Solar eclipse of June 21, 2020
| Solar eclipse of June 21, 2020 | |
|---|---|
 Annularity as seen from Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Annular |
| Gamma | 0.1209 |
| Magnitude | 0.994 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 38 s (0 min 38 s) |
| Coordinates | 30°30′N 79°42′E / 30.5°N 79.7°E |
| Max. width of band | 21 km (13 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 6:41:15 |
| References | |
| Saros | 137 (36 of 70) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9553 |
An annular solar eclipse occurred on June 21, 2020. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.
This solar eclipse occurred one lunar year after the July 2, 2019 eclipse.
Visibility
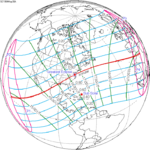
The central path of this annular eclipse passed through parts of Central and Eastern Africa, including Congo Republic, DR Congo, the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, and Djibouti; the southern Arabian Peninsula, including Yemen, Oman, and southern Saudi Arabia; parts of South Asia and the Himalayas, including southern Pakistan, northern India, Nepal, and Tibet; parts of East Asia, including South China and Taiwan, and part of Micronesia, including Guam.[1] A partial eclipse was visible throughout much of the rest of Africa, southeastern Europe, most of Asia (except the north part of Siberia and most of the island of Java), and in New Guinea and the north of Australia just before sunset. In Europe, the partial eclipse was visible for places southeast of the line roughly passing through Perugia, Miskolc, Lviv, and Yaroslavl.[1]
For Oman and India, it was the second annular eclipse 6 months after the December 2019 eclipse.[2]
Images
Gallery
-
Partial from Sana'a, Yemen, 5:09 UTC
-
Partial from Gyumri, Armenia, 5:45 UTC
-
Partial from Abu Dhabi, UAE, 5:48 UTC
-
Partial from Colombo, Sri Lanka, 5:48 UTC
-
Partial from Chennai, India, 6:41 UTC
-
Partial from Lahore, Pakistan, 6:49 UTC
-
Partial from Kathmandu, Nepal, 6:51 UTC
-
Partial from Bacoor, Philippines, 7:31 UTC
-
Partial from Kolkata, India, 7:41 UTC
-
Partial from Beijing, China, 7:50 UTC
-
Partial from Jinan, China, 7:56 UTC
-
Partial from Dongping County, Shandong, China, 7:56 UTC
-
Partial from Gandara, Samar, Philippines, 8:01 UTC
-
Partial from Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 8:05 UTC
-
Partial from Yau Tong, Hong Kong, 8:08 UTC
-
Partial from Taichung, Taiwan, 8:09 UTC
-
Partial from Pangkal Pinang, Indonesia, 8:10 UTC
-
From Xiamen, China, 8:11 UTC
-
Partial from Fukuoka, Japan, 8:12 UTC
-
From Chiayi, Taiwan, 8:13 UTC
-
Partial from San Jose del Monte, Philippines, 8:23 UTC
-
Eclipse progression as seen from Oria, Italy
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2020
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on January 10.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on June 5.
- An annular solar eclipse on June 21.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on July 5.
- A penumbral lunar eclipse on November 30.
- A total solar eclipse on December 14.
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of May 10, 2013
- Followed: Solar eclipse of August 2, 2027
Half-Saros cycle
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of June 15, 2011
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of June 26, 2029
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of July 22, 2009
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 21, 2031
Solar Saros 137
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of June 10, 2002
- Followed: Solar eclipse of July 2, 2038
Inex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of July 11, 1991
- Followed: Solar eclipse of May 31, 2049
Triad
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of August 21, 1933
- Followed: Solar eclipse of April 23, 2107
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[3]
The partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018 and August 11, 2018 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2018 to 2021 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
117 Partial in Melbourne, Australia |
July 13, 2018 Partial |
−1.35423 | 122 Partial in Nakhodka, Russia |
January 6, 2019 Partial |
1.14174 | |
127 Totality in La Serena, Chile |
July 2, 2019 Total |
−0.64656 | 132 Annularity in Jaffna, Sri Lanka |
December 26, 2019 Annular |
0.41351 | |
137 Annularity in Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan |
June 21, 2020 Annular |
0.12090 | 142 Totality in Gorbea, Chile |
December 14, 2020 Total |
−0.29394 | |
147 Partial in Halifax, Canada |
June 10, 2021 Annular |
0.91516 | 152 From HMS Protector off South Georgia |
December 4, 2021 Total |
−0.95261 | |
Saros 137
It is a part of Saros cycle 137, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 70 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 25, 1389. It contains total eclipses from August 20, 1533 through December 6, 1695, first set of hybrid eclipses from December 17, 1713 through February 11, 1804, first set of annular eclipses from February 21, 1822 through March 25, 1876, second set of hybrid eclipses from April 6, 1894 through April 28, 1930, and second set of annular eclipses from May 9, 1948 through April 13, 2507. The series ends at member 70 as a partial eclipse on June 28, 2633. The longest duration of totality was 2 minutes, 55 seconds on September 10, 1569. Solar Saros 137 has 55 umbral eclipses from August 20, 1533 through April 13, 2507 (973.62 years).
| Series members 30–40 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 April 17, 1912 |
 April 28, 1930 |
 May 9, 1948 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
 May 20, 1966 |
 May 30, 1984 |
 June 10, 2002 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
 June 21, 2020 |
 July 2, 2038 |
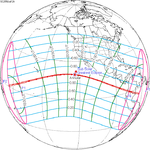 July 12, 2056 |
| 39 | 40 | |
 July 24, 2074 |
 August 3, 2092 | |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
 November 9, 1817 (Saros 130) |
 October 20, 1846 (Saros 131) |
 September 29, 1875 (Saros 132) |
 September 9, 1904 (Saros 133) |
 August 21, 1933 (Saros 134) |
 July 31, 1962 (Saros 135) |
 July 11, 1991 (Saros 136) |
 June 21, 2020 (Saros 137) |
 May 31, 2049 (Saros 138) |
 May 11, 2078 (Saros 139) |
 April 23, 2107 (Saros 140) |
 April 1, 2136 (Saros 141) |
 March 12, 2165 (Saros 142) |
 February 21, 2194 (Saros 143) |
|
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's ascending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982 and June 21, 2058 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 21 | April 8–9 | January 26 | November 13–14 | September 1–2 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 21, 1982 |
 April 9, 1986 |
 January 26, 1990 |
 November 13, 1993 |
 September 2, 1997 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
 June 21, 2001 |
 April 8, 2005 |
 January 26, 2009 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 September 1, 2016 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 June 21, 2020 |
 April 8, 2024 |
 January 26, 2028 |
 November 14, 2031 |
 September 2, 2035 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 21, 2039 |
 April 9, 2043 |
 January 26, 2047 |
 November 14, 2050 |
 September 2, 2054 |
| 157 | ||||
 June 21, 2058 | ||||
Notes
- ^ a b "Annular Solar Eclipse on June 21, 2020". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2019-12-26.
- ^ World Atlas of Solar Eclipse Paths
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- solar-eclipse.de: The annular solar eclipse of 06/21/2020
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




























