28th Test and Evaluation Squadron
| 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Active | 1940–1946; 1953; 1993–present |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Role | Operational testing |
| Part of | Air Combat Command |
| Motto(s) | OT Zealots Delivering Capabilities to the Warfighter[citation needed] |
| Mascot(s) | Scorpion[citation needed] |
| Decorations | Air Force Outstanding Unit Award[1] |
| Insignia | |
| 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron emblem (approved 27 February 2015)[1] |  |
| 28th Fighter Squadron emblem (approved 19 May 1945)[1][note 2] | 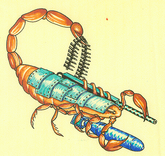 |
The 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron is an active United States Air Force unit. Its current assignment is with the 53d Wing, based at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida.
Mission
The 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron evaluates the effectiveness and suitability of weapons and avionics systems being procured or improved to support current and future United States Air Force air combat capabilities. Squadron personnel direct test project planning and execution, as well as data gathering, analyzing, and reporting for tests involving conventional and nuclear air munitions, avionics subsystems, chemical warfare defense, aircrew life support, chemical defense systems, munitions and avionics support equipment, weapon release systems, and automated mission planning systems.
The IATF's[clarification needed What is IATF?] primary objective is to improve the combat capability, reliability, and lethality of Air Force weapon systems through operationally realistic testing. Missions are performed through ground test, flight test, ground-based jammer testing, and various combinations of these techniques. The IATF's primary mission is to perform force development evaluations on the operational flight programs of the McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle and General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon fire control radar systems. This includes experimental changes to the OFPs[clarification needed What is OFP?] as well as modifications to fielded OFPs. Additional responsibilities and capabilities include the following: Perform OFP operational testing and evaluation and operational utility evaluations of F-15 and F-16 radars with the AIM-120 AMRAAM, identify radar system maintenance deficiencies and develop work-around solutions. Support advanced EA and EP[clarification needed What are EA and EP?] system development and evaluation. Provide resident Air Force technical expertise on Air Combat Command radar and missile systems. Support other electronic warfare projects from Air Force, Department of Defense and various external customers with technical assistance or specialized hardware
Detachment 1 of the squadron, located at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada performs functional management for acquisition, modification, testing and certification for fighter, bomber and combat support aircrew training systems. The group also conducts foreign military exploitation and special access projects.
Detachment 2 of the squadron, located at Tyndall Air Force Base, Florida plans, executes, and reports on Air Combat Command directed operational tests for multi-service integrated fighter avionics, weapons, and electronic warfare systems via operation of the $103 million Integrated Avionics Test Facility. Detachment personnel determine operational effectiveness and suitability for current and future weapons systems using Air Force and threat fighter radars, air-to-air missiles, electronic attack and electronic protection suites. The detachment also provides input and assistance to Headquarters U.S. Air Force, Air Combat Command, Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center, and Air Force Materiel Command in the development of test plans, conduct of test projects, collection of test data and production of final test and evaluation reports.
History

World War II
Established in 1939 as the 28th Pursuit Squadron and activated on 1 February 1940 at Albrook Field, Panama Canal Zone.[1] The squadron was formed from a collection of four officers and enlisted ranks drawn from Headquarters and Headquarters Squadron, 16th Pursuit Group, the 24th Pursuit Squadron, the 44th Reconnaissance Squadron, the 29th Pursuit Squadron, the 74th Bombardment Squadron and the 15th Air Base Squadron. Initially equipped with Boeing P-26A Peashooters, the mission of the squadron was air defense of the Panama Canal. This remained the squadron's mission throughout its existence in Sixth Air Force.
After the Pearl Harbor Attack, the squadron was dispersed to Paitilla Point Field, Panama, 08°58′37″N 079°30′31″W / 8.97694°N 79.50861°W and re-equipped with some Curtiss P-40 Warhawks. By March 1942, was moved to La Joya #2 Aerodrome 09°04′59″N 079°19′00″W / 9.08306°N 79.31667°W in Panama where it remained until 2 May 1942, only to return to Paitilla Point again in June. Was redesignated as the 28th Fighter Squadron on 15 May as part of a USAAF-wide renaming program. The unit then remained there until November, when it moved again to Chame Field, Panama. In November 1943, the Squadron was assigned directly to XXVI Fighter Command,[1] and by December, the unit had been re-equipped with Bell P-39Q Airacobras.
By February 1944, the Squadron was maintaining a detachment at Pocri Field, Panama. In May 1945, conversion to Lockheed P-38 Lightnings began, however, no sooner had conversion to the P-38s been completed than the unit was moved to Howard Field, where the entire complement of P-38s was hangared and the unit activities ran down with the end of the war in Europe. The squadron ceased all flying activities in June, and the P-38s were reassigned to other units in the command while personnel were returned to the United States. By October 1945, the squadron was reduced to a non-operational administrative organization. Inactivated on 15 October 1946.
