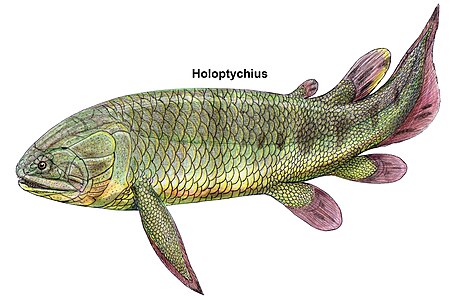
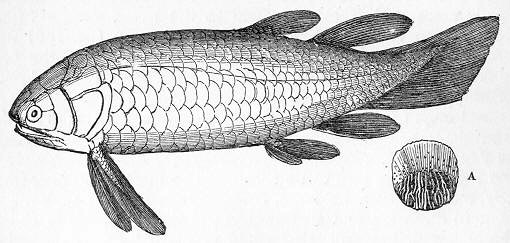
Holoptychius
| Holoptychius | |
|---|---|

| |
| Fossil of H. quebecensis in the Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Sarcopterygii |
| Class: | †Porolepimorpha |
| Order: | †Porolepiformes |
| Family: | †Holoptychiidae |
| Genus: | †Holoptychius Agassiz 1839 |
| Type species | |
| Holoptychius nobilissimus | |
| Species | |
| |
Holoptychius (from Greek: όλος holos, 'whole' and Greek: πτυχή ptyche 'fold')[1] is an extinct genus of porolepiform lobe-finned fish from the Middle Devonian to Carboniferous (Mississippian) periods. It is known from fossils worldwide. The genus was first described by Louis Agassiz in 1839.[2]
Description
[edit]Holoptychius was a streamlined predator about 50 centimetres (20 in) long (though largest specimen could grew up to 2.5 metres (8.2 ft)), which fed on other bony fish. Its rounded scales and body form indicate that it could have swum quickly through the water to catch prey.[3][4] Similar to other rhipidistians, it had fang-like teeth on its palate in addition to smaller teeth on the jaws. Its asymmetrical tail sported a caudal fin on its lower end. To compensate for the downward push caused by this fin placement, the pectoral fins of Holoptychius were placed high on the body.
Species
[edit]Of the genus Holoptychius the following species have been described:[2]
- H. americanus
- H. andersoni
- H. bergmanni (Downs et al, 2013) from the Frasnian-aged Fram Formation of Ellesmere Island, Arctic Canada[5]
- H. flemingi
- H. giganteus
- H. halli
- H. hopkinsii
- H. nobilissimus
- H. quebecensis[citation needed]
- H. sp. indet. from the Kennebecasis Formation of New Brunswich, Canada.[6]
- H. sp. indet. from the Cuche Formation of Colombia, known from an isolated tooth (UN-DG-PALV86) and preserved scales (UN-DG-PALV50-51).[7]
Distribution
[edit]Fossils of Holoptychius have been found in the Mississippian of the United Kingdom and the Devonian of Belgium, Colombia (Cuche Formation, Boyacá),[8][7] Norway, Canada,[5][6] the Russian Federation, and the United States (Pennsylvania).[9]
Gallery
[edit]-
H. andersoni
-
Life restoration of Holoptychius sp.
-
H. nobilissimus and scale
References
[edit]- ^ Roberts, George (1839). An etymological and explanatory dictionary of the terms and language of geology. London: Longman, Orme, Brown, Green, & Longmans. p. 78. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ a b Species Holoptychius[permanent dead link]
- ^ Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 43. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
- ^ Holland, Timothy (2010). "Upper Devonian osteichthyan remains from the Genoa River, Victoria, Australia" (PDF). Memoirs of Museum Victoria. 67: 35–44. doi:10.24199/j.mmv.2010.67.04. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016. Retrieved 2017-04-04.
- ^ a b Downs, Jason P.; Daeschler, Edward B.; Jenkins, Farish A.; Shubin, Neil H. (2013-03). "Holoptychius bergmannisp. nov. (Sarcopterygii, Porolepiformes) from the Upper Devonian of Nunavut, Canada, and a Review ofHoloptychiusTaxonomy". Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 162 (1): 47–59. doi:10.1635/053.162.0104. ISSN 0097-3157.
- ^ a b Miller, Randall F.; Brazeau, Martin D. (2007-01-01). "A Late Devonian porolepiform fish (Holoptychius) and the age of the kennebecasis formation, southern New Brunswick, Canada". Atlantic Geology. 43: 187–197. doi:10.4138/5650.
- ^ a b Mondéjar-Fernández, Jorge; Janvier, Philippe (2014-10-01). "Further evidence for the presence of holoptychiid porolepiforms (Sarcopterygii, Dipnomorpha) from the Frasnian of Colombia". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 13 (7): 587–597. Bibcode:2014CRPal..13..587M. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2014.03.009. ISSN 1631-0683.
- ^ Janvier & Villarroel, 1998
- ^ Holoptychius at Fossilworks.org
Bibliography
[edit]- Janvier, Philippe; Villarroel A, Carlos (1998). "Los Peces Devónicos del Macizo de Floresta (Boyacá, Colombia). Consideraciones taxonómicas, bioestratigráficas, biogeográficas y ambientales". Geología Colombiana. 23: 3–18. Retrieved 2017-03-31.
![]() Media related to Holoptychius at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Holoptychius at Wikimedia Commons