Solar irradiance
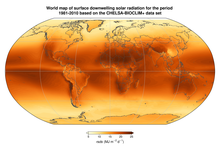

Solar irradiance is the power per unit area (surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument. Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre (W/m2) in SI units.
Solar irradiance is often integrated over a given time period in order to report the radiant energy emitted into the surrounding environment (joule per square metre, J/m2) during that time period. This integrated solar irradiance is called solar irradiation, solar exposure, solar insolation, or insolation.
Irradiance may be measured in space or at the Earth's surface after atmospheric absorption and scattering. Irradiance in space is a function of distance from the Sun, the solar cycle, and cross-cycle changes.[2] Irradiance on the Earth's surface additionally depends on the tilt of the measuring surface, the height of the Sun above the horizon, and atmospheric conditions.[3] Solar irradiance affects plant metabolism and animal behavior.[4]
The study and measurement of solar irradiance have several important applications, including the prediction of energy generation from solar power plants, the heating and cooling loads of buildings, climate modeling and weather forecasting, passive daytime radiative cooling applications, and space travel.
Types


There are several measured types of solar irradiance.
- Total solar irradiance (TSI) is a measure of the solar power over all wavelengths per unit area incident on the Earth's upper atmosphere. It is measured facing (pointing at / parallel to) the incoming sunlight (i.e. the flux through a surface perpendicular to the incoming sunlight; other angles would not be TSI and be reduced by the dot product).[3] The solar constant is a conventional measure of mean TSI at a distance of one astronomical unit (AU).
- Direct normal irradiance (DNI), or beam radiation, is measured at the surface of the Earth at a given location with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun direction.[6] It excludes diffuse solar radiation (radiation that is scattered or reflected by atmospheric components). Direct irradiance is equal to the extraterrestrial irradiance above the atmosphere minus the atmospheric losses due to absorption and scattering. Losses depend on time of day (length of light's path through the atmosphere depending on the solar elevation angle), cloud cover, moisture content and other contents. The irradiance above the atmosphere also varies with time of year (because the distance to the Sun varies), although this effect is generally less significant compared to the effect of losses on DNI.
- Diffuse horizontal irradiance (DHI), or diffuse sky radiation is the radiation at the Earth's surface from light scattered by the atmosphere. It is measured on a horizontal surface with radiation coming from all points in the sky excluding circumsolar radiation (radiation coming from the sun disk).[6][7] There would be almost no DHI in the absence of atmosphere.[6]
- Global horizontal irradiance (GHI) is the total irradiance from the Sun on a horizontal surface on Earth. It is the sum of direct irradiance (after accounting for the solar zenith angle of the Sun z) and diffuse horizontal irradiance:[8]
- Global tilted irradiance (GTI) is the total radiation received on a surface with defined tilt and azimuth, fixed or Sun-tracking. GTI can be measured[7] or modeled from GHI, DNI, DHI.[9][10][11] It is often a reference for photovoltaic power plants, while photovoltaic modules are mounted on the fixed or tracking constructions.
- Global normal irradiance (GNI) is the total irradiance from the Sun at the surface of Earth at a given location with a surface element perpendicular to the Sun.
Spectral versions of the above irradiances (e.g. spectral TSI, spectral DNI, etc.) are any of the above with units divided either by meter or nanometer (for a spectral graph as function of wavelength), or per-Hz (for a spectral function with an x-axis of frequency).[citation needed] When one plots such spectral distributions as a graph, the integral of the function (area under the curve) will be the (non-spectral) irradiance. e.g.: Say one had a solar cell on the surface of the earth facing straight up, and had DNI in units of W/m^2 per nm, graphed as a function of wavelength (in nm). Then, the unit of the integral (W/m^2) is the product of those two units.[citation needed]
Units
The SI unit of irradiance is watts per square metre (W/m2 = Wm−2). The unit of insolation often used in the solar power industry is kilowatt hours per square metre (kWh/m2).[12]
The Langley is an alternative unit of insolation. One Langley is one thermochemical calorie per square centimetre or 41,840 J/m2.[13]
Irradiation at the top of the atmosphere

The average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is about 1361 W/m2. This represents the power per unit area of solar irradiance across the spherical surface surrounding the Sun with a radius equal to the distance to the Earth (1 AU). This means that the approximately circular disc of the Earth, as viewed from the Sun, receives a roughly stable 1361 W/m2 at all times. The area of this circular disc is πr2, in which r is the radius of the Earth. Because the Earth is approximately spherical, it has total area , meaning that the solar radiation arriving at the top of the atmosphere, averaged over the entire surface of the Earth, is simply divided by four to get 340 W/m2. In other words, averaged over the year and the day, the Earth's atmosphere receives 340 W/m2 from the Sun. This figure is important in radiative forcing.
Derivation
The distribution of solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere is determined by Earth's sphericity and orbital parameters. This applies to any unidirectional beam incident to a rotating sphere. Insolation is essential for numerical weather prediction and understanding seasons and climatic change. Application to ice ages is known as Milankovitch cycles.
