現代標準漢語音系
此條目目前正依照其他维基百科上的内容进行翻译。 (2018年12月15日) |
本文總結了現代標準漢語的音系。
現代標準漢語是由以北京官話為基礎音,廣泛通行於華人地區的語言。現代標準漢語共有四種聲調,並在弱音節中使用輕聲。
本文使用國際音標為主要標音系統,並與拼音、注音二系統相互進行比較。關於其他的中文標音系統,請參見威妥瑪拼音、國語羅馬字與漢字拉丁化。
音節
現代現代標準漢語的音系常用音節作爲分析單位,往往一個漢字對應一個音節。關於漢語音節結構的劃分,主要有三種方法:傳統上採用的將一字分爲聲調和音段,再將音段分爲聲母和韻母,其中韻母再分爲韻頭(介音)、韻腹和韻尾。單字的音節成分主要有聲母、介音(韻頭)、韻腹、韻尾和聲調
此外,還有結構派的嚴格二分的劃分方式,則是先將一個完整的音節S劃分爲聲調T(實現爲調值tt)和音段σ,再將音段σ劃分爲聲母O(實現爲輔音C)和韻母F,再將韻母F劃分爲介音M(實現爲滑音G)和韻體R,再將韻體R劃分爲韻腹Nu(實現爲元音V)和韻尾Co(實現爲鼻音N或滑音G),如圖。另外還有朱曉農(2005)所採用的多維分析法[1],即將一個完整音節S三分爲聲母O(實現爲輔音C或零聲母Ø)、介音M(實現爲滑音G)和韻體R,其中聲調T附麗於韻體R,韻體R可再細分爲韻腹Nu和韻尾Co(實現爲滑音G或鼻音N)。

其中,有些模型下聲母是可省的,有些則不可,介音則是可省的,韻腹不可省,韻尾可省[1]。
輔音
下表使用國際音標轉錄了現代標準漢語的輔音。括號中顯示的聲音通常不會作為獨立音素進行分析(相關資訊請參考下文的齦齶音)。若不包括括號中的音,現代標準漢語中有19個輔音音素。
| 唇 | 齒、 齒齦 |
捲舌 | 齦顎 | 軟顎 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鼻音 | m | n | ŋ | |||
| 塞音 | 送氣 | pʰ | tʰ | kʰ | ||
| 不送氣 | p | t | k | |||
| 塞擦音 | 送氣 | t͡sʰ | ʈ͡ʂʰ | (t͡ɕʰ) | ||
| 不送氣 | t͡s | ʈ͡ʂ | (t͡ɕ) | |||
| 擦音 | f | s | ʂ | (ɕ) | x | |
| 流音 | l | ɻ | ||||
同一個表格中的一對輔音使用同樣的發音器官與發音方法,而兩者之間的主要差別在於送氣與否。雖然表格中並沒有濁音,在弱音節的不送氣清音也可能變濁音(參見下文的Syllable reduction)。這些輔音在拼音系統中的符號在羅曼語族中普遍都用以區分清/濁音(如[p] 和 [b]),在日耳曼語族中則用以區分強音與弱音(字首的不送氣清音與濁音,如[pʰ] 與 [b])。然而這在拼音系統中卻用來區分送氣/不送氣音,例如/pʰ/ 與 /p/ 分別以 p 與 b 表示。
下方的表格是關於輔音的詳細資訊,並與英語的輔音做比較:
| 音素 | 描述 | 拼音 | 注音 | 註解 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /p/ | 同英語不送氣的 p ,如 spy | b | ㄅ | |
| /pʰ/ | 同英語送氣的 p,如 pie | p | ㄆ | |
| /m/ | 同英語的 m | m | ㄇ | |
| /f/ | 同英語的 f | f | ㄈ | |
| /t/ | 同英語不送氣的 t ,如 sty | d | ㄉ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /tʰ/ | 同英語送氣的 t, 如 tie | t | ㄊ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /n/ | 同英語的 n | n | ㄋ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。此音素(即不考慮國際音標以外的拼音系統)可以出現在音節首和/或音節尾。 |
| /l/ | 同英語的「明l」音,如標準英音的 lay | l | ㄌ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /k/ | 同英語不送氣的 k,如 sky | g | ㄍ | |
| /kʰ/ | 同英語送氣的 k,如 key | k | ㄎ | |
| /ŋ/ | 同英語的 ng,如 sing | ng | ㄥ | 只出現在音節尾 |
| /x/ ([h ~ x])[2] |
音素 h 的發音在英語的 hat 與德語的 Bach之間。 | h | ㄏ | |
| /s/ | 同英語的 s,但通常舌頭會抵住下排牙齒 | s | ㄙ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /t͡s/ | 同英語不送氣的 ts ,如 cats | z | ㄗ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /t͡sʰ/ | 同英語送氣的 ts | c | ㄑ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| [ɕ] | 與 sh 相似但用齦顎發音。 | x | ㄒ | 參見下文的齦齶音段落。 |
| [t͡ɕ] | 與英語不送氣的 ch 相似但用齦顎發音。 | j | ㄐ | 參見下文的齦齶音段落。 |
| [t͡ɕʰ] | 同上,但送氣 | q | ㄑ | 參見下文的齦齶音段落。 |
| /ʂ/ | 類似英語的 sh 但捲舌 | sh | ㄕ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /ʈ͡ʂ/ | 類似英語的 ch (如 chat)但不送氣,且捲舌 | zh | ㄓ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /ʈ͡ʂʰ/ | 同上,但送氣 | ch | ㄔ | 參見下文的齒齒齦與捲舌音段落。 |
| /ɻ/ ([ɻ~ʐ])[a] |
與英語以 r 開頭的字(如room)相似但捲舌 | r | ㄖ | 關於此音素在意字尾的使用,請參見下文的兒化段落。 |
以上幾乎所有輔音都可能出現在音節首,唯一的例外是/ŋ/(除非在零聲母的情況;見下文)。相對地,能夠出現在音節尾的輔音僅有/n/以及/ŋ/而已(雖然[m]也可以作為/n/在唇音前的同位異音)。音節尾的/n/、/ŋ/音發音時,氣流通路可能未被完全阻礙,導致字尾的鼻輔音與元音結合,變成一個鼻音化的長元音。[4]參見下文的Syllable reduction段落。
齒齒齦音與捲舌音
上文第一個表格中的齒齒齦音(標註為齒、齒齦)有時候被當作是齒齦音,而有時候被當作是齒音. 這些擦音與塞擦音更常被當作是齒音,由於大多數的語言使用者在發此音時是使用舌頭與下排牙齒。[2]
而現代標準漢語的捲舌音,事實上是舌尖音而非舌尖下音,也因此部分學者認為這些輔音並非真的「捲舌」;更準確地來說,它們是齒齦後音。[5][6] 許多現代標準漢語使用者的母語中並沒有捲舌音,因此它們可能會將這些音發成齒音。[7]
齦齶音
齦齶音 [t͡ɕ, t͡ɕʰ, ɕ](j/ㄐ, q/ㄑ, x/ㄒ)會被某些使用者發音成顎化的齒音:[t͡sʲ]、[t͡sʰʲ]與[sʲ]。這種情況在兒童和女性中尤為常見。[8]
在音韻學的分析中時常假設:當齦齶音沒有[i]或[y]等高元音緊接在後時,它們會自動產生一個與其相黏的半元音([j]或[ɥ])。也就是說,以ji-/ㄐㄧ-、qi-/ㄑㄧ-、 xi-/ㄒㄧ-、ju-/ㄐㄩ-、qu-/ㄑㄩ-、xu-/ㄒㄩ-為首的音節的音標是[t͡ɕj], [t͡ɕʰj], [ɕj], [t͡ɕɥ], [t͡ɕʰɥ], [ɕɥ],而其實際發音更接近[t͡ɕ], [t͡ɕʰ], [ɕ], [t͡ɕʷ], [t͡ɕʰʷ], [ɕʷ](或對把齦齶音念成齒音的使用者而言,則為[t͡sʲ], [t͡sʰʲ], [sʲ], [t͡sᶣ], [t͡sʰᶣ], [sᶣ])。即音節中的半元音可以被當作是前一個輔音的顎化和/或唇化。
