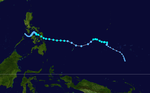
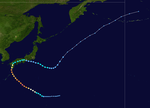
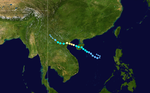
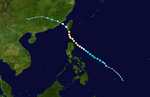
1996年太平洋台风季
| 1996年太平洋台风季 | |
|---|---|
| 气旋季长度 | |
| 首个系统形成 | {{{First storm formed}}} |
| 末个系统消散 | {{{Last storm dissipated}}} |
| 气旋季统计 | |
| 死亡人数 | 不明 |
| 财产损失 | 不明 |
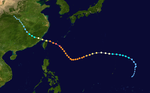
1996年太平洋台风季泛指在1996年全年内的任何时间,于赤道以北及国际换日线以西的太平洋水域所产生的热带气旋。虽然有关方面并没有设下本台风季的指定期限,但大部分于西北太平洋的热带气旋通常都会于六月至十二月期间形成。
本条目的范围仅局限于赤道以北及国际换日线以西的太平洋水域。于赤道以北及国际换日线以东的太平洋水域产生的风暴则被称为飓风。在西太平洋产生的热带风暴是由联合台风警报中心命名,而在该地区的热带低压的编号都以 W 字母作结。而凡进入或产生于菲律宾风暴责任范围以内的热带低压,菲律宾大气地理天文部门 (PAGASA) 都会为它们订立一个菲律宾名称,作当地警报用途;因此同一个风暴有时候会有两个不同的名称。
以下各热带气旋资讯以热带气存在期间的最强形态为准。
| 区域专责气象中心东京台风中心 热带气旋等级 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 等级 | 风速 | |||
| 猛烈台风 | ≥105节 ≥194公里每小时 | |||
| 强烈台风 | 85–104节 157–193公里每小时 | |||
| 台风 | 64–84节 118–156公里每小时 | |||
| 强热带风暴 | 48–63节 88–117公里每小时 | |||
| 热带风暴 | 34–47节 63–87公里每小时 | |||
| 热带低压 | 22–33节 41–62公里每小时 | |||
热带气旋
热带风暴安茵
| 热带风暴(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年4月2日-1996年4月9日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 75 km/h(45 mph) (一分钟) |
台风巴特
热带风暴锦雯
台风丹尼
台风伊芙 (Eve)
| 5级 超级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年7月13日-1996年7月20日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 260 km/h(160 mph) (一分钟) 898 hPa(mbar) |
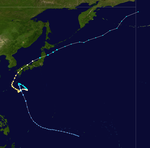
A Tropical Upper Tropospheric Trough spawned Tropical Depression 7W on July 10 over the open Western Pacific. It tracked generally west-northwestward, strengthening to a tropical storm on the 13th. On the 14th Eve became a typhoon, which was followed by a period of explosive deepening to a 160 mph Super Typhoon, with a pressure drop of 70 mb from early on the 15th to early on the 16th. An eyewall replacement cycle weakened Eve to a 115 mph typhoon, but as the outer eyewall contracted, the storm again reached wind speeds of 135 mph before hitting southern Japan on the 18th. Rapidly weakening over the mountains, Eve turned eastward over the islands and the last warning was issued on the 20th. It restrengthened to a tropical storm east of Japan, and continued northeastward until dissipation on the 27th. Eve, despite being a Category 4 at landfall, caused no reported deaths and only 9 injuries.[1]
台风法兰基 (Frankie)
| 2级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年7月21日-1996年7月24日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 165 km/h(105 mph) (一分钟) 954 hPa(mbar) |
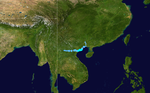
An active monsoon trough over the Western Pacific Ocean developed 3 typhoons; Frankie, Gloria, and Herb. The first, Frankie, developed in the South China Sea on July 19。It tracked west-northwestward and became a tropical storm on the 21st. After crossing the island of Hainan Frankie rapidly intensified to a 100 mph typhoon over the Gulf of Tonkin。It northern Vietnam on the 23rd, and dissipated 2 days later over China. 104 people were reported killed or missing in association with Frankie, and damage figures are estimated at over $200 million (1996 US Dollars).[1]
台风姬罗莉亚
| 2级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年7月22日-1996年7月27日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 165 km/h(105 mph) (一分钟) 954 hPa(mbar) |
The same monsoon trough that spawned Frankie also spawned a tropical depression on July 19 east of the Philippines。It headed northwestward, slowly organizing into a tropical storm on the 22nd. The next day Gloria reached typhoon strength, and a day later it reached its peak of 100 mph winds. Gloria brushed the northern coast of the Philippines and turned northward to hit Taiwan on the 26th. After crossing the island and the Taiwan Straight, Gloria hit China where she dissipated on the 27th. Gloria caused 23 casualties, 20 of which were in the northern Philippines. In addition, damage was estimated at $20 million (1996 USD).[1]
