Portal:Birds
The Birds Portal

Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (Latin: [ˈaveːs]), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the 5.5 cm (2.2 in) bee hummingbird to the 2.8 m (9 ft 2 in) common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. The study of birds is called ornithology.
Birds are feathered theropod dinosaurs and constitute the only known living dinosaurs. Likewise, birds are considered reptiles in the modern cladistic sense of the term, and their closest living relatives are the crocodilians. Birds are descendants of the primitive avialans (whose members include Archaeopteryx) which first appeared during the Late Jurassic. According to recent estimates, modern birds (Neornithes) evolved in the Late Cretaceous and diversified dramatically around the time of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago, which killed off the pterosaurs and all non-ornithuran dinosaurs.
Many social species preserve knowledge across generations (culture). Birds are social, communicating with visual signals, calls, and songs, and participating in such behaviour as cooperative breeding and hunting, flocking, and mobbing of predators. The vast majority of bird species are socially (but not necessarily sexually) monogamous, usually for one breeding season at a time, sometimes for years, and rarely for life. Other species have breeding systems that are polygynous (one male with many females) or, rarely, polyandrous (one female with many males). Birds produce offspring by laying eggs which are fertilised through sexual reproduction. They are usually laid in a nest and incubated by the parents. Most birds have an extended period of parental care after hatching.
Many species of birds are economically important as food for human consumption and raw material in manufacturing, with domesticated and undomesticated birds being important sources of eggs, meat, and feathers. Songbirds, parrots, and other species are popular as pets. Guano (bird excrement) is harvested for use as a fertiliser. Birds figure throughout human culture. About 120 to 130 species have become extinct due to human activity since the 17th century, and hundreds more before then. Human activity threatens about 1,200 bird species with extinction, though efforts are underway to protect them. Recreational birdwatching is an important part of the ecotourism industry. (Full article...)
Featured articles
Selected general bird topic
| Influenza (flu) |
|---|
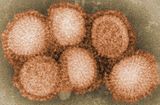 |
Symptoms of avian influenza vary according to both the strain of virus underlying the infection, and on the species of bird or mammal affected. Classification of a virus strain as either low pathogenic avian influenza (LPAI) or high pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) is based on the severity of symptoms in domestic chickens and does not predict severity of symptoms in other species. Chickens infected with LPAI display mild symptoms or are asymptomatic, whereas HPAI causes serious breathing difficulties, significant drop in egg production, and sudden death. Domestic poultry may potentially be protected from specific strains of the virus by vaccination. (Full article...)
Selected taxon
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North Pacific. They are absent from the North Atlantic, although fossil remains of short-tailed albatross show they once lived there up to the Pleistocene, and occasional vagrants are found. Great albatrosses are among the largest of flying birds, with wingspans reaching up to 2.5–3.5 metres (8.2–11.5 ft) and bodies over 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length. The albatrosses are usually regarded as falling into four genera, but disagreement exists over the number of species.
Albatrosses are highly efficient in the air, using dynamic soaring and slope soaring to cover great distances with little exertion. They feed on squid, fish, and krill by either scavenging, surface seizing, or diving. Albatrosses are colonial, nesting for the most part on remote oceanic islands, often with several species nesting together. Pair bonds between males and females form over several years, with the use of "ritualised dances", and last for the life of the pair. A breeding season can take over a year from laying to fledging, with a single egg laid in each breeding attempt. A Laysan albatross, named Wisdom, on Midway Island is the oldest-known wild bird in the world; she was first banded in 1956 by Chandler Robbins.
Of the 22 species of albatrosses recognised by the IUCN, 21 are listed as at some level of concern; two species are Critically Endangered, seven species are Endangered, six species are Vulnerable, and six species are Near Threatened. Numbers of albatrosses have declined in the past due to harvesting for feathers. Albatrosses are threatened by introduced species, such as rats and feral cats that attack eggs, chicks, and nesting adults; by pollution; by a serious decline in fish stocks in many regions largely due to overfishing; and by longline fishing. Longline fisheries pose the greatest threat, as feeding birds are attracted to the bait, become hooked on the lines, and drown. Identified stakeholders such as governments, conservation organisations, and people in the fishing industry are all working toward reducing this phenomenon. (Full article...)
