlines Crash". Stratfor. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ "Preliminary report – Crash involving Malaysia Airlines Boeing 777-200 Flight MH17" (PDF), DSB, 17 July 2014, retrieved 24 September 2014
- ^ Prof. mr. dr. Erwin Muller. "Investigation crash MH17, 17 July 2014 Donetsk". Dutch Safety Board. Onderzoeksraad voor Veiligheid. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ "Dutch board says Russian-made missile downed MH17". 13 October 2015.
- ^ "Investigation crash MH17, 17 July 2014". onderzoeksraad.nl. Dutch Safety Board. Archived from the original on 19 September 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) () - ^ Abeyratne, Ruwantissa (1 December 2014). "Flight MH 17 and State Responsibility for Ensuring Safety and Security of Air Transport". Journal of Transportation Security. 7 (4): 347–348. doi:10.1007/s12198-014-0148-0. ISSN 1938-7741.
- ^ "Dutch Safety Board: MH17 brought down by missile in airspace that should have been closed". ASN News. 13 October 2015. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ "MH17 report: Five key findings from the Dutch Safety Board". BBC News. 13 October 2015. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ Mu Xuequan, ed. (15 August 2014), MH17 criminal investigation largest ever in the Netherlands, archived from the original on 26 August 2014, retrieved 27 October 2014
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - ^ MH17 crash: Investigation focuses on '25 metal shards', BBC News, 12 September 2014, retrieved 27 October 2014
- ^ a b "MH17: Malaysia accepted as full member of probe team". The Star. Petaling Jaya, Malaysia. 1 December 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2014.
- ^ "Speculation on MH17 is damaging to investigations". Free Malaysia Today. Bernama. 22 November 2014. Archived from the original on 29 November 2014. Retrieved 22 November 2014.
- ^ van Oosterom, Karel J.G (16 December 2014). "Letter to President of the UNSC" (PDF). Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ^ "US Submits Classified Information on MH17 to Investigators: State Dep't". Sputnik. 17 December 2014. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- ^ "Call for witnesses". Joint Investigation Team. Retrieved 30 March 2015.
- ^ MH17 Politie [Police] International Joint Investigation Team
- ^ van der Graaf, Jolande (9 April 2015). "Tientallen bruikbare tips over MH17" [Dozens of useful tips about MH17]. De Telegraaf (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- ^ Van Jaarsveldt, Janene (9 April 2015). "Hundreds respond to call for MH17 witnesses". NL Times. Retrieved 17 June 2015.
- ^ "Examining the Evidence of Russia's Involvement in a Malaysia Airlines Crash". Stratfor. Retrieved 13 May 2016.
- ^ "The image Russia doesn't want the world to see". NewsComAu. Retrieved 16 May 2016.
- ^ "Wat we niet mogen zien: 147 documenten MH17 blijven geheim". RTL Nieuws. Retrieved 30 July 2015.
- ^ "Presentation preliminary results criminal investigation MH17 28-09-2016".
- ^ ""The purpose is to bring MH17 matter to court"". Новая газета – Novayagazeta.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 16 October 2017.
- ^ a b c "Update in criminal investigation MH17 disaster". Openbaar Ministerie. 24 May 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ^ a b "Владимир Путин пообещал изучить выводы следствия о катастрофе Boeing MH17". Kommersant (in Russian). 24 May 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2018.
- ^ The Associated Press (25 May 2018). "Netherlands, Australia holding Russia 'accountable' for downing of MH17". CBC News. Retrieved 25 May 2018.
