七鰓鰻亞綱:修订间差异
外观
删除的内容 添加的内容
| (未显示8个用户的13个中间版本) | |||
| 第2行: | 第2行: | ||
| name = 七鰓鰻亞綱 |
| name = 七鰓鰻亞綱 |
||
| fossil_range = {{Fossil range|360|0|ref=<ref name=FB>{{FishBase_order|order=Petromyzontiformes|year=2009|month=1}}</ref>}} |
| fossil_range = {{Fossil range|360|0|ref=<ref name=FB>{{FishBase_order|order=Petromyzontiformes|year=2009|month=1}}</ref>}} |
||
| taxon = |
| taxon = Petromyzontida |
||
| authority = [[ |
| authority = [[列夫·贝尔格|Berg]], 1940<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://fossilworks.org/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=34112 |title=Fossilworks: Order Petromyzontiforme |accessdate=2019-01-02 |archive-date=2018-10-05 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181005153633/http://fossilworks.org/bridge.pl?a=taxonInfo&taxon_no=34112 |dead-url=no }}</ref> |
||
| image =Jõesilmud2.jpg |
| image =Jõesilmud2.jpg |
||
| image_width = 250px |
| image_width = 250px |
||
| 第10行: | 第10行: | ||
| subdivision_ranks = 类群 |
| subdivision_ranks = 类群 |
||
| subdivision = |
| subdivision = |
||
*†科 Hardistiellidae |
*†[[哈迪斯蒂鰻科]] Hardistiellidae |
||
*†科 Mayomyzonidae |
*†[[麻异鳗属|麻异鳗科]] Mayomyzonidae |
||
*†科 Pipisciidae |
*†科 Pipisciidae |
||
*†[[普利斯鳗属]] ''Priscomyzon'' |
*†[[普利斯鳗属]] ''Priscomyzon'' |
||
*†[[中生鳗属]] ''Mesomyzon'' |
*†[[中生鳗属]] ''Mesomyzon'' |
||
*'''七鳃鳗目 Petromyzontiformes''' |
*'''[[七鳃鳗目]] Petromyzontiformes''' |
||
**[[七鳃鳗科]] Petromyzontidae |
**[[七鳃鳗科]] Petromyzontidae |
||
**[[囊口七鳃鳗科]] Geotriidae |
**[[囊口七鳃鳗科]] Geotriidae |
||
| 第23行: | 第23行: | ||
'''七鰓鰻亞綱'''([[學名]]:{{lang|la|Petromyzontida}}),又名'''八目鰻綱''',是[[脊索動物門]][[圓口綱]]下的一亞綱。 |
'''七鰓鰻亞綱'''([[學名]]:{{lang|la|Petromyzontida}}),又名'''八目鰻綱''',是[[脊索動物門]][[圓口綱]]下的一亞綱。 |
||
目前已知共有現存 38 種、已滅絕 5 種的七鰓鰻<ref>{{cite journal|last1=DOCKER|first1=Margaret F|title=Bill Beamish's Contributions to Lamprey Research and Recent Advances in the Field.|journal=Guelph Ichthyology Reviews|date=2006|volume=7|url=http://gir.uoguelph.ca/article/view/61/127|accessdate=12 June 2014|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140827081335/http://gir.uoguelph.ca/article/view/61/127|archivedate=2014-08-27}}</ref>,其中 18 種為寄生性的[[肉食動物]],鑽入魚類的血肉之中以[[吸血 (生物學)|吸血]]維生<ref>{{cite book |last1=Hardisty |first1=M. W. |last2=Potter |first2=I. C. |editor1-last=Hardisty |editor1-first=M. W. |editor2-last=Potter |editor2-first=I. C.|year=1971 |title=The Biology of Lampreys |url=https://archive.org/details/biologyoflamprey0001hard |edition=1 |publisher=Academic Press |isbn=9780123248015}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Gill|first1=Howard S.|last2=Renaud|first2=Claude B.|last3=Chapleau|first3=François|last4=Mayden|first4=Richard L.|last5=Potter|first5=Ian C.|last6=Douglas|first6=M. E.|title=Phylogeny of Living Parasitic Lampreys (Petromyzontiformes) Based on Morphological Data|journal=Copeia|volume=2003|issue=4|pages=687–703|doi=10.1643/IA02-085.1|year=2003|url=http://www.bioone.org/doi/10.1643/IA02-085.1}}</ref>。這 18 種七鰓鰻中有 9 種會進行[[溯河洄游]],另外 9 種則完全生活於淡水。所有非肉食性的物種均生活於淡水<ref>{{Citation|last=Potter|first=Ian C.