Deshret: Difference between revisions
Removing Commons category link that does not match this article (commons:Category:Red crown (n hieroglyph)) |
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Red crown of Lower Egypt}} |
{{short description|Red crown of Lower Egypt}} |
||
{{redirect hatnote|Red crown|the Missouri tavern|Red Crown Tourist Court}} |
|||
[[Image:Deshret.svg|thumb|Deshret, the Red Crown of Lower Egypt]] |
|||
{{Hiero|Deshret, Red Crown<br>(crown as<br>[[determinative]])|<hiero>D46:N37:D21-X1-S3</hiero>|align=right|era=egypt}} |
{{Infobox crown|name=Deshret|color=#D13232|image=Red crown.svg|caption=Deshret, the Red Crown of Lower Egypt|nation=[[Ancient Egypt|Ancient]] [[Lower Egypt]]|successors=[[Pschent]]}}{{Hiero|Deshret, Red Crown<br>(crown as<br>[[determinative]])|<hiero>D46:N37:D21-X1-S3</hiero>|align=right|era=egypt}} |
||
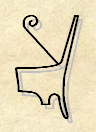
'''Deshret''' |
'''Deshret''' ({{langx|egy|{{huge|'''𓂧𓈙𓂋𓏏𓋔'''}}|translit=[[wikt:dšrt#Etymology|dšrt]]|lit=Red One|italics=no}}) was the Red Crown of [[Lower Egypt]]. It was red bowl shaped with a protruding curlicue (possibly symbolising the proboscis or sting of the honey bee). When combined with the [[Hedjet]] (White Crown) of [[Upper Egypt]], it forms the [[Pschent]] (Double Crown), in ancient Egyptian called the ''sekhemti''. |
||
The Red Crown in [[Egyptian language]] [[Egyptian hieroglyphs|hieroglyphs]] eventually was used as the vertical letter "n" |
The Red Crown in [[Egyptian language]] [[Egyptian hieroglyphs|hieroglyphs]] eventually was used as the vertical letter "n". The original "n" hieroglyph from the [[Predynastic Period]] and the [[Old Kingdom]] was the [[N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)|sign]] depicting ripples of water. |
||
The word '''Deshret''' also referred to the desert Red Land on either side of [[Km (hieroglyph)|Kemet]] (Black Land), the fertile Nile river basin. |
|||
==Significance== |
==Significance== |
||
In mythology, the earth deity [[Geb]], original ruler of Egypt, invested [[Horus]] with the rule over [[Lower Egypt]].<ref>Ewa Wasilewska, ''Creation Stories of the Middle East'', Jessica Kingsley Publishers 2000, p.128</ref> The Egyptian |
In mythology, the earth deity [[Geb]], original ruler of Egypt, invested [[Horus]] with the rule over [[Lower Egypt]].<ref>Ewa Wasilewska, ''Creation Stories of the Middle East'', Jessica Kingsley Publishers 2000, p.128</ref> The Egyptian [[pharaoh]]s, who saw themselves as successors of Horus, wore the ''deshret'' to symbolize their authority over Lower Egypt.<ref>Toby A. H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge 1999, p.194</ref> Other deities wore the ''deshret'' too, or were identified with it, such as the protective serpent goddess [[Wadjet]] and the creator-goddess of Sais, [[Neith]], who often is shown wearing the Red Crown.<ref>George Hart, ''The Routledge Dictionary Of Egyptian Gods And Goddesses'', p.100</ref> |
||
The Red Crown would later be combined with the [[Hedjet|White Crown]] of [[Upper Egypt]] to form the [[Pschent|Double Crown]], symbolizing the rule over the whole country, "The Two Lands" as the Egyptians expressed it.<ref>Ana Ruiz, ''The Spirit of Ancient Egypt'', Algora Publishing 2001, p.8</ref> |
The Red Crown would later be combined with the [[Hedjet|White Crown]] of [[Upper Egypt]] to form the [[Pschent|Double Crown]], symbolizing the rule over the whole country, "The Two Lands" as the Egyptians expressed it.<ref>Ana Ruiz, ''The Spirit of Ancient Egypt'', Algora Publishing 2001, p.8</ref> |
||
As concerns ''deshret'', the Red Land which comprised the deserts and foreign lands surrounding Egypt, [[Set (mythology)|Seth]] was its lord.<ref>John D. Baines, Byron Esely Shafer, Leonard H. Lesko, [[David P. Silverman]], ''Religion in Ancient Egypt: Gods, Myths, and Personal Practice'', Cornell University Press 1991, p.93</ref> It was considered a region of chaos, without law and full of dangers. |