在以上分析中,齦齶音 are in 互補分布 with the dentals [t͡s, t͡sʰ, s], with the velars [k, kʰ, x], and with the retroflexes [ʈ͡ʂ, ʈ͡ʂʰ, ʂ], as none of these can occur before high front vowels or palatal glides, whereas the alveolo-palatals occur only before high front vowels or palatal glides. Therefore, linguists often prefer to classify [t͡ɕ, t͡ɕʰ, ɕ] not as independent phonemes, but as allophones of one of the other three series.[9] The existence of the above-mentioned dental variants inclines some to prefer to identify the alveolo-palatals with the dentals, but identification with any of the three series is possible (unless the empty rime is identified with /i/, in which case the velars become the only candidate; see below). The Yale and Wade–Giles systems mostly treat the alveolo-palatals as allophones of the retroflexes; Tongyong Pinyin mostly treats them as allophones of the dentals; and 現行盲文 treats them as allophones of the velars. In standard pinyin and bopomofo, however, they are represented as a separate sequence.
齦顎音在歷史上乃源於在高元音與滑音前齒音[t͡s, t͡sʰ, s])與軟顎音[k, kʰ, x]的合併。 before high front vowels and glides. Previously, some instances of modern [t͡ɕ(ʰ)i] were instead [k(ʰ)i], and others were [t͡s(ʰ)i] . The change took place in the last two or three centuries at different times in different areas, but not in the Jianghuai dialect used at the imperial court. This explains why some European transcriptions of Chinese names (especially in postal romanization) contain ki-, hi-, tsi- or si- where an alveolo-palatal might be expected. Examples are Peking for Beijing, Chungking for Chongqing, Fukien for Fujian, Tientsin for Tianjin; Sinkiang for Xinjiang, and Sian for Xi'an. The complementary distribution with the retroflex series arose when syllables that had a retroflex consonant followed by a medial glide lost the medial glide.
零聲母
在像是 ai(ㄞ)的音節中,母音前並沒有任何的輔音或半元音,這樣的情況就稱為零聲母。即使漢語拼音與注音符號皆未標出,[ɣ]、[ʔ]、[ŋ]與[ɦ] 皆有可能是實際上的輔音,有人認為這樣的開頭當作為一種特殊的音素,or as an instance of the phoneme /ŋ/, although it can also be treated as no phoneme (absence of onset). By contrast, in the case of the particle 啊 a, which is a weak onsetless syllable, linking occurs with the previous syllable (as described under Syllable reduction, below).[10]
When a stressed vowel-initial Chinese syllable follows a consonant-final syllable, the consonant does not directly link with the vowel. Instead, the zero onset seems to intervene in between. 棉袄 mián'ǎo ("cotton jacket") becomes [mjɛnʔau], [mjɛnɣau]. However, in connected speech none of these output forms is natural. Instead, when the words are spoken together the most natural pronunciation is [mjɛ̃ːau], in which there is no nasal closure or any version of the zero onset.
四呼
現代現代標準漢語根据介音可把韵母分为四类,称为開齊合撮四呼:
- 開口呼:無介音,開頭為/a/、/ɤ/等母音(漢語拼音:a, ê, o, e;注音符號:ㄚ、ㄝ、ㄜ、ㄛ)。
- 齊齒呼:以/i/作為開頭介音(漢語拼音:i;注音符號:ㄧ)。
- 合口呼:以/u/作為開頭介音(漢語拼音:u;注音符號:ㄨ)。
- 撮口呼:以/y/作為開頭介音(漢語拼音:ü;注音符號:ㄩ)。
| 不園脣 | 園脣 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 無前介音 | 開口呼 /Ø/ | 合口呼 /zhwiki/w/或/u/ | |
| 有前介音 | 齊齒呼 /j/或/i/ | 撮口呼 /ɥ/或/y/ |
半元音
半元音[j]、[ɥ]和[w]的聲音分別像是英語的 yes、法語的huit和英語的 we。(北京方言使用者當遇到[o]出現在[w]後時,會將[w]替換成唇齒近音[ʋ][11]。The glides are commonly analyzed not as independent phonemes, but as consonantal allophones of the high vowels: [i̯, y̯, u̯]. This is possible because there is no ambiguity in interpreting a sequence like yao/-iao as /iau/, and potentially problematic sequences such as */iu/ do not occur.
