Periaqueductal gray
| Periaqueductal gray | |
|---|---|
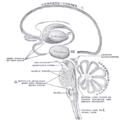
 Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve. Periaqueductal gray is the gray area just peripheral to the cerebral aqueduct. | |
 Transverse section through mid-brain.
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | substantia grisea centralis |
| MeSH | D010487 |
| NeuroNames | 1584 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_973 |
| TA98 | A14.1.06.321 |
| TA2 | 5909 |
| FMA | 83134 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The periaqueductal gray (PAG), also known as the central gray, is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function, motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli.[1][2] PAG is also the primary control center for descending pain modulation. It has enkephalin-producing cells that suppress pain.
The periaqueductal gray is the gray matter located around the cerebral aqueduct within the tegmentum of the midbrain. It projects to the nucleus raphe magnus, and also contains descending autonomic tracts. The ascending pain and temperature fibers of the spinothalamic tract send information to the PAG via the spinomesencephalic pathway (so-named because the fibers originate in the spine and terminate in the PAG, in the mesencephalon or midbrain).
This region has been used as the target for brain-stimulating implants in patients with chronic pain.
Role in analgesia
[edit]Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain activates enkephalin-releasing neurons that project to the raphe nuclei in the brainstem. 5-HT (serotonin) released from the raphe nuclei descends to the dorsal horn of the spinal cord where it forms excitatory connections with the inhibitory interneurons located in Laminae II (aka the substantia gelatinosa). When activated, these interneurons release either enkephalin or dynorphin (endogenous opioid peptides), which bind to mu and kappa opioid receptors, respectively, on the axons of incoming C and A-delta fibers carrying pain signals from nociceptors activated in the periphery.
The activation of the mu-opioid receptor inhibits the release of substance P from these incoming first-order neurons and, in turn, inhibits the activation of the second-order neuron that is responsible for transmitting the pain signal up the spinothalamic tract to the ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) of the thalamus. The nociceptive signal is thus inhibited before reaching the cortical areas that interpret the signal as pain, such as the anterior cingulate. This is sometimes referred to as the gate control theory of pain and is supported by the fact that electrical stimulation of the PAG results in immediate and profound analgesia.[3] The periaqueductal gray is also activated by viewing distressing images associated with pain.[4]
Notably, the anterior cingulate cortex is thought to be responsible for emotional responses to pain, including perceived social or emotional pain. Reducing nociceptive signaling to this area not only reduces overall pain signaling, but appears to also reduce sensitivity to pain. Furthermore, activation of mu-opioid receptors has been shown to provide an "analgesic" effect for emotional pain.[5][6]
Role in defensive behavior
[edit]Dorsal PAG neurons are activated during various defensive behaviors.[7] Stimulation of the dorsal and lateral aspects of the PAG can provoke defensive responses characterised by freezing immobility, running, jumping, tachycardia, and increases in blood pressure and muscle tonus. In contrast, stimulation of the caudal ventrolateral PAG can result in an immobile, relaxed posture known as quiescence, whereas its inhibition leads to increased locomotor activity.[citation needed]
Lesions of the caudal ventrolateral PAG can greatly reduce conditioned freezing, whereas lesions of the dorsal aspect can reduce innate defensive behavior, virtually "taming" the animal[8][9].
Role in reproductive behavior
[edit]Neurons of the PAG are excited by endorphins and by opiate analgesics. It also plays a role in female copulatory behavior (see lordosis behavior) via a pathway from the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus.[citation needed]
Role in maternal behavior
[edit]The PAG may be specifically involved in human maternal behavior. The PAG contains a high density of vasopressin and oxytocin receptors, and it has direct connections with the orbitofrontal cortex, which might mediate the role of the PAG in maternal love. The lateral orbitofrontal cortex is activated by pleasant visual, tactile, and olfactory stimuli. Its response depends on pleasantness rather than on intensity of stimulation. Here, its activity is likely to reflect one aspect of the pleasant emotions associated with motherly love.[10]
Additional images
[edit]-
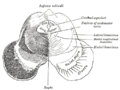
Schematic representation of the chief ganglionic categories (I to V).
-
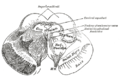
Transverse section of mid-brain at level of inferior colliculi.
-
Transverse section of mid-brain at level of superior colliculi.
-
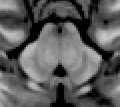
MRI section of human mid-brain showing periaqueductal gray
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Faull, Olivia K.; Subramanian, Hari H.; Ezra, Martyn; Pattinson, Kyle T. S. (2019). "The midbrain periaqueductal gray as an integrative and interoceptive neural structure for breathing". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 98: 135–144. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.020. hdl:20.500.11850/317617. ISSN 1873-7528. PMID 30611797.
- ^ Silva, Carlos; McNaughton, Neil (2019-02-17). "Are periaqueductal grey and dorsal raphe the foundation of appetitive and aversive control? A comprehensive review". Progress in Neurobiology. 177: 33–72. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.02.001. ISSN 1873-5118. PMID 30786258. S2CID 73478335.
- ^ Basbaum AI, Fields HL (November 1978). "Endogenous pain control mechanisms: review and hypothesis". Ann. Neurol. 4 (5): 451–62. doi:10.1002/ana.410040511. PMID 216303. S2CID 72620829.
- ^ Jenkins, Dacher Keltner, Keith Oatley, Jennifer M. (2013-01-29). Understanding emotions (3rd ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley. ISBN 9781118147436.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Eisenberger NI, Lieberman MD, Williams KD (October 2003). "Does rejection hurt? An FMRI study of social exclusion". Science. 302 (5643): 290–2. Bibcode:2003Sci...302..290E. doi:10.1126/science.1089134. PMID 14551436. S2CID 21253445.
- ^ Gorka SM, Fitzgerald DA, de Wit H, Angstadt M, Phan KL (December 2014). "Opioid modulation of resting-state anterior cingulate cortex functional connectivity". J. Psychopharmacol. 28 (12): 1115–24. doi:10.1177/0269881114548436. PMC 5613932. PMID 25237122.
- ^ Deng, Hanfei; Xiao, Xiong; Wang, Zuoren (2016). "Periaqueductal Gray Neuronal Activities Underlie Different Aspects of Defensive Behaviors". Journal of Neuroscience. 36 (29): 7580–7588. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4425-15.2016. PMC 6705556. PMID 27445137.
- ^ Blanchard, Dixie Caroline; Williams, Gregg; Lee, Eugene M. C.; Blanchard, Robert J. (2013). "Taming of wild Rattus norvegicus by lesions of the mesencephalic central gray". Physiological Psychology. 9 (2): 157–163. doi:10.3758/BF03332917.
- ^ Sukikara, Marcia Harumi; Mota-Ortiz, Sandra Regina; Baldo, Marcus Vinícius; Felicio, Luciano Freitas; Canteras, Newton Sabino (2010). "The periaqueductal gray and its potential role in maternal behavior inhibition in response to predatory threats". Behavioural Brain Research. 209 (2): 226–233. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2010.01.048. PMID 20138922.
- ^ Andreas Bartels; Semir Zeki (March 2004). "The neural correlates of maternal and romantic love" (PDF). NeuroImage. 21 (3): 1155–1166. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.003. PMID 15006682. S2CID 15237043. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-29. Retrieved 2013-01-27.