CYLD (gene)
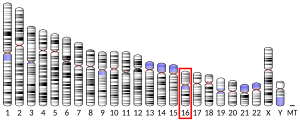
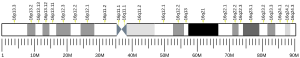
The CYLD lysine 63 deubiquitinase gene, also termed the CYLD gene,[5] CYLD is an evolutionary ancient gene found to be present as far back on the evolutionary scale as in sponges.[6] In humans, this gene is located in band 12.1 on the long (or "q") arm of chromosome 16[7] and is known to code (i.e. direct the production of) multiple proteins through the process of alternative splicing.[8]
The CYLD gene in known to code for a cytoplasmic protein, termed CYLD lysine 63 deubiquitinase (here termed CYLD protein), which has three cytoskeletal-associated protein-glycine-conserved (CAP-GLY) domains (areas or the protein controlling critical functions[9]). CYLD protein is a deubiquitinating enzyme, i.e. a protease that removes ubiquitin from certain proteins and thereby regulates these proteins' activities. CYLD protein removes ubiquitin from proteins involved in regulating the NF-κB, Wnt, notch, TGF-β,[10] and JNK[11] cell signaling pathways; these pathways normally act to regulate hair formation, cell growth, cell survival, inflammatory responses, and/or tumor development.[10][11]
The CYLD gene is classified as a tumor suppressor gene, i.e. a gene that regulates cell growth and when inactivated by a mutation leads to uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of tumors.[12] Inactivating mutations in this gene occur in essentially all cases of the CYLD cutaneous syndrome, a hereditary disorder in which individuals develop multiple skin tumors. The CYLD cutaneous syndrome includes three somewhat different forms of the disease: the multiple familial trichoepithelioma-type, Brooke–Spiegler syndrome-type, and familial cylindromatosis-type.[10] CYLD gene mutations are also associated with T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia,[12] multiple myeloma, hepatocellular carcinoma, neuroblastoma, pancreatic cancer,[13] uterine cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, and human papillomavirus-associated cancers.[11]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000083799 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000036712 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Symbol report for CYLD". www.genenames.org/. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- ^ Hadweh P, Chaitoglou I, Gravato-Nobre MJ, Ligoxygakis P, Mosialos G, Hatzivassiliou E (2018). "Functional analysis of the C. elegans cyld-1 gene reveals extensive similarity with its human homolog". PLOS ONE. 13 (2): e0191864. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1391864H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0191864. PMC 5796713. PMID 29394249.
- ^ Arruda AP, Cardoso-Dos-Santos AC, Mariath LM, Feira MF, Kowalski TW, Bezerra KR, da Silva LA, Ribeiro EM, Schuler-Faccini L (July 2020). "A large family with CYLD cutaneous syndrome: medical genetics at the community level". Journal of Community Genetics. 11 (3): 279–284. doi:10.1007/s12687-019-00447-2. PMC 7295879. PMID 31792733.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CYLD cylindromatosis (turban tumor syndrome)".
- ^ Weisbrich A, Honnappa S, Jaussi R, Okhrimenko O, Frey D, Jelesarov I, Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO (October 2007). "Structure-function relationship of CAP-Gly domains". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 14 (10): 959–67. doi:10.1038/nsmb1291. PMID 17828277. S2CID 37088265.
- ^ a b c Nagy N, Dubois A, Szell M, Rajan N (2021). "Genetic Testing in CYLD Cutaneous Syndrome: An Update". The Application of Clinical Genetics. 14: 427–444. doi:10.2147/TACG.S288274. PMC 8566010. PMID 34744449.
- ^ a b c Cui Z, Kang H, Grandis JR, Johnson DE (January 2021). "CYLD Alterations in the Tumorigenesis and Progression of Human Papillomavirus-Associated Head and Neck Cancers". Molecular Cancer Research. 19 (1): 14–24. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0565. PMC 7840145. PMID 32883697.
- ^ a b Lei H, Wang J, Hu J, Zhu Q, Wu Y (August 2021). "Deubiquitinases in hematological malignancies". Biomarker Research. 9 (1): 66. doi:10.1186/s40364-021-00320-w. PMC 8401176. PMID 34454635.
- ^ Davies HR, Hodgson K, Schwalbe E, Coxhead J, Sinclair N, Zou X, Cockell S, Husain A, Nik-Zainal S, Rajan N (October 2019). "Epigenetic modifiers DNMT3A and BCOR are recurrently mutated in CYLD cutaneous syndrome". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 4717. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10.4717D. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12746-w. PMC 6797807. PMID 31624251.
Further reading
- Nakajima D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, Kikuno R, Ohara O, Nagase T (June 2002). "Construction of expression-ready cDNA clones for KIAA genes: manual curation of 330 KIAA cDNA clones". DNA Research. 9 (3): 99–106. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.500.923. doi:10.1093/dnares/9.3.99. PMID 12168954.
- Lian F, Cockerell CJ (2006). "Cutaneous appendage tumors: familial cylindromatosis and associated tumors update". Advances in Dermatology. 21: 217–34. doi:10.1016/j.yadr.2005.06.005. PMID 16350444.
- Biggs PJ, Wooster R, Ford D, Chapman P, Mangion J, Quirk Y, Easton DF, Burn J, Stratton MR (December 1995). "Familial cylindromatosis (turban tumour syndrome) gene localised to chromosome 16q12-q13: evidence for its role as a tumour suppressor gene". Nature Genetics. 11 (4): 441–3. doi:10.1038/ng1295-441. PMID 7493027. S2CID 33637152.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (January 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Biggs PJ, Chapman P, Lakhani SR, Burn J, Stratton MR (March 1996). "The cylindromatosis gene (cyld1) on chromosome 16q may be the only tumour suppressor gene involved in the development of cylindromas". Oncogene. 12 (6): 1375–7. PMID 8649842.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (October 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Suyama M, Kikuno R, Hirosawa M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (December 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Research. 5 (6): 355–64. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.6.355. PMID 10048485.
- Thomson SA, Rasmussen SA, Zhang J, Wallace MR (1999). "A new hereditary cylindromatosis family associated with CYLD1 on chromosome 16". Human Genetics. 105 (1–2): 171–3. doi:10.1007/s004399900077. PMID 10480375.
- Bignell GR, Warren W, Seal S, Takahashi M, Rapley E, Barfoot R, Green H, Brown C, Biggs PJ, Lakhani SR, Jones C, Hansen J, Blair E, Hofmann B, Siebert R, Turner G, Evans DG, Schrander-Stumpel C, Beemer FA, van Den Ouweland A, Halley D, Delpech B, Cleveland MG, Leigh I, Leisti J, Rasmussen S (June 2000). "Identification of the familial cylindromatosis tumour-suppressor gene". Nature Genetics. 25 (2): 160–5. doi:10.1038/76006. PMID 10835629. S2CID 22829077.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, Ren SX, Zhao M, Zhao CJ, Fu G, Shen Y, Fan HY, Lu G, Zhong M, Xu XR, Han ZG, Zhang JW, Tao J, Huang QH, Zhou J, Hu GX, Gu J, Chen SJ, Chen Z (October 2000). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Research. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Trompouki E, Hatzivassiliou E, Tsichritzis T, Farmer H, Ashworth A, Mosialos G (August 2003). "CYLD is a deubiquitinating enzyme that negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation by TNFR family members". Nature. 424 (6950): 793–6. Bibcode:2003Natur.424..793T. doi:10.1038/nature01803. hdl:21.11116/0000-0007-948F-1. PMID 12917689. S2CID 4424549.
- Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R (August 2003). "Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB". Nature. 424 (6950): 797–801. Bibcode:2003Natur.424..797B. doi:10.1038/nature01811. hdl:1874/17767. PMID 12917690. S2CID 4416878.
- Kovalenko A, Chable-Bessia C, Cantarella G, Israël A, Wallach D, Courtois G (August 2003). "The tumour suppressor CYLD negatively regulates NF-kappaB signalling by deubiquitination". Nature. 424 (6950): 801–5. Bibcode:2003Natur.424..801K. doi:10.1038/nature01802. PMID 12917691. S2CID 4397177.
- Hu G, Onder M, Gill M, Aksakal B, Oztas M, Gürer MA, Celebi JT (October 2003). "A novel missense mutation in CYLD in a family with Brooke-Spiegler syndrome". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 121 (4): 732–4. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12514.x. hdl:20.500.12648/7847. PMID 14632188.
- Regamey A, Hohl D, Liu JW, Roger T, Kogerman P, Toftgard R, Huber M (December 2003). "The tumor suppressor CYLD interacts with TRIP and regulates negatively nuclear factor kappaB activation by tumor necrosis factor". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 198 (12): 1959–64. doi:10.1084/jem.20031187. PMC 2194148. PMID 14676304.
- Zhang XJ, Liang YH, He PP, Yang S, Wang HY, Chen JJ, Yuan WT, Xu SJ, Cui Y, Huang W (March 2004). "Identification of the cylindromatosis tumor-suppressor gene responsible for multiple familial trichoepithelioma". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 122 (3): 658–64. doi:10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22321.x. PMID 15086550.
- Jono H, Lim JH, Chen LF, Xu H, Trompouki E, Pan ZK, Mosialos G, Li JD (August 2004). "NF-kappaB is essential for induction of CYLD, the negative regulator of NF-kappaB: evidence for a novel inducible autoregulatory feedback pathway". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (35): 36171–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406638200. hdl:21.11116/0000-0007-9489-7. PMID 15226292.
External links
- Human CYLD genome location and CYLD gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.