1996 Portuguese presidential election
| ||||||||||||||||
| Turnout | 66.29% ( | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
Presidential elections were held in Portugal on 14 January 1996.
Incumbent president Mário Soares was constitutionally barred from a third consecutive term. The Social Democrats were coming from a clear defeat in 1995 Portuguese legislative election, and their former leader, Aníbal Cavaco Silva, who had left the office of Prime Minister after 10 years at the helm, lost by 400,000 votes to the Mayor of Lisbon, Jorge Sampaio.
The other left candidates, Jerónimo de Sousa and Alberto Matos, presented by the Portuguese Communist Party and the People's Democratic Union respectively, both left the race one week before the elections, announcing their support for Jorge Sampaio, as the victory of a left-wing candidate was in doubt. These parties had already supported Sampaio in a coalition that won the local elections in Lisbon. It would be the last time that People's Democratic Union presented a candidate, as two years later it merged with other small left-wing parties and formed the Left Bloc.
Cavaco Silva was supported by the two major right-wing parties, the Social Democratic Party and the People's Party, and once more, the right-wing parties did not manage to win the presidential election. The election was, therefore, a rematch between Jorge Sampaio and Cavaco Silva as in the 1991 general election, Cavaco Silva defeated Jorge Sampaio by a 51 to 29 percent margin.
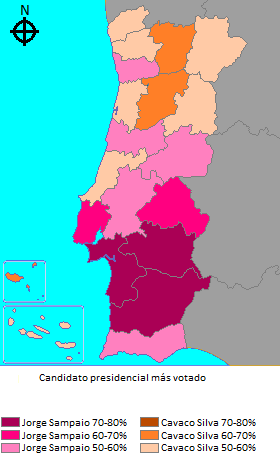
Sampaio gathered the majority of the votes in all the districts in the South of Portugal, including the Communist strongholds in Alentejo and Setúbal district. Cavaco won in the more conservative districts of the North (excluding Porto district, where Sampaio edged out Cavaco by a narrow 52 to 48 percent margin) and also in Leiria district, traditional strongholds of the right-wing parties.
With only two candidates left on the race, no second round was needed, and Sampaio was inaugurated to his first term in office on 9 March 1996.
Aníbal Cavaco Silva would have to wait ten more years to be elected president in 2006.
Electoral system
Any Portuguese citizen over 35 years old has the opportunity to run for president. In order to do so it is necessary to gather between 7,500 and 15,000 signatures and submit them to the Portuguese Constitutional Court.
According to the Portuguese Constitution, to be elected, a candidate needs a majority of votes. If no candidate gets this majority there will take place a second round between the two most voted candidates.
Candidates
- Jorge Sampaio, Mayor of Lisbon between 1989 and 1995, leader of the Socialist Party between 1989 and 1992, supported by the Socialist Party;
- Aníbal Cavaco Silva, Prime Minister between 1985 and 1995, leader of the Social Democratic Party between 1985 and 1995, supported by the Social Democratic Party and the People's Party;
- Jerónimo de Sousa, Official candidate of the Portuguese Communist Party and Ecologist Party "The Greens", Left the race to support Jorge Sampaio;
- Alberto Matos, Official candidate of the People's Democratic Union, Left the race to support Jorge Sampaio;
Campaign period
Party slogans
| Candidate | Original slogan | English translation | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jorge Sampaio | « Um por todos » | "One for all" | [1] | |
| Aníbal Cavaco Silva | « Em nome de Portugal » | "In the name of Portugal" | [2] | |
| [3] | ||||
| [4] | ||||
Candidates' debates
| 1996 Portuguese presidential election debates | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Organisers | Moderator(s) | P Present A Absent invitee N Non-invitee | |||||||||||||||||
| Sampaio | Cavaco | Jerónimo | Refs | |||||||||||||||||
| 14 Dec 1995 | RTP1 | Maria Elisa Domingues José Eduardo Moniz |
P | P | P | [5] | ||||||||||||||
| 21 Dec 1995 | SIC | Margarida Marante Miguel Sousa Tavares |
P | P | N | [6] | ||||||||||||||
Opinion polls
Note, until 2000, the publication of opinion polls in the last week of the campaign was forbidden.