|title=The Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and Distribution of Lampreys|date=2014-11-25|url=https://www.springer.com/cda/content/document/cda_downloaddocument/9789401793056-c1.pdf?SGWID=0-0-45-1486832-p176846628|work=Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control|pages=35–73|publisher=Springer Netherlands|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-94-017-9306-3_2|isbn=9789401793056|access-date=2018-10-21|last2=Gill|first2=Howard S.|last3=Renaud|first3=Claude B.|last4=Haoucher|first4=Dalal|archive-date=2018-08-03|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180803014120/https://www.springer.com/cda/content/document/cda_downloaddocument/9789401793056-c1.pdf?SGWID=0-0-45-1486832-p176846628|dead-url=no}}</ref>,成年不進食,依靠[[幼體]]所吸收的營養維持,幼體則為 |
目前已知共有現存 38 種、已滅絕 5 種的七鰓鰻<ref>{{cite journal|last1=DOCKER|first1=Margaret F|title=Bill Beamish's Contributions to Lamprey Research and Recent Advances in the Field.|journal=Guelph Ichthyology Reviews|date=2006|volume=7|url=http://gir.uoguelph.ca/article/view/61/127|accessdate=12 June 2014|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140827081335/http://gir.uoguelph.ca/article/view/61/127|archivedate=2014-08-27}}</ref>,其中 18 種為寄生性的[[肉食動物]],鑽入魚類的血肉之中以[[吸血 (生物學)|吸血]]維生<ref>{{cite book |last1=Hardisty |first1=M. W. |last2=Potter |first2=I. C. |editor1-last=Hardisty |editor1-first=M. W. |editor2-last=Potter |editor2-first=I. C.|year=1971 |title=The Biology of Lampreys |url=https://archive.org/details/biologyoflamprey0001hard |edition=1 |publisher=Academic Press |isbn=9780123248015}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|last1=Gill|first1=Howard S.|last2=Renaud|first2=Claude B.|last3=Chapleau|first3=François|last4=Mayden|first4=Richard L.|last5=Potter|first5=Ian C.|last6=Douglas|first6=M. E.|title=Phylogeny of Living Parasitic Lampreys (Petromyzontiformes) Based on Morphological Data|journal=Copeia|volume=2003|issue=4|pages=687–703|doi=10.1643/IA02-085.1|year=2003|url=http://www.bioone.org/doi/10.1643/IA02-085.1}}</ref>。這 18 種七鰓鰻中有 9 種會進行[[溯河洄游]],另外 9 種則完全生活於淡水。所有非肉食性的物種均生活於淡水<ref>{{Citation|last=Potter|first=Ian C.|title=The Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and Distribution of Lampreys|date=2014-11-25|url=https://www.springer.com/cda/content/document/cda_downloaddocument/9789401793056-c1.pdf?SGWID=0-0-45-1486832-p176846628|work=Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control|pages=35–73|publisher=Springer Netherlands|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-94-017-9306-3_2|isbn=9789401793056|access-date=2018-10-21|last2=Gill|first2=Howard S.|last3=Renaud|first3=Claude B.|last4=Haoucher|first4=Dalal|archive-date=2018-08-03|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180803014120/https://www.springer.com/cda/content/document/cda_downloaddocument/9789401793056-c1.pdf?SGWID=0-0-45-1486832-p176846628|dead-url=no}}</ref>,成年不進食,依靠[[幼體]]所吸收的營養維持,幼體則為[[濾食性]]。 |
||
== 棲息地 == |
== 棲息地 == |
||
| 第36行: | 第36行: | ||
== 参考文献 == |
== 参考文献 == |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist|30em}} |
||
{{Wikispecies|Petromyzontiformes}} |
{{Wikispecies|Petromyzontiformes}} |
||
{{Wikibooks|Dichotomous Key|Petromyzonidae}} |
{{Wikibooks|Dichotomous Key|Petromyzonidae}} |
||
{{Petromyzontiformes|state=collapsed}} |
{{Petromyzontiformes|state=collapsed}} |