這些半元音可能出現在音節首。This occurs with [ɥ] in the syllables written yu, yuan, yue and yun in pinyin; with [j] in other syllables written with initial y in pinyin (ya, yi, etc.); and with [w] in syllables written with initial w in pinyin (wa, wu, etc.). When a glide is followed by the vowel of which that glide is considered an allophone, the glide may be regarded as epenthetic (automatically inserted), and not as a separate realization of the phoneme. Hence the syllable yi, pronounced [ji], may be analyzed as consisting of the single phoneme /i/, and similarly yin may be analyzed as /in/, yu as /y/, and wu as /u/.[12]
這些半元音也可能出現在medial position, ,也就是 after the initial consonant but before the main vowel. Here they are represented in pinyin as vowels: for example, the i in bie represents [j], and the u in duan represents [w]. There are some restrictions on the possible consonant-glide combinations: [w] does not occur after labials (except for some speakers in bo, po, mo, fo); [j] does not occur after retroflexes and velars (or after [f]); and [ɥ] occurs medially only in lüe and nüe and after alveolo-palatals (for which see above.) A consonant-glide combination at the start of a syllable is articulated as a single sound – the glide is not in fact pronounced after the consonant, but is realized as palatalization [ʲ], labialization [ʷ], or both [ᶣ], of the consonant.[13] (The same modifications of initial consonants occur in syllables where they are followed by a high vowel, although normally no glide is considered to be present there. Hence a consonant is generally palatalized [ʲ] when followed by /i/, labialized [ʷ] when followed by /u/, and both [ᶣ] when followed by /y/.)
The glides [j] and [w] are also found as the final element in some syllables. These are commonly analyzed as diphthongs rather than vowel-glide sequences. For example, the syllable bai is assigned the underlying representation /pai̯/. (In pinyin, the second element is generally written i or u, but /au̯/ is written ao.)
音節輔音
現代標準漢語中共有七組音節 zi/ㄗ、ci/ㄘ、si/ㄙ、zhi/ㄓ、chi/ㄔ、shi/ㄕ 與 ri/ㄖ可以被視為音節輔音:
另一種理解方式則將其音節核當成元音,而非音節輔音:
Phonologically, these syllables may be analyzed as having their own vowel phoneme, /ɨ/. However, it is possible to merge this with the phoneme /i/ (with which it is historically related), since the two are in complementary distribution – provided that the alveolo-palatal series is either left unmerged, or is merged with the velars rather than the retroflex or alveolar series. (That is, [t͡ɕi], [t͡sɨ] and [ʈ͡ʂɨ] all exist, but there is neither *[ki] nor *[kɨ], so there is no problem merging both [i]~[ɨ] and [k]~[t͡ɕ] at the same time.)
Another approach is to regard the syllables assigned above to /ɨ/ as having (underlyingly) an empty nuclear slot ("empty rime", Chinese (中文)), i.e. as not containing a vowel phoneme at all. This is more consistent with the syllabic consonant description of these syllables.
當音節減弱時,音節輔音也可能出現(見下文)。在某些感嘆詞中也會聽到鼻音化的音節輔音;這些詞的發音包括[m]、[n]、[ŋ]、[hm]與[hŋ]等。
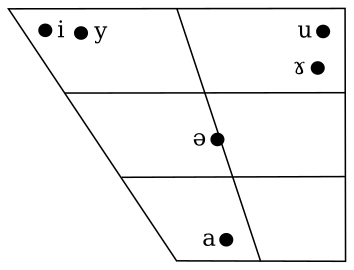
元音
- 現代標準漢語元音
-
北京使用的現代標準漢語單元音(來源:Lee & Zee (2003:110頁))。
-
北京使用的現代標準漢語雙元音(第一部分,來源:Lee & Zee (2003:110頁))。
-
北京使用的現代標準漢語雙元音(第二部分,來源:Lee & Zee (2003:110頁))。
現代現代標準漢語中有/a/、/ǝ/、/i/、/u/、/y/共五個元音音位Template:NoteRef。每個音位在實際發音中,根據語言環境會有不同的發音,但由於其呈互補分布,故被視爲一個音位。例如,/ə/具有同位異音[e]Template:NoteRef與[o]Template:NoteRef;/a/則有
