HIV/AIDS in Europe
This article needs to be updated. (November 2015) |
This article needs attention from an expert in medicine. Please add a reason or a talk parameter to this template to explain the issue with the article. (November 2008) |
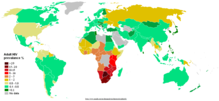
In Western Europe, the routes of transmission of HIV are diverse, including paid sex, sex between men, intravenous drugs, mother to child transmission and heterosexual sex. However, many new infections in this region occur through contact with HIV-infected individuals from other regions. In some areas of Europe, such as the Baltic countries, the most common route of HIV transmission is through injecting drug use and heterosexual sex, including paid sex.[1]
The adult (15–49) prevalence in Europe in 2018 varied from a high of 1.20% in Russia to a low of 0.1% in eleven countries.[2] Due to the availability of antiretroviral therapy, deaths from AIDS have stayed low since the introduction of protease inhibitors and combination therapy in the late 1990s. The Economist reported in January 2000 that almost 40% of "AIDS victims" are intravenous drug users.[3]
At the end of 2007, it was estimated that around 800,000 people were living with HIV in Western and Central Europe. This represents 8.1% increase over the estimated 740,000 in 2006. The highest rates were reported from Estonia, Portugal and Russia; the lowest rates were reported by Slovakia, the Czech Republic (0.025%) and Romania. Although the numbers are relatively small when compared to the number of people living with HIV in areas such as Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, HIV/AIDS in Western and Central Europe is still considered a major public health issue.[4][5]
Regarding the social effects of the HIV/AIDS pandemic, there has been since the 1980s a "profound re-medicalization of sexuality".[6][7]
Albania
Albania remains to have a low number of HIV death-related cases. Between 1992 and until the end of 2011, Albania reported a total of 487 HIV cases. Among these 487 cases: 83.1% heterosexual contact, 12.7% were transmitted through sexual contact between men, and 4.2% were transmitted from mother to child. No HIV cases were transmitted through injecting drug use.
In the year 2011, Albania had a total 71 new HIV infections, 38 AIDS cases, and 9 AIDS-related deaths. Of the newly reported HIV cases, 73% were male.
However, Albania remains to have a low HIV testing coverage for its general public. Only 2% of clinics and health facilities in Albania offered HIV testing services. Within those who acquired testing, 48% were men who were in sexual contact with another man.
Between the years 2018 - 2019, 51 individuals suffering from AIDS lost their lives in Albania, sparking outrage among organizations working on the issue.[8]
Austria
First case diagnosed in 1983. In 2010 32% of the population was infected through heterosexual contact. Austria has the highest conduct of HIV testing in Europe.[9]
Bosnia and Herzegovina
In reference to the global HIV/AIDS epidemic, Bosnia and Herzegovina is considered to be a low prevalence country (less than 0.1%). Ever since the first registered case of AIDS in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1986 up until the end of 2017, 350 HIV infected persons have been registered and AIDS has developed in 102 cases. 80% of people who live with HIV in Bosnia are males, and the average age of the infected is between 30 and 39 years. The number of infected persons might be a bit higher, because of the fear and stigma people don't get tested. Some professionals estimate that there are between 900 - 1000 people who are HIV positive in Bosnia.
In addition, significant attention should be paid to the Roma section of the population due to their marginalisation, and youths, particularly adolescents and primary school pupils in Urban areas.
In the past couple of years HIV infection has been kept under control in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Only 0.009% (350) of the countries population (4.000.000) is confirmed to have the HIV virus, its safe to say that Bosnia and Herzegovina is a very low prevalence country. Most groups of people that are identified as being exposed to a higher risks of HIV infection are being successfully followed thanks to the BiH programme to combat HIV/AIDS with support provided by the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria.
Through UNDP support, 22 centres were established across the country, which provide free, confidential HIV testing for all. Although Bosnia has free HIV therapy and medicaments, the biggest problem is that there is no access to modern medicaments that are available in some other European countries for example Germany, Austria, France etc.
Belgium
Belgium had a total of 18,908 HIV cases by the end of 2017 (not taking into account the people who are not aware of their infection). Prevalence is 1.7 cases per 1000 inhabitants.
2.4 new cases are diagnosed daily. Most of the newly diagnosed cases were transmitted through heterosexual contact, 49.6%. Secondly, HIV cases transmitted through sexual contact among men having sex with men (MSM) were at 46.6%. Third, 1.3% of HIV cases were transmitted through injected drug use. Despite easy access to HIV blood testing in Belgium, 36% of new cases are diagnosed at late stage of the disease. Late diagnosis is more frequent in the heterosexual population (46%) than in MSM group (27%). Unlike other countries in Europe, Belgium offers HIV testing by all practitioners, clinics, hospitals, and student services. Most diagnosis centers offer rapid and/or 4th generation testing without any costs and anonymously.
