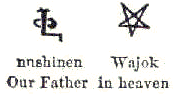Mi'kmaw hieroglyphs
| Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing Suckerfish script Gomgwejui'gasit | |
|---|---|
 The Ave Maria written in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing. | |
| Script type | |
Time period |
|
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Languages | Mi'kmaq |
Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing or Suckerfish script (Mi'kmawi'sit: Gomgwejui'gasit) was a writing system for the Mi'kmaw language, later superseded by various Latin scripts which are currently in use. Mi'kmaw are a Canadian First Nation whose homeland, called Mi'kma'ki, overlaps much of the Atlantic provinces, specifically all of Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, and parts of New Brunswick and Newfoundland and Labrador.
These glyphs, or gomgwejui'gaqan, were derived from a pictograph and petroglyph tradition,[1] and are logograms, with phonetic elements used alongside, including logographic, alphabetic, and ideographic information.[2] The gomgwejui'gasultijig take their name from the gomgwej (plural: gomgwejg) or sucker fish whose tracks are visibly left on the muddy river bottom. Mi'kmawi'sit uses several spelling systems, and the script is consequently sometimes called komqwejwi'kasikl or gomgwejui'gas'gl.
Classification
[edit]Scholars have debated whether the earliest known Mi'kmaw "hieroglyphs", from the 17th century, qualified fully as a writing system or served as a pictographic mnemonic device. In the 17th century, French Jesuit missionary Chrétien Le Clercq "formed" the Mi'kmaw characters as a logographic system for pedagogical purposes, in order to teach Catholic prayers, liturgy and doctrine to the Mi'kmaq.[3]
In 1978, Ives Goddard and William Fitzhugh of the Department of Anthropology at the Smithsonian Institution, contended that the pre-missionary system was purely mnemonic.[citation needed] They said that it could not have been used to write new compositions.[citation needed]
By contrast, in a 1995 book, David L. Schmidt and Murdena Marshall published some of the post-missionary prayers, narratives, and liturgies, as represented by hieroglyphs—pictographic symbols, which the French missionaries had used in the last quarter of the seventeenth century, to teach prayers and hymns.[2] Schmidt and Marshall showed that these hieroglyphics served as a fully functional writing system.[2] They said that it was the oldest writing system for a native language in North America north of Mexico.[2]
Michelle Sylliboy[4] indicates that "(a) French missionary stole our historical narrative with outlandish claims about our written language", and cites her Mi'kmaw grandmother (Lillian B. Marshall, 1934–2018) who stated in her "last conversation before she died, to make sure to tell “them” that we’ve always had our language," seemingly asserting that Le Clercq did not invent the script, and it had been in use by the people long before him. However, this seems to contradict the fact that after Le Clerq's return to France in 1687, the script had to be taught to other groups of Mi'kmaq by other missionaries, indicating it was not a script that the indigenous peoples already knew.[5]
History
[edit]Father Le Clercq, a Catholic missionary on the Gaspé Peninsula in New France from 1675, saw Mi'kmaw children writing "marks" on birchbark and then counting them to help in the memorization of prayers.[6] Le Clercq then formed symbols to write prayers and liturgy.[6] Mi'kmak also used porcupine quills pressed directly into the bark in the shape of symbols.[6]
This adapted writing system proved popular among Mi'kmaq. They were still using it in the 19th century.[citation needed] Since there is no historical or archaeological evidence of these symbols from before the arrival of this missionary, it is unclear how ancient the use of the pre-missionary mnemonic glyphs was. The relationship of these symbols to Mi'kmaq petroglyphs, which predated European encounter, is unclear.
The Kejimkujik National Park and National Historic Site (KNPNHS), petroglyphs of "life-ways of the Mi'kmaw", include written hieroglyphics, human figures, Mi'kmaq houses and lodges, decorations including crosses, sailing vessels, and animals, etched into slate rocks. These are attributed to the Mi'kmaq, who have continuously inhabited the area since prehistoric times.[7]: 1 The petroglyphs date from the late prehistoric period through the nineteenth century.[7]: 32 A Mi'kmaq healer, Jerry Lonecloud, transcribed some of these petroglyphs in 1912, and donated his copies to the provincial museum.[7]: 6 [8]
Pierre Maillard, Catholic priest, during the winter of 1737–1738[9] created a system of hieroglyphics to transcribe Mi'kmaq words. He used these symbols to write formulas for the principal prayers and the responses of the faithful, in the catechism, so that his followers might learn them more readily. There is no direct evidence that Maillard was aware of Le Clercq's work in this same field. Maillard left numerous works in the language, which continued in use among the Mi'kmaq into the 20th century.