。然而,作爲反例,邊緣音系中還有感嘆詞的「喔 [ɔ]」、「誒[ɛ]」、「唷[jɔ]」或「囉[lɔ]」等。
同位異音
同位異音(即同一元音在特定語音環境中的不同發音方式)在不同來源之間有不同的轉錄方式。下表提供了一組典型的描述(不包括兒化音)[b]。
| 音節核 | /i/ | /u/ | /y/ | /ə/ | /a/ | 音節化輔音 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中間位 | ∅ | ∅ | /j/ | ∅ | ∅ | /j/ | /zhwiki/w/ | /ɥ/ | ∅ | /j/ | /zhwiki/w/ | /ɥ/ | |||||||||||||||
| 音節尾 | ∅ | [i] | [u] | [y] | [ɤ] | [je] | [wo] | [ɥe] | [a] | [ja] | [wa] | [ɨ] | |||||||||||||||
| yi | ㄧ | wu | ㄨ | yu | ㄩ | e | ㄝ | ye | ㄧㄝ | wo | ㄨㄛ | yue | ㄩㄝ | a | ㄚ | ya | ㄧㄚ | wa | ㄨㄚ | ㄭ3 | |||||||
| -i | -u | -ü1 | -e | -ie | -uo/-o2 | ㄨㄛ/ㄛ2 | -üe1 | -a | -ia | -ua | -i | ||||||||||||||||
| /i/ | [ei̯] | [wei̯] | [ai̯] | [wai̯] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ei | ㄟ | wei | ㄨㄟ | ai | ㄞ | wai | ㄨㄞ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| -ei | -ui | -ai | -uai | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| /u/ | [ou̯] | [jou̯] | [au̯] | [jau̯] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| ou | ㄡ | you | ㄧㄡ | ao | ㄠ | yao | ㄧㄠ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| -ou | -iu | -ao | -iao | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| /n/ | [in] | [yn] | [ən] | [wən] | [an] | [jɛn] | [wan] | [ɥɛn] | |||||||||||||||||||
| yin | ㄧㄣ | yun | ㄩㄣ | en | ㄣ | wen | ㄨㄣ | an | ㄢ | yan | ㄧㄢ | wan | ㄨㄢ | yuan | ㄩㄢ | ||||||||||||
| -in | -ün1 | -en | -un | -an | -ian | -uan | -üan1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| /ŋ/ | [iŋ] | [ʊŋ] | [jʊŋ] | [əŋ] | [wəŋ] | [aŋ] | [jaŋ] | [waŋ] | |||||||||||||||||||
| ying | ㄧㄥ | yong | ㄩㄥ | eng | ㄥ | weng | ㄨㄥ | ang | ㄤ | yang | ㄧㄤ | wang | ㄨㄤ | ||||||||||||||
| -ing | -ong | ㄨㄥ | -iong | -eng | -ang | -iang | -uang | ||||||||||||||||||||
- 1 拼音ü 在 j、q或x後寫成 u,注音則皆為ㄩ。
- 2 拼音uo在b、p、m或f後寫成o;注音ㄨㄛ在ㄅ、ㄆ、ㄇ或ㄈ後寫成ㄛ。
- 3 符號「ㄭ」僅作為發音輔助說明用,實際上於拼寫時不寫出。
下表提供了關於單一元音之同位異音的更多細節。
| 音素 | 同位異音 | 描述(英文) |
|---|---|---|
| /i/ | [i] | 如英文be |
| /u/ | [u] | 如英文do |
| [ʊ] | 根據使用者的語音習慣,此音介於[o][14]與[u]之間。 | |
| /y/ | [y] | 如法語的u或德語的ü |
| /ǝ/ | [e] | 如英文bed |
| [o] | 如英式英語的awe | |
| [ɤ] | 發音同[ɰɤ]. | |
| [ə] | Schwa, 如英文about. | |
| /a/ | [a] | 如英文father |
| [ɛ] | 根據使用者的語音習慣,此音介於[e]與[a]之間。 |
作為通則,在開音節(指元音後沒有音節尾的音節)中的元音長度較長,其他情況中則較短。此規則並不適用於弱音節(即聲調為輕聲的字),在弱音節中,所有元音都非常短。[15]
音節尾對中央元音的影響
在現代標準漢語中,元音 [a] 與 [ə] 的元音舌位在音節尾時和諧。[16][17] 如 [a],在 /i, n/ 之前讀成較前的 [a̟],而在 /u, ŋ/ 之前則讀成較後的 [a̠] 。同理, [ə] 在 /n/之前讀成較前的 [ə̟] ,而在 /ŋ/ 前則讀成較後的 [ə̠] 。
聲調對中元音的影響
一些漢語母語者在第一聲與第二聲時,會將[wei̯]、[jou̯] 與 [wən] 分別念成 [ui]、[iu] 與 [un] 。[18]
其他分析
Some linguists prefer to reduce the number of vowel phonemes still further (at the expense of including underlying glides in their systems). Edwin G. Pulleyblank has proposed a system which includes underlying glides, but no vowels at all.[19] More common are systems with two vowels; for example, in Mantaro Hashimoto's system,[20] there are just two vowel nuclei, /ə, a/, which may be preceded by a glide /j, w, ɥ/, and may be followed by a coda /i, u, n, ŋ/ (additional sequences are afforded by the rhotic coda /ɚ̯/; see Erhua). The various combinations of glide, vowel, and coda have different surface manifestations, as shown in the table below. Any of the three positions may be empty, i.e. occupied by a null meta-phoneme ∅; for example, the high vowels [i, u, y] are analyzed as glide + ∅, and the vowel [ɨ] or empty rime is analyzed as having all three values null, e.g. si [sɨ] is analyzed as an underlying syllabic /s̩/.
