Chlorobis(dppe)iron hydride

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Chlorohydridobis(bis-1,2-(diphenylphosphino)ethane)iron(II)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C52H49ClFeP4 | |
| Molar mass | 889.09 |
| Appearance | red-violet solid |
| Melting point | 195 °C (383 °F; 468 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chlorobis(dppe)iron hydride is a coordination complex with the formula HFeCl(dppe)2, where dppe is the bidentate ligand 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane. It is a red-violet solid. The compound has attracted much attention as a precursor to dihydrogen complexes.[1]
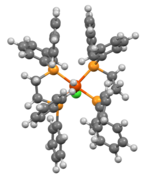
Structure
The complex exhibits octahedral molecular geometry. The chloride and hydride ligands are mutually trans.[2] The bond distances between the iron metal atom and the coordinating ligands are given by the following:
| Bond | Bond distance |
| Fe-P1 | 2.238 |
| Fe-P2 | 2.256 |
| Fe-P3 | 2.236 |
| Fe-P4 | 2.255 |
| Fe-Cl | 2.404 |
| Fe-H | 1.313 |
Synthesis and reactions
The compound is synthesized according to the following idealized reaction:[3]
- FeCl2 + 2 dppe + Na[BH4] → NaCl + ½ B2H6 + HFeCl(dppe)2
In the course of this conversion, high-spin complex FeCl2(dppe)2 converts to low-spin HFeCl(dppe)2.
The complex HFeCl[(dppe)2 exhibits a number of reactions associated with the remaining Fe-Cl bond. Reaction of the complex with sodium borohydride gives the dihydride complex:
- HFeCl(dppe)2 + NaBH4 → H2Fe(dppe)2 + NaCl + "BH3"
Removal of chloride using sodium tetrafluorborate under and atmostphere of hydrogen or nitrogen gives the dinitrogen and dihydrogen complexes:[4]
- HFeCl(dppe)2 + NaBF4 + N2 → [HFe(N2)(dppe)2]BF4 + NaCl
- HFeCl(dppe)2 + NaBF4 + H2 → [HFe(H2)(dppe)2]BF4 + NaCl
References
- ^ Morris RH (2008). "Dihydrogen, Dihydride and in Between: Nmr and Structural Properties of Iron Group Complexes". Coord. Chem. Rev. 2252 (21–22): 2381–2394. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.01.010.
- ^ Lee, J.; Jung, G.; Lee, S. W. Structure of trans-chlorohydridobis(diphenylphosphinoethane)iron(II). Bull. Korean. Chem. 1998, 19, 267. ISSN 0253-2964
- ^ Giannoccaro, P.; Sacco, A. (1977). "Bis[Ethylenebis(Diphenylphosphine)]-Hydridoiron Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 17. pp. 69–71. doi:10.1002/9780470132487.ch19. ISBN 9780470132487.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Bautista MT, Bynum LD, Schauer CK (1996). "Synthesis of η2-Dihydrogen Complex, trans-{Fe(η2-H2)(H)[1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane]2}[BF4]: An Experiment for an Advanced Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Involving Synthesis and NMR Properties of an η2-H2 Complex". Journal of Chemical Education. 73 (10): 988–991. doi:10.1021/ed073p988.