台风赫拔 (Herb)
| 5级 超级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年7月23日-1996年8月1日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 260 km/h(160 mph) (一分钟) 898 hPa(mbar) |
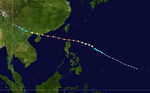
7月23日热带低压10W在塞班岛附近形成,先往北移动,而后往西。热带低压10W在7月24日增强为热带风暴赫拔。热带风暴赫拔持续往西移动,并在7月25日增强为台风。由于与台风姬罗莉亚的藤原效应,赫拔的风速有所减慢。但在那之后,台风赫拔又再度增强,并在7月30日发展为超级台风。台风赫拔是1996年最大的台风,也是自1977年以来第8大的台风。
台风吹袭的琉球群岛,并在7月31日在台湾北部登陆。8月1日登陆中国后,台风赫拔迅速减弱,并在8月3日消散。
强热带风暴载仪
台风却克
| 2级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年8月3日-1996年8月16日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 175 km/h(110 mph) (一分钟) 949 hPa(mbar) |
A monsoon depression developed on July 28 over the open Pacific Ocean. It headed northwestward, slowly consolidating to become a tropical storm on the 5th. While south of Japan, Kirk drifted to the southeast and looped back to the west, strengthening to a typhoon on the 8th while looping. It continued slowly northwestward, and while curving to the northeast Kirk reached a peak of 110 mph winds. The typhoon struck southwestern Japan at that intensity on the 14th. It weakened over the country, and dissipated on the 16th over the northern Pacific. Kirk caused heavy flooding, resulting in at least 2 deaths and moderate damage.[1]
热带低压丽莎
热带风暴马田
| 热带风暴(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年8月13日-1996年8月14日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 85 km/h(50 mph) (一分钟) 991 hPa(mbar) |
The monsoon trough spawned a tropical depression over southern China on August 11。It drifted southwestward, entering the Gulf of Tonkin on the 12th. An extremely small cyclone, it reached tropical storm strength on the 13th and a peak of 60 mph on the 14th. Marty made landfall on the 14th on northern Vietnam, where it dissipated 3 days later. Though small and somewhat weak, Marty managed to cause moderate damage and flooding, amounting to the deaths of 125 with 107 people missing.[1]
台风丽洁
台风奥臣
热带风暴佩萍
热带低压历克
台风莎莉
| 5级 超级 台风(SSHWS) | |
| 持续日期 | 1996年9月2日-1996年9月9日 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 260 km/h(160 mph) (一分钟) 898 hPa(mbar) |
一个热带低压在9月2日于菲律宾以东海域形成。该热带低压以西北偏西方向移动,并在9月5日增强为热带风暴及于6日增强为台风。在9月7日台风莎莉迅速增强其中心风力达每小时160海里之超级台风,并穿越菲律宾。当进入南中国海时,莎莉的中心风力略减为每小时115海里。莎莉于9月9日在雷州半岛登陆,并在翌日消散。莎莉为中国大陆带来连场狂风暴雨和破坏,导致114人死亡﹑110人失踪,经济损失估计约达15亿美元(1996年值)。[1]
台风汤姆
台风维奥莉
强热带风暴威利
| 持续日期 | 不详-不详 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 风力不详 |
An active monsoon trough that also developed Typhoons Tom (25W) and Violet (26W) spawned a tropical depression in the Gulf of Tonkin on September 16。It moved counter-clockwise around Hainan Island,becoming a tropical storm on the 17th and a typhoon on the 19th. It crossed the narrow Hainan Straight between Hainan and China, and continued west-southwestward across the Gulf of Tonkin. Willie made landfall on Vietnam on the 22nd, and dissipated the next day. The typhoon resulted in 38 fatalities from flooding.[1]
台风雅芝
台风赞宁
台风雅贝尔
台风贝芙
台风卡路
台风汀露
热带低压安里
热带风暴芳雅
热带风暴格雷
| 持续日期 | 不详-不详 |
|---|---|
| 强度 | 风力不详 |
Two active monsoon troughs that also developed Typhoon Fern and Southern Hemisphere Cyclones Ophelia, Phil, and Fergus spawned Tropical Depression 43W in the South China Sea on December 21。Due to the troughs' nature, the depression headed east-southeastward, where it strengthened into the final tropical storm of the year on the 24th; Greg. After reaching a peak of 50 mph winds it crossed the northern part of Borneo on the 25th. It continued east-southeastward until dissipation on the 27th, south of the Philippines. Greg caused extensive property damage on Borneo from torrential flooding, resulting in 127 deaths and 100 people missing.[1]
其它热带气旋
除了被命名的热带气旋外,还有一些没被命名的热带低压的热带气旋。以下列出那些热带气旋的资料。
参考文献
- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Chapter 3. Retrieved on 2007-01-07.