- ^ "Internationale reacties op MH17: Rusland moet verantwoordelijkheid nemen". NOS (in Dutch). 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "Foreign Secretary statement on the MH17 investigation". Foreign & Commonwealth Office. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "Declaration by the High Representative on behalf of the EU on the findings of the Joint Investigation Team on the downing of flight MH17". European Council. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "Die Schuldigen ermitteln". Bundesregierung (in German). 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "Calling Russia To Account for Malaysia Airlines Flight MH-17". United States Department of State. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "Statement by the NATO Secretary General on MH17 investigation". NATO. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ "St Petersburg International Economic Forum plenary session". Kremlin. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ Sipalan, Joseph (20 June 2019). "Malaysian PM says Russia being made a scapegoat for downing of flight MH17". Reuters. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ^ Deutsch, Anthony (23 June 2015). "Exclusive: International tribunal looks like best chance for MH17 justice – Dutch sources". Reuters. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- ^ "Russia rejects calls for UN tribunal to prosecute MH17 suspects". The Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 26 June 2015. Retrieved 28 June 2015.
- ^ Edith M. Lederer (20 July 2015). "Russia's UN Draft on MH17 Crash Doesn't Call for Tribunal". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 22 July 2015.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ^ "Statement by the minister of Foreign Affairs on MH17, 5 July 2017". Government of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Minister of Security and Justice signs MH17 treaty with Ukraine". Government of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Ministry of Security and Justice. 7 July 2017.
- ^ "Verdrag tussen het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden en Oekraïne inzake internationale juridische samenwerking met betrekking tot misdrijven die verband houden met het neerhalen van vlucht MH17 van Malaysia Airlines op 17 juli 2014". Tractatenblad van het Koninkrijk der Nederlanden. 7 September 2018.
- ^ "Legislation Clears Way for MH17 Trials in the Netherlands". Bloomberg.com. Associated Press. 21 March 2018. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- ^ "Dutch court may be allowed to prosecute those involved in MH17 crash by video link". UNIAN. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ "MH17 - Russian GRU Commander 'Orion' Identified as Oleg Ivannikov". bellingcat. 25 May 2018. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ Hall, Kevin (26 May 2018). "How an online purchase helped find the Russian blamed for downing MH17". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ "Four charged with shooting down MH17 plane". BBC News Online. Retrieved 19 June 2019.
- ^ "Prosecution of four suspects for downing flight MH17". Openbaar Ministerie. 19 June 2019. Retrieved 19 June 2019.
- ^ "The Arrest of Vladimir Tsemakh and Its Implications for the MH17 Investigation". bellingcat. 9 July 2019. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ^ "Кремль признал "своим" водителя "Бука" Владимира Цемаха и требует обменять его на Сенцова". The Insider (in Russian). 30 August 2019. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ^ a b Gershkovich, Evan (7 September 2019). "Signaling Readiness for Thaw, Russia and Ukraine Swap Prisoners: The exchange brings peace talks between the neighboring countries closer, analysts say". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 7 September 2019.
- ^ a b c Lapin, Denis; Pavlova, Olga; Britton, Bianca; Dean, Sarah (7 September 2019). "Film director Oleg Sentsov and MH17 suspect among those freed in Russia-Ukraine prisoner swap". CNN. Retrieved 7 September 2019.
- ^ Olearchyk, Roman; Foy, Henry (5 September 2019). "Ukraine court releases man of interest to MH17 probe on bail: Move raises speculation he could be part of imminent prisoner swap between Kiev and Moscow". Financial Times. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ^ a b c "Nederland vraagt Rusland om MH17-verdachte: Het Openbaar Ministerie heeft Rusland gevraagd MH17-verdachte Vladimir Tsemach uit te leveren. Dat liet het OM de nabestaanden van de vliegramp vanmiddag weten. Nederland betreurt zeer dat Oekraïne de Oekraïense separatist überhaupt aan Rusland heeft overgedragen" [The Netherlands asks Russia for MH17 suspect: The Public Prosecution Service has asked Russia to extradite MH17 suspect Vladimir Tsemach. The OM informed the relatives of the plane crash this afternoon. The Netherlands deeply regrets that Ukraine has handed over the Ukrainian separatist to Russia at all.]. AD.nl (in Dutch). 7 September 2019. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ^ "Dutch did question MH17 witness before he was returned to Russia: minister". DutcNews.nl. 8 September 2019. Retrieved 9 September 2019.