Distribution is based on a fundamental identity from spherical trigonometry, the spherical law of cosines: where a, b and c are arc lengths, in radians, of the sides of a spherical triangle. C is the angle in the vertex opposite the side which has arc length c. Applied to the calculation of solar zenith angle Θ, the following applies to the spherical law of cosines:
This equation can be also derived from a more general formula:[14] where β is an angle from the horizontal and γ is an azimuth angle.

The separation of Earth from the Sun can be denoted RE and the mean distance can be denoted R0, approximately 1 astronomical unit (AU). The solar constant is denoted S0. The solar flux density (insolation) onto a plane tangent to the sphere of the Earth, but above the bulk of the atmosphere (elevation 100 km or greater) is:
The average of Q over a day is the average of Q over one rotation, or the hour angle progressing from h = π to h = −π:
Let h0 be the hour angle when Q becomes positive. This could occur at sunrise when , or for h0 as a solution of or
If tan(φ) tan(δ) > 1, then the sun does not set and the sun is already risen at h = π, so ho = π. If tan(φ) tan(δ) < −1, the sun does not rise and .
is nearly constant over the course of a day, and can be taken outside the integral
Therefore:
Let θ be the conventional polar angle describing a planetary orbit. Let θ = 0 at the March equinox. The declination δ as a function of orbital position is[15][16] where ε is the obliquity. (Note: The correct formula, valid for any axial tilt, is .[17]) The conventional longitude of perihelion ϖ is defined relative to the March equinox, so for the elliptical orbit:[18] or
With knowledge of ϖ, ε and e from astrodynamical calculations[19] and So from a consensus of observations or theory, can be calculated for any latitude φ and θ. Because of the elliptical orbit, and as a consequence of Kepler's second law, θ does not progress uniformly with time. Nevertheless, θ = 0° is exactly the time of the March equinox, θ = 90° is exactly the time of the June solstice, θ = 180° is exactly the time of the September equinox and θ = 270° is exactly the time of the December solstice.
A simplified equation for irradiance on a given day is:[20][21]
where n is a number of a day of the year.
Variation
Total solar irradiance (TSI)[22] changes slowly on decadal and longer timescales. The variation during solar cycle 21 was about 0.1% (peak-to-peak).[23] In contrast to older reconstructions,[24] most recent TSI reconstructions point to an increase of only about 0.05% to 0.1% between the 17th century Maunder Minimum and the present.[25][26][27] However, current understanding based on various lines of evidence suggests that the lower values for the secular trend are more probable.[27] In particular, a secular trend greater than 2 Wm-2 is considered highly unlikely.[27][28][29] Ultraviolet irradiance (EUV) varies by approximately 1.5 percent from solar maxima to minima, for 200 to 300 nm wavelengths.[30] However, a proxy study estimated that UV has increased by 3.0% since the Maunder Minimum.[31]

Some variations in insolation are not due to solar changes but rather due to the Earth moving between its perihelion and aphelion, or changes in the latitudinal distribution of radiation. These orbital changes or Milankovitch cycles have caused radiance variations of as much as 25% (locally; global average changes are much smaller) over long periods. The most recent significant event was an axial tilt of 24° during boreal summer near the Holocene climatic optimum. Obtaining a time series for a for a particular time of year, and particular latitude, is a useful application in the theory of Milankovitch cycles. For example, at the summer solstice, the declination δ is equal to the obliquity ε. The distance from the Sun is
For this summer solstice calculation, the role of the elliptical orbit is entirely contained within the important product , the precession index, whose variation dominates the variations in insolation at 65° N when eccentricity is large. For the next 100,000 years, with variations in eccentricity being relatively small, variations in obliquity dominate.
Measurement
The space-based TSI record comprises measurements from more than ten radiometers and spans three solar cycles. All modern TSI satellite instruments employ active cavity electrical substitution radiometry. This technique measures the electrical heating needed to maintain an absorptive blackened cavity in thermal equilibrium with the incident sunlight which passes through a precision aperture of calibrated area. The aperture is modulated via a shutter. Accuracy uncertainties of < 0.01% are required to detect long term solar irradiance variations, because expected changes are in the range 0.05–0.15 W/m2 per century.[32]
Intertemporal calibration
In orbit, radiometric calibrations drift for reasons including solar degradation of the cavity, electronic degradation of the heater, surface degradation of the precision aperture and varying surface emissions and temperatures that alter thermal backgrounds. These calibrations require compensation to preserve consistent measurements.[32]
For various reasons, the sources do not always agree. The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment/Total Irradiance Measurement (SORCE/TIM) TSI values are lower than prior measurements by the Earth Radiometer Budget Experiment (ERBE) on the Earth Radiation Budget Satellite (ERBS), VIRGO on the Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SoHO) and the ACRIM instruments on the Solar Maximum Mission (SMM), Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) and ACRIMSAT. Pre-launch ground calibrations relied on component rather than system-level measurements since irradiance standards at the time lacked sufficient absolute accuracies.[32]
Measurement stability involves exposing different radiometer cavities to different accumulations of solar radiation to quantify exposure-dependent degradation effects. These effects are then compensated for in the final data. Observation overlaps permits corrections for both absolute offsets and validation of instrumental drifts.[32]
Uncertainties of individual observations exceed irradiance variability (~0.1%). Thus, instrument stability and measurement continuity are relied upon to compute real variations.
