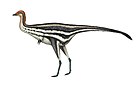
Elopteryx
| Elopteryx Temporal range: Maastrichtian
| |
|---|---|

| |
| The holotype femur fragment in several views | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Clade: | Paraves |
| Genus: | †Elopteryx Andrews, 1913 |
| Type species | |
| †Elopteryx nopcsai Andrews, 1913
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Elopteryx is a genus of paravian theropod dinosaur based on fragmentary fossils found in Late Cretaceous rocks of Romania. The single species, Elopteryx nopcsai, was known only from very incomplete material until new specimens were reported in the 21st century. Balaur bondoc might represent a junior synonym of this taxon.[1][2]
History of discovery and naming
[edit]Initial finds
[edit]In the late nineteenth or early twentieth century, the famous Hungarian paleontologist Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás found near Sînpetru, in what is now the Romanian region of Transylvania, some bone fragments of a small theropod. These were acquired by the British Museum of Natural History. In 1913, curator Charles William Andrews named these as the type species Elopteryx nopcsai. The genus name Elopteryx is from Ancient Greek helos (ἕλος), "marsh" + pteryx (πτέρυξ), "wing". The specific name honors Nopcsa. Initially, Elopteryx was described from its holotype, a proximal left femur, specimen BMNH A1234. A second upper left thighbone fragment, BMNH A1235, was referred. A distal left tibiotarsus was also tentatively assigned to this taxon; it was initially classified with the same specimen number as the holotype and was found in close proximity, but may not be from the same individual (see below). This has since been relabeled and is now specimen BMNH A4359. The exact location and time of the discoveries are today unknown. The fossils date from the early-late Maastrichtian (Begudian) faunal stage, circa 70-66 million years ago, originating from the Sânpetru Formation of the Hațeg Island. The animal was by Andrews believed to be a pelecaniform seabird.[3][4]
In 1929 the Hungarian paleontologist Kálmán Lambrecht referred two more specimens: BMNH A PAL.1528 and BMNH A PAL.1588, respectively a left and a right tibiotarsus.[5] In 1933 Lambrecht named a separate family Elopterygidae.[6] The supposed family Elopterygidae was initially placed in the suborder Sulae – then still in the polyphyletic "Pelecaniformes" – in 1963 by Pierce Brodkorb in his fossil bird catalogue, and the Cenozoic genera Argillornis and Eostega were moved to it.[7] These two are unequivocal derived neornith birds and the latter indeed seems to be an ancient sulid, whereas Argillornis has turned out to be referrable to the giant pseudotooth bird Dasornis which was almost certainly not very closely related to the Sulae.[8] Reconstruction attempts of E. nopcsai like this are based on this presumed affiliation with gannets and cormorants. But more recent studies would result in radically different interpretations.
Later finds
[edit]
In 1975, the distal tibiotarsi BMNH A1588 and BMNH A1528, together with BMNH A4359, were by Colin James Oliver Harrison and Cyril Alexander Walker removed from Elopteryx, redescribed as Bradycneme draculae and Heptasteornis andrewsi respectively, and used to establish a supposed family of gigantic two metre tall owls, the Bradycnemidae.[3] In 1978 Brodkorb had changed his opinion after the supposed Elopteryx material was divided among three species in total, and was actually the first scholar in modern times to suggest that these Mesozoic bones were not of birds but of non-avian dinosaurs.[9]
In 1981, Dan Grigorescu and Eugen Kessler stated that Elopteryx was a non-avian coelurosaurian dinosaur. They also referred a supposed distal femur (FGGUB R.351) to Elopteryx,[10] but both researchers (with Zoltan Csiki) later identified this specimen as a hadrosauroid distal metatarsal.[11]
In 1992, it was proposed by Jean Le Loeuff e.a. that Bradycneme and Heptasteornis should be synonymized with E. nopcsai again, and a femur (MDE-D203), an anterior dorsal vertebra (MDE-D01), a posterior sacral vertebra (MDE collection, unnumbered) and some dorsal rib fragments from the Jurassic Grès à Reptiles formation of France were described as an indeterminate species of Elopteryx; that study placed all this material in the Dromaeosauridae or a family or subfamily (Elopteryginae) very close to these.[12] The vertebrae were in 1998 separated again and assigned to a new dromaeosaurid, Variraptor mechinorum.[13] The French femur is similar in general appearance to the Elopteryx type but it differs in diagnostic traits, e.g. lacking a fourth trochanter. Also, neither the ribs nor the tibiotarsi can be compared to the type specimen of Elopteryx, there being no overlapping material.
