USS Coeur de Lion

| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Launched | 1853 |
| Acquired | 1861 |
| Commissioned | 2 October 1861 |
| Decommissioned | 2 June 1865 |
| Fate | Returned to the Lighthouse Board 3 June 1865 |
| General characteristics | |
| Displacement | 110 tons |
| Length | 100 ft (30 m) |
| Beam | 20 ft 6 in (6.25 m) |
| Draft | 4 ft 6 in (1.37 m) |
| Depth of hold | 4 ft 10 in (1.47 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Complement | 29 |
| Armament |
|
USS Coeur de Lion was an armed side-wheeled steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She served as a patrol boat, capable of engaging the enemy with her powerful guns.
Service history
[edit]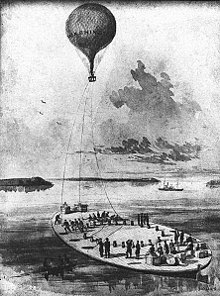
Coeur de Lion, a side wheel steamer, was loaned to the Navy Department by the Lighthouse Board in 1861; outfitted at New York Navy Yard; and sailed 2 October 1861 for Washington, D.C. On 10 November 1861 the "Coeur de Lion" towed the barge USS George Washington Parke Custis (1861) the first de facto aircraft carrier. Until the end of the war Coeur de Lion patrolled in the Potomac River, James River, and other rivers of Virginia. She burned the schooners Charity, Gazelle, and Flight in the Appomattox River on 27 May 1862 and the schooners Sarah Margaret and Odd Fellow up the Coan River 1 June 1862. Enforcing the blockade, Coeur de Lion captured the schooners Emily Murray off Machodoc Creek, Virginia, 9 February 1863, and Robert Knowles 16 September 1863, and Malinda 3 June 1864, in the Potomac. During a reconnaissance up the Nansemond River, she exchanged fire with enemy batteries on 17 and 19 April 1863, taking the surrender of one of these on the 19th. Arriving at Washington Navy Yard 15 May 1865, Coeur de Lion was decommissioned 2 June 1865 and returned to the Lighthouse Board the following day.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