Long-term radiometer drifts can potentially be mistaken for irradiance variations which can be misinterpreted as affecting climate. Examples include the issue of the irradiance increase between cycle minima in 1986 and 1996, evident only in the ACRIM composite (and not the model) and the low irradiance levels in the PMOD composite during the 2008 minimum.
Despite the fact that ACRIM I, ACRIM II, ACRIM III, VIRGO and TIM all track degradation with redundant cavities, notable and unexplained differences remain in irradiance and the modeled influences of sunspots and faculae.
Persistent inconsistencies
Disagreement among overlapping observations indicates unresolved drifts that suggest the TSI record is not sufficiently stable to discern solar changes on decadal time scales. Only the ACRIM composite shows irradiance increasing by ~1 W/m2 between 1986 and 1996; this change is also absent in the model.[32]
Recommendations to resolve the instrument discrepancies include validating optical measurement accuracy by comparing ground-based instruments to laboratory references, such as those at National Institute of Science and Technology (NIST); NIST validation of aperture area calibrations uses spares from each instrument; and applying diffraction corrections from the view-limiting aperture.[32]
For ACRIM, NIST determined that diffraction from the view-limiting aperture contributes a 0.13% signal not accounted for in the three ACRIM instruments. This correction lowers the reported ACRIM values, bringing ACRIM closer to TIM. In ACRIM and all other instruments but TIM, the aperture is deep inside the instrument, with a larger view-limiting aperture at the front. Depending on edge imperfections this can directly scatter light into the cavity. This design admits into the front part of the instrument two to three times the amount of light intended to be measured; if not completely absorbed or scattered, this additional light produces erroneously high signals. In contrast, TIM's design places the precision aperture at the front so that only desired light enters.[32]
Variations from other sources likely include an annual systematics in the ACRIM III data that is nearly in phase with the Sun-Earth distance and 90-day spikes in the VIRGO data coincident with SoHO spacecraft maneuvers that were most apparent during the 2008 solar minimum.
TSI Radiometer Facility
TIM's high absolute accuracy creates new opportunities for measuring climate variables. TSI Radiometer Facility (TRF) is a cryogenic radiometer that operates in a vacuum with controlled light sources. L-1 Standards and Technology (LASP) designed and built the system, completed in 2008. It was calibrated for optical power against the NIST Primary Optical Watt Radiometer, a cryogenic radiometer that maintains the NIST radiant power scale to an uncertainty of 0.02% (1σ). As of 2011 TRF was the only facility that approached the desired <0.01% uncertainty for pre-launch validation of solar radiometers measuring irradiance (rather than merely optical power) at solar power levels and under vacuum conditions.[32]
TRF encloses both the reference radiometer and the instrument under test in a common vacuum system that contains a stationary, spatially uniform illuminating beam. A precision aperture with an area calibrated to 0.0031% (1σ) determines the beam's measured portion. The test instrument's precision aperture is positioned in the same location, without optically altering the beam, for direct comparison to the reference. Variable beam power provides linearity diagnostics, and variable beam diameter diagnoses scattering from different instrument components.[32]
The Glory/TIM and PICARD/PREMOS flight instrument absolute scales are now traceable to the TRF in both optical power and irradiance. The resulting high accuracy reduces the consequences of any future gap in the solar irradiance record.[32]
| Instrument | Irradiance, view-limiting aperture overfilled |
Irradiance, precision aperture overfilled |
Difference attributable to scatter error |
Measured optical power error |
Residual irradiance agreement |
Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SORCE/TIM ground | — | −0.037% | — | −0.037% | 0.000% | 0.032% |
| Glory/TIM flight | — | −0.012% | — | −0.029% | 0.017% | 0.020% |
| PREMOS-1 ground | −0.005% | −0.104% | 0.098% | −0.049% | −0.104% | ~0.038% |
| PREMOS-3 flight | 0.642% | 0.605% | 0.037% | 0.631% | −0.026% | ~0.027% |
| VIRGO-2 ground | 0.897% | 0.743% | 0.154% | 0.730% | 0.013% | ~0.025% |
2011 reassessment
The most probable value of TSI representative of solar minimum is 1360.9±0.5 W/m2, lower than the earlier accepted value of 1365.4±1.3 W/m2, established in the 1990s. The new value came from SORCE/TIM and radiometric laboratory tests. Scattered light is a primary cause of the higher irradiance values measured by earlier satellites in which the precision aperture is located behind a larger, view-limiting aperture. The TIM uses a view-limiting aperture that is smaller than the precision aperture that precludes this spurious signal. The new estimate is from better measurement rather than a change in solar output.[32]
A regression model-based split of the relative proportion of sunspot and facular influences from SORCE/TIM data accounts for 92% of observed variance and tracks the observed trends to within TIM's stability band. This agreement provides further evidence that TSI variations are primarily due to solar surface magnetic activity.[32]