97% of diagnosed patients have access to adequate therapy, with viral charge being undetectable in the blood (uninfectious status) and stopping the spread of the disease.
https://doi.org/10.25608/C57T-F917
Czech Republic
As of 31 December 2018, there are 3,368 HIV-positive people diagnosed in the Czech Republic, the overall count—including foreigners (446 people)—is then 3,814 people. In 2018, this number increased by 208. The most affected area is the city of Prague (1651 cases). Since 1994, the Czech Republic has performed 28.8 million HIV tests. 415,813 people have received examinations at their own request. 75% of test recipients indicated that the reason for seeking a test was that they were a man who had sex with men. AIDS outbreak at 506 people (as of 31 December 2016, The statistics led from 1 October 1985), of which 255 of them died. The average age of diagnosis is 35 years for men and 39 years for women. In 2018 there was a decrease in diagnoses. There was a decrease of 46 people (citizens and residents) compared to 2017. [10]
Estonia
Biological surveillance of HIV in Estonia started in 1987 and starting from 2016, HIV testing is free of charge for all people, including those who do not have health insurance (for them, costs are covered directly from the state budget). The first HIV case in Estonia was diagnosed in 1988. The rate of newly diagnosed cases of HIV has decreased over the last decade (from 46.0 cases in 2005 to 20.5 cases per 100,000 in 2015), but has been quite stable in the last few years (25 cases per 100,000 in 2013 and 23 cases in 2014). From 2005 to 2015, hetero and homosexual transmission has increased as well as the proportion of cases among people older than 34 years. The number of cases among children and youth has decreased considerably. The proportion of women is stable around 40%. Transmission among people who inject drugs has stabilized but prevalence rates are very high.[11] So far injecting drug use remains the most important transmission route and the HIV epidemic continues to affect vulnerable populations more, particularly injecting drug users (IDUs) and their sexual partners.[12]
In 2018, 190 new cases of HIV and 25 cases of AIDS were diagnosed in Estonia. In 2017, a total of 219 people were diagnosed with HIV and 20 with AIDS. Since testing began in Estonia, a total of 9,878 cases of HIV and 536 cases of AIDS have been diagnosed.[13]
As per data available, 1.3 percent of adults are HIV positive — the highest percentage among all the countries in the European Union.[14] Unfortunately this number is presumed to be exaggerated because of duplicate registration until 2008 as a result of which 20-30 percent more diagnoses could have been recorded. The statistical error lies in that up until 2009 all anonymous diagnoses of HIV were also entered into official statistics. This means that a person who went to see a doctor after testing positive for the virus at an anonymous center could have been recorded twice – first anonymously and then with their name and personal identification code recorded. At the height of the epidemic, some people could have even been tested more than 2 times because a positive diagnosis is so devastating it can send people back to take the test again in hopes of a negative result and assurance by the doctor that mistakes had been made before. Of persons with HIV, 42% lived in Ida-Viru County and 39% in Harju County.[15]
Finland
During the 21st century, there have been less than 200 new HIV diagnoses annually in Finland. The amount of new infections has been slowly increasing during the past decade. The amount of AIDS deaths has stayed at an annual level of 15–30, year 2015 was the first year with no AIDS deaths in Finland. During 1980–2016, around 3,700 people have been diagnosed with HIV and circa 450 people have died of AIDS. In addition, it is estimated that there are around 500 people who carry the virus but are unaware of their infection. Most HIV infections are diagnosed in 30–34-year-olds, although most of HIV cases in Finland are discovered only in the AIDS stage.
Germany
HIV has a typical prevalance to western Europe. Gay and drug users are high risk populations.