| 音節核 | ∅ | /ə/ | /a/ | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 音節尾 | ∅ | /i/ | /u/ | /n/ | /ŋ/ | ∅ | /i/ | /u/ | /n/ | ŋ/ | |||||||||||||
| 中間位 | ∅ | [ɨ] | [ɤ] | [ei̯] | [ou̯] | [ən] | [əŋ] | [a] | [ai̯] | [au̯] | [an] | [aŋ] | |||||||||||
| ㄭ | e | ㄝ | ei | ㄟ | ou | ㄡ | en | ㄣ | eng | ㄥ | a | ㄚ | ai | ㄞ | ao | ㄠ | an | ㄢ | ang | ㄤ | |||
| -i | -e | -ei | -ou | -en | -eng | -a | -ai | -ao | -an | -ang | |||||||||||||
| /j/ | [i] | [je] | [jou̯] | [in] | [iŋ] | [ja] | [jau̯] | [jɛn] | [jaŋ] | ||||||||||||||
| yi | ㄧ | ye | ㄧㄝ | you | ㄧㄡ | yin | ㄧㄣ | ying | ㄧㄥ | ya | ㄧㄚ | yao | ㄧㄠ | yan | ㄧㄢ | yang | ㄧㄤ | ||||||
| -i | -ie | -iu | -in | -ing | -ia | -iao | -ian | -iang | |||||||||||||||
| /zhwiki/w/ | [u] | [wo] | [wei̯] | [wən] | [wəŋ], [ʊŋ] | [wa] | [wai̯] | [wan] | [waŋ] | ||||||||||||||
| wu | ㄨ | wo | ㄨㄛ | wei | ㄨㄟ | wen | ㄨㄣ | weng | ㄨㄥ | wa | ㄨㄚ | wai | ㄨㄞ | wan | ㄨㄢ | wang | ㄨㄤ | ||||||
| -u | -uo2 | -ui | -un | -ong | -ua | -uai | -uan | -uang | |||||||||||||||
| /ɥ/ | [y] | [ɥe] | [yn] | [jʊŋ] | [ɥɛn] | ||||||||||||||||||
| yu | ㄩ | yue | ㄩㄝ | yun | ㄩㄣ | yong | ㄩㄥ | yuan | ㄩㄢ | ||||||||||||||
| -ü1 | -üe1 | -ün1 | -iong | -üan1 | |||||||||||||||||||
- 1 ü 在j、q 或 x 後寫成 u 。
- 2 uo 在 b、p、m 或 f 後寫成 o。
- 3 符號「ㄭ」僅作為發音輔助說明用,實際上於拼寫時不寫出。
這個音位系統用常用於台灣的注音符號。
兒化
現代現代標準漢語中,位於詞尾的大部分「兒」字不獨立成音節,而是與前方的音節縮合,成爲其捲舌韻尾。語音學上則認爲前方的韻尾脫落,元音發生兒化現象。兒化是北京話的典型特徵之一, 在現代現代標準漢語得到不同程度的保留,在
end with a rhotic coda /ɚ/. This feature, known in Chinese as erhua, is particularly characteristic of the Beijing dialect; many other dialects do not use it as much, and some not at all.[21] It occurs in two cases:
- In a small number of independent words or morphemes pronounced [ɚ] or [aɚ̯], written in pinyin as er (with some tone), such as 二 èr "two", 耳 ěr "ear", and 儿 (traditional 兒) ér "son".
- In syllables in which the rhotic coda is added as a suffix to another morpheme. This suffix is represented by the character 儿 [兒] ("son"), to which meaning it is historically related, and in pinyin as r. The suffix combines with the final sound of the syllable, and regular but complex sound changes occur as a result (described in detail under erhua).
The r final is pronounced with a relatively lax tongue, and has been described as a "retroflex vowel".[22]
In dialects that do not make use of the rhotic coda, it may be omitted in pronunciation, or in some cases a different word may be selected: for example, Beijing 这儿 zhèr "here" and 那儿 nàr "there" may be replaced by the synonyms 这里 zhèli and 那里 nàli.
音節
在現代標準漢語中,一個音節的最大形式可以表現為 CGVXT[23],其中C是音節首(輔音),G是中間位(滑音,為 [j, w, ɥ] 其中之一),V是音節核(元音),X是音節尾(輔音,為 [n, ŋ, ɚ̯, i̯, u̯] 其中之一),T是聲調,且C、G 與 X (在一些研究中甚至包含 V)在一個音節中可以不存在。在傳統的分析中,則習慣將一個音節劃分為聲母(即C與G)與韻母(即V與X[24],有時包含T)[25] 。
Many of the possible combinations under the above scheme do not actually occur. There are only some 35 final combinations (medial+rime) in actual syllables (see pinyin finals). In all, there are only about 400 different syllables when tone is ignored, and about 1300 when tone is included. This is a far smaller number of distinct syllables than in a language such as English. Since Chinese syllables usually constitute whole words, or at least morphemes, the smallness of the syllable inventory results in large numbers of homophones. However, in Standard Chinese, the average word length is actually almost exactly two syllables, practically eliminating most homophony issues even when tone is disregarded, especially when context is taken into account as well.[26]
For a list of all Standard Chinese syllables (excluding tone and rhotic coda) see the pinyin table or zhuyin table.
Full and weak syllables
Syllables can be classified as full (or strong), and weak. Weak syllables are usually grammatical markers such as 了 le, or the second syllables of some compound words (although many other compounds consist of two or more full syllables).
A full syllable carries one of the four main tones, and some degree of stress. Weak syllables are unstressed, and have neutral tone. The contrast between full and weak syllables is distinctive; there are many minimal pairs such as 要事 yàoshì "important matter" and 钥匙 yàoshi "key", or 大意 dàyì "main idea" and (with the same characters) dàyi "careless", the second word in each case having a weak second syllable. Some linguists consider this contrast to be primarily one of stress, while others regard it as one of tone. For further discussion, see under Neutral tone and Stress, below.
There is also a difference in syllable length. Full syllables can be analyzed as having two morae ("heavy"), the vowel being lengthened if there is no coda. Weak syllables, however, have a single mora ("light"), and are pronounced approximately 50% shorter than full syllables.[27] Any weak syllable will usually be an instance of the same morpheme (and written with the same character) as some corresponding strong syllable; the weak form will often have a modified pronunciation, however, as detailed in the following section.