Instrument inaccuracies add a significant uncertainty in determining Earth's energy balance. The energy imbalance has been variously measured (during a deep solar minimum of 2005–2010) to be +0.58±0.15 W/m2,[33] +0.60±0.17 W/m2[34] and +0.85 W/m2. Estimates from space-based measurements range +3–7 W/m2. SORCE/TIM's lower TSI value reduces this discrepancy by 1 W/m2. This difference between the new lower TIM value and earlier TSI measurements corresponds to a climate forcing of −0.8 W/m2, which is comparable to the energy imbalance.[32]
2014 reassessment
In 2014 a new ACRIM composite was developed using the updated ACRIM3 record. It added corrections for scattering and diffraction revealed during recent testing at TRF and two algorithm updates. The algorithm updates more accurately account for instrument thermal behavior and parsing of shutter cycle data. These corrected a component of the quasi-annual spurious signal and increased the signal-to-noise ratio, respectively. The net effect of these corrections decreased the average ACRIM3 TSI value without affecting the trending in the ACRIM Composite TSI.[35]
Differences between ACRIM and PMOD TSI composites are evident, but the most significant is the solar minimum-to-minimum trends during solar cycles 21-23. ACRIM found an increase of +0.037%/decade from 1980 to 2000 and a decrease thereafter. PMOD instead presents a steady decrease since 1978. Significant differences can also be seen during the peak of solar cycles 21 and 22. These arise from the fact that ACRIM uses the original TSI results published by the satellite experiment teams while PMOD significantly modifies some results to conform them to specific TSI proxy models. The implications of increasing TSI during the global warming of the last two decades of the 20th century are that solar forcing may be a marginally larger factor in climate change than represented in the CMIP5 general circulation climate models.[35]
Irradiance on Earth's surface


Average annual solar radiation arriving at the top of the Earth's atmosphere is roughly 1361 W/m2.[36] The Sun's rays are attenuated as they pass through the atmosphere, leaving maximum normal surface irradiance at approximately 1000 W/m2 at sea level on a clear day. When 1361 W/m2 is arriving above the atmosphere (when the Sun is at the zenith in a cloudless sky), direct sun is about 1050 W/m2, and global radiation on a horizontal surface at ground level is about 1120 W/m2.[37] The latter figure includes radiation scattered or reemitted by the atmosphere and surroundings. The actual figure varies with the Sun's angle and atmospheric circumstances. Ignoring clouds, the daily average insolation for the Earth is approximately 6 kWh/m2 = 21.6 MJ/m2.
The output of, for example, a photovoltaic panel, partly depends on the angle of the sun relative to the panel. One Sun is a unit of power flux, not a standard value for actual insolation. Sometimes this unit is referred to as a Sol, not to be confused with a sol, meaning one solar day.[38]
Absorption and reflection

Part of the radiation reaching an object is absorbed and the remainder reflected. Usually, the absorbed radiation is converted to thermal energy, increasing the object's temperature. Humanmade or natural systems, however, can convert part of the absorbed radiation into another form such as electricity or chemical bonds, as in the case of photovoltaic cells or plants. The proportion of reflected radiation is the object's reflectivity or albedo.
Projection effect

Insolation onto a surface is largest when the surface directly faces (is normal to) the sun. As the angle between the surface and the Sun moves from normal, the insolation is reduced in proportion to the angle's cosine; see effect of Sun angle on climate.
In the figure, the angle shown is between the ground and the sunbeam rather than between the vertical direction and the sunbeam; hence the sine rather than the cosine is appropriate. A sunbeam one mile wide arrives from directly overhead, and another at a 30° angle to the horizontal. The sine of a 30° angle is 1/2, whereas the sine of a 90° angle is 1. Therefore, the angled sunbeam spreads the light over twice the area. Consequently, half as much light falls on each square mile.
This projection effect is the main reason why Earth's polar regions are much colder than equatorial regions. On an annual average, the poles receive less insolation than does the equator, because the poles are always angled more away from the Sun than the tropics, and moreover receive no insolation at all for the six months of their respective winters.
Absorption effect
At a lower angle, the light must also travel through more atmosphere. This attenuates it (by absorption and scattering) further reducing insolation at the surface.
Attenuation is governed by the Beer-Lambert Law, namely that the transmittance or fraction of insolation reaching the surface decreases exponentially in the optical depth or absorbance (the two notions differing only by a constant factor of ln(10) = 2.303) of the path of insolation through the atmosphere. For any given short length of the path, the optical depth is proportional to the number of absorbers and scatterers along that length, typically increasing with decreasing altitude. The optical depth of the whole path is then the integral (sum) of those optical depths along the path.
