双射:修订间差异
外观
删除的内容 添加的内容
无编辑摘要 |
→另見: 調整格式、排版 內容擴充 |
||
| 第56行: | 第56行: | ||
*[[雙射計數法]] |
*[[雙射計數法]] |
||
==參考文獻== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{refbegin}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{cite book|last=Wolf|title=Proof, Logic and Conjecture: A Mathematician's Toolbox|year=1998|publisher=Freeman}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Sundstrom|title=Mathematical Reasoning: Writing and Proof|year=2003|publisher=Prentice-Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Smith|last2=Eggen|last3=St.Andre|title=A Transition to Advanced Mathematics (6th Ed.)|year=2006|publisher=Thomson (Brooks/Cole)}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Schumacher|title=Chapter Zero: Fundamental Notions of Abstract Mathematics|year=1996|publisher=Addison-Wesley}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=O'Leary|title=The Structure of Proof: With Logic and Set Theory|year=2003|publisher=Prentice-Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Morash|title=Bridge to Abstract Mathematics|publisher=Random House}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Maddox|title=Mathematical Thinking and Writing|year=2002|publisher=Harcourt/ Academic Press}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Lay|title=Analysis with an introduction to proof|year=2001|publisher=Prentice Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Gilbert|last2=Vanstone|title=An Introduction to Mathematical Thinking|year=2005|publisher=Pearson Prentice-Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Fletcher|last2=Patty|title=Foundations of Higher Mathematics|publisher=PWS-Kent}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Iglewicz|last2=Stoyle|title=An Introduction to Mathematical Reasoning|publisher=MacMillan}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Devlin|first=Keith|title=Sets, Functions, and Logic: An Introduction to Abstract Mathematics|year=2004|publisher=Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=D'Angelo|last2=West|title=Mathematical Thinking: Problem Solving and Proofs|year=2000|publisher=Prentice Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Cupillari|title=The Nuts and Bolts of Proofs|publisher=Wadsworth}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Bond|title=Introduction to Abstract Mathematics|publisher=Brooks/Cole}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last1=Barnier|last2=Feldman|title=Introduction to Advanced Mathematics|year=2000|publisher=Prentice Hall}} |
|||
* {{cite book|last=Ash|title=A Primer of Abstract Mathematics|publisher=MAA}} |
|||
{{refend}} |
|||
==外部鏈接== |
|||
{{Commons|Category:Bijectivity|Bijectivity}} |
|||
* {{springer|title=Bijection|id=p/b016230}} |
|||
* {{MathWorld|title=Bijection|urlname=Bijection}} |
|||
* [http://jeff560.tripod.com/i.html Earliest Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics: entry on Injection, Surjection and Bijection has the history of Injection and related terms.] |
|||
{{集合论}} |
{{集合论}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
2015年12月16日 (三) 03:54的版本

數學中,一個由集合X映射至集合Y的函數,若對每一在Y內的y,存在唯一一個在X內的x与其对应,則此函數為對射函數。
換句話說,f為雙射的若其為兩集合間的一一對應,亦即同時為單射和滿射。
例如,由整數集合至的函數succ,其將每一個整數x連結至整數succ(x)=x+1,這是一個雙射函數;再看一個例子,函數sumdif,其將每一對實數(x,y)連結至sumdif(x,y) = (x + y, x − y),這也是個雙射函數。
一雙射函數亦簡稱為雙射(英語:bijection)或置換。後者一般較常使用在X=Y時。以由X至Y的所有雙射組成的集合標記為XY.