In 2005, another (distal) femur piece, FGGUB R.1957, has been described as a new specimen of Elopteryx on the basis of the bone texture.[11] In 2019, a potential pelvis specimen identified as cf. E. nopcsai was reported.[14] In 2024, a new femur specimen from Romania was attributed to Elopteryx, and the specimen shows that it was secondarily flightless.[2]
Phylogeny
[edit]Modern interpretations have differed on the question whether the Bradycneme and Heptasteornis material should be included — they have meanwhile been synonymized and split from each other and Elopteryx many times — and what the exact affiliations of the material would be. Various solutions were proposed for this problem.[15] Previously, some researchers proposed Elopteryx was a member of the Dromaeosauridae or Troodontidae,[16] without being able to support this with much empirical evidence.[11] In 1998 Csiki & Grigorescu suggested that Elopteryx belonged to the Maniraptora, while Bradycneme had a more basal position in the Tetanurae.[17]
Since the 21st century, Elopteryx has been supported widely as a member of the Maniraptora, with most studies recovering it as a member of the Paraves. In 2004, Darren Naish and Gareth Dyke considered Elopteryx as a Eumaniraptora incertae sedis, possibly either a non-ornithuromorphan pygostylian bird[18] or a troodontid, while Bradycneme would be a maniraptoran, and the dubious Heptasteornis (at least its holotype BMNH A4359) a member of the Alvarezsauridae.[19] Thus E. nopcsai seems to be some sort of birdlike eumaniraptoran, but not related to modern birds. In 2005, Kessler, Grigorescu and Csiki reunited all the material in Elopteryx but considered it an alvarezsaurid.[11] In a 2011 classification, Tom Holtz assigned Elopteryx to the Troodontidae.[20] In 2013, Stephen L. Brusatte and colleagues mentioned a possibility of Elopteryx and the paravian Balaur bondoc being the same taxon, though the authors did not consider it the most likely case.[1] Later, in 2019, two studies have found it to be an avialan once again, but a basal one; Hartman and colleagues recover it as a confuciusornithiform[21] while Mayr and colleagues note similarities with Gargantuavis and Balaur, suggesting they form a clade native to the Late Cretaceous European archipelago.[14] Mayr and colleagues also claimed that the synonymy of Elopteryx and Balaur remains possible and that more work is needed for confirmation.[14] In 2024, Stoicescu and colleagues suggested that Elopteryx is indeed a paravian and a member of the Avialae based on its new specimen, and that Balaur bondoc is probably a junior synonym of Elopteryx.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Brusatte, S. L.; Vremir, M. T. S.; Csiki-Sava, Z. N.; Turner, A. H.; Watanabe, A.; Erickson, G. M.; Norell, M. A. (2013). "The Osteology of Balaur bondoc, an Island-Dwelling Dromaeosaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Late Cretaceous of Romania" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 374: 1–100. doi:10.1206/798.1. S2CID 59932467.
- ^ a b c Stoicescu, V.; Codrea, V.A.; Bordeianu, M.; Solomon, A.A. (2024). "Elopteryx at Nălaț-Vad: new theropod material described from the Hațeg Basin (Romania)" (PDF). North-Western Journal of Zoology. 20 (1): 73–80.