Iceland
HIV-1 was first reported in Iceland in 1985. By the end of 2012 a total of 300 patients had been diagnosed with HIV-1 infection in the country, of which 66 had developed AIDS and 39 died as a result of the disease.[16][17] Following the first introduction of HIV-1 to Iceland onwards to the end of 2012, the infection has been dominated by subtype B with a relatively low fraction of founders compared to the total number of introductions. HIV-1 infection in the country appeared to be highly concentrated among men who have sex with men and injection drug users and less among heterosexuals. The genetic diversity of HIV-1 in Iceland has increased significantly over time, most likely related to the increased proportion of foreign-born residents in the country from the mid-1990s.[18][19] In the most recent study investigating the prevalence and trends of transmitted drug resistance among antiretroviral-therapy naive patients in Iceland, the prevalence was found to be at moderate level (8.5%), with an evidence of decreasing prevalence of transmitted drug resistance in Iceland during 1996–2012.[20]
Latvia
In 2018, there were 5,300 HIV cases in total in Latvia.[21]
Latvia has one the highest HIV infection rates in the European Union.[22] The dominant identified HIV infection pattern in Latvia is heterosexual relations (33% of new cases in 2018), followed by intravenous drug use (22%), followed by homosexual relations (6%). In 37% of new cases the way of infection is unknown.[23]
Lithuania
In 2016, there were 2,749 cases in the country in total. New infections had remained consistently under 200 per year but surpassed this mark in 2016 with 214 cases.[24]
The data regularly show that intravenous drug use is the main HIV infection pattern in the country: in 2017, 51.7% of new HIV cases were observed among drug users. During the same year, 24.3% new infections stemmed from heterosexual relations and 6.8% from homosexual relations.[25]
Russia
By 2017 the number of reported cases in Russia was over 1 million, according to the World Health Organization,[26] up from 15,000 in 1995.
Spain
Spain has had a high prevalence of HIV/AIDS, but is now on the level with the rest of Western Europe. Spain, the US, France, Germany, Italy, Turkey and the United Kingdom accounted for three quarters of the infected population in the Western region.[27] The first reported cases of AIDS were in 1983. Two hemophiliacs, after receiving blood transfusions from the United States, died in Andalucía of the disease.[28] Later on, it was found that a male patient in 1981 was infected with AIDS after having had sex with other men while he travelled to the United States and Turkey.[29]
In 1997, Spain had 104 cases of AIDS per 100,000 which was triple the European Union average at the time. Spain also accounted for a quarter of the HIV infected population of Western Europe at that time.[30] However, in 2016 Spain had plateaued to a national average that echoed the average adult HIV prevalence in Western Europe & North American at 0.3%. 77% of those infected with HIV in Spain received antiretroviral treatment (ART), which is on par with the rest of of Western Europe and North America at 78 %.[27][31] The five demographics that have the highest prevalence of HIV infection are sex workers (2%), injecting drug users (2.3%), prisoners (5.4%), men who have sex with men (11.3%), and transgender people (13.3%).[30]
Sweden
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
From the end of the 1980s to the early 2000s, infection rate in Sweden was about 300 new cases per year, then the rate increased.[33] From 2006 to 2016 the number of patients applying for treatment for HIV increased from 1 684 to 6 273 (373%), which according to National Board of Health and Welfare was due to increased immigration from countries with higher levels of HIV.[33]
United Kingdom
In 2017, the prevalence of HIV in the United Kingdom was estimated at 101,600 (credible interval 99,300 to 106,400) with 92% (credible interval 88 to 94%) diagnosed.[34] Prevalence is highest in gay/bisexual men in London with an estimated 83 (credible interval 73 to 96) per 1000 gay and bisexual men aged 15 to 74 years. HIV prevalence in this group was higher in London compared with the rest of England (134/1,000 CrI 113 to 156 and 63/1,000 CrI 53 to 76, respectively).[35] However, the 2017 statistics showed a tremendous decrease in the number of newly HIV infected gay men during 2015-17. The number of newly HIV infected gay men decreased by a third in just two years.[36]
Ukraine
See also
- Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS
- HIV/AIDS in Africa
- HIV/AIDS in Asia
- HIV/AIDS in North America
- HIV/AIDS in South America
- International Stele Always Remember, Berlin, Germany
References
- ^ https://www.avert.org/professionals/hiv-around-world/western-central-europe-north-america/overview
- ^ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/363rank.html
- ^ "Going Dutch?". The Economist. 13 January 2000. Retrieved 11 October 2011.
- ^ "Euro report on HIV" (PDF). 2009.
- ^ "HIV & AIDS in Western Europe". TheBody.com.
- ^ Aggleton, Peter; Parker, Richard Bordeaux; Barbosa, Regina Maria (2000). Framing the sexual subject: the politics of gender, sexuality, and power. Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-520-21838-3.
- ^ Carole S. Vance (1991). "Anthropology Rediscovers Sexuality: A Theoretical Comment". Social Science and Medicine. 33 (8): 875–884. doi:10.1016/0277-9536(91)90259-f. PMID 1745914.