- ^ "MH17 Witness Appeal November 2019". politie.nl. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ^ "MH17 disaster: Phone-taps 'show Russia directed Ukraine rebels'". BBC News. 14 November 2019. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
- ^ Toler, Aric. "British Intelligence Report Confirms Russian Military Origin of MH17 Murder Weapon". Bellingcat. Retrieved 21 December 2017.
- ^ "ISCP Annual Report 2016-2017" (PDF).
- ^ [1]. MH-17-Russian-separatist-leader-sued-for-900-million-by-crash-victims
- ^ "MH17 crash: Victims' families sue Putin and Russia". BBC News. Retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ^ Blakkarly, Jarni (22 May 2016). UPDATE 1-Australian firm names Russia, Putin in MH17 compensation claim -report. Reuters. Retrieved: 22 May 2016.
- ^ "Nabestaanden MH17 naar Europees Hof voor schadeclaim tegen Rusland". NOS (in Dutch). 25 May 2018. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ^ Yap Tzu Ging (15 July 2016). "MH17 kin sue Malaysia Airlines, seek damages ahead of lawsuit deadline". Malay Mail Online.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines sued by relatives of MH17 crew shot down over Ukraine". The Associated Press. 2 June 2016.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines crash: President Poroshenko calls shooting down of Malaysian plane an 'act of terrorism'". The Daily Telegraph. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia to Work with Russia, Ukrainian Governments on MH17". English.cri.cn. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysian PM Demands Swift Justice if Plane Was Shot Down". Voice of America. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- ^ Yong Yen Nie (18 July 2014). "Malaysia Airlines MH17 crash: Flags to fly at half-mast over next three days, says Najib". Straits Times Asia Report. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Verklaring premier Rutte over crash MH17 | Binnenland". De Telegraaf (in Dutch). Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Statement of His Majesty King Willem-Alexander on Malaysian Flight MH17". Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Netherlands Embassy in Washington, D.C., United States. 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 18 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Timmermans mee met onderzoekers naar Oekraïne". ANP (in Dutch). 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Novum (17 July 2014). "Vlaggen overheidsgebouwen halfstok na vliegramp" (in Dutch). Nieuws.nl. Archived from the original on 26 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Novum (18 July 2014). "Vierdaagse Nijmegen: muziek geschrapt wegens vliegramp" (in Dutch). nieuws.nl. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Thomas Escritt; Angus MacSwan (21 July 2014). "Netherlands opens war crimes investigation into airliner downing". Yahoo! News.
- ^ Marije Willems (22 July 2014). "Terugluisteren en -lezen: de indrukwekkende speech van Timmermans". NRC.
- ^ Jeronimus; et al. (2018). "Acute stress responses after indirect exposure to the MH17 airplane crash". British Journal of Psychology. 0: 1–24. doi:10.1111/bjop.12358.
- ^ a b Maiden, Samantha (19 July 2014). "MH17: Russia says Tony Abbott 'operating only on speculation' in his tough stance over separatist involvement in plane tragedy". The Daily Telegraph. Australia. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines MH17: Russia says Tony Abbott's comments blaming separatists are 'unacceptable', Julie Bishop criticises Moscow for lack of talks – ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Prime Minister Tony Abbott hits out at 'shambolic' recovery effort; Government considers listing outrage as terrorist act; rebels move bodies to refrigerated train – ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation)". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Sabra Lane (13 October 2014). "Tony Abbott promises to 'shirtfront' Putin at G20 Summit". 7:30. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ Путин: за авиакатастрофу несет ответственность Украина [Putin: Ukraine responsible for the crash] (in Russian). RIA Novosti. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
"Безусловно, государство, над территорией которого это произошло, несет ответственность за эту страшную трагедию", – сказал глава РФ
- ^ a b "Joe Biden: Malaysia Airlines flight 'apparently' shot down". MSNBC. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysia Airlines MH17 plane crash in Ukraine LIVE UPDATES". RT. 17 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Silke Mülherr und Inga Pylypchuk (26 July 2014). "Putin realisiert, dass er die Falschen bewaffnete". Die Welt (in German). Retrieved 1 August 2014.