|||
==Records== |
==Records== |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
The Red Crown frequently is mentioned in texts and depicted in reliefs and statues. An early example is the depiction of the victorious pharaoh wearing the ''deshret'' on the [[Narmer Palette]]. A label from the reign of [[Djer]] records a royal visit to the shrine of the Deshret which may have been located at Buto in the Nile delta.<ref>Toby A. H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge 1999, p.284</ref> |
The Red Crown frequently is mentioned in texts and depicted in reliefs and statues. An early example is the depiction of the victorious pharaoh wearing the ''deshret'' on the [[Narmer Palette]]. A label from the reign of [[Djer]] records a royal visit to the shrine of the Deshret which may have been located at Buto in the Nile delta.<ref>Toby A. H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge 1999, p.284</ref> |
||
The fact that no crown has ever been found buried with any of the pharaohs, even in relatively intact tombs, might suggest that it was passed from one |
The fact that no crown has ever been found buried with any of the pharaohs, even in relatively intact tombs, might suggest that it was passed from one reign to the next, much as in present-day monarchies. |
||
Toby Wilkinson has cited the iconography on rock art in the Eastern Desert region as depicting what he interpreted to be among the earliest representations of the royal crowns and suggested the Red Crown could have originated in the southern Nile Valley.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Wilkinson |first1=Toby |title=Genesis of the Pharaohs : dramatic new discoveries rewrite the origins of ancient Egypt |date=2003 |publisher=Thames & Hudson |location=London |isbn=0500051224 |pages=54–82}}</ref> |
|||
==Phonogram== |
==Phonogram== |
||
| Line 25: | Line 27: | ||
Deshret, the [[ancient Egypt]]ian Red Crown, is one of the oldest [[Egyptian hieroglyphs]]. As an [[iconography|iconographic]] element, it is used on the famous [[Narmer Palette|palette]] of Pharaoh [[Narmer]] as the ''"Red Crown of the Delta"'', the Delta being [[Lower Egypt]]. |
Deshret, the [[ancient Egypt]]ian Red Crown, is one of the oldest [[Egyptian hieroglyphs]]. As an [[iconography|iconographic]] element, it is used on the famous [[Narmer Palette|palette]] of Pharaoh [[Narmer]] as the ''"Red Crown of the Delta"'', the Delta being [[Lower Egypt]]. |
||
The first usage of the Red Crown was in iconography as the symbol for [[Lower Egypt]] with the [[Nile Delta]], horizontal letter 'n', [[Gardiner's sign list|Gardiner]] no. 35, <hiero>N35</hiero> |
The first usage of the Red Crown was in iconography as the symbol for [[Lower Egypt]] with the [[Nile Delta]], horizontal letter 'n', [[Gardiner's sign list|Gardiner]] no. 35, <hiero>N35</hiero> Later it came to be used in the Egyptian language as an [[alphabet]]ic [[Egyptian uniliteral signs|uniliteral]], vertical form for letter "n" as a [[phoneme]] or [[preposition]]. It became functional in running hieroglyphic texts, where either the horizontal or vertical form preposition satisfied space requirements. |
||
Both the vertical and horizontal forms are prepositional equivalents, with the horizontal letter n, the [[N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)]] being more common, as well as more common to form parts of [[Egyptian language]] words requiring the [[phoneme]] 'n'. |
Both the vertical and horizontal forms are prepositional equivalents, with the horizontal letter n, the [[N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)]] being more common, as well as more common to form parts of [[Egyptian language]] words requiring the [[phoneme]] 'n'. |