When the density of absorbers is layered, that is, depends much more on vertical than horizontal position in the atmosphere, to a good approximation the optical depth is inversely proportional to the projection effect, that is, to the cosine of the zenith angle. Since transmittance decreases exponentially with increasing optical depth, as the sun approaches the horizon there comes a point when absorption dominates projection for the rest of the day. With a relatively high level of absorbers this can be a considerable portion of the late afternoon, and likewise of the early morning. Conversely, in the (hypothetical) total absence of absorption, the optical depth remains zero at all altitudes of the sun, that is, transmittance remains 1, and so only the projection effect applies.
Solar potential maps
Assessment and mapping of solar potential at the global, regional and country levels have been the subject of significant academic and commercial interest. One of the earliest attempts to carry out comprehensive mapping of solar potential for individual countries was the Solar & Wind Resource Assessment (SWERA) project,[39] funded by the United Nations Environment Program and carried out by the US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) provides data for global solar potential maps through the CERES experiment and the POWER project. Global mapping by many other similar institutes are available on the Global Atlas for Renewable Energy provided by the International Renewable Energy Agency. A number of commercial firms now exist to provide solar resource data to solar power developers, including 3E, Clean Power Research, SoDa Solar Radiation Data, Solargis, Vaisala (previously 3Tier), and Vortex, and these firms have often provided solar potential maps for free. In January 2017 the Global Solar Atlas was launched by the World Bank, using data provided by Solargis, to provide a single source for high-quality solar data, maps, and GIS layers covering all countries.
- Maps of GHI potential by region and country (Note: colors are not consistent across maps)
-
Sub-Saharan Africa
-
Latin America and Caribbean
-
China
-
India
-
Mexico
-
South Africa
Solar radiation maps are built using databases derived from satellite imagery, as for example using visible images from Meteosat Prime satellite. A method is applied to the images to determine solar radiation. One well validated satellite-to-irradiance model is the SUNY model.[40] The accuracy of this model is well evaluated. In general, solar irradiance maps are accurate, especially for Global Horizontal Irradiance.
Applications
Solar power
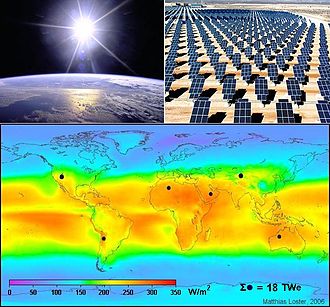
Solar irradiation figures are used to plan the deployment of solar power systems.[41] In many countries, the figures can be obtained from an insolation map or from insolation tables that reflect data over the prior 30–50 years. Different solar power technologies are able to use different components of the total irradiation. While solar photovoltaics panels are able to convert to electricity both direct irradiation and diffuse irradiation, concentrated solar power is only able to operate efficiently with direct irradiation, thus making these systems suitable only in locations with relatively low cloud cover.
Because solar collectors panels are almost always mounted at an angle towards the Sun, insolation figures must be adjusted to find the amount of sunlight falling on the panel. This will prevent estimates that are inaccurately low for winter and inaccurately high for summer.[42] This also means that the amount of sunlight falling on a solar panel at high latitude is not as low compared to one at the equator as would appear from just considering insolation on a horizontal surface. Horizontal insolation values range from 800 to 950 kWh/(kWp·y) in Norway to up to 2,900 kWh/(kWp·y) in Australia. But a properly tilted panel at 50° latitude receives 1860 kWh/m2/y, compared to 2370 at the equator.[43] In fact, under clear skies a solar panel placed horizontally at the north or south pole at midsummer receives more sunlight over 24 hours (cosine of angle of incidence equal to sin(23.5°) or about 0.40) than a horizontal panel at the equator at the equinox (average cosine equal to 1/π or about 0.32).
Photovoltaic panels are rated under standard conditions to determine the Wp (peak watts) rating,[44] which can then be used with insolation, adjusted by factors such as tilt, tracking and shading, to determine the expected output.[45]
Buildings

In construction, insolation is an important consideration when designing a building for a particular site.[46]
The projection effect can be used to design buildings that are cool in summer and warm in winter, by providing vertical windows on the equator-facing side of the building (the south face in the northern hemisphere, or the north face in the southern hemisphere): this maximizes insolation in the winter months when the Sun is low in the sky and minimizes it in the summer when the Sun is high. (The Sun's north–south path through the sky spans 47° through the year).
Civil engineering
In civil engineering and hydrology, numerical models of snowmelt runoff use observations of insolation. This permits estimation of the rate at which water is released from a melting snowpack. Field measurement is accomplished using a pyranometer.
Climate research
Irradiance plays a part in climate modeling and weather forecasting. A non-zero average global net radiation at the top of the atmosphere is indicative of Earth's thermal disequilibrium as imposed by climate forcing.