音節簡化
除了聲調,元音長度和輕重音的不同之外,弱音節還會受到某些其他發音變化的影響 [28]
- 如果一個音節的音節首是個不送氣的阻礙音(如 b, d, g, z, j),則該音可能會由清音轉變為濁音。例如「嘴巴」(zuǐba)的 b 很可能發音成 [b],而非不送氣的 [p]。
- 弱音節的元音時常會弱化,而使發音位置變得更靠近中央。舉例,「嘴巴」(zuǐba)的 a 發音接近中央元音 [ə]。
- 弱音節的音節尾常常會脫落(這與上面提到弱音節的較短單音節性質有關),且若脫落的是一個鼻音,則元音很可能會被鼻音化。[27] 舉例,「腦袋」(nǎodai )的結尾會讀成單元音 [ɛ] ,而非原本的雙元音 [ai̯] ;「春天」(chūntian)的結尾會讀成鼻化的中央元音 [ə̃]。
- 在某些情況下,元音可能會完全丟失。這在元音為高元音、音節首是擦音或送氣音時特別容易發生。例如可以將「豆腐」(dòufu)說成dòu-f,「問題」 (wènti )說成 wèn-t (元音丟失後,留下的音節首變為音節輔音)。同樣的情況可能發生在半三聲的字詞:[29]元音(與音節尾)在鼻音後可能丟失,如將我們(wǒmen)與「什麼」(shénme)念成wǒm 與 shém – 這種兩個音節合併成一個音節的例子時常出現在自然的對話當中。
「什麼」shénme → shém 的過程也涉及了語音同化,這在快速談話時時常出現(如廣播 guǎngbō → guǎmbō). A particular case of assimilation is that of the sentence-final exclamatory particle 啊 a, a weak syllable, which has different characters for its assimilated forms:
| Preceding sound | Form of particle (pinyin) | Character |
|---|---|---|
| [ŋ], [ɨ] | a | 啊 |
| [i], [y], [e], [o], [a] | ya (from ŋja) | 呀 |
| [u] | wa | 哇 |
| [n] | na | 哪 |
| le (grammatical marker) |
combines to form la | 啦 |
聲調

現代現代標準漢語,如同大部分的漢語方言,是聲調語言的一種。這意味著現代標準漢語中除了輔音和元音之外,音調的不同也會影響單詞的意義。 This means that in addition to consonants and vowels, the pitch contour of a syllable is used to distinguish words from each other. Many non-native Chinese speakers have difficulties mastering the tones of each character, but correct tonal pronunciation is essential for intelligibility because of the vast number of words in the language that only differ by tone (i.e. are minimal pairs with respect to tone). Statistically, tones are as important as vowels in Standard Chinese.[30]
聲調類別
下表顯示現代標準漢語的四種主要音調以及輕聲(或稱中性調、第五聲)。
| 調值 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 調名 | 陰平 | 陽平 | 上 | 去 | 輕聲 |
| 拼音 | ā | á | ǎ | à | a |
| 注音 | ㄚˉ | ㄚˊ | ㄚˇ | ㄚˋ | ˙ㄚ |
| 聲調記號 | ˥ (55) | ˧˥ (35) | ˨˩, ˩, ˩˧, ˨˩˦ (21, 11, 13, 214) |
˥˩ (51) | - |
| IPA | /á/ | /ǎ/ [a᷄] | /à/[c] [à̤, a̤᷆, a̤᷅, a̤᷉] | /â/ | - |
四種聲調的正式名稱依序分別是陰平、陽平、上(shǎng、ㄕㄤˇ)[32][33]、去。由於這套名稱系統乃承襲自中古漢語,故其字面意思與實際聲調並不符,參見下文。現代現代標準漢語的聲調如下:
- 第一調, or high-level tone, is a steady high sound, produced as if it were being sung instead of spoken. (In a few syllables the quality of the vowel is changed when it carries first tone; see the vowel table, above.)
- 第二調,又稱升調或高升調,從中音升至高音。In a three-syllable expression, if the first syllable has first or second tone and the final syllable is not weak, then a second tone on the middle syllable may change to first tone.[34]
- 第三調, low or dipping tone, descends from mid-low to low; between other tones it may simply be low. This tone is often demonstrated as having a rise in pitch after the low fall; however, when a third-tone syllable is not said in isolation, this rise is normally heard only if it appears at the end of a sentence or before a pause, and then usually only on stressed monosyllables.[35] The third tone without the rise is sometimes called half third tone. Third tone syllables that include the rise are significantly longer than other syllables. For further variation in syllables carrying this tone, see Third tone sandhi, below. Unlike the other tones, third tone is pronounced with breathiness or murmur.[36]
- 第四調,又稱降調或高降調, features a sharp fall from high to low (as is heard in curt commands in English, such as "Stop!"). When followed by another fourth-tone syllable, the fall may be only from high to mid-level.[37]
- For the neutral tone or fifth tone, see the following section.
Most romanization systems, including pinyin, represent the tones as diacritics on the vowels (as does zhuyin), although some, like Wade–Giles, use superscript numbers at the end of each syllable. The tone marks and numbers are rarely used outside of language textbooks: in particular, they are usually absent in public signs, company logos, and so forth. Gwoyeu Romatzyh is a rare example of a system where tones are represented using normal letters of the alphabet (although without a one-to-one correspondence).
輕聲
Also called fifth tone or zeroth tone (in Chinese 轻声 [輕聲] qīngshēng, literal meaning: "light tone"), neutral tone is sometimes thought of as a lack of tone. It is associated with weak syllables, which are generally somewhat shorter than tonic syllables. The pitch of a syllable with neutral tone is determined by the tone of the preceding syllable. The following table shows the pitch at which the neutral tone is pronounced in Standard Chinese after each of the four main tones.[38] The situation differs by dialect, and in some regions, notably Taiwan, the neutral tone is relatively uncommon.
| Tone of preceding syllable | Pitch of neutral tone[d] (5=high, 1=low) |
舉例 | 拼音 | Overall tone pattern[d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First ˥ | ˨ ( ꜋ ) 2 | 玻璃 | bōli | ˥.˨ ( ˥꜋ ) |
| Second ˧˥ | ˧ ( ꜊ ) 3 | 伯伯 | bóbo | ˧˥.˧ ( ˧˥꜊ ) |
| Third ˨˩ | ˦ ( ꜉ ) 4 | 喇叭 | lǎba | ˨˩.˦ ( ˨˩꜉ ) |
| Fourth ˥˩ | ˩ ( ꜌ ) 1 | 兔子 | tùzi | ˥˩.˩ ( ˥˩꜌ ) |
Although the contrast between weak and full syllables is often distinctive, the neutral tone is often not described as a full-fledged tone; some linguists feel that it results from a "spreading out" of the tone on the preceding syllable. This idea is appealing because without it, the neutral tone needs relatively complex tone sandhi rules to be made sense of; indeed, it would have to have four allotones, one for each of the four tones that could precede it. However, the "spreading" theory incompletely characterizes the neutral tone, especially in sequences where more than one neutral-tone syllable is found adjacent.[39] Some words with a toneless final syllable variant (重·次轻词语) can be read with neutral tone or with the original tone.