||
| Line 33: | Line 35: | ||
The Red Crown is also used as a [[determinative]], most notably in the word for deshret. It is also used in other words or names of gods. |
The Red Crown is also used as a [[determinative]], most notably in the word for deshret. It is also used in other words or names of gods. |
||
;Use in the Rosetta Stone |
;Use in the Rosetta Stone |
||
[[Image:RosettaStoneDetail.jpg|thumb|right|190px|[[Rosetta Stone]] usage of Red Crown, not as preposition: |
[[Image:RosettaStoneDetail.jpg|thumb|right|190px|[[Rosetta Stone]] usage of Red Crown, not as preposition: part of [[Pschent]] (Double Crown), and part of '''"Taui"''', the name for [[Upper and Lower Egypt]] (used combined with a [[Crossroads (hieroglyph)]])]] |
||
In the 198 BC [[Rosetta Stone]], the '' 'Red Crown' '' as hieroglyph has the usage mostly of the vertical form of the [[preposition]] "n". In running text, word endings are not always at the end of [[quadrat (hieroglyph block)|hieroglyph blocks]]; when they are at the end, a simple transition to start the next block is a vertical separator, in this case the preposition, vertical n, (thus a space saver). |
In the 198 BC [[Rosetta Stone]], the '' 'Red Crown' '' as hieroglyph has the usage mostly of the vertical form of the [[preposition]] "n". In running text, word endings are not always at the end of [[quadrat (hieroglyph block)|hieroglyph blocks]]; when they are at the end, a simple transition to start the next block is a vertical separator, in this case the preposition, vertical n, (thus a space saver). |
||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
{{commons category|Red crown}} |
{{commons category|Red crown}} |
||
* [[Atef]] – [[Hedjet]] Crown with feathers identified with [[Osiris]] |
* [[Atef]] – [[Hedjet]] Crown with feathers identified with [[Osiris]] |
||
* [[Gardiner's Sign List]] |
|||
* [[Gardiner's Sign List#S. Crowns, Dress, Staves, etc.]] |
|||
* [[Hedjet]] – White Crown of Upper Egypt |
|||
* [[Khepresh]] – Blue or War Crown also called Royal Crown |
* [[Khepresh]] – Blue or War Crown also called Royal Crown |
||
* [[N-water ripple (n hieroglyph)]] |
|||
* [[Pharaoh-seated, with flail & red crown (hieroglyph)]] |
|||
* [[Pschent]] – Double Crown of Lower & Upper Egypt |
|||
* [[Uraeus]] – Rearing Cobra |
|||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
| Line 60: | Line 55: | ||
|Image:HierS.png|The vertical letter N, as [[preposition]], or [[determinative]] in the [[Egyptian language]] |
|Image:HierS.png|The vertical letter N, as [[preposition]], or [[determinative]] in the [[Egyptian language]] |
||
|Image:NarmerPalette-CloseUpOfProcession-ROM.png|Close-up of [[Narmer Palette]], Pharaoh Narmer with crown |
|Image:NarmerPalette-CloseUpOfProcession-ROM.png|Close-up of [[Narmer Palette]], Pharaoh Narmer with crown |
||
|File:Bronze statuette of a Kushite king wearing the crown of Lower Egypt. 25th Dynasty, 670 BCE. Neues Museum.jpg|Bronze statuette of a Kushite king wearing the red crown of Lower Egypt |
|File:Bronze statuette of a Kushite king wearing the crown of Lower Egypt. 25th Dynasty, 670 BCE. Neues Museum.jpg|Bronze statuette of a Kushite king wearing the red crown of Lower Egypt; 25th Dynasty, c. 670 BCE, Neues Museum, Berlin |
||
|Ägyptisches Museum Kairo 2016-03-29 Mentuhotep 02.jpg|Sandstone statue of [[Mentuhotep II]]; [[Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt|11th Dynasty]], c. 2060–2009 BCE, [[Egyptian Museum]], Cairo |
|||
}} |
|||