The impact of the lower 2014 TSI value on climate models is unknown. A few tenths of a percent change in the absolute TSI level is typically considered to be of minimal consequence for climate simulations. The new measurements require climate model parameter adjustments.
Experiments with GISS Model 3 investigated the sensitivity of model performance to the TSI absolute value during the present and pre-industrial epochs, and describe, for example, how the irradiance reduction is partitioned between the atmosphere and surface and the effects on outgoing radiation.[32]
Assessing the impact of long-term irradiance changes on climate requires greater instrument stability[32] combined with reliable global surface temperature observations to quantify climate response processes to radiative forcing on decadal time scales. The observed 0.1% irradiance increase imparts 0.22 W/m2 climate forcing, which suggests a transient climate response of 0.6 °C per W/m2. This response is larger by a factor of 2 or more than in the IPCC-assessed 2008 models, possibly appearing in the models' heat uptake by the ocean.[32]
Global cooling
Measuring a surface's capacity to reflect solar irradiance is essential to passive daytime radiative cooling, which has been proposed as a method of reversing local and global temperature increases associated with global warming.[47][48] In order to measure the cooling power of a passive radiative cooling surface, both the absorbed powers of atmospheric and solar radiations must be quantified. On a clear day, solar irradiance can reach 1000 W/m2 with a diffuse component between 50 and 100 W/m2. On average the cooling power of a passive daytime radiative cooling surface has been estimated at ~100-150 W/m2.[49]
Space
Insolation is the primary variable affecting equilibrium temperature in spacecraft design and planetology.
Solar activity and irradiance measurement is a concern for space travel. For example, the American space agency, NASA, launched its Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) satellite with Solar Irradiance Monitors.[2]
See also
- Earth's energy budget
- PI curve (photosynthesis-irradiance curve)
- Irradiance
- Albedo
- Flux
- Power density
- Sun chart
- Sunlight
- Sunshine duration
References
- ^ Brun, P., Zimmermann, N.E., Hari, C., Pellissier, L., Karger, D.N. (preprint): Global climate-related predictors at kilometre resolution for the past and future. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-2022-212
- ^ a b Michael Boxwell, Solar Electricity Handbook: A Simple, Practical Guide to Solar Energy (2012), pp. 41–42.
- ^ a b Stickler, Greg. "Educational Brief - Solar Radiation and the Earth System". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Archived from the original on 25 April 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ^ C.Michael Hogan. 2010. Abiotic factor. Encyclopedia of Earth. eds Emily Monosson and C. Cleveland. National Council for Science and the Environment. Washington, DC
- ^ a b World Bank. 2017. Global Solar Atlas. https://globalsolaratlas.info
- ^ a b c "RReDC Glossary of Solar Radiation Resource Terms". rredc.nrel.gov. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ a b "What is the Difference between Horizontal and Tilted Global Solar Irradiance? - Kipp & Zonen". www.kippzonen.com. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ "RReDC Glossary of Solar Radiation Resource Terms". rredc.nrel.gov. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Gueymard, Christian A. (March 2009). "Direct and indirect uncertainties in the prediction of tilted irradiance for solar engineering applications". Solar Energy. 83 (3): 432–444. Bibcode:2009SoEn...83..432G. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2008.11.004.
- ^ Sengupta, Manajit; Habte, Aron; Gueymard, Christian; Wilbert, Stefan; Renne, Dave (2017-12-01). "Best Practices Handbook for the Collection and Use of Solar Resource Data for Solar Energy Applications: Second Edition": NREL/TP–5D00–68886, 1411856. doi:10.2172/1411856. OSTI 1411856.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Gueymard, Chris A. (2015). "Uncertainties in Transposition and Decomposition Models: Lesson Learned" (PDF). Retrieved 2020-07-17.
- ^ "Solar Radiation Basics". U. S. Department of Energy. Retrieved April 23, 2022.
- ^ Thompson, Ambler; Taylor, Barry N. (February 17, 2022). "NIST Guide to the SI, Appendix B.8: Factors for Units Listed Alphabetically". SP 811 - The NIST Guide for the use of International System of Units (Report). National Institute of Standards and Technology.
- ^ "Part 3: Calculating Solar Angles - ITACA". www.itacanet.org. Retrieved 21 April 2018.
- ^ "Insolation in The Azimuth Project". www.azimuthproject.org. Retrieved 21 April 2018.
- ^ "Declination Angle - PVEducation". www.pveducation.org. Retrieved 21 April 2018.
- ^ Van Brummelen, Glen (2012). Heavenly Mathematics: The Forgotten Art of Spherical Trigonometry. Princeton University Press. Bibcode:2012hmfa.book.....V.
- ^ Berger, AndréL (1978-12-01). "Long-Term Variations of Daily Insolation and Quaternary Climatic Changes". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 35 (12): 2362–2367. Bibcode:1978JAtS...35.2362B. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1978)035<2362:LTVODI>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0022-4928.
