Pentagonal pyramid
| Pentagonal pyramid | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Johnson J1 - J2 - J3 |
| Faces | 5 triangles 1 pentagon |
| Edges | 10 |
| Vertices | 6 |
| Vertex configuration | 5(32.5) (35) |
| Schläfli symbol | ( ) ∨ {5} |
| Symmetry group | C5v, [5], (*55) |
| Rotation group | C5, [5]+, (55) |
| Dual polyhedron | self |
| Properties | convex |
| Net | |
 | |
In geometry, a pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a pentagonal base upon which are erected five triangular faces that meet at a point (the vertex). Like any pyramid, it is self-dual.
The regular pentagonal pyramid has a base that is a regular pentagon and lateral faces that are equilateral triangles. It is one of the Johnson solids (J2). Its height H, from the midpoint of the pentagonal face to the apex, (as a function of a, where a is the side length), can be computed as:
Its surface area, A, can be computed as the area of pentagonal base plus five times the area of one triangle:
Its volume when an edge length is known can be figured out with this formula:
It can be seen as the "lid" of an icosahedron; the rest of the icosahedron forms a gyroelongated pentagonal pyramid, J11, one of the 92 Johnson solids named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.
More generally an order-2 vertex-uniform pentagonal pyramid can be defined with a regular pentagonal base and 5 isosceles triangle sides of any height.
Related polyhedra
The pentagrammic star pyramid has the same vertex arrangement, but connected onto a pentagram base:
| Regular pyramids | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digonal | Triangular | Square | Pentagonal | Hexagonal | Heptagonal | ... | ||
| Improper | Regular | Equilateral | Isosceles | |||||
|

|
... | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
... | ||
 Pentagonal frustum is a pentagonal pyramid with its apex truncated |
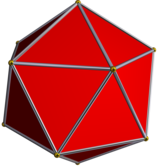 The top of an icosahedron is a pentagonal pyramid |
Dual polyhedron
The pentagonal pyramid is topologically a self-dual polyhedron. The dual edge lengths are different due to the polar reciprocation.
| Dual pentagonal pyramid | Net of dual |
|---|---|

|

|
Example

External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Pentagonal pyramid" ("Johnson solid") at MathWorld.
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra www.georgehart.com: The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra ( VRML model)