- ^ "Russian Hybrid Warfare" (PDF). Danish Institute for International Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2017.
- ^ Mason, Jeff; Holland, Steve (18 July 2014). "White House urges Ukraine ceasefire for plane probe, Obama talks to Putin". Reuters. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ a b Shear, Michael D.; Sengupta, Somini; Tavernise, Sabrina (18 July 2014). "Obama Points to Pro-Russia Separatists in Downing of Malaysia Airlines Plane". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Leonard, Peter. "Ukraine: 295 on Malaysia plane shot down over east". Associated Press. The Big Story. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17 plane crash: David Cameron urges those responsible for downing jet to be 'held to account'". The Daily Telegraph. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ David M. Herszenhorn (25 July 2014), Russia Steps Up Help for Rebels in Ukraine War, The New York Times.
- ^ "Onthulling Nationaal Monument MH17: 'Deze dag sloeg een gat in ons leven'". NOS (in Dutch). 17 July 2017. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ^ "EUROPA PRESS RELEASES – Press release – Joint statement by the President of the European Commission, José Manuel Barroso, and the President of the European Council, Herman Van Rompuy, on the crash of the Malaysian airliner in Ukraine". Europa (web portal). 17 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysian plane MH17 crash investigators face struggle : Asia, News". India Today. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ "Ukraine Requests ICAO Assistance in MH17 Accident Investigation". ICAO. 18 July 2014. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ "ICAO Clarifies State Responsibilities Arising from Conflict Zones". ICAO. 24 July 2014. Retrieved 10 October 2014.
- ^ "Australia mourns MH17 victims at memorial service". ITV News. 20 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Woensdag 23 juli dag van nationale rouw | nu.nl/binnenland | Het laatste nieuws het eerst op". Nu.nl. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "Malaysian Airlines Flight MH17: Netherlands Declares National Day of Mourning For MH17 Victims". International Business Times. 20 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Jahshan, Elias (20 July 2014). "AIDS 2014 opening ceremony tinged with sombre mood". Star Observer. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Leyl, Sharanjit (21 July 2014). "MH17 crash: Malaysians mourn at makeshift memorials". BBC News. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Russian newspaper Novaya Gazeta prints front-page apology for MH17 disaster in Dutch". News.com.au. 25 July 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ Groll, Elias (25 July 2014). "Russian Paper Issues Front Page Apology to Netherlands for MH17". Foreign Policy. Retrieved 25 July 2014.
- ^ Adamczyk, Ed (22 July 2014). "Russia offers alternate scenarios for Malaysia Airlines crash". United Press International. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
Russian media offers explanations conflicting with the information provided by the rest of the world.
- ^ Ioffe, Julia (20 July 2014). "The Russian Public Has a Totally Different Understanding of What Happened to Malaysia Airlines Flight 17: And it's more of a problem than you think". New Republic. Archived from the original on 21 July 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
The picture of the catastrophe that the Russian people are seeing on their television screens is very different from that on screens in much of the rest of the world, and the discrepancy does not bode well for a sane resolution to this stand-off
- ^ "The Kremlin's Shifting, Self-Contradicting Narratives on MH17 - bellingcat". bellingcat. 5 January 2018. Retrieved 5 January 2018.
- ^ "Катастрофа "Боинга" под Донецком". Levada.ru. 30 July 2014. Retrieved 10 August 2014.
- ^ Luhn, Alec. "MH17: vast majority of Russians believe Ukraine downed plane, poll finds". The Guardian. Guardian News and Media Limited. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- ^ "More Than 80% of Russians Blame Ukrainian Army for MH17 Crash". The Moscow Times. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "Russian Colonel General Identified as Key MH17 Figure – bellingcat". bellingcat. 8 December 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ "Russian general ID'd in activity around shootdown of Malaysian passenger jet". mcclatchydc. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ Ополченцы сообщили о сбитом Ан-26 на востоке Украины (in Russian). 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 July 2014.
On July 17 near the village of Rassypnoye over the Torez city in Donetsk region an An-26 transport plane of Ukrainian Air Force was taken down, said the militia. According to them, the plane crashed somewhere near the "Progress" mine, away from residential areas. According to one of the militias, at about 17:30 local time an An-26 flew over the city. It was hit by a rocket, there was an explosion and the plane went to the ground, leaving a black smoke. Debris fell from the sky
- ^ "Транспортный Ан-26 сбит на востоке Украины, заявили очевидцы". ria.ru. RIA Novosti. 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 13 October 2015.
- ^ "Rebel leader gives bizarre account of plane crash". Yahoo! News. Associated Press. 18 July 2014. Archived from the original on 21 July 2014. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ Игорь Стрелков (18 July 2014). Игорь Стрелков: часть людей из Боинга умерли за несколько суток до катастрофы [Some of the Boeing's passengers died a few days before the crash] (in Russian). RusVesna. Archived from the original on 19 July 2014. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Squires, Nick (18 July 2014). "British journalist working for Russian TV resigns over bias in Ukraine MH17 coverage". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Radziwinowicz, Wacław (18 July 2014). "'Zamach na Putina', 'Ile odszkodowań zapłacą Ukraińcy' i zmiany w Wikipedii. Ofensywa propagandowa Moskwy" ["The attempt on Putin", "How much compensation will pay Ukrainians" and changes in Wikipedia. Moscow's propaganda offensive]. Gazeta Wyborcza (in Polish). Retrieved 19 July 2014.
- ^ Szoldra, Paul (18 July 2014). "Here's The Ridiculous Way Russia's Propaganda Channel Is Covering The Malaysia Airlines Crash". Business Insider. Archived from the original on 20 July 2014.
- ^ "MH17: Russia reveals 'witness' who blames Ukraine pilot". BBC. 24 December 2014. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ Mills, Laura (22 July 2014). "Russians Fed Conspiracy Theories on Ukraine Crash". Yahoo News. Associated Press. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
- ^ "Как и почему погиб рейс МН17 над Донбассом? Брифинг Министерства обороны России". buran.ru. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ^ "Снимок малайзийского "Боинга", сбитого под Донецком, обсуждают во всем мире". Channel One Russia. 15 November 2014.
- ^ "Russia's Channel One show satellite photo evidencing MH17 was downed by fighter jet", TASS, 14 November 2014, retrieved 15 November 2014
- ^ Miller, Nick (15 November 2014). "'Sensational' Russian photo of MH17 being shot debunked by citizen journalist group". The Age. Retrieved 15 November 2014.
- ^ a b Seddon, Max (15 November 2014), "Russian TV Airs Clearly Fake Image To Claim Ukraine Shot Down MH17", BuzzFeed, retrieved 15 October 2014
- ^ Yaffa, Joshua (9 December 2019). "The Kremlin's Creative Director". The New Yorker. Retrieved 11 December 2019.
- ^ "MH17 fallout: Russian reporter Sara Firth quits over Ukraine 'lies'". News.com.au. 28 March 2014. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ "Russia Today reporter resigns in protest at MH17 coverage". The Guardian. Retrieved 18 July 2014.
- ^ "Hoe twijfel rond MH17 in de hand wordt gewerkt". NRC (in Dutch). Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- ^ "Это был "Бук-М1"" [This was "Buk-M1"]. Novaya Gazeta. 5 May 2015. Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ Nick Miller (2 June 2015). "MH17 plane was shot down by a Buk missile, Russian weapons manufacturer says".