- ^ [1] Archived November 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Duffie, John A.; Beckman, William A. (2013-04-10). Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes: Duffie/Solar Engineering 4e. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. doi:10.1002/9781118671603. ISBN 978-1-118-67160-3.
- ^ "Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes" (PDF).
- ^ Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, Total Solar Irradiance Data (retrieved 16 July 2015)
- ^ Willson, Richard C.; H.S. Hudson (1991). "The Sun's luminosity over a complete solar cycle". Nature. 351 (6321): 42–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.351...42W. doi:10.1038/351042a0. S2CID 4273483.
- ^ Board on Global Change, Commission on Geosciences, Environment, and Resources, National Research Council. (1994). Solar Influences on Global Change. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press. p. 36. doi:10.17226/4778. hdl:2060/19950005971. ISBN 978-0-309-05148-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Wang, Y.-M.; Lean, J. L.; Sheeley, N. R. (2005). "Modeling the Sun's magnetic field and irradiance since 1713" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal. 625 (1): 522–38. Bibcode:2005ApJ...625..522W. doi:10.1086/429689. S2CID 20573668. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 2, 2012.
- ^ Krivova, N. A.; Balmaceda, L.; Solanki, S. K. (2007). "Reconstruction of solar total irradiance since 1700 from the surface magnetic flux". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 467 (1): 335–46. Bibcode:2007A&A...467..335K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066725.
- ^ a b c Chatzistergos, Theodosios; Krivova, N. A.; Yeo, K. L. (2023). "Long-term changes in solar activity and irradiance". Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics. 252: 106150. arXiv:2303.03046. Bibcode:2023JASTP.25206150C. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2023.106150.
- ^ Yeo, K. L.; Solanki, S. K.; Krivova, N. A.; Rempel, M.; Anusha, L. S.; Shapiro, A. I.; Tagirov, R. V.; Witzke, V. (2020-10-16). "The Dimmest State of the Sun". Geophysical Research Letters. 47 (19). arXiv:2102.09487. Bibcode:2020GeoRL..4790243Y. doi:10.1029/2020GL090243. ISSN 0094-8276.
- ^ Lockwood, Mike; Ball, William T. (2020). "Placing limits on long-term variations in quiet-Sun irradiance and their contribution to total solar irradiance and solar radiative forcing of climate". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 476 (2238): 20200077. Bibcode:2020RSPSA.47600077L. doi:10.1098/rspa.2020.0077. ISSN 1364-5021. PMC 7428030. PMID 32831591.
- ^ Lean, J. (14 April 1989). "Contribution of Ultraviolet Irradiance Variations to Changes in the Sun's Total Irradiance". Science. 244 (4901): 197–200. Bibcode:1989Sci...244..197L. doi:10.1126/science.244.4901.197. PMID 17835351. S2CID 41756073.
1 percent of the sun's energy is emitted at ultraviolet wavelengths between 200 and 300 nanometers, the decrease in this radiation from 1 July 1981 to 30 June 1985 accounted for 19 percent of the decrease in the total irradiance
(19% of the 1/1366 total decrease is 1.4% decrease in UV) - ^ Fligge, M.; Solanki, S. K. (2000). "The solar spectral irradiance since 1700". Geophysical Research Letters. 27 (14): 2157–2160. Bibcode:2000GeoRL..27.2157F. doi:10.1029/2000GL000067. S2CID 54744463.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Kopp, Greg; Lean, Judith L. (14 January 2011). "A new, lower value of total solar irradiance: Evidence and climate significance". Geophysical Research Letters. 38 (1): L01706. Bibcode:2011GeoRL..38.1706K. doi:10.1029/2010GL045777.
- ^ James Hansen, Makiko Sato, Pushker Kharecha and Karina von Schuckmann (January 2012). "Earth's Energy Imbalance". NASA. Archived from the original on 2012-02-04.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Stephens, Graeme L.; Li, Juilin; Wild, Martin; Clayson, Carol Anne; Loeb, Norman; Kato, Seiji; L'Ecuyer, Tristan; Jr, Paul W. Stackhouse; Lebsock, Matthew (2012-10-01). "An update on Earth's energy balance in light of the latest global observations". Nature Geoscience. 5 (10): 691–696. Bibcode:2012NatGe...5..691S. doi:10.1038/ngeo1580. ISSN 1752-0894.
- ^ a b Scafetta, Nicola; Willson, Richard C. (April 2014). "ACRIM total solar irradiance satellite composite validation versus TSI proxy models". Astrophysics and Space Science. 350 (2): 421–442. arXiv:1403.7194. Bibcode:2014Ap&SS.350..421S. doi:10.1007/s10509-013-1775-9. ISSN 0004-640X. S2CID 3015605.
- ^ Coddington, O.; Lean, J. L.; Pilewskie, P.; Snow, M.; Lindholm, D. (22 August 2016). "A Solar Irradiance Climate Data Record". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 97 (7): 1265–1282. Bibcode:2016BAMS...97.1265C. doi:10.1175/bams-d-14-00265.1.
