Venturicidin
Venturicidins (also known as aabomycins) are a group of antifungal compounds. The first member of this class was isolated from Streptomyces bacteria in 1961.[1] Additional members of this class were subsequently isolated and characterized.[2] An antifungal substance "aabomycin A" was isolated from Streptomyces in 1969.[3][4] However, in 1990 it was reported that aabomycin A is actually a 3:1 mixture of two related components, which were then named aabomycin A1 and aabomycin A2.[5] The structures of these were shown to be identical with those of the previously characterized compounds venturicidin A and venturicidin B, respectively.[5] A new analog, venturicidin C, was recently reported from a Streptomyces isolated from thermal vents associated with the Ruth Mullins coal fire in Kentucky.[6]
Venturicidins are active against Pyricularia oryzae and Trichophyton species.[7]
Chemical structures
[edit]-
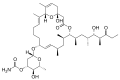
Venturicidin A
(aabomycin A1) -
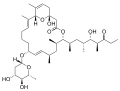
Venturicidin B
(aabomycin A2)
References
[edit]- ^ Rhodes, A.; Fantes, K. H.; Boothroyd, B.; McGonagle, Moira P.; Crosse, R. (1961). "Venturicidin: A new antifungal antibiotic of potential use in agriculture". Nature. 192 (4806): 952–954. Bibcode:1961Natur.192..952R. doi:10.1038/192952a0. PMID 14491780. S2CID 5529775.
- ^ Brufani, M.; Keller-Schierlein, W.; Loeffler, W.; Mansperger, I.; Zaehner, H. (1968). "Metabolic products of microorganisms. LXIX. Venturicidin B, cotrycidin, and the sugar structural units of venturicidin A and B". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 51 (6): 1293–1304. doi:10.1002/hlca.19680510612. PMID 5680738.
- ^ Aizawa, Shojiro; Nakamura, Yuko; Shirato, Shiro; Taguchi, Ryusuke; Yamaguchi, Isamu; Misato, Tomomasa (1969). "Aabomycin A, a new antibiotic. I. Production, isolation, and properties of aabomycin A". Journal of Antibiotics. 22 (10): 457–462. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.22.457. PMID 5350501.
- ^ Yamaguchi, Isamu; Taguchi, Ryusuke; Huang, Keng Tang; Misato, Tomomasa (1969). "Aabomycin A, a new antibiotic. II. Biological studies on aabomycin A". Journal of Antibiotics. 22 (10): 463–466. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.22.463. PMID 5350502.
- ^ a b Akita, Hiroyuki; Yamada, Harutami; Oishi, Takeshi; Yamaguchi, Isamu (1990). "Identity of aabomycin A with venturicidins". Agricultural and Biological Chemistry. 54 (9): 2465–2466. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.54.2465. PMID 1368582.
- ^ Shaaban, KA; Singh, S; Elshahawi, SI; Wang, X; Ponomareva, LV; Sunkara, M; Copley, GC; Hower, JC; Morris, AJ; Kharel, MK; Thorson, JS (March 2014). "Venturicidin C, a new 20-membered macrolide produced by Streptomyces sp. TS-2-2". The Journal of Antibiotics. 67 (3): 223–30. doi:10.1038/ja.2013.113. PMC 3969387. PMID 24252813.
- ^ Matolcsy, György; Nádasy, Miklós; Andriska, Viktor (1988). Pesticide Chemistry. Elsevier. p. 482. ISBN 978-0-444-98903-1. Retrieved 24 July 2012.