Bárány chair
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (June 2020) |
| Bárány chair | |
|---|---|
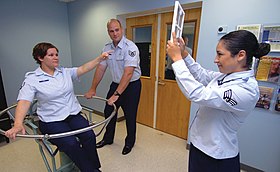 Air Force personnel demonstrating the effect on the sensory perception and spatial orientation of a test person in a Bárány chair. After first having been rotated in the chair and then stopped, the test person tries to point at a test board. | |
| ICD-9-CM | 95.45 |
The Barany chair or Bárány chair is a device used for aerospace physiology training, particularly for student pilots.
Test
[edit]The subject is placed in the swivel chair, blindfolded, then spun about the vertical axis while keeping their head upright or tilted forward or to the side. The subject is then asked to perform tasks such as determine their direction of rotation while blindfolded, or rapidly change the orientation of their head, or attempt to point at a stationary object without blindfold after the chair is stopped. The chair is used to demonstrate spatial disorientation effects, proving that the vestibular system is not to be trusted in flight. Pilots are taught that they should instead rely on their flight instruments.[citation needed]
Uses
[edit]The device is also used in motion sickness therapy.[1]
Nobel Prize
[edit]The chair was named for Hungarian physiologist Robert Bárány, who used this device in his research into the role of the inner ear in the sense of balance. He won the 1914 Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine "for his work on the physiology and pathology of the vestibular apparatus".[2]
See also
[edit]- Aerotrim
- Flight simulator
- Link Trainer
- Sensory illusions in aviation – Misjudgment of true orientation by pilots
- Spatial disorientation – Inability of a person to correctly determine their body position in space
- G-seat
- R360
References
[edit]- ^ McGloin, Brian (November 2010). "Squadron aims to reduce use of air-sickness bags". U.S. Air Force. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1914". NobelPrize.org. Retrieved 2024-07-04.