||
{{圓口綱|P.}} |
|||
{{魚類演化}} |
{{魚類演化}} |
||
{{脊索動物}} |
{{脊索動物}} |
||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q261485}} |
{{Taxonbar|from=Q21286786|from2=Q261485}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
[[Category:七鰓鰻綱]] |
[[Category:七鰓鰻綱]] |
||
[[Category:吸血]] |
[[Category:吸血]] |
||
2024年12月14日 (六) 06:26的最新版本
| 七鰓鰻亞綱 化石时期:
| |
|---|---|

| |
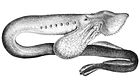
| 歐洲七鰓鰻 (Lampetra fluviatilis) | |
| 科学分类 | |
| 界: | 动物界 Animalia |
| 门: | 脊索动物门 Chordata |
| 纲: | 圆口纲 Cyclostomata |
| 亚纲: | 七鳃鳗亚纲 Petromyzontida Berg, 1940[2] |
| 类群 | |
| 異名 | |
|
Hyperoartia | |
七鰓鰻亞綱(學名:Petromyzontida),又名八目鰻綱,是脊索動物門圓口綱下的一亞綱。
目前已知共有現存 38 種、已滅絕 5 種的七鰓鰻[3],其中 18 種為寄生性的肉食動物,鑽入魚類的血肉之中以吸血維生[4][5]。這 18 種七鰓鰻中有 9 種會進行溯河洄游,另外 9 種則完全生活於淡水。所有非肉食性的物種均生活於淡水[6],成年不進食,依靠幼體所吸收的營養維持,幼體則為濾食性。
棲息地
[编辑]
七鰓鰻多半棲息於淡水與沿岸,甚至是內流湖中,然而部分物種(例如:澳洲囊口七鰓鰻(Geotria australis)、海七鰓鰻(Petromyzon marinus)與三峰七鰓鰻(Entosphenus tridentatus))會在進行遠距離遷徙時游到開放海域[7],證據在於牠們在不同水域的族群上並沒有生殖隔離。七鰓鰻的幼體對高水溫的容忍程度低,這也解釋了為什麼牠們不分布於熱帶水域,除此之外七鰓鰻分布於除非洲之外的大部分溫帶水域之中。
七鰓鰻的分布會受到汙染以及過度捕魚影響。在諾曼征服英格蘭時期,七鰓鰻可以在泰晤士河上游的倫敦彼得森村附近發現。而近年來泰晤士河與威爾河汙染的減少也使得七鰓鰻再次出沒於倫敦以及切斯特勒街附近的水域[8][9]。
七鰓鰻的分布同時也會受到水壩以及其他干擾洄游路徑的人造建築影響,這些建設會阻止牠們回到產卵地,而新建的人造水道則可能引導牠們游至新的水域,例如北美洲五大湖的海七鰓鰻。人類正計畫利用化學物質來控制這些入侵七鰓鰻的數量,但仍然有影響部分地區飲用水的疑慮[10]。
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Froese, R. & Pauly, D. (eds.) (2009). Petromyzontiformes. FishBase. Version 2009-01.
- ^ Fossilworks: Order Petromyzontiforme. [2019-01-02]. (原始内容存档于2018-10-05).
- ^ DOCKER, Margaret F. Bill Beamish's Contributions to Lamprey Research and Recent Advances in the Field.. Guelph Ichthyology Reviews. 2006, 7 [12 June 2014]. (原始内容存档于2014-08-27).
- ^ Hardisty, M. W.; Potter, I. C. Hardisty, M. W.; Potter, I. C. , 编. The Biology of Lampreys 1. Academic Press. 1971. ISBN 9780123248015.
- ^ Gill, Howard S.; Renaud, Claude B.; Chapleau, François; Mayden, Richard L.; Potter, Ian C.; Douglas, M. E. Phylogeny of Living Parasitic Lampreys (Petromyzontiformes) Based on Morphological Data. Copeia. 2003, 2003 (4): 687–703. doi:10.1643/IA02-085.1.
- ^ Potter, Ian C.; Gill, Howard S.; Renaud, Claude B.; Haoucher, Dalal, The Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and Distribution of Lampreys (PDF), Lampreys: Biology, Conservation and Control (Springer Netherlands), 2014-11-25: 35–73 [2018-10-21], ISBN 9789401793056, doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9306-3_2, (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2018-08-03) (英语)
- ^ Silva, S.; Araújo, M. J.; Bao, M.; Mucientes, G.; Cobo, F. The haematophagous feeding stage of anadromous populations of sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus: low host selectivity and wide range of habitats. Hydrobiologia. 2014, 734 (1): 187–199. doi:10.1007/s10750-014-1879-4. hdl:10261/98126.
- ^ Prehistoric bloodsucker in Thames. BBC News. 1 July 2009 [27 September 2012]. (原始内容存档于2017-08-31).
- ^ Giant blood sucker found in River Wear. The Northern Echo. 25 June 2009 [2019-02-15]. (原始内容存档于2018-10-04).
- ^ Lehman, Don. Chemical concerns may halt Lake Champlain treatments. poststar.com. The Post Star. [2019-02-15]. (原始内容存档于2019-05-10).
維基教科書中的相關電子教程:Petromyzonidae