雙射函數在許多數學領域扮演著很基本的角色,如在同構的定義(以及如同胚和微分同構等相關概念)、置換群、投影映射及許多其他概念的基本上。
複合函數與反函數
一函數f為雙射的若且唯若其逆關係f−1也是個函數。在這情況,f−1也會是雙射函數。
兩個雙射函數f XY及g YZ的複合函數g o f亦為雙射函數。其反函數為(g o f)−1 = (f−1) o (g−1)。
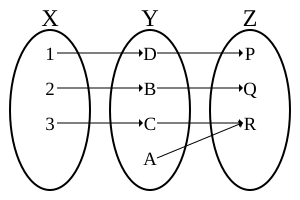
另一方面,若g o f為雙射的,可知f是單射的且g是滿射的,但也僅限於此。
一由X至Y的關係f為雙射函數若且唯若存在另一由Y至X的關係g,使得g o f為X上的恆等函數,且f o g為Y上的恆等函數。必然地,此兩個集合會有相同的勢。
雙射與勢
若X和Y為有限集合,則其存在一兩集合的雙射函數若且唯若兩個集合有相同的元素個數。確實,在公理集合論裡,這正是「相同元素個數」的定義,且廣義化至無限集合,並導致了基數的概念,用以分辨無限集合的不同大小。
例子與反例
- 對任一集合X,其恆等函數為雙射函數。
- 函數f : R R,,其形式為f(x) = 2x + 1,是雙射的,因為對任一y,存在一唯一x = (y − 1)/2使得f(x) = y。
- 指數函數g : R R,其形式為g(x) = ex,不是雙射的:因為不存在一R內的x使得g(x) = −1,故g非為雙射。但若其陪域改成正實數R+ = (0,+∞),則g便是雙射的了;其反函數為自然對數函數 ln。
- 函數h : R [0,+∞),其形式為h(x) = x²,不是雙射的:因為h(−1) = h(1) = 1,故h非為雙射。但如果把定義域也改成[0,+∞),則h便是雙射的了;其反函數為正平方根函數。
- 不是雙射函數,因為−1, 0和1都在其定義域裡且都映射至0。
- 不是雙射函數,因為π/3和2π/3都在其定義域裡且都映射至。
性質
- 一由實數R至R的函數f是雙射的,若且唯若其圖像和任一水平線相交且只相交於一點。
- 設X為一集合,則由X至其本身的雙射函數,加上其複合函數(o)的運算,會形成一個群,即為X的對稱群,其標記為S(X)、SX或X!。
- 取一定義域的子集A及一陪域的子集B,則
- |f(A)| = |A| 且 |f−1(B)| = |B|。
- f 為一雙射函數。
- f 為一滿射函數。
- f 為一單射函數。
雙射與範疇論
另見
參考文獻
- Wolf. Proof, Logic and Conjecture: A Mathematician's Toolbox. Freeman. 1998.
- Sundstrom. Mathematical Reasoning: Writing and Proof. Prentice-Hall. 2003.
- Smith; Eggen; St.Andre. A Transition to Advanced Mathematics (6th Ed.). Thomson (Brooks/Cole). 2006.
- Schumacher. Chapter Zero: Fundamental Notions of Abstract Mathematics. Addison-Wesley. 1996.
- O'Leary. The Structure of Proof: With Logic and Set Theory. Prentice-Hall. 2003.
- Morash. Bridge to Abstract Mathematics. Random House.
- Maddox. Mathematical Thinking and Writing. Harcourt/ Academic Press. 2002.
- Lay. Analysis with an introduction to proof. Prentice Hall. 2001.
- Gilbert; Vanstone. An Introduction to Mathematical Thinking. Pearson Prentice-Hall. 2005.
- Fletcher; Patty. Foundations of Higher Mathematics. PWS-Kent.
- Iglewicz; Stoyle. An Introduction to Mathematical Reasoning. MacMillan.
- Devlin, Keith. Sets, Functions, and Logic: An Introduction to Abstract Mathematics. Chapman & Hall/ CRC Press. 2004.
- D'Angelo; West. Mathematical Thinking: Problem Solving and Proofs. Prentice Hall. 2000.
- Cupillari. The Nuts and Bolts of Proofs. Wadsworth.
- Bond. Introduction to Abstract Mathematics. Brooks/Cole.
- Barnier; Feldman. Introduction to Advanced Mathematics. Prentice Hall. 2000.
- Ash. A Primer of Abstract Mathematics. MAA.
外部鏈接
维基共享资源中相关的多媒体资源:Bijectivity






![{\displaystyle \mathbf {R} \to [-1,1]:x\mapsto \sin(x)}](https://wikimedia.org/zhwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/64adff70e4e8615c17b1ee75da84316a0f44927b)

