Portal:Hungary
The Hungary Portal




Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square kilometres (35,920 sq mi) of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of 9.5 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian is the official language and Budapest is the country's capital and largest city.
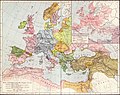
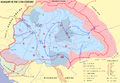
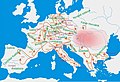
Prior to the foundation of the Hungarian state, various peoples settled in the territory of present-day Hungary, most notably the Celts, Romans, Huns, Germanic peoples, Avars and Slavs. The Principality of Hungary was established in the late 9th century by Álmos and his son Árpád through the conquest of the Carpathian Basin. King Stephen I ascended the throne in 1000, converting his realm to a Christian kingdom. The medieval Kingdom of Hungary was a European power, reaching its height in the 14th–15th centuries. After a long period of Ottoman wars, Hungary's forces were defeated at the Battle of Mohács and its capital was captured in 1541, opening roughly a 150 years long period when the country was divided into three parts: Royal Hungary, loyal to the Habsburgs; Ottoman Hungary; and the largely independent Principality of Transylvania. The reunited Hungary came under Habsburg rule at the turn of the 18th century, fighting a war of independence in 1703–1711, and a war of independence in 1848–1849 until a compromise allowed the formation of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy in 1867, a major power into the early 20th century. Austria-Hungary collapsed after World War I, and the subsequent Treaty of Trianon in 1920 established Hungary's current borders, resulting in the loss of 71% of its historical territory, 58% of its population, and 32% of its ethnic Hungarians.
In the interwar period, after initial turmoil, Miklós Horthy ascended as a determining politician, representing the monarchy as regent in place of the Habsburgs. Hungary joined the Axis powers in World War II, suffering significant damage and casualties. As a result, the Hungarian People's Republic was established as a satellite state of the Soviet Union. Following the failed 1956 revolution, Hungary became comparatively freer, but still remained a repressed member of the Eastern Bloc. In 1989, concurrently with the Revolutions of 1989, Hungary peacefully transitioned into a democratic parliamentary republic, joining the European Union in 2004 and being part of the Schengen Area since 2007. Since the election of Viktor Orbán in 2010, Hungary has undergone democratic backsliding becoming an illiberal democracy and hybrid regime.
Hungary is a high-income economy with universal health care and tuition-free secondary education. Hungary has a long history of significant contributions to arts, music, literature, sports, science and technology. It is a popular tourist destination in Europe, drawing 24.5 million international tourists in 2019. It is a member of numerous international organisations, including the Council of Europe, European Union, NATO, United Nations, World Health Organization, World Trade Organization, World Bank, Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, and the Visegrád Group. (Full article...)
Edward Teller (Hungarian: Teller Ede; January 15, 1908 – September 9, 2003) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist and chemical engineer who is known colloquially as "the father of the hydrogen bomb" and one of the creators of the Teller–Ulam design based on Stanisław Ulam's design.
Born in Austria-Hungary in 1908, Teller emigrated to the United States in the 1930s, one of the many so-called "Martians", a group of prominent Hungarian scientist émigrés. He made numerous contributions to nuclear and molecular physics, spectroscopy (in particular the Jahn–Teller and Renner–Teller effects), and surface physics. His extension of Enrico Fermi's theory of beta decay, in the form of Gamow–Teller transitions, provided an important stepping stone in its application, while the Jahn–Teller effect and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) theory have retained their original formulation and are still mainstays in physics and chemistry. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Béla Kun (Hungarian: Kun Béla, born Béla Kohn; 20 February 1886 – 29 August 1938) was a Hungarian communist revolutionary and politician who governed the Hungarian Soviet Republic in 1919. After attending Franz Joseph University at Kolozsvár (today Cluj-Napoca, Romania), Kun worked as a journalist up until the First World War. He served in the Austro-Hungarian Army and was captured by the Imperial Russian Army in 1916, after which he was sent to a prisoner-of-war camp in the Urals. Kun embraced communist ideas during his time in Russia, and in 1918 he co-founded a Hungarian arm of the Russian Communist Party in Moscow. He befriended Vladimir Lenin and fought for the Bolsheviks in the Russian Civil War.
In November 1918, Kun returned to Hungary with Soviet support and set up the Party of Communists in Hungary. Adopting Lenin's tactics, he agitated against the government of Mihály Károlyi and achieved great popularity despite being imprisoned. After his release in March 1919, Kun led a successful coup d'état, formed a Communist-Social Democratic coalition government and proclaimed the Hungarian Soviet Republic. Though the de jure leader of the republic was prime minister Sándor Garbai, the de facto power was in the hands of foreign minister Kun, who maintained direct contact with Lenin via radiotelegraph and received direct orders and advice from the Kremlin. (Full article...)