與中古漢語聲調的關係
中古漢語的聲調與現代現代標準漢語的聲調並沒有一對一的關係,下表顯示了中古漢語至現代現代標準漢語聲調的演變。字詞音調的演變取決於音節首,可以分為清音(voiceless consonant,記為 v−)、濁阻礙音(voiced obstruent,記為 v+)或響音(soronant,記為 s)。(現代現代標準漢語已經失去了清濁音的區別。)
| 中古漢語 | 聲調 | 平 | 上 | 去 | 入 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 音節首 | v− | s | v+ | v− | s | v+ | v− | s | v+ | v− | s | v+ | |
| 現代現代標準漢語 | 調名 | 陰平
(一聲) |
陽平
(二聲) |
上 (三聲) |
去 (四聲) |
不規則 | 去 (四聲) |
陽平 (二聲) | |||||
| 聲調輪廓 | 55 | 35 | 21(4) | 51 | 51 | 35 | |||||||
變調
Pronunciation also varies with context according to the rules of 變調 Some such changes have been noted above in the descriptions of the individual tones; however, the most prominent phenomena of this kind relate to consecutive sequences of third-tone syllables. There are also a few common words that have variable tone.
三聲變調
三聲變調的主要規則是:
- 在一個詞組中有連續兩個三聲的字時,第一個字發成二聲。
舉例說明,「老鼠」(lǎoshǔ)發成 láoshǔ [lau̯˧˥ʂu˨˩]。It has been investigated whether the rising contour (˧˥) on the prior syllable is in fact identical to a normal second tone; it has been concluded that it is, at least in terms of auditory perception.[40]
When there are three or more third tones in a row, the situation becomes more complicated, since a third tone that precedes a second tone resulting from third tone sandhi may or may not be subject to sandhi itself. The results may depend on word boundaries, stress, and dialectal variations. General rules for three-syllable third-tone combinations can be formulated as follows:
- If the first word is two syllables and the second word is one syllable, then the first two syllables become second tones. For example, bǎoguǎn hǎo takes the pronunciation báoguán hǎo [pau̯˧˥kwan˧˥xau̯˨˩˦].
- If the first word is one syllable, and the second word is two syllables, the second syllable becomes second tone, but the first syllable remains third tone. For example: lǎo bǎoguǎn takes the pronunciation lǎo báoguǎn [lau̯˨˩pau̯˧˥kwan˨˩˦].
Some linguists have put forward more comprehensive systems of sandhi rules for multiple third tone sequences. For example, it is proposed[41] that modifications are applied cyclically, initially within rhythmic feet (trochees; see below), and that sandhi "need not apply between two cyclic branches."
特殊音節的聲調
一些常用的字擁有自己的特殊變調規則,如不(bù)與 一(yī)。
不 bù:
- 「不」的後面若接著四聲的字,則讀作二聲。
- 例: 不是(bù+shì)念作 búshì [pu˧˥ʂɻ̩˥˩]。
- 其他情況下,不則維持原本的聲調,讀作第四聲。然而,在 A-not-A 問句中,則讀作輕聲(如:是不是 shìbushì)。
一 yī:
- 「一」後面若接著四聲的字,則讀作二聲。
- 例:一定(yī+dìng)念作 yídìng [i˧˥tiŋ˥˩]。
- 「一」後面若接著第一、三、四聲的字,則讀作四聲。
- 「一」用於句尾、多音節詞組的詞尾(不管下一個單詞的第一個音)時, 讀作一聲。 It also has first tone when used as an ordinal number (or part of one), and when it is immediately followed by any digit (including another 一; hence both syllables of the word 一一 yīyī and its compounds have first tone).
- When 一 is used between two reduplicated words, it may become neutral in tone (e.g. 看一看 kànyikàn).
The numbers 七 qī ("seven") and 八 bā ("eight") sometimes display similar tonal behavior as 一 yī, but for most modern speakers they are always pronounced with first tone. (All of these numbers, and 不 bù, were historically Ru tones, and as noted above, that tone does not have predictable reflexes in modern Chinese; this may account for the variation in tone on these words.)[42]
重音、韻律與腔調
現代標準漢語中字詞的輕重音對於母語者來說不太明顯,但相對重音(contrastive stress)則很容易就察覺的出來。One of the reasons for the weaker perception of stress in Chinese may be that variations in the fundamental frequency of speech, which in many other languages serve as a cue for stress, are used in Chinese primarily to realize the tones.儘管如此,壓力和音高之間仍然存在著聯繫—在加重音的音節上,給定音調的變化範圍會比不加重音時更大。[43]
As discussed above, weak syllables have neutral tone and are unstressed. Although this property can be contrastive, the contrast is interpreted by some as being primarily one of tone rather than stress. (Some linguists analyze Chinese as lacking word stress entirely.)[44]
Apart from this contrast between full and weak syllables, some linguists have also identified differences in levels of stress among full syllables. In some descriptions, a multi-syllable word or compound[e] is said to have the strongest stress on the final syllable, and the next strongest generally on the first syllable. Others, however, reject this analysis, noting that the apparent final-syllable stress can be ascribed purely to natural lengthening of the final syllable of a phrase, and disappears when a word is pronounced within a sentence rather than in isolation. San Duanmu[45] takes this view, and concludes that it is the first syllable that is most strongly stressed. He also notes a tendency for Chinese to produce trochees – feet consisting of a stressed syllable followed by one (or in this case sometimes more) unstressed syllables. On this view, if the effect of "final-lengthening" is factored out:
- 在兩個音節的複合詞中,第一個音節有主要重音,第二個音節則無重音。
- 在三個音節的複合詞中,第一個音節有主要重音,第二個音節無重音,第三個音節則可能無重音或者有次重音。
- 在四個音節的複合詞中,第一個音節有最強的重音,第二個音節無重音,第三個或第四個音節則可能無重音或者有次重音,取決於該詞的複合句法結構。
The positions described here as lacking stress are the positions in which weak (neutral-tone) syllables may occur, although full syllables frequently occur in these positions also.
