OpenBiblio
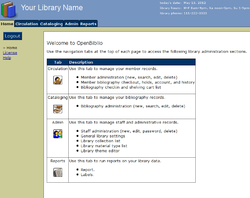 Main screen of OpenBiblio | |
| Developer(s) | OpenBiblio development team |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2002 |
| Stable release | 0.7.3g
/ January 1, 2018 |
| Written in | PHP |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Integrated library system |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | obiblio |
OpenBiblio is an open source Integrated Library System. The software is popular with small and rural libraries worldwide due to its simplicity, extensive language support, and good documentation.[1]
History
Openbiblio was created in 2002 by Dave Stevens, who was interested in creating an easy-to-use, well-documented, easy-to-install library system.[2] The current maintainer is Hans van der Weij. After 2017, the current version with a variety of options and bugfixes was published on openbiblio.de.
Implementations and usage
Though the system is still under active development, it has already become widely used in small libraries and archives worldwide. Researchers from the National Autonomous University of Mexico have recommended the use of the system in indigenous community libraries in Mexico, particularly because of its support of the Nahuatl language.[3] The National Library of Armenia has recommended the use of OpenBiblio for the country's 900 small (fewer than 40,000 volumes) and rural libraries.[4]
The system has been translated into Spanish by a professor of Castilian, and is used in the primary school system in Chile. In addition, Colombia, Cuba and Venezuela have expressed an interest in this program, according to Werner Westerman of the Chilean Educalibre group.[5]
Researchers from the Federal University of Paraíba's Information Science department also discuss the use of OpenBiblio in teaching future librarians about library automation systems.[6]
Forks
- Jorge Lara began translating OpenBiblio's code base into Spanish, and ultimately created a fork of the project called EspaBiblio.[7]
- Jack Eapen based the WebBiblio Subject Gateway System on OpenBiblio.[8]
Features
- Circulation: for staff to check items in and out to patrons, and to add new patrons.
- Cataloguing: for staff to create, modify, or delete bibliographic records, including uploading of MARC and MARCXML records.
- Online public access catalog (OPAC): a public catalog for patrons to find books
- Administration: Configuration and management of the system, including library, staff, material, fines, and website settings.
- Reports: Retrieve and format information from the database, including overdue letters and statistical models for the use of the library's materials. OpenBiblio uses a special syntax called RPT for its reports, so that users do not have to learn PHP to create these reports.[9]
While OpenBiblio provides all the essential functionalities for a small or medium-sized library, it does not include the more complex features, such as acquisitions and serials management, provided by other open source integrated library systems, such as Koha or Evergreen.[10]
See also
References
- ^ Kamble, V.T.; Hans Raj; Sangeeta (September 2012). "Open Source Library Management and Digital Library Software". DESIDOC Journal of Library & Information Technology. 32 (5): 388–392 [390]. doi:10.14429/djlit.32.5.2647.
- ^ Arriola Navarrete, Oscar; Katya Butrón Yáñez (2008). "Sistemas integrales para la automatización de bibliotecas basados en software libre". Acimed. 18 (6): 90. hdl:10760/12760.
- ^ León, Alejandro Jiménez; Vallejo, María Graciela Gutiérrez (March 2010). "Software libre como alternativa para desarrollar sistemas informáticos basados en la lengua indígena de la población. El caso de OpenBiblio distribución náhuatl". Apertura: Revista de Innovación Educativa (Special Issue): 52–63. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ Zargaryan, Tigran (November 2011). "OpenBiblio in Armenia: Automation of Small Libraries". EIFL-FOSS. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ Morales, Pablo (9 August 2005). "Aprender a innovar desde abajo". La Nación. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ Da Silva, Márcio Bezerra (2010). "The library automation system OpenBiblio applied to discipline library automation". Biblionline. 6 (1): 53–71. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
- ^ Aldana, Julio Santillán (April–June 2006). "Sistemas de Gestión Bibliotecaria desarrollados en Latinoamérica I: La experiencia de Presys y EspaBiblio". Biblios. 7 (24). hdl:10760/8098.
- ^ "Derivatives". OpenBiblio. SourceForge.net. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ^ Stetson, Micah. "RPTSyntax". OpenBiblio. Sourceforge.net. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ^ Kumar, Vimal (16 November 2005). Free/Open source integrated library management systems: comparative analysis of Koha, PHPMyLibrary and OpenBiblio. Modern trends in IT application in Library and Information services. Modern trends in IT application in Library and Information services. University of Calicut. hdl:10760/8578.