- ^ "СБУ: Новые "доказательства" крушения Boeing на Донбассе основаны на фейковых снимках" [SBU called the Russian analysis on Boeing based on fake photos]. StopFake.org. 6 May 2015. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ^ Lukashevich, Vadim (6 May 2015). "Я не увидел в этом докладе экспертов ВПК". Авиационный эксперт Лукашевич о том, кто и зачем готовил документ, раздобытый "Новой газетой" ["I haven't seen military experts in that report", aviation expert Lukashevich who and why published the report leaked by Novaya Gazeta]. TV Rain. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ^ "ЗМІ: Російські експерти в секретній доповіді підтвердили, що Боїнг збили з "Бука"" [Media: Russian experts confirmed in secret report, that Boeing was shot by "Buk"]. Ukrainska Pravda. 6 May 2015. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ^ Solonin, Mark (12 May 2015). "Сверим траектории". Novaya Gazeta.
- ^ "There Was No Buk in Our Field". The Interpreter. Retrieved 11 June 2015.
- ^ "На нашем поле "Бука" не было. Ни следа – ни от гусениц, ни от велосипеда". Retrieved 8 June 2015.
- ^ "MH17 – Forensic Analysis of Satellite Images Released by the Russian Ministry of Defence". Bellingcat. 31 May 2015.
- ^ Dillon, Conor (1 June 2015). "Forensic report: Russia faked MH17 satellite photos". Deutsche Welle.
- ^ Röpcke, Julian (8 May 2015). "BILD entlarvt falsche Satellitenaufnahme" [BILD exposes false satellite image]. Bild (in German).
- ^ "Russia: Missile That Shot Down Flight MH17 Was Ukrainian". The New York Times. 17 September 2018.
- ^ "MH17 crash: Dutch ask Russia to submit new claims". BBC News. 18 September 2018. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ Landelijk Parket. "Reaction JIT to press conference of Russian Ministry of Defense". Openbaar Ministerie. Retrieved 18 September 2018.
- ^ "Russian propaganda? Moscow releases audio blaming Ukraine downing MH17 flight that killed almost 300". Newsweek. 17 September 2018.
External links
- MH17 Witness Appeal November 2019 with the release of further recorded conversations.
- MH17 Crash – final report from Dutch Safety Board, 2015-10-13 Template:Ref-en
- Investigation crash MH17, 17 July 2014 Donetsk – Dutch Safety Board
- MH17 crash – the Joint Investigation Team (JIT) updates – Dutch Public Prosecution Service
- MH17-dossier Dutch Court Template:Ref-en
- Media Statement & Information on Flight MH17 – Malaysia Airlines
- Malaysia Airlines Flight 17 (Archive) – Malaysia Ministry of Transport
- Official MH17 Passenger Manifest – Malaysia Airlines
- Full flight history for Malaysia Airlines Flight MH17 – Flightradar24
- Malaysia Airlines plane MH17 'shot down' in Ukraine – as it happened, The Guardian
- Map of a Tragedy: How MH17 Came Apart Over Ukraine – The Wall Street Journal
- Google Fusion Tables, clickable Google map, that tells the story of every Dutch victim, created by newspaper Algemeen Dagblad Template:Nl icon
- Malaysia Airlines Flight 17
- 2014 controversies
- 2014 in international relations
- 2014 in Malaysia
- 2014 in the Netherlands
- 2014 in Ukraine
- Accidents and incidents involving the Boeing 777
- Airliner shootdown incidents
- Attacks in 2014
- Aviation accidents and incidents in 2014
- Aviation accidents and incidents in Ukraine
- Donetsk People's Republic
- History of Donetsk Oblast
- Malaysia Airlines accidents and incidents
- Malaysia–Netherlands relations
- Malaysia–Ukraine relations
- Netherlands–Ukraine relations
- War in Donbass
- 21st-century aircraft shootdown incidents
- July 2014 events in Europe