- ^ a b Harrison & Walker (1975)
- ^ Andrews (1913)
- ^ Lambrecht, K., 1929, "Mesozoische und tertiäre Vogelreste aus Siebenbürgen" Comptes-Rendus Xe Congres International de Zoologie, Budapest, section 8, 1262-1275
- ^ Lambrecht, K., 1933, Handbuch der Palaeornithologie. Gebrüder Borntraeger, Berlin
- ^ Brodkorb (1963): pp.248-249
- ^ Mayr (2008)
- ^ Brodkorb (1978): pp.223-224
- ^ Grigorescu, D. & Kessler, E., 1981, "A new specimen of Elopteryx nopcsai from the dinosaurian beds of Hateg Basin", Révue Roumaine de Géologie, Géophysique et Géographie, Géologie, 24: 171-175
- ^ a b c d Kessler, E.; Grigorescu D.; Csiki, Z. (2005). "Elopteryx revisited - a new bird-like specimen from the Maastrichtian of the Hateg Basin" (PDF). Acta Palaeontologica Romaniae. 5: 249–258. S2CID 87287034.
- ^ Le Loeuff et al. (1992)
- ^ Le Loeuff and Buffetaut (1998)
- ^ a b c Mayr, G.; Codrea, V.; Solomon, A.; Bordeianu, M.; Smith, T. (2019). "A well-preserved pelvis from the Maastrichtian of Romania suggests that the enigmatic Gargantuavis is neither an ornithurine bird nor an insular endemic". Cretaceous Research. 106: 104271. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.104271. S2CID 210302354.
- ^ E.g. Le Loeuff et al. (1992), Csiki & Grigorescu (1998)
- ^ Paul (1988), Weishampel et al. (1991)
- ^ Csiki & Grigorescu (1998)
- ^ Most of these - like Confuciusornis or Enantiornithes - are only known since the late 20th century.
- ^ Naish & Dyke (2004)
- ^ Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2011) Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages, Winter 2010 Appendix.
- ^ Hartman, Scott; Mortimer, Mickey; Wahl, William R.; Lomax, Dean R.; Lippincott, Jessica; Lovelace, David M. (2019). "A new paravian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of North America supports a late acquisition of avian flight". PeerJ. 7: e7247. doi:10.7717/peerj.7247. PMC 6626525. PMID 31333906.
Bibliography
[edit]- Andrews, C.W. (1913): On some bird remains from the Upper Cretaceous of Transylvania. Geological Magazine 5: 193–196.
- Brodkorb, Pierce (1963): Catalogue of fossil birds. Part 1 (Archaeopterygiformes through Ardeiformes). Bulletin of the Florida State Museum, Biological Sciences 7(4): 179–293. PDF fulltext
- Brodkorb, Pierce (1978): Catalogue of fossil birds, Part 5 (Passeriformes). Bulletin of the Florida State Museum, Biological Sciences 23(3): 139–228.
- Csiki, G. & Grigorescu, D. (1998): Small theropods from the Late Cretaceous of the Hateg Basin (western Romania) - an unexpected diversity at the top of the food chain. Oryctos 1: 87-104.
- Harrison, Colin James Oliver & Walker, Cyril Alexander (1975): The Bradycnemidae, a new family of owls from the Upper Cretaceous of Romania. Palaeontology 18(3): 563–570. PDF fulltext
- Le Loeuff, J. & Buffetaut, E. (1998): A new dromaeosaurid theropod from the Upper Cretaceous of Southern France. Oryctos 1: 105–112.
- Le Loeuff, J.; Buffetaut, E.; Méchin, P. & Méchin-Salessy, A. (1992): The first record of dromaeosaurid dinosaurs (Saurischia, Theropoda) in the Maastrichtian of southern Europe: palaeobiogeographical implications. Bulletin de la Société géologique de la France 163(3): 337–343.
- Mayr, Gerald (2008): A skull of the giant bony-toothed bird Dasornis (Aves: Pelagornithidae) from the Lower Eocene of the Isle of Sheppey. Palaeontology 51(5): 1107–1116. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2008.00798.x (HTML abstract)
- Naish, Darren & Dyke, Gareth J. (2004): Heptasteornis was no ornithomimid, troodontid, dromaeosaurid or owl: the first alvarezsaurid (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from Europe. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Monatshefte 7: 385–401.
- Paul, Gregory S. (1988): Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. New York, Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-61946-2
- Weishampel, D.B.; Grigorescu, D. & Norman, D.B. (1991): The dinosaurs of Transylvania. National Geographic Research and Exploration 7(2): 196–215. PDF fulltext