This preference for a trochaic metrical structure is also cited as a reason for certain phenomena of word order variation within complex compounds, and for the strong tendency to use disyllabic words rather than monosyllables in certain positions.[46] Many Chinese monosyllables have alternative disyllabic forms with virtually identical meaning – see Chinese grammar § Word formation.
Another function of voice pitch is to carry intonation. Chinese makes frequent use of particles to express certain meanings such as doubt, query, command, etc., reducing the need to use intonation. However, intonation is still present in Chinese (expressing meanings rather similarly as in standard English), although there are varying analyses of how it interacts with the lexical tones. Some linguists describe an additional intonation rise or fall at the end of the last syllable of an utterance, while others have found that the pitch of the entire utterance is raised or lowered according to the desired intonational meaning.[47]
註釋
- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lee & Zee (2003) and Lin (2007) transcribe these as approximants, while Duanmu (2007) transcribes these as voiced fricatives. The actual pronunciation has been acoustically measured to be more approximant-like.[3]
- ^ 元音的質量參考自 Lee & Zee (2003:110–111頁)、Duanmu (2007:55–58頁)與Lin (2007:65頁)
- ^ Phonologically the third tone is simply low. Phonetically, however, it may be realized as low falling, low rising or low dipping, depending on context.[31]
- ^ 4.0 4.1 The second notation given, which may require additional font support to display properly, uses modified Chao tone letters composed of staves plus dots.
- ^ The concepts of "word" and "compound" in Chinese are not easily defined.
參考資料
- 引文
- ^ 1.0 1.1 朱晓农. 语音学. 北京. 2010-03: 312. ISBN 978-7-100-06681-5.
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Duanmu (2000),第27頁.
- ^ Lee-Kim, Sang-Im, Revisiting Mandarin ‘apical vowels’: An articulatory and acoustic study, Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 2014, 44 (3): 261–282, doi:10.1017/s0025100314000267
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第72頁.
- ^ Ladefoged & Wu (1984).
- ^ Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996),第150–154頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第26頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第33頁.
- ^ Norman (1988),第140–141頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第43頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第25頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第274ff頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第28頁.
- ^ Wan, I-Ping; Jaeger, Jeri J. The Phonological Representation of Taiwan Mandarin Vowels: A Psycholinguistic Study. Journal of East Asian Linguistics. 2003, 12 (3): 205–257. doi:10.1023/A:1023666819363.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第42頁.
- ^ Mou, Xiaomin. Nasal codas in Standard Chinese : a study in the framework of the distinctive feature theory (学位论文). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 2006.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第72–73頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2007),第69頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第37頁.
- ^ Hashimoto, Mantaro. Notes on Mandarin Phonology. Jakobson, Roman; Kawamoto, Shigeo (编). Studies in General and Oriental Linguistics. Tokyo: TEC. 1970: 207–220. ISBN 978-0-404-20311-5.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第195頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第41頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2007),第48頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2007),第16頁.
- ^ Norman (1988),第138–139頁.
- ^ Mair, Victor H. Mair, Victor H. , 编. Two Non-Tetragraphic Northern Sinitic Languages: a) Implications of the Soviet Dungan Script for Chinese Language Reform (PDF). Sino-Platonic Papers (Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania). May 1990, (18): A–10 [17 June 2016].
- ^ 27.0 27.1 Duanmu (2000),第88頁.
- ^ Yip, Po-ching. The Chinese lexicon: a comprehensive survey. Psychology Press. 2000: 29. ISBN 978-0-415-15174-0.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第258頁.
- ^ Surendran, Dinoj and Levow, Gina-Anne (2004), "The functional load of tone in Mandarin is as high as that of vowels", Proceedings of the International Conference on Speech Prosody 2004, Nara, Japan, pp. 99–102.
- ^ Zhu & Wang (2015),第514頁.
- ^ 上聲 - 教育部重編國語辭典修訂本. 中華民國教育部. 1994 [2010-05-15].[永久失效連結]
- ^ 《古代汉语词典》编写组. 古代汉语大词典大字本. Beijing: 商务印书馆. 2002: 1369. ISBN 978-7-100-03515-6.
- ^ Chao (1968),第27頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第222頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第213頁.
- ^ Chao (1968),第28頁.
- ^ Wang Jialing, The Neutral Tone in Trisyllabic Sequences in Chinese Dialects, Tianjin Normal University, 2004
- ^ Yiya Chen and Yi Xu, Pitch Target of Mandarin Neutral Tone (abstract (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)), presented at the 8th Conference on Laboratory Phonology (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第237頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第248頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第228頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第134, p. 231頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第134頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第136ff頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第145–194頁.
- ^ Duanmu (2000),第234頁.
- 參考文獻
- Chao, Yuen Ren. A Grammar of Spoken Chinese 2nd. University of California Press. 1968. ISBN 978-0-520-00219-7.
- Duanmu, San. The Phonology of Standard Chinese. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2000.
- ———. The Phonology of Standard Chinese 2nd. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2007.
- Lin, Yen-Hwei. The Sounds of Chinese. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2007.
- Ladefoged, Peter; Wu, Zongji. Places of Articulation: An Investigation of Pekingese Fricatives. Journal of Phonetics. 1984, 12: 267–78.
- ———; Maddieson, Ian. The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. 1996.
- Lee, Wai-Sum; Zee, Eric. Standard Chinese (Beijing). Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 2003, 33 (1): 109–112. doi:10.1017/S0025100303001208.
- Norman, Jerry. Chinese. Cambridge University Press. 1988. ISBN 978-0-521-29653-3.
- Zhu, Xiaonong; Wang, Caiyu. Tone. Wang, William S.-Y.; Sun, Chaofen (编). The Oxford Handbook of Chinese Linguistics. Oxford University Press. 2015: 503–515. ISBN 978-0-19-985633-6.
- 國立台灣師範大學, 國音教材編輯委員會. 國音學 8th. 正中书局. 2008. ISBN 978-9-570-91808-3.