|File:GuardianStatueofAmenemhmatII.jpg|A guardian statue wearing the red crown which reflected the facial features of the reigning king, probably Amenemhat II or Senwosret II, and which functioned as a divine guardian for the [[Imiut fetish|imiut]]; made of cedar wood and plaster {{circa}} 1919–1885 BC<ref>{{cite web |title=Guardian Figure |url=https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/543864 |website=www.metmuseum.org |publisher=[[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] |access-date=9 February 2022}}</ref>}} |
|||
{{Gallery |
{{Gallery |
||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 13 December 2024
| Deshret | |
|---|---|
 Deshret, the Red Crown of Lower Egypt | |
| Details | |
| Country | Ancient Lower Egypt |
| Successors | Pschent |
| ||||
| Deshret, Red Crown (crown as determinative) in hieroglyphs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Deshret (Ancient Egyptian: 𓂧𓈙𓂋𓏏𓋔, romanized: dšrt, lit. 'Red One') was the Red Crown of Lower Egypt. It was red bowl shaped with a protruding curlicue (possibly symbolising the proboscis or sting of the honey bee). When combined with the Hedjet (White Crown) of Upper Egypt, it forms the Pschent (Double Crown), in ancient Egyptian called the sekhemti.
The Red Crown in Egyptian language hieroglyphs eventually was used as the vertical letter "n". The original "n" hieroglyph from the Predynastic Period and the Old Kingdom was the sign depicting ripples of water.
The word Deshret also referred to the desert Red Land on either side of Kemet (Black Land), the fertile Nile river basin.
Significance
[edit]In mythology, the earth deity Geb, original ruler of Egypt, invested Horus with the rule over Lower Egypt.[1] The Egyptian pharaohs, who saw themselves as successors of Horus, wore the deshret to symbolize their authority over Lower Egypt.[2] Other deities wore the deshret too, or were identified with it, such as the protective serpent goddess Wadjet and the creator-goddess of Sais, Neith, who often is shown wearing the Red Crown.[3]
The Red Crown would later be combined with the White Crown of Upper Egypt to form the Double Crown, symbolizing the rule over the whole country, "The Two Lands" as the Egyptians expressed it.[4]
Records
[edit]No Red Crown has been found. Several ancient representations indicate it was woven like a basket from plant fiber such as grass, straw, flax, palm leaf, or reed.
The Red Crown frequently is mentioned in texts and depicted in reliefs and statues. An early example is the depiction of the victorious pharaoh wearing the deshret on the Narmer Palette. A label from the reign of Djer records a royal visit to the shrine of the Deshret which may have been located at Buto in the Nile delta.[5]
The fact that no crown has ever been found buried with any of the pharaohs, even in relatively intact tombs, might suggest that it was passed from one reign to the next, much as in present-day monarchies.
Toby Wilkinson has cited the iconography on rock art in the Eastern Desert region as depicting what he interpreted to be among the earliest representations of the royal crowns and suggested the Red Crown could have originated in the southern Nile Valley.[6]
Phonogram
[edit]
| ||
| 1 Red Crown, Deshret 2 also, vertical "N" in hieroglyphs | ||
|---|---|---|
Deshret, the ancient Egyptian Red Crown, is one of the oldest Egyptian hieroglyphs. As an iconographic element, it is used on the famous palette of Pharaoh Narmer as the "Red Crown of the Delta", the Delta being Lower Egypt.
The first usage of the Red Crown was in iconography as the symbol for Lower Egypt with the Nile Delta, horizontal letter 'n', Gardiner no. 35,
| |
Later it came to be used in the Egyptian language as an alphabetic uniliteral, vertical form for letter "n" as a phoneme or preposition. It became functional in running hieroglyphic texts, where either the horizontal or vertical form preposition satisfied space requirements.