- ^ "Introduction to Solar Radiation". Newport Corporation. Archived from the original on October 29, 2013.
- ^ Michael Allison & Robert Schmunk (5 August 2008). "Technical Notes on Mars Solar Time". NASA. Retrieved 16 January 2012.
- ^ "Solar and Wind Energy Resource Assessment (SWERA) | Open Energy Information".
- ^ Nonnenmacher, Lukas; Kaur, Amanpreet; Coimbra, Carlos F.M. (2014-01-01). "Verification of the SUNY direct normal irradiance model with ground measurements". Solar Energy. 99: 246–258. Bibcode:2014SoEn...99..246N. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2013.11.010. ISSN 0038-092X.
- ^ "Determining your solar power requirements and planning the number of components".
- ^ "Heliostat Concepts". redrok.com.
- ^ Converted to yearly basis from Charles R. Landau (2017). "Optimum Tilt of Solar Panels".
- ^ [2] Archived July 14, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "How Do Solar Panels Work?". glrea.org. Archived from the original on 15 October 2004. Retrieved 21 April 2018.
- ^ Nall, D. H. "Looking across the water: Climate-adaptive buildings in the United States & Europe" (PDF). The Construction Specifier. 57 (2004–11): 50–56. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-18.
- ^ Han, Di; Fei, Jipeng; Li, Hong; Ng, Bing Feng (August 2022). "The criteria to achieving sub-ambient radiative cooling and its limits in tropical daytime". Building and Environment. 221 (1): 109281. Bibcode:2022BuEnv.22109281H. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109281 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ^ Munday, Jeremy (2019). "Tackling Climate Change through Radiative Cooling". Joule. 3 (9): 2057–2060. Bibcode:2019Joule...3.2057M. doi:10.1016/j.joule.2019.07.010. S2CID 201590290.
- ^ Chen, Meijie; Pang, Dan; Chen, Xingyu; Yan, Hongjie; Yang, Yuan (2022). "Passive daytime radiative cooling: Fundamentals, material designs, and applications". EcoMat. 4. doi:10.1002/eom2.12153. S2CID 240331557.
Bibliography
- Willson, Richard C.; H.S. Hudson (1991). "The Sun's luminosity over a complete solar cycle". Nature. 351 (6321): 42–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.351...42W. doi:10.1038/351042a0. S2CID 4273483.
- "The Sun and Climate". U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 0095-00. Retrieved 2005-02-21.
- Foukal, Peter; et al. (1977). "The effects of sunspots and faculae on the solar constant". Astrophysical Journal. 215: 952. Bibcode:1977ApJ...215..952F. doi:10.1086/155431.
- Stetson, H.T. (1937). Sunspots and Their Effects. New York: McGraw Hill.
- Yaskell, Steven Haywood (31 December 2012). Grand Phases On The Sun: The case for a mechanism responsible for extended solar minima and maxima. Trafford Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4669-6300-9.
External links
- Global Solar Atlas - browse or download maps and GIS data layers (global or per country) of the long-term averages of solar irradiation data (published by the World Bank, provided by Solargis)]
- Solcast - solar irradiance data updated every 10–15 minutes. Recent, live, historical and forecast, free for public research use
- Recent Total Solar Irradiance data updated every Monday
- San Francisco Solar Map
- European Commission- Interactive Maps
- Yesterday's Australian Solar Radiation Map
- Solar Radiation using Google Maps
- SMARTS, software to compute solar insolation of each date/location of earth Solar Resource Data and Tools
- NASA Surface meteorology and Solar Energy
- insol: R package for insolation on complex terrain
- Online insolation calculator














![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\int _{\pi }^{-\pi }Q\,dh&=\int _{h_{o}}^{-h_{o}}Q\,dh\\[5pt]&=S_{o}{\frac {R_{o}^{2}}{R_{E}^{2}}}\int _{h_{o}}^{-h_{o}}\cos(\Theta )\,dh\\[5pt]&=S_{o}{\frac {R_{o}^{2}}{R_{E}^{2}}}{\Bigg [}h\sin(\varphi )\sin(\delta )+\cos(\varphi )\cos(\delta )\sin(h){\Bigg ]}_{h=h_{o}}^{h=-h_{o}}\\[5pt]&=-2S_{o}{\frac {R_{o}^{2}}{R_{E}^{2}}}\left[h_{o}\sin(\varphi )\sin(\delta )+\cos(\varphi )\cos(\delta )\sin(h_{o})\right]\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cc1961aab28d29a2377ace388d269595e1d78bb2)
![{\displaystyle {\overline {Q}}^{\text{day}}={\frac {S_{o}}{\pi }}{\frac {R_{o}^{2}}{R_{E}^{2}}}\left[h_{o}\sin(\varphi )\sin(\delta )+\cos(\varphi )\cos(\delta )\sin(h_{o})\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bd3c84a8678a632cf6620cd267422432c1126903)
















