Portal:Nuclear technology
The Nuclear Technology Portal
Introduction

- Nuclear technology is technology that involves the nuclear reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear reactors, nuclear medicine and nuclear weapons. It is also used, among other things, in smoke detectors and gun sights. (Full article...)
- Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear decay processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as Voyager 2. Reactors producing controlled fusion power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. (Full article...)
- A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. (Full article...)
General images -
Selected article -
After a series of attempts, the successful reactor was assembled in November 1942 by a team of about 30 that, in addition to Fermi, included scientists Leo Szilard (who had previously formulated an idea for non-fission chain reaction), Leona Woods, Herbert L. Anderson, Walter Zinn, Martin D. Whitaker, and George Weil. The reactor used natural uranium. This required a very large amount of material in order to reach criticality, along with graphite used as a neutron moderator. The reactor contained 45,000 ultra-pure graphite blocks weighing 360 short tons (330 tonnes) and was fueled by 5.4 short tons (4.9 tonnes) of uranium metal and 45 short tons (41 tonnes) of uranium oxide. Unlike most subsequent nuclear reactors, it had no radiation shielding or cooling system as it operated at very low power – about one-half watt.
The pursuit of a reactor had been touched off by concern that Nazi Germany had a substantial scientific lead. The success of Chicago Pile-1 in producing the chain reaction provided the first vivid demonstration of the feasibility of the military use of nuclear energy by the Allies, as well as the reality of the danger that Nazi Germany could succeed in producing nuclear weapons. Previously, estimates of critical masses had been crude calculations, leading to order-of-magnitude uncertainties about the size of a hypothetical bomb. The successful use of graphite as a moderator paved the way for progress in the Allied effort, whereas the German program languished partly because of the belief that scarce and expensive heavy water would have to be used for that purpose. The Germans had failed to account for the importance of boron and cadmium impurities in the graphite samples on which they ran their test of its usability as a moderator, while Leo Szilard and Enrico Fermi had asked suppliers about the most common contaminations of graphite after a first failed test. They consequently ensured that the next test would be run with graphite entirely devoid of them. As it turned out, both boron and cadmium were strong neutron poisons.
In 1943, CP-1 was moved to Site A, a wartime research facility near Chicago, where it was reconfigured to become Chicago Pile-2 (CP-2). There, it was operated for research until 1954, when it was dismantled and buried. The stands at Stagg Field were demolished in August 1957 and a memorial quadrangle now marks the experiment site's location, which is now a National Historic Landmark and a Chicago Landmark. (Full article...)
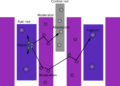
Selected picture -
Did you know?
- ... that the area of Cultybraggan Camp has been a royal hunting ground, a prison for fervent Nazis and the site of an underground bunker intended for use in a nuclear war?
- ... that Jeya Wilson invited New Zealand prime minister David Lange to debate the moral indefensibility of nuclear weapons at the Oxford Union?
- ... that the Russian and Belarussian military exercise Zapad 2009 involved nuclear-capable ballistic missiles?
- ... that campaigning by climate activist Kimiko Hirata halted plans to build 17 new coal-fired power plants following the Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan?
- ... that Project Carryall proposed the detonation of 23 nuclear devices in California to build a road?
- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
Related WikiProjects
Things you can do
| Parts of this portal (those related to section) need to be updated. Please help update this portal to reflect recent events or newly available information. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. (September 2021) |
Selected biography -
Born in Walkerton, Indiana, Urey studied thermodynamics under Gilbert N. Lewis at the University of California, Berkeley. After he received his PhD in 1923, he was awarded a fellowship by the American-Scandinavian Foundation to study at the Niels Bohr Institute in Copenhagen. He was a research associate at Johns Hopkins University before becoming an associate professor of chemistry at Columbia University. In 1931, he began work with the separation of isotopes that resulted in the discovery of deuterium.
During World War II, Urey turned his knowledge of isotope separation to the problem of uranium enrichment. He headed the group located at Columbia University that developed isotope separation using gaseous diffusion. The method was successfully developed, becoming the sole method used in the early post-war period. After the war, Urey became professor of chemistry at the Institute for Nuclear Studies, and later Ryerson professor of chemistry at the University of Chicago.
Urey speculated that the early terrestrial atmosphere was composed of ammonia, methane, and hydrogen. One of his Chicago graduate students was Stanley L. Miller, who showed in the Miller–Urey experiment that, if such a mixture were exposed to electric sparks and water, it can interact to produce amino acids, commonly considered the building blocks of life. Work with isotopes of oxygen led to pioneering the new field of paleoclimatic research. In 1958, he accepted a post as a professor at large at the new University of California, San Diego (UCSD), where he helped create the science faculty. He was one of the founding members of UCSD's school of chemistry, which was created in 1960. He became increasingly interested in space science, and when Apollo 11 returned Moon rock samples from the Moon, Urey examined them at the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. Lunar astronaut Harrison Schmitt said that Urey approached him as a volunteer for a one-way mission to the Moon, stating "I will go, and I don't care if I don't come back." (Full article...)
Nuclear technology news
- 10 December 2024 – Belarus–Russia relations, Nuclear risk during the Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko confirms the presence of nuclear weapons in his country, including Russia's Oreshnik missile system. (AP)
- 6 December 2024 – Belarus–Russia relations, Nuclear risk during the Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Russian President Vladimir Putin and Belarusian President Alexander Lukashenko sign an agreement in Minsk, Belarus, offering security guarantees to Belarus including nuclear security and the possible use of Russian nuclear weapons in order to repel aggressions. (AP)
- 1 December 2024 – Ukraine–United States relations
- U.S. National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan says that the United States will not return the nuclear weapons that they dismantled to Ukraine. (Reuters)
- 19 November 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Nuclear risk during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Russia and weapons of mass destruction
Related portals
Related topics
Subcategories
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus