Pannonia
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2016) |
| Provincia Pannonia | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||
| 20 AD–107 AD | |||||||||
 Province of Pannonia highlighted (red) within the Roman Empire (pink) | |||||||||
| Capital | Carnuntum,[1] Sirmium,[2] Savaria,[3] Aquincum,[4] Poetovio[5] or Vindobona[6] | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 20 AD | ||||||||
• Division of Pannonia | Between the years 102 and 107, Trajan divided Pannonia into Pannonia Superior (western part with the capital Carnuntum), and Pannonia Inferior (eastern part with the capitals in Aquincum and Sirmium) 107 AD | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Pannonia (/pəˈnoʊniə/) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory of present-day western Hungary, eastern Austria, northern Croatia, north-western Serbia, northern Slovenia and northern Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Name
Julius Pokorny believed the name Pannonia is derived from Illyrian, from the Proto-Indo-European root *pen-, "swamp, water, wet" (cf. English fen, "marsh"; Hindi pani, "water").[7]
Others[who?] believe that the name is related to the god of the nature, goats and shepherds Pan and/or pan, the Proto-Indo-European word for lord/master, which could mean Pan's Land or Land of the Master(s), which is more probable due the fact the Ionian fleet supplied Pannonia via the Black Sea and Danube, and Panionium festivities were also well known in the region to its Celtic, Adriatic Veneti and Scythian inhabitants.
Pliny the Elder, in Natural History, places the eastern regions of the Hercynium jugum, the "Hercynian mountain chain", in Pannonia (present-day Hungary) and Dacia (present-day Romania).[8] He also gives us some dramaticised description[9] of its composition, in which the close proximity of the forest trees causes competitive struggle among them (inter se rixantes). He mentions its gigantic oaks.[10] But even he—if the passage in question is not an interpolated marginal gloss—is subject to the legends of the gloomy forest. He mentions unusual birds, which have feathers that "shine like fires at night". Medieval bestiaries named these birds the Ercinee. The impenetrable nature of the Hercynian Silva hindered the last concerted Roman foray into the forest, by Drusus, during 12–9 BC: Florus asserts that Drusus invisum atque inaccessum in id tempus Hercynium saltum (Hercynia saltus, the "Hercynian ravine-land")[11] patefecit.[12]
History
Prior to Roman conquest
The first inhabitants of this area known to history were the Pannonii (Pannonians), a group of Indo-European tribes akin to Illyrians. From the 4th century BC, it was invaded by various Celtic tribes. Little is known of Pannonia until 35 BC, when its inhabitants, allies of the Dalmatians, were attacked by Augustus, who conquered and occupied Siscia (Sisak). The country was not, however, definitively subdued by the Romans until 9 BC, when it was incorporated into Illyricum, the frontier of which was thus extended as far as the Danube.
Under Roman rule

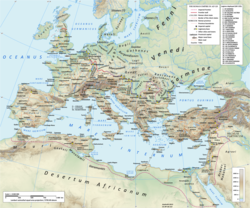
In AD6 , the Pannonians, with the Dalmatians and other Illyrian tribes, engaged in the so-called Great Illyrian Revolt, and were overcome by Tiberius and Germanicus, after a hard-fought campaign, which lasted for three years. After the rebellion was crushed in AD,9, the province of Illyricum was dissolved, and its lands were divided between the new provinces of Pannonia in the north and Dalmatia in the south. The date of the division is unknown, most certainly after AD 20 but before AD 50. The proximity of dangerous barbarian tribes (Quadi, Marcomanni) necessitated the presence of a large number of troops (seven legions in later times), and numerous fortresses were built on the bank of the Danube.
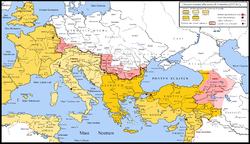
Some time between the years 102 and 107, between the first and second Dacian wars, Trajan divided the province into Pannonia Superior (western part with the capital Carnuntum), and Pannonia Inferior (eastern part with the capitals in Aquincum and Sirmium[13]). According to Ptolemy, these divisions were separated by a line drawn from Arrabona in the north to Servitium in the south; later, the boundary was placed further east. The whole country was sometimes called the Pannonias (Pannoniae).
Pannonia Superior was under the consular legate, who had formerly administered the single province, and had three legions under his control. Pannonia Inferior was at first under a praetorian legate with a single legion as the garrison; after Marcus Aurelius, it was under a consular legate, but still with only one legion. The frontier on the Danube was protected by the establishment of the two colonies Aelia Mursia and Aelia Aquincum by Hadrian.
Under Diocletian, a fourfold division of the country was made:
- Pannonia Prima in the northwest, with its capital in Savaria / Sabaria, it included Upper Pannonia and the major part of Central Pannonia between the Raba and Drava,
- Pannonia Valeria in the northeast, with its capital in Sopianae, it comprised the remainder of Central Pannonia between the Raba, Drava and Danube,
- Pannonia Savia in the southwest, with its capital in Siscia,
- Pannonia Secunda in the southeast, with its capital in Sirmium
Diocletian also moved parts of today's Slovenia out of Pannonia and incorporated them in Noricum. In 324 AD, Constantine I enlarged the borders of Roman Pannonia to the east, annexing the plains of what is now eastern Hungary, northern Serbia and western Romania up to the limes that he created: the Devil's Dykes.[citation needed]
In the 4th-5th century, one of the dioceses of the Roman Empire was known as the Diocese of Pannonia. It had its capital in Sirmium and included all four provinces that were formed from historical Pannonia, as well as the provinces of Dalmatia, Noricum Mediterraneum and Noricum Ripense.[citation needed]
-
Pannonia in the 1st century
-
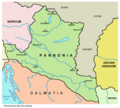
Pannonia in the 2nd century
-
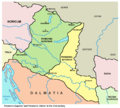
Pannonia in the 4th century
-
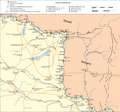
Pannonia with Constantine I "limes" in 330 AD
Post-Roman

During the Migrations Period in the 5th century, some parts of Pannonia was ceded to the Huns in 433 by Flavius Aetius, the magister militum of the Western Roman Empire.[14] After the collapse of the Hunnic empire in 454, large numbers of Ostrogoths were settled by Marcian in the province as foederati. The Eastern Roman Empire controlled it for a time in the 6th century, and a Byzantine province of Pannonia with its capital at Sirmium was temporarily restored, but it included only a small southeastern part of historical Pannonia.
Afterwards, it was again invaded by the Avars in the 560s, the Slavs, who first settled c. 480s but became independent only from the 7th century, and the Franks, who named a frontier march the March of Pannonia in the late 8th century. The term Pannonia was also used for a Slavic duchy that was vassal to the Franks.
Between the 5th and the 10th centuries, the romanized population of Pannonia developed the Romance Pannonian language, mainly around Lake Balaton in present-day western Hungary, where there was the keszthely culture. This language and the related culture became extinct with the arrival of the Magyars.
Cities and auxiliary forts



The native settlements consisted of pagi (cantons) containing a number of vici (villages), the majority of the large towns being of Roman origin. The cities and towns in Pannonia were:
Now in Austria:
Now in Bosnia and Hercegovina:
Now in Croatia:
- Ad Novas (Zmajevac)
- Andautonia (Ščitarjevo)
- Aqua Viva (Petrijanec)
- Aquae Balisae (Daruvar)
- Certissa (Đakovo)
- Cibalae (Vinkovci)
- Cornacum (Sotin)
- Cuccium (Ilok)
- Iovia or Iovia Botivo (Ludbreg)
- Marsonia (Slavonski Brod)
- Mursa (Osijek)
- Siscia (Sisak)
- Teutoburgium (Dalj)
Now in Hungary:
- Ad Flexum (Mosonmagyaróvár)
- Ad Mures (Ács)
- Ad Statuas (Vaspuszta)
- Ad Statuas (Várdomb)
- Alisca (Szekszárd)
- Alta Ripa (Tolna)
- Aquincum (Óbuda, Budapest)
- Arrabona (Győr)
- Brigetio (Szőny)
- Caesariana (Baláca)
- Campona (Nagytétény)
- Cirpi (Dunabogdány)
- Contra-Aquincum (Budapest)
- Contra Constantiam (Dunakeszi)
- Gorsium-Herculia (Tác)
- Intercisa (Dunaújváros)
- Iovia (Szakcs)
- Lugio (Dunaszekcső)
- Lussonium (Dunakömlőd)
- Matrica (Százhalombatta)
- Morgentianae (Tüskevár (?))
- Mursella (Mórichida)
- Quadrata (Lébény)
- Sala (Zalalövő)
- Savaria or Sabaria (Szombathely)
- Scarbantia (Sopron)
- Solva (Esztergom)
- Sopianae (Pécs)
- Ulcisia Castra (Szentendre)
- Valcum (Fenékpuszta)
Now in Serbia:
- Acumincum (Stari Slankamen)
- Ad Herculae (Čortanovci)
- Bassianae (Donji Petrovci)
- Bononia (Banoštor)
- Burgenae (Novi Banovci)
- Cusum (Petrovaradin)
- Graio (Sremska Rača)
- Onagrinum (Begeč)
- Rittium (Surduk)
- Sirmium (Sremska Mitrovica)
- Taurunum (Zemun)
Now in Slovakia:
Now in Slovenia:
Economy and country features
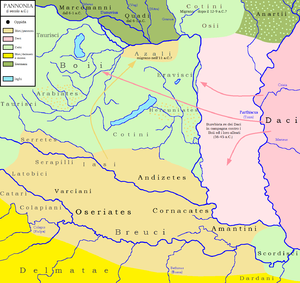
The country was fairly productive, especially after the great forests had been cleared by Probus and Galerius. Before that time, timber had been one of its most important exports. Its chief agricultural products were oats and barley, from which the inhabitants brewed a kind of beer named sabaea. Vines and olive trees were little cultivated. Pannonia was also famous for its breed of hunting dogs. Although no mention is made of its mineral wealth by the ancients, it is probable that it contained iron and silver mines. Its chief rivers were the Dravus, Savus, and Arrabo, in addition to the Danuvius (less correctly, Danubius), into which the first three rivers flow.