Exit poll
| Polling firm | Date released | Sample size |

|

|
Lead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sampaio PS |
Cavaco Silva PSD | ||||
| Election results | 14 Jan 1996 | — | 53.9 | 46.1 | 7.8 |
| Euroteste/RTP | 14 Jan 1996 | — | 56.0–60.0 | 40.0–44.0 | 16.0 |
| Metris/SIC | 14 Jan 1996 | — | 56.8–61.2 | 38.8–43.2 | 18.0 |
| UCP-CESOP/TVI | 14 Jan 1996 | — | 54.6–58.2 | 41.8–45.6 | 12.8 |
| UCP-CESOP | 6 Jan 1996 | — | 52.1 | 47.9 | 4.2 |
| Metris | 6 Jan 1996 | — | 57.1 | 42.9 | 14.2 |
| Euroteste | 6 Jan 1996 | — | 57.5 | 42.5 | 15.0 |
| Euroexpansão | 6 Jan 1996 | — | 57.7 | 42.3 | 15.4 |
Results
| Candidate | Party | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jorge Sampaio | Socialist Party | 3,035,056 | 53.91 | |
| Aníbal Cavaco Silva | Social Democratic Party–People's Party | 2,595,131 | 46.09 | |
| Total | 5,630,187 | 100.00 | ||
| Valid votes | 5,630,187 | 97.70 | ||
| Invalid votes | 63,463 | 1.10 | ||
| Blank votes | 69,328 | 1.20 | ||
| Total votes | 5,762,978 | 100.00 | ||
| Registered voters/turnout | 8,693,636 | 66.29 | ||
| Source: Comissão Nacional de Eleições | ||||
Results by district
| District | Sampaio | Cavaco | Turnout | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Votes | % | Votes | % | |||
| Aveiro | 162,495 | 43.04% | 215,046 | 56.96% | 69.01% | |
| Azores | 40,746 | 43.60% | 52,715 | 56.40% | 50.81% | |
| Beja | 71,833 | 79.15% | 18,926 | 20.85% | 61.31% | |
| Braga | 204,069 | 45.79% | 241,580 | 54.21% | 71.55% | |
| Bragança | 34,358 | 40.17% | 51,173 | 59.83% | 57.42% | |
| Castelo Branco | 69,136 | 55.50% | 55,428 | 44.50% | 63.13% | |
| Coimbra | 133,644 | 54.37% | 112,181 | 45.63% | 65.90% | |
| Évora | 72,369 | 73.32% | 26,398 | 26.68% | 67.16% | |
| Faro | 110,748 | 58.45% | 78,736 | 41.55% | 63.09% | |
| Guarda | 45,820 | 44.00% | 58,306 | 56.00% | 60.75% | |
| Leiria | 98,577 | 40.41% | 145,352 | 59.59% | 66.95% | |
| Lisbon | 740,987 | 60.98% | 474,060 | 39.02% | 66.75% | |
| Madeira | 49,243 | 39.58% | 75,160 | 60.42% | 62.99% | |
| Portalegre | 52,647 | 69.38% | 23,231 | 30.62% | 66.84% | |
| Porto | 500,903 | 51.82% | 465,803 | 48.18% | 70.28% | |
| Santarém | 149,119 | 57.50% | 110,202 | 42.50% | 67.25% | |
| Setúbal | 313,083 | 74.51% | 107,080 | 25.49% | 67.36% | |
| Viana do Castelo | 58,621 | 41.57% | 82,411 | 58.43% | 64.34% | |
| Vila Real | 51,087 | 39.64% | 77,779 | 60.36% | 59.10% | |
| Viseu | 78,996 | 36.97% | 134,669 | 63.03% | 61.63% | |
| Source: SGMAI Presidential Election Results | ||||||
Maps
-
Strongest candidate by electoral district.
-
Strongest candidate by municipality.
Notes
References
- ^ "Os cartazes das eleições presidenciais desde 1976". Público (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Os cartazes das eleições presidenciais desde 1976". Público (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Os cartazes das eleições presidenciais desde 1976". Público (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Os cartazes das eleições presidenciais desde 1976". Público (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Candidatos à Presidência da República – Parte I". RTP (in Portuguese). 14 December 1995. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ "Os debates" (in Portuguese). Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "CNE Resultados". Comissão Nacional de Eleições. Archived from the original on 8 April 2005. Retrieved 17 May 2005.
- "Centro de Estudos do Pensamento Político". Archived from the original on 2006-08-18. Retrieved 17 May 2005.
External links
- Portuguese Electoral Commission
- NSD: European Election Database - Portugal Archived 2014-12-20 at the Wayback Machine publishes regional level election data; allows for comparisons of election results, 1990-2010