- ^ https://www.historia-ime.com/english/in-2020-albania-fails-its-hiv-fight/
- ^ "Country Progress Report" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Tisková zpráva NRL pro HIV/AIDS v ČR v roce 2018" (PDF) (in Czech). Czech National Institute of Public Health. 29 January 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ https://www.unaids.org/en/file/110927/download?token=hfImcvDw
- ^ http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/communicable-diseases/hivaids/publications/2011/hiv-epidemic-in-estonia-analysis-of-strategic-information.-case-study-2011
- ^ https://news.err.ee/897589/190-new-cases-of-hiv-diagnosed-in-estonia-in-2018
- ^ https://www.aidshealth.org/global/estonia/
- ^ https://news.postimees.ee/3967981/estonia-has-fewer-hiv-positive-people-than-thought
- ^ The directorate of health in Iceland. 2015 [cited 2015 Sep 2]. Available from: www.landlaeknir.is
- ^ Statistics Iceland: the centre for official statistics in Iceland. 2016 [cited 2016 Feb 11]. Available from: www.statice.is
- ^ Sallam, Malik; Esbjörnsson, Joakim; Baldvinsdóttir, Guðrún; Indriðason, Hlynur; Björnsdóttir, Thora Björg; Widell, Anders; Gottfreðsson, Magnús; Löve, Arthur; Medstrand, Patrik (2017). "Molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 in Iceland: Early introductions, transmission dynamics and recent outbreaks among injection drug users". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 49: 157–163. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2017.01.004. PMID 28082188.
- ^ Indridason H, Gudmundsson S, Karlsdottir B, et al. Long term nationwide analysis of HIV and AIDS in Iceland, 1983-2012. J AIDS Clin Res. 2014;5:387.
- ^ Sallam, Malik; Şahin, Gülşen Özkaya; Indriðason, Hlynur; Esbjörnsson, Joakim; Löve, Arthur; Widell, Anders; Gottfreðsson, Magnus; Medstrand, Patrik (2017). "Decreasing prevalence of transmitted drug resistance among ART-naive HIV-1-infected patients in Iceland, 1996–2012". Infection Ecology & Epidemiology. 7 (1): 1328964. doi:10.1080/20008686.2017.1328964. PMC 5475329. PMID 28649306.
- ^ http://aidsinfo.unaids.org/
- ^ https://www.tvnet.lv/6466173/kapec-visaugstakais-hiv-inficesanas-limenis-es-ir-latvija
- ^ https://www.spkc.gov.lv/lv/statistika-un-petijumi/infekcijas-slimibas/datu-vizualizacija/hivaids
- ^ McDermott, Doireann (4 May 2017). "Latvia surpasses Estonia with highest new cases of HIV". The Baltic Times. No. 902.
- ^ http://www.ulac.lt/naujienos/pranesimai-spaudai/kas-antras-uzsikrete-ziv-per-narkotikus-2017-m.-duomenys
- ^ https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/russianfederation
- ^ a b "HIV AND AIDS IN W & C EUROPE & N AMERICA REGIONAL OVERVIEW". Avert. 26 March 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ Relaño, Alfredo. “Confirmado oficialmente que dos hermanos murieron en Sevilla a causa del síndrome de inmunodeficiencia.” El País 5 May 1983. Web. 11 Mar. 2015.
- ^ Allbritton, Dean (March 2016). "It Came from California: The AIDS Origin Story in Spain". Revista de Estudios Hispánicos. 50 (1): 143–166. doi:10.1353/rvs.2016.0015. S2CID 164157530.
- ^ a b "Spain's War on AIDS Visits the Prado". New York Times. 27 August 1997. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ "Spain UNAIDS Report". Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ "Statistikdatabas för diagnoser i specialiserad öppen vård". www.socialstyrelsen.se (in Swedish). Retrieved 30 December 2017.
- ^ a b Göransson, Josefine (30 November 2017). "Allt fler söker vård för HIV i Skåne". 24 Malmö. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- ^ "Progress towards ending the HIV epidemic in the United Kingdom 2018 report )" (PDF). Public Health England. 2018. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ^ "Progress towards ending the HIV epidemic in the United Kingdom 2018 report )" (PDF). Public Health England. 2018. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ^ "HIV diagnoses in gay men in the UK decreased by a third in two years". Aidsmap.com. Retrieved 5 March 2019.
External links
- World Health Organization: Regional office for Europe
- AIDS epidemic update 2005 (PDF)
- Specific country data from UNAIDS
- AIDSPortal Eastern Europe page (the UK) - latest research, case studies and news stories
- AIDSPortal Western Europe page (Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Russia and Ukraine) - latest research, case studies and news stories