During the Cold War, the squadron was reactivated by Tactical Air Command as the 28th Fighter-Bomber Squadron at Clovis Air Force Base, New Mexico on 8 April 1953 and was programmed to receive North American F-86F Sabres. However, the squadron did not become operational[2] and it was inactivated on 25 June.[1]
Test unit
The squadron was redesignated the 28th Test Squadron and activated as an Air Combat Command test squadron at Eglin Air Force Base, Florida in 1993. It became the 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron on 12 April 2006.[1]
Lineage
- Constituted as the 28th Pursuit Squadron (Interceptor) on 22 December 1939
- Activated on 1 February 1940.
- Redesignated 28th Fighter Squadron on 15 May 1942
- Inactivated on 15 October 1946
- Redesignated 28th Fighter-Bomber Squadron on 3 March 1953
- Activated on 8 April 1953
- Inactivated on 25 June 1953
- Redesignated 28th Test Squadron on 9 April 1993
- Activated on 15 April 1993
- Redesignated 28th Test and Evaluation Squadron on 12 April 2006[1]
Assignments
- 37th Pursuit Group (later 37th Fighter Group), 1 February 1940
- XXVI Fighter Command, 1 November 1943
- 6th Fighter Wing, 25 August–15 October 1946
- 37th Fighter-Bomber Group, 8 April–25 June 1953
- 79th Test and Evaluation Group (later 53d Test and Evaluation Group), 15 April 1993
- 53d Test Management Group, 1 October 2002[1]
- 53rd Test and Evaluation Group,[3] 1 October 2021 – present
Stations
- Albrook Field, Panama Canal Zone, 1 February 1940
- Rio Hato Airfield, Panama, 5 October 1940
- Albrook Field, Panama Canal Zone, 13 November 1940
- Patina Point Airfield, Panama, 9 December 1941
- Detachment at La Chorrera Army Airfield, Panama, 26 March – 2 May 1942[4]
- Chame Airfield, Panama, 10 November 1942
- Detachment at Pocri Airfield, Panama, 22 February – 2 August 1944[4]
- Howard Field, Panama Canal Zone, 25 September 1945 – 15 October 1946
- Clovis Air Force Base, New Mexico, 8 April – 25 June 1953
- Eglin Air Force Base, Florida, 15 April 1993 – present[5]
Aircraft
- Boeing P-26 Peashooter, 1940–1941
- Curtiss P-40 Warhawk, 1941–1942
- Bell P-39 Airacobra, 1942–1945
- Lockheed P-38 Lightning, 1945[4]
References
Notes
- Explanatory notes
- ^ The MiG-29 (29 + 10) is flown by the commander of Luftwaffe Jagdgeschwader 73 "Steinhoff", from Laage, Germany. It is in formation with a U.S. Air Force McDonnell Douglas F-15C-33-MC Eagle (serial 82-15) over the Gulf of Mexico during a joint training exercise on 14 May 2003.
- ^ Heraldry: A brown scorpion with light blue armor plate fastened to back by rivets, holding in the right claw and legs a large, medium blue aerial bomb, and in the left claw and legs a light blue and black aerial machine gun with black and white cartridge belt affixed thereto, draped over stinger on tail.
- ^ Aircraft is Bell P-39Q-20-BE Airacobra serial 44-3866. Markings include squadron number 97 and tail code of Triangle H, assigned by Sixth Air Force, about December 1944.
- Citations
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Musser, James (19 December 2016). "Factsheet 28 Test and Evaluation Squadron (ACC)". Air Force Historical Research Agency. Archived from the original on 15 June 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2018.
- ^ Ravenstein, pp.65–66
- ^ No byline. "53rd Wing Fact Sheets". Air Force History Index. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ^ a b c Maurer, Combat Squadrons, p. 143
- ^ Station information in Musser, except as noted.
Bibliography
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency
- Hagdedorn, Dan (1995). Alae Supra Canalem: Wings Over the Canal. Nashville, TN: Turner Publishing. ISBN 1-56311-153-5.
- Maurer, Maurer, ed. (1983) [1961]. Air Force Combat Units of World War II (PDF) (reprint ed.). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-02-1. LCCN 61060979. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- Maurer, Maurer, ed. (1982) [1969]. Combat Squadrons of the Air Force, World War II (PDF) (reprint ed.). Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-405-12194-6. LCCN 70605402. OCLC 72556. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- Ravenstein, Charles A. (1984). Air Force Combat Wings, Lineage & Honors Histories 1947–1977. Washington, DC: Office of Air Force History. ISBN 0-912799-12-9. Retrieved 17 December 2016.