Both the vertical and horizontal forms are prepositional equivalents, with the horizontal letter n, the N-water ripple (n hieroglyph) being more common, as well as more common to form parts of Egyptian language words requiring the phoneme 'n'.
One old use of the red crown hieroglyph is to make the word: 'in'!, (formerly an-(a-with dot)-(the "vertical feather" hieroglyph a, plus the red crown). Egyptian "in" is used at the beginning of a text and translates as: Behold!, or Lo!, and is an emphatic.
The Red Crown is also used as a determinative, most notably in the word for deshret. It is also used in other words or names of gods.
- Use in the Rosetta Stone

In the 198 BC Rosetta Stone, the 'Red Crown' as hieroglyph has the usage mostly of the vertical form of the preposition "n". In running text, word endings are not always at the end of hieroglyph blocks; when they are at the end, a simple transition to start the next block is a vertical separator, in this case the preposition, vertical n, (thus a space saver).
Since the start of the next hieroglyphic block could also be started with a horizontal "n" at the bottom of the previous block, it should be thought that the vertical "n" is also chosen for a visual effect; in other words, it visually spreads out the running text of words, instead of piling horizontal prepositions in a more tight text. Visually it is also a hieroglyph that takes up more 'space'-(versus a straight-line type for the horizontal water ripple); so it may have a dual purpose of a less compact text, and a better segue-transition to the next words.
The Red Crown hieroglyph is used 35 times in the Rosetta Stone; only 4 times is it used as a non-preposition. It averages once per line usage in the 36 line Decree of Memphis (Ptolemy V)-(Rosetta Stone).
See also
[edit]- Atef – Hedjet Crown with feathers identified with Osiris
- Khepresh – Blue or War Crown also called Royal Crown
Gallery
[edit]-
Ramesside Period ostracon, pharaoh wearing Red Crown
-
Narmer Palette, front
-
Close-up of Narmer Palette, Pharaoh Narmer with crown
-
Bronze statuette of a Kushite king wearing the red crown of Lower Egypt; 25th Dynasty, c. 670 BCE, Neues Museum, Berlin
-
Philistine captives at Medinet Habu
-
Stele of Tchia at the Louvre
-
Apep being slain
References
[edit]- ^ Ewa Wasilewska, Creation Stories of the Middle East, Jessica Kingsley Publishers 2000, p.128
- ^ Toby A. H. Wilkinson, Early Dynastic Egypt, Routledge 1999, p.194
- ^ George Hart, The Routledge Dictionary Of Egyptian Gods And Goddesses, p.100
- ^ Ana Ruiz, The Spirit of Ancient Egypt, Algora Publishing 2001, p.8
- ^ Toby A. H. Wilkinson, Early Dynastic Egypt, Routledge 1999, p.284
- ^ Wilkinson, Toby (2003). Genesis of the Pharaohs : dramatic new discoveries rewrite the origins of ancient Egypt. London: Thames & Hudson. pp. 54–82. ISBN 0500051224.
- ^ "Guardian Figure". www.metmuseum.org. Metropolitan Museum of Art. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- Budge. An Egyptian Hieroglyphic Dictionary, E.A.Wallace Budge, (Dover Publications), c 1978, (c 1920), Dover edition, 1978. (In two volumes) (softcover, ISBN 0-486-23615-3)
- Budge. The Rosetta Stone, E.A.Wallace Budge, (Dover Publications), c 1929, Dover edition(unabridged), 1989. (softcover, ISBN 0-486-26163-8)






![A guardian statue wearing the red crown which reflected the facial features of the reigning king, probably Amenemhat II or Senwosret II, and which functioned as a divine guardian for the imiut; made of cedar wood and plaster c. 1919–1885 BC[7]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/GuardianStatueofAmenemhmatII.jpg/134px-GuardianStatueofAmenemhmatII.jpg)