Topics
Anatomy: Anatomy • Skeleton • Flight • Eggs • Feathers • Plumage
Evolution and extinction: Evolution • Archaeopteryx • Hybridisation • Late Quaternary prehistoric birds • Fossils • Taxonomy • Extinction
Behaviour: Singing • Intelligence • Migration • Reproduction • Nesting • Incubation • Brood parasites
Bird orders: Struthioniformes • Tinamiformes • Anseriformes • Accipitriformes • Galliformes • Gaviiformes • Podicipediformes • Procellariiformes • Sphenisciformes • Pelecaniformes • Ciconiiformes • Phoenicopteriformes • Falconiformes • Gruiformes • Charadriiformes • Pteroclidiformes • Columbiformes • Psittaciformes • Cuculiformes • Strigiformes • Caprimulgiformes • Apodiformes • Coraciiformes • Piciformes • Trogoniformes • Coliiformes • Passeriformes
Bird lists: Families and orders • Lists by region
Birds and humans: Ringing • Ornithology • Bird collections • Birdwatching • Birdfeeding • Conservation • Aviculture
Quotes
| “ | To a man, ornithologists are tall, slender, and bearded so that they can stand motionless for hours, imitating kindly trees, as they watch for birds. | ” |
Resources
Free online resources:
- SORA: The Searchable Online Research Archive (SORA) has decades worth of archives of the following journals: The Auk, The Condor, Journal of Field Ornithology, North American Bird Bander, Studies in Avian Biology, Pacific Coast Avifauna, and The Wilson Bulletin. Coverage ends around 2000. The ability to search all journals or browse exists on the front page.
- Notornis: The Journal of the Ornithological Society of New Zealand covers New Zealand and the South Pacific.
- New Zealand Journal of Ecology: This journal often publishes bird-related articles. Like Notornis, this journal is concerned with New Zealand and surrounding areas.
- Marine Ornithology: Published by the numerous seabird research groups, Marine Ornithology is specific and goes back many years.
- BirdLife International: The Data Zone has species accounts for every species, although threatened species and some key groups have greater detail with others only having status and evaluation.
- Author Index: This is a good source for binomial authorities for taxoboxes.
There is also Birds of North America, Cornell University's massive project collecting information on every breeding bird in the ABA area. It is available for US$40 a year.
For more sources, including printed sources, see WikiProject Birds.
WikiProjects
Selected images
Selected bird anatomy topic

The hyoid apparatus is the collective term used in veterinary anatomy for the bones which suspend the tongue and larynx. It consists of pairs of stylohyoid, thyrohyoid, epihyoid and ceratohyoid bones, and a single basihyoid bone. The hyoid apparatus resembles the shape of a trapeze, or a bent letter "H". The basihyoid bone lies within the muscle at the base of the tongue.
In humans, the single hyoid bone is an equivalent of the hyoid apparatus. (Full article...)
Selected species
Did you know
- ...that the rufous hornero, a common species in the ovenbird family, is the national bird of Argentina?
- ...that the eastern whipbird (pictured) of the Australian wet forests is so named for its loud call which resembles the cracking of a whip?
- ...that the rusty-barred owl is one of the only two members of the Strix genus of birds to be found in South America?
Categories
Related portals
Things you can do
Create requested articles (WikiProject Birds – Article requests):
Do these tasks:
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
More outstanding tasks at the project's cleanup listing, Category:Birds articles needing attention, and Wikipedia:WikiProject Birds/Todo.
Taxonomy of Aves
| Class Aves, divided into superorders, orders, suborders (where indicated), and families. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Sources
- ^ Gaither, C.C.; Cavazos-Gaither, A.E. (2012). Gaither's Dictionary of Scientific Quotations. Springer New York. p. 1660. ISBN 978-1-4614-1114-7. Retrieved February 7, 2020.