Examples
[edit]-
The beginning of the Lord's Prayer in Míkmaq hieroglyphs. The text reads Nujjinen wásóq – "Our father / in heaven"
-
The full text.
-
Text of the Rite of Confirmation in Míkmaq hieroglyphs. The text reads Koqoey nakla msɨt telikaqumilálaji? – literally 'Why / those / all / after he did that to them?', or "Why are all these different steps necessary?"
-
Page 5 of Buch das gut, enthaltend den Katechismus by Christian Kauder
See also
[edit]- Wiigwaasabak – Ojibwe hieroglyphic birchbarks
References
[edit]- ^ Edwards, Brendan Frederick R. (2005). Paper Talk: A History of Libraries, Print Culture, and Aboriginal Peoples in Canada Before 1960. Scarecrow Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-8108-5113-9.
- ^ a b c d Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic prayers: readings in North America's first indigenous script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus Pub. ISBN 978-1-55109-069-6.
- ^ Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq Hieroglyphic Prayers: Readings in North America's First Indigenous Script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus. pp. 6–7. ISBN 1-55109-069-4.
- ^ Sylliboy, Michelle (26 June 2022). "Artist's Notes: Nm'ultes is an Active Dialogue I: Reclaiming Komqwejwi'kasikl". Journal18: a journal of eighteenth-century art and culture.
- ^ Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Mi'kmaq Hieroglyphic Prayers: Readings in North America's First Indigenous Script. Halifax, Nova Scotia: Nimbus. pp. 8–9. ISBN 1-55109-069-4.
- ^ a b c Dubé, Alexandre (2003). "Tradition, Change and Survival: Mi'kmaq Tourist Art". McCord Museum. Archived from the original on October 21, 2020. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ a b c Cave, Beverley (September 2005). The Petroglyphs of Kejimkujik National Park, Nova Scotia: A Fresh Perspective on their Physical and Cultural Contexts (PDF) (Thesis). Memorial University. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Whitehead, Ruth Holmes (2002). Tracking Doctor Lonecloud: Showman to Legend Keeper. Fredericton: Goose Lane Editions. ISBN 0-86492-356-2.
- ^ Johnson, Micheline D. (1974). "Maillard, Pierre". In Halpenny, Francess G (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography. Vol. III (1741–1770) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press. Retrieved 4 October 2009.
Bibliography
[edit]- Goddard, Ives; Fitzhugh, William W. (1978). "Barry Fell Reexamined". The Biblical Archaeologist. 41 (3): 85–88. doi:10.2307/3209452. JSTOR 3209452. S2CID 166199331.
- Hewson, John (1982). Paddock, Harold (ed.). Micmac Hieroglyphs in Newfoundland. Languages in Newfoundland and Labrador (2nd ed.). St John's, Newfoundland: Memorial University. pp. 188–199.
- Hewson, John (1988). "Introduction to Micmac Hieroglyphics". Cape Breton Magazine (47): 55–61. (text of 1982, plus illustrations of embroidery and some photos)
- Kauder, Christian (1921). Sapeoig Oigatigen tan teli Gômgoetjoigasigel Alasotmaganel, Ginamatineoel ag Getapefiemgeoel; Manuel de Prières, instructions et changs sacrés en Hieroglyphes micmacs; Manual of Prayers, Instructions, Psalms & Hymns in Micmac Ideograms. New edition of Father Kauder's Book published in 1866. Ristigouche, Quebec: The Micmac Messenger.
- Lenhart, John. History relating to Manual of prayers, instructions, psalms and hymns in Micmac Ideograms used by Micmac Indians of Eastern Canada and Newfoundland. Sydney, Nova Scotia: The Nova Scotia Native Communications Society.
- Schmidt, David L.; Balcom, B. A. (Autumn 1993). "The Règlements of 1739: A Note on Micmac Law and Literacy". Acadiensis. XXIII (1): 110–127. ISSN 0044-5851.
- Schmidt, David L.; Marshall, Murdena (1995). Míkmaq Hieroglyphic Prayers: Readings in North America's First Indigenous Script. Nimbus Publishing. ISBN 1-55109-069-4.
External links
[edit]- Míkmaq Portraits Collection Includes tracings and images of Mi'kmaw petroglyphs
- Micmac at ChristusRex.org A large collection of scans of prayers in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphs.
- Écriture sacrée en Nouvelle France: Les hiéroglyphes micmacs et transformation cosmologique (PDF, in French) A discussion of the origins of Mi'kmaw hieroglyphs and sociocultural change in the 17th century Mi'kmaw society.