Legacy
The ancient name Pannonia is retained in the modern term Pannonian plain.
See also
References
- ^ Vienna, Anthony Haywood, Caroline (CON) Sieg, Lonely Planet Vienna, 2010, page 21.
- ^ The third book of history: containing ancient history in connection with ancient geography, Samuel Griswold Goodrich, Jenks, Palmer, 1835, page 111.
- ^ The Archaeology of Roman Pannonia, Alfonz Lengyel, George T. Radan, University Press of Kentucky, 1980, page 247.
- ^ People and nature in historical perspective, Péter Szabó, Central European University Press, 2003, page 144.
- ^ Historical outlook: a journal for readers, students and teachers of history, Том 9, American Historical Association, National Board for Historical Service, National Council for the Social Studies, McKinley Publishing Company, 1918, page 194.
- ^ THE COTTAGE CYCLOPEDIA OF HISTORY AND BIOGRAPHY, ED.M.PIERCE, 1869, page 915.
- ^ J. Pokorny, Indogermanisches etymologisches Wörterbuch, No. 1481 Archived 2011-06-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Pliny, iv.25
- ^ The threatening nature of the pathless woodland in Pliny is explored by Klaus Sallmann, "Reserved for Eternal Punishment: The Elder Pliny's View of Free Germania (HN. 16.1–6)" The American Journal of Philology 108.1 (Spring 1987:108–128) pp 118ff.
- ^ Pliny xvi.2
- ^ Compare the inaccessible Carbonarius Saltus west of the Rhine
- ^ Florus, ii.30.27.
- ^ The Routledge Handbook of Archaeological Human Remains and Legislation, Taylor & Francis, page 381.
- ^ Attila, the Hun – Google Knihy. Books.google.cz. 2003. ISBN 0-7910-7221-5. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
Sources
- Curta, Florin (2001). The Making of the Slavs: History and Archaeology of the Lower Danube Region, c. 500–700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Curta, Florin (2006). Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500–1250. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Given, John (2014). The Fragmentary History of Priscus. Merchantville, New Jersey: Evolution Publishing.
- Janković, Đorđe (2004). "The Slavs in the 6th Century North Illyricum". Гласник Српског археолошког друштва. 20: 39–61.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mirković, Miroslava B. (2017). Sirmium: Its History from the First Century AD to 582 AD. Novi Sad: Center for Historical Research.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Mócsy, András (2014) [1974]. Pannonia and Upper Moesia: A History of the Middle Danube Provinces of the Roman Empire. New York: Routledge.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Popović, Radomir V. (1996). Le Christianisme sur le sol de l'Illyricum oriental jusqu'à l'arrivée des Slaves. Thessaloniki: Institute for Balkan Studies.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Várady, László (1969). Das Letzte Jahrhundert Pannoniens (376–476). Amsterdam: Verlag Adolf M. Hakkert.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Whitby, Michael (1988). The Emperor Maurice and his Historian: Theophylact Simocatta on Persian and Balkan warfare. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Wozniak, Frank E. (1981). "East Rome, Ravenna and Western Illyricum: 454-536 A.D." Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 30 (3): 351–382.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Zeiller, Jacques (1918). Les origines chrétiennes dans les provinces danubiennes de l'Empire romain. Paris: E. De Boccard.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 20 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 680.
- "Pannonia". Encyclopædia Britannica (online ed.). 29 March 2018.
- "Pannonia". unrv.com. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- Pannonia map
- Pannonia map
- Aerial photography: Gorsium - Tác - Hungary
- Aerial photography: Aquincum - Budapest - Hungary
44°54′00″N 19°01′12″E / 44.9000°N 19.0200°E
 |
| Notes:
|
- Pannonia
- Provinces of the Roman Empire
- Provinces of Pannonia
- Austria in the Roman era
- Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Roman era
- Croatia in the Roman era
- Hungary in the Roman era
- Roman Illyria
- Serbia in the Roman era
- Slovakia in the Roman era
- Slovenia in the Roman era
- Ancient history of Vojvodina
- States and territories established in the 1st century
- States and territories disestablished in the 2nd century
- 20 establishments
- 20s establishments in the Roman Empire
- 100s disestablishments in the Roman Empire
- 20s establishments
- 107 disestablishments