People
- Musicians
Béla Bartók – János Bihari – Ernő Dohnányi – Béni Egressy – Ferenc Erkel – Zoltán Kocsis – Zoltán Kodály – Franz Liszt - Eugene Ormandy - George Szell - András Schiff
- Painters
Gyula Benczúr – Tivadar Csontváry Kosztka – Béla Czóbel – Árpád Feszty – Károly Lotz – Viktor Madarász – Mihály Munkácsy – József Rippl-Rónai – Pál Szinyei Merse – István Szőnyi – Victor Vasarely
- Photographers
Brassaï – Cornell Capa – Robert Capa – Lucien Hervé – André Kertész – László Moholy-Nagy – Martin Munkácsi
- Scientists
Béla H. Bánáthy – Zoltán Bay – Georg von Békésy – Farkas Bolyai – János Bolyai – Károly Bund – József Eötvös – Loránd Eötvös – Dennis Gabor – John Charles Harsanyi – George de Hevesy – Alexander Csoma de Kőrös – László Lovász – John von Neumann – George Andrew Olah – Ernő Rubik – Hans Selye – Ignaz Semmelweis – Charles Simonyi – János Szentágothai – Albert Szent-Györgyi – Leó Szilárd – Edward Teller – Eugene Wigner
- Writers and poets
Endre Ady – János Arany – József Eötvös – György Faludy – Béla Hamvas – Mór Jókai – Attila József – Ferenc Kazinczy – Imre Kertész – János Kodolányi – Ferenc Kölcsey – Imre Madách – Sándor Márai – Ferenc Molnár – Sándor Petőfi – Miklós Radnóti – Magda Szabó – Antal Szerb – Miklós Vámos – Mihály Vörösmarty
- Statesmen, Politicians and Military
Gyula Andrássy – Lajos Batthyány – Gabriel Bethlen – Stephen Bocskay – Matthias Corvinus – Ferenc Deák – Miklós Horthy – Lajos Kossuth – Ferenc Nagy – Imre Nagy – Bertalan Szemere – István Széchenyi – Miklós Wesselényi – Vilmos Nagy of Nagybaczon
- Sportspeople
József Bozsik – Krisztina Egerszegi – Zoltán Gera – Dezső Gyarmati – Ágnes Keleti – Péter Lékó – Csaba Mérő – Tibor Nyilasi – László Papp – Judit Polgár – Zsuzsa Polgár – Ferenc Puskás
- Film & Stage
Nimród Antal – Michael Curtiz – John Garfield – Miklós Jancsó – Sir Alexander Korda – Peter Lorre – Béla Lugosi – Emeric Pressburger – Miklós Rózsa – Andy G. Vajna – Gábor Zsazsa
Géza I (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈɡeːzɒ]; Hungarian: I. Géza; c. 1040 – 25 April 1077) was King of Hungary from 1074 until his death. He was the eldest son of King Béla I. His baptismal name was Magnus. With German assistance, Géza's cousin Solomon acquired the crown when his father died in 1063, forcing Géza to leave Hungary. Géza returned with Polish reinforcements and signed a treaty with Solomon in early 1064. In the treaty, Géza and his brother Ladislaus acknowledged the rule of Solomon, who granted them their father's former duchy, which encompassed one-third of the Kingdom of Hungary.
Géza closely cooperated with Solomon, but their relationship became tense from 1071. The king invaded the duchy in February 1074 and defeated Géza in a battle. However, Géza was victorious at the decisive battle of Mogyoród on 14 March 1074. He soon acquired the throne, although Solomon maintained his rule in the regions of Moson and Pressburg (present-day Bratislava, Slovakia) for years. Géza initiated peace negotiations with his dethroned cousin in the last months of his life. Géza's sons were children when he died and he was succeeded by his brother Ladislaus. (Full article...)
Selected picture
Wikiprojects
Related projects:
Related portals
Things you can do
| The following stub articles would benefit from expansion. | |
General images -
The following are images from various Hungary-related articles on Wikipedia.
Topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-11-22 20:45 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Alojzije Palić (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mudroslov (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-11-22, score: 20
- Oszkár Maleczky (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jomajor8 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-22, score: 60
- Maria Dunszt (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jomajor8 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-22, score: 50
- Hans-Dieter Wacker (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SuperSkaterDude45 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-11-22, score: 20
- Stano Bubán (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jozef Heriban (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 40
- International Criminal Court arrest warrants for Israeli figures (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bakhos2010 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 20
- 2024–25 FC Ararat-Armenia season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Klio654 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 30
- Funerary architecture of Budapest (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 12akd (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 150
- Milivoj Jambrišak (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tomobe03 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 20
- Zachary David (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thfeeder (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 20
- Orbanism (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Uhtregorn (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-21, score: 40
- Al Boliska (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (158)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 30
- Guzmics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rakeck (talk · contribs · new pages (75)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- Stanko Banić (priest, born 1886) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tomobe03 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- William Dunst (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jomajor8 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 40
- József Bihari (linguist) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Texaner (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 80
- Keren Tzur (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Willthacheerleader18 (talk · contribs · new pages (46)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 30
- List of unusual deaths in the Middle Ages (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gildir (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 20
- Příhoda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fskel (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-11-20, score: 40
- Balduin Saria (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PJakopin (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 50
- Relief of Jajce (1518) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Franjo Tahy (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 20
- Bulgarian epigraphic monuments (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Viktor (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 30
- Alon Mindlin (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yoavd (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 20
- Frieda Vizel (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ForsythiaJo (talk · contribs · new pages (66)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 30
- Rising from the North (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ca (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-11-19, score: 20
- List of Billie Eilish live performances (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Luh78 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Dávid Horváth (footballer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cassandro (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-18, score: 60
- Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (Vietnam) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by VNW060222 (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2024-11-18, score: 20
- 2024–25 Women's EHF European League qualification round (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ILoveSport2006 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 40
- 2024–25 BC Rytas season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Konepe123 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 30
- 2007 in classical music (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Deb (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 20
- Ladislav Bartolomeides (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shyamal (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 20
- Resolute Mining (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CountHacker (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-11-17, score: 20
- Phonological history of Hungarian (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Botterweg (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 40
- Estonia national football team results (1920–1940) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FastCube (talk · contribs · new pages (111)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- Chop Border Detachment (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by M Waleed (talk · contribs · new pages (26)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- Viitorul (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dahn (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 60
- Anti-Masonic Congress of Trent (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mousieplousie (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 40
- Adam Erdmann Trčka of Lípa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FromCzech (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- Parailurus anglicus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by That Northern Irish Historian (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-16, score: 20
- 2024–25 Kansas Jayhawks women's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Elijah 1022 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Dvojka (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RandomMe98 (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-11-15, score: 20
- Russia women's national futsal team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mishajang (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-15, score: 20
- TwiGIS (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Petr Průša (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-15, score: 40
- Grupul 9 Vânătoare (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alin2808 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-15, score: 20
- New Synagogue (Poznań) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oliwiasocz (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-11-14, score: 20
- List of prose works by Richard Wagner (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wonder29 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-14, score: 20
- ARM (soundtrack) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 223.178.81.49 (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2024-11-14, score: 30
- Venice Preserv'd (painting) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lord Cornwallis (talk · contribs · new pages (106)) started on 2024-11-14, score: 20
- Kőváry (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (50)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 80
- Ottoman raids on Moravia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lenovya (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 50
- Kóbor János (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Xoak (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 120
- Meine Welt Tour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by ClementoPio1. (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Adolphe Basler (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Eli185.2 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 30
- 1853 State of the Union Address (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by A68-n (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Kazimierz Ferenc (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jmanlucas (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2024-11-13, score: 20
- Yankel Kalich (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jessamyn (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 20
- Botond (warrior) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Norden1990 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 110
- Marie Antoinette Gottesman (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Whispyhistory (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 60
- Helen Chaman Lall (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Whispyhistory (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 20
- Patrik Kovács (footballer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (61)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 60
- Gábor Kolosváry (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shyamal (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-11-12, score: 80
- Boris Bakrač (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tomobe03 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 20
- Josef Jungwirth (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Er nesto (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 40
- Friedrich Goldscheider (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PigeonChickenFish (talk · contribs · new pages (55)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 30
- 2024 IBA Youth World Boxing Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stojan212 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 30
- Maria Andrea Castanon Villanueva (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (50)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 20
- Zdenko Hudeček (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anatol Svahilec (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-11, score: 40
- József Somogyi (footballer born in 1955) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jankec666 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 110
- Hajnalka Burány (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CJCurrie (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 40
- Kammerkonzert (Hartmann) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gerda Arendt (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 30
- Mav (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mav (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 40
- Aneta Laboutková (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sczipo (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- V.1 Città di Jesi (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anatol Svahilec (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- Bruno del Pino (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Егор Затяжкин (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- M.III Körting (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anatol Svahilec (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 40
- Vladimir Radenković (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RuthStevens (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 40
- List of Nyíregyháza Spartacus FC managers (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RuthStevens (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 100
- Jewish refugees from Nazism (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Boxes12 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-11-10, score: 20
- Gábor Galambos (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oberhof (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 60
- Team United Shipping (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Šimisborec (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 80
- 1972–73 in Swiss football (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Huligan0 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 30
- Daniel Wilhelm Moller (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shyamal (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 20
- 1994 European Women's Handball Championship squads (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pressburg10 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-09, score: 20
- Sandor Guido (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Captain Parmenter (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-11-08, score: 20
- Fedor Oleshchuk (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wlbw68 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-11-08, score: 20
- Népsziget (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SafariScribe (talk · contribs · new pages (296)) started on 2024-11-08, score: 40
- Max Quedenfeldt (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shyamal (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-11-08